Method and apparatus for making products from polymer wood fiber composite
a technology of wood fiber and composite, which is applied in the field of wood fiber and polymer binder, can solve the problems of increasing the overall cost of the finished product, affecting the quality of the resulting product, and increasing the cost of wood materials used, and achieves the effect of high tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
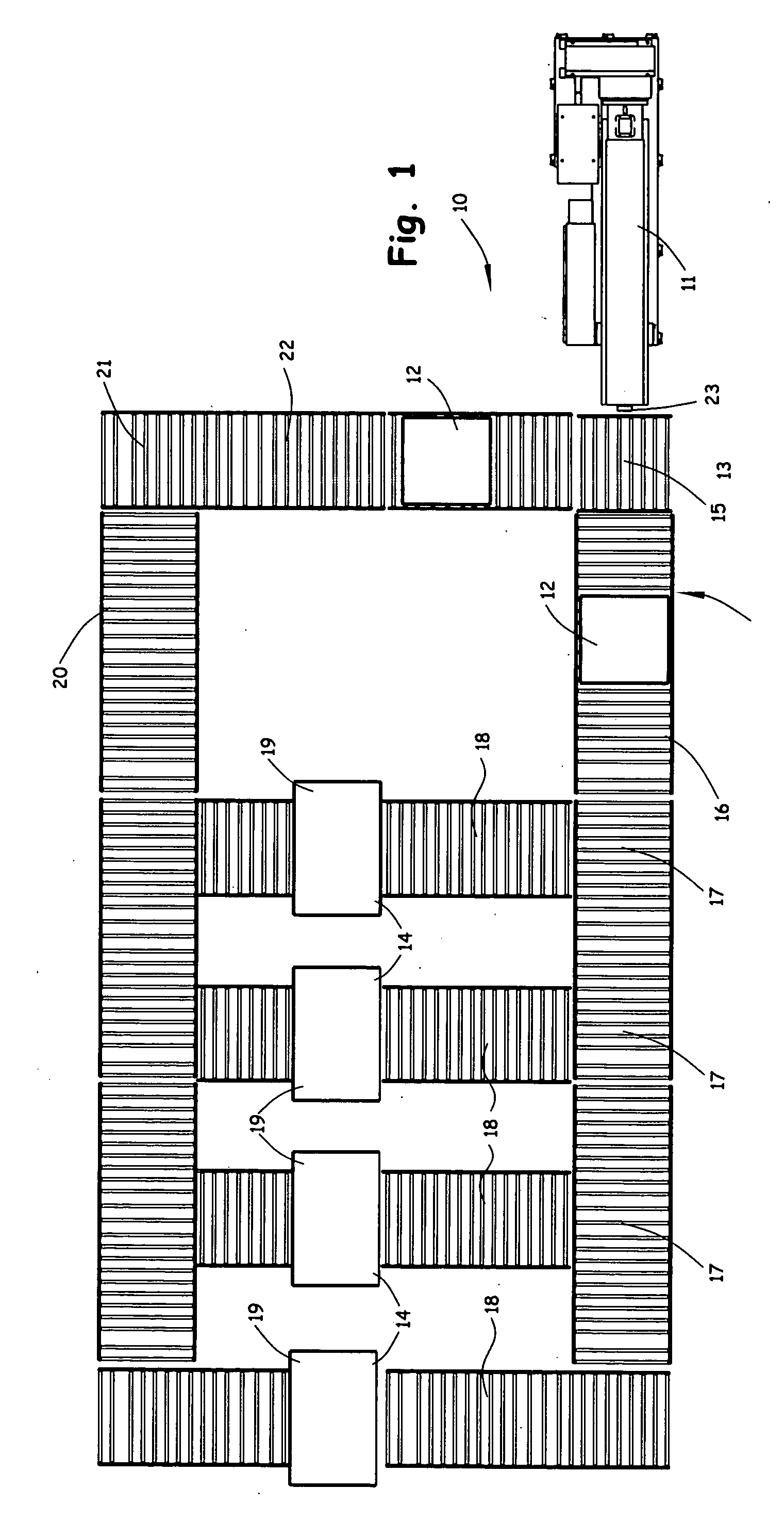
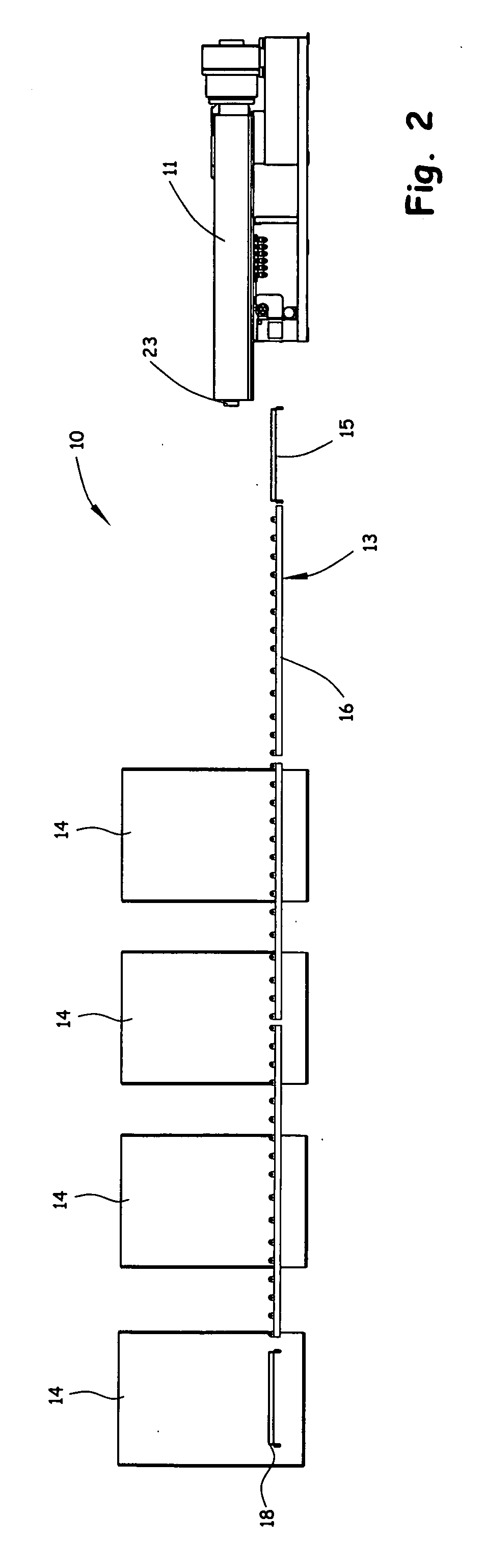
[0042] An example of a simple product made from the method of the present invention is a plank, with dimension of approximately 4 inches (100 mm) wide and ¾ inches (20 mm) thick with a sample length of 3 feet (1 m). A product have similar dimensions would be used in a variety of applications, such as marine docks, wood walkways or pallet slats. The molding process is performed using a mold that allows for multiple planks or boards to be formed in a single mold and compression cycle, with a single panel molded and finish cut after processing to desired final dimensions. The material used is a 50% mixture of HDPE and wood fiber. The wood fiber material was waste hardwood material with particles having typical lengths up to 2 inches (100 mm), widths up to 0.5 inches (12 mm) and thickness up to 0.05 inches (1 mm). The material is processed in an extruder having a 2-inch (50-mm) diameter twin non-intermeshing screws, with a throughput of 500 lb (227 kg) and an exit temperature of 340° F....
example 2
[0044] A sample nestable pallet skid was molded using the method of the present invention. The extruded mixture was made using a counter-rotating twin screw extruder having 2-inch diameter non-intermeshing screws, a 42-to-1 ratio, operating at 300 rpm, with two vents, one atmosphere vent and one vacuum vent. The material supplied to the extruder was a mixture of approximately 47½% by weight wood fiber material and approximately 47½% by weight high density polyethylene, with approximately 5% by weight additives, such as wax and compatabilizer. The wood fiber material was waste hardwood material with particles having typical lengths up to 2 inches (100 mm), widths up to 0.5 inches (12 mm) and thickness up to 0.05 inches (1 mm). The extruder provided a throughput of 390 lb / hr (180 kg / hr). Extruded material was produced in dollops or masses of approximately 58 lb (26 kg) each and transferred to a compression molding machine comprising a 1200-ton press. The mixture was held in the mold i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com