Cell culture media
a cell culture and media technology, applied in the field of cell culture media, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of obtaining serum, reducing the nutritional content of the basic media, and affecting the production efficiency of the biotech drug, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing the performance of serum-free media and reducing or eliminating the use of serum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method to Obtain Cholesterol-Rich Fraction From Bovine Serum
[0147] Starting material for a process according to the present invention can be maintained at a temperature of about 0° C. to about 50° C. Typically, the temperature is maintained at about 2° C. to about 15° C. A process according to the present invention can begin by subjecting the starting material to filtration. The filtration can be carried out utilizing one or more filtration steps. According to one embodiment, two filtration steps are sequentially utilized with filters having a nominal porosity of about 5 μ and about 1 μ. Any suitable filter in this range can be utilized.
[0148] If the starting material is serum, it is preferred to add a soluble salt, such as sodium citrate, to an ionic strength of about 0.25 to about 1. Other suitable salts include sodium chloride, sodium phosphate, potassium phosphate, ammonium sulfate and sodium sulfate. The addition of a soluble salt to the above concentration will increase the...
example 2
Use of EX-CYTE® to Reduce the Use of Serum
[0172] Methods
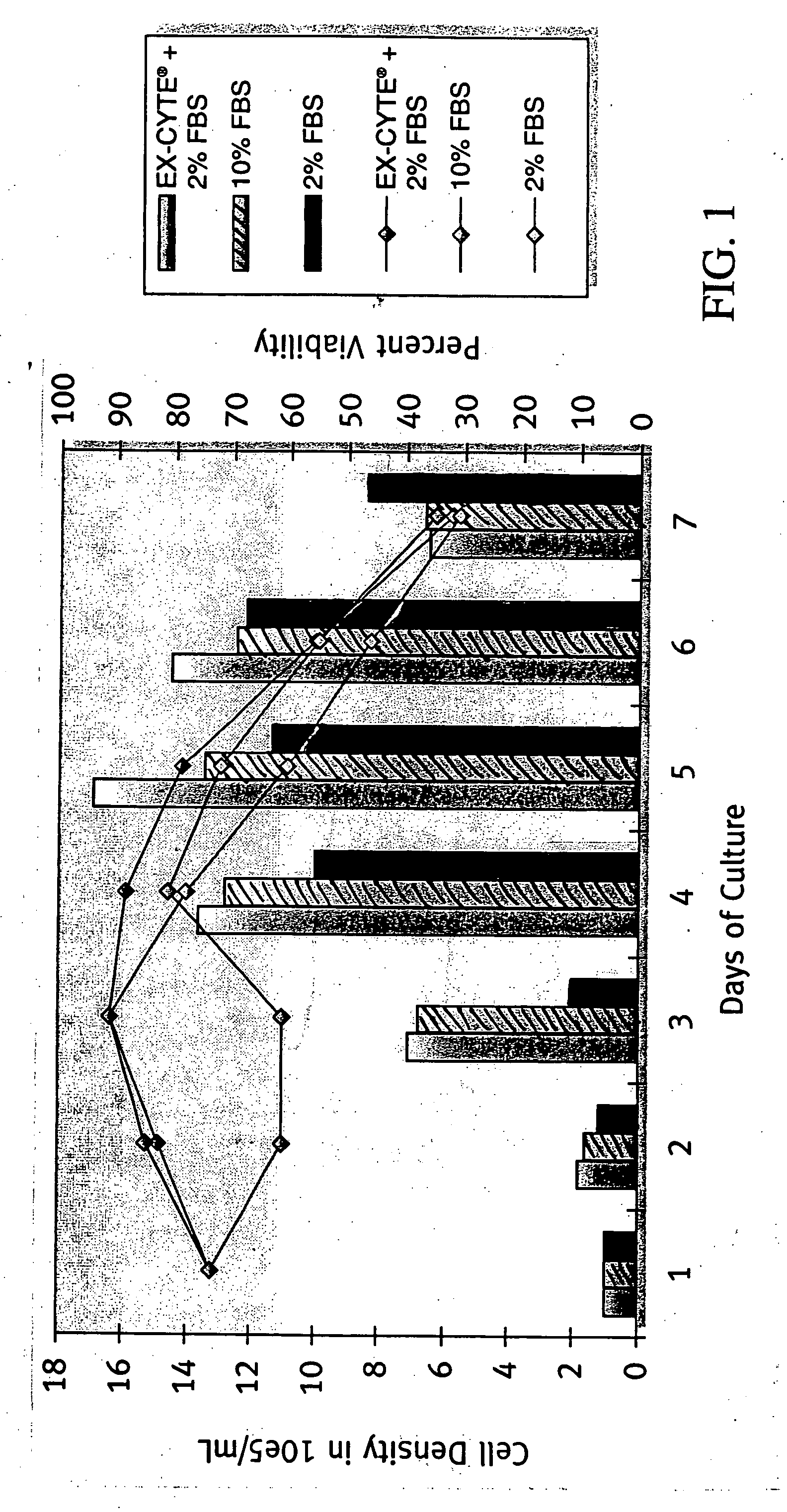
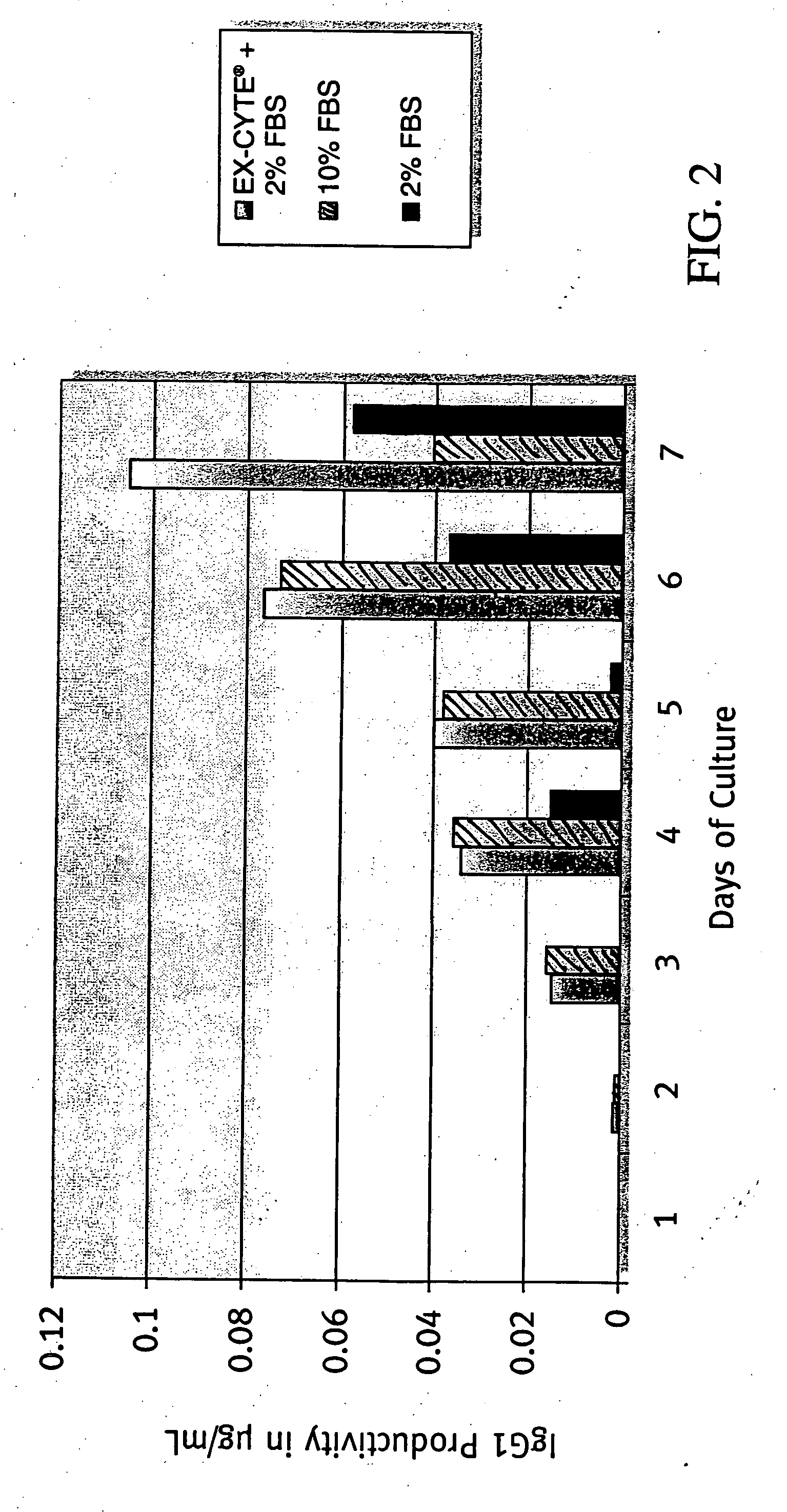
[0173] MK2.7 hybridoma cells were used. Seed inoculum was cultured in DME / F12 and FBS in spinners then adapted to less than 1% FBS by gradual reduction of FSB concentration. To begin the experiment, cells were washed in PBS and seeded at 1×102 cells / mL in each test condition. Batch cultures were sampled daily to monitor cell density and viability until culture viability was below 30%. Daily samples of culture supernatant were taken and processed to measure antibody production by ELISA.
[0174] Results
[0175] A combination of 0.5% EX-CYTE® and 2% FBS allowed for higher cell density and prolonged viability throughout the life of the culture as compared with 10% FBS (FIG. 1). The accumulative antibody level in the 0.5% EX-CYTE® and 2% FBS condition was more than double that of the 10% FBS culture on day 7 (FIG. 2). As a result, 0.5% EX-CYTE® effectively allowed the reduction of FBS from 10% to 2%.
example 3
Use of EX-CYTE® to Replace Serum
[0176] Methods
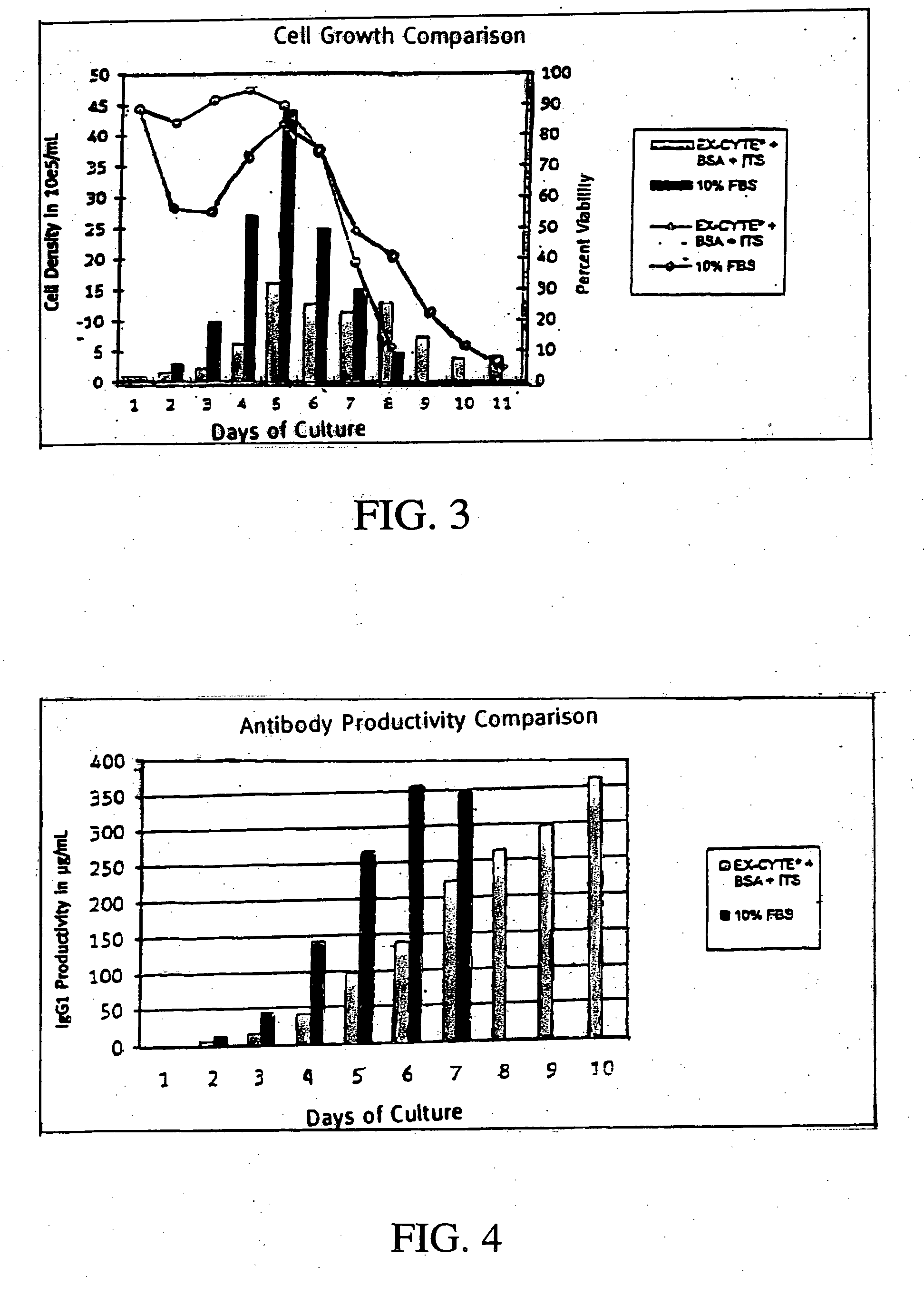
[0177] MK2.7 hybridoma cells were used. Seed inoculum was cultured in DMEM and FBS in spinners then adapted to less than 1% FBS by gradual reduction of FBS concentration. To begin the experiment, cells were washed in PBS and seeded at 1×105 cells / mL in each media condition. The test condition consisted of 0.75% EX-CYTE® 0.4% BSA, 6.7 ug / L sodium selenite. 10 mg / L insulin and 5.5 mg / L transferrin. (BSA (Serologicals Catalogue Number 81-068). Insulin (Serologicals Catalogue Number 4506), Transferrin (Serologicals Catalogue Number 4465)). Batch cultures were sampled daily to monitor cell density and viability until culture viability was below 10%. Daily samples of culture supernatant were taken to measure antibody production by ELISA.
[0178] Results
[0179] A combination of 0.75% EX-CYTE® and 0.4% BSA in DMEM constituted a complete serum-free media formulation. The temporary drop in culture viability in the test condition on days two and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com