Tin alloy electroplating system
a technology of tin alloy and electroplating system, which is applied in the field of plating a tin alloy, can solve the problems of tin plating suffering from a significant drawback, undesirable formation of spontaneous latent whisker, and ductile finish that can scratch or mar easily, so as to reduce the number of latent whiskering, and reduce the effect of disposal, environmental and health concerns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
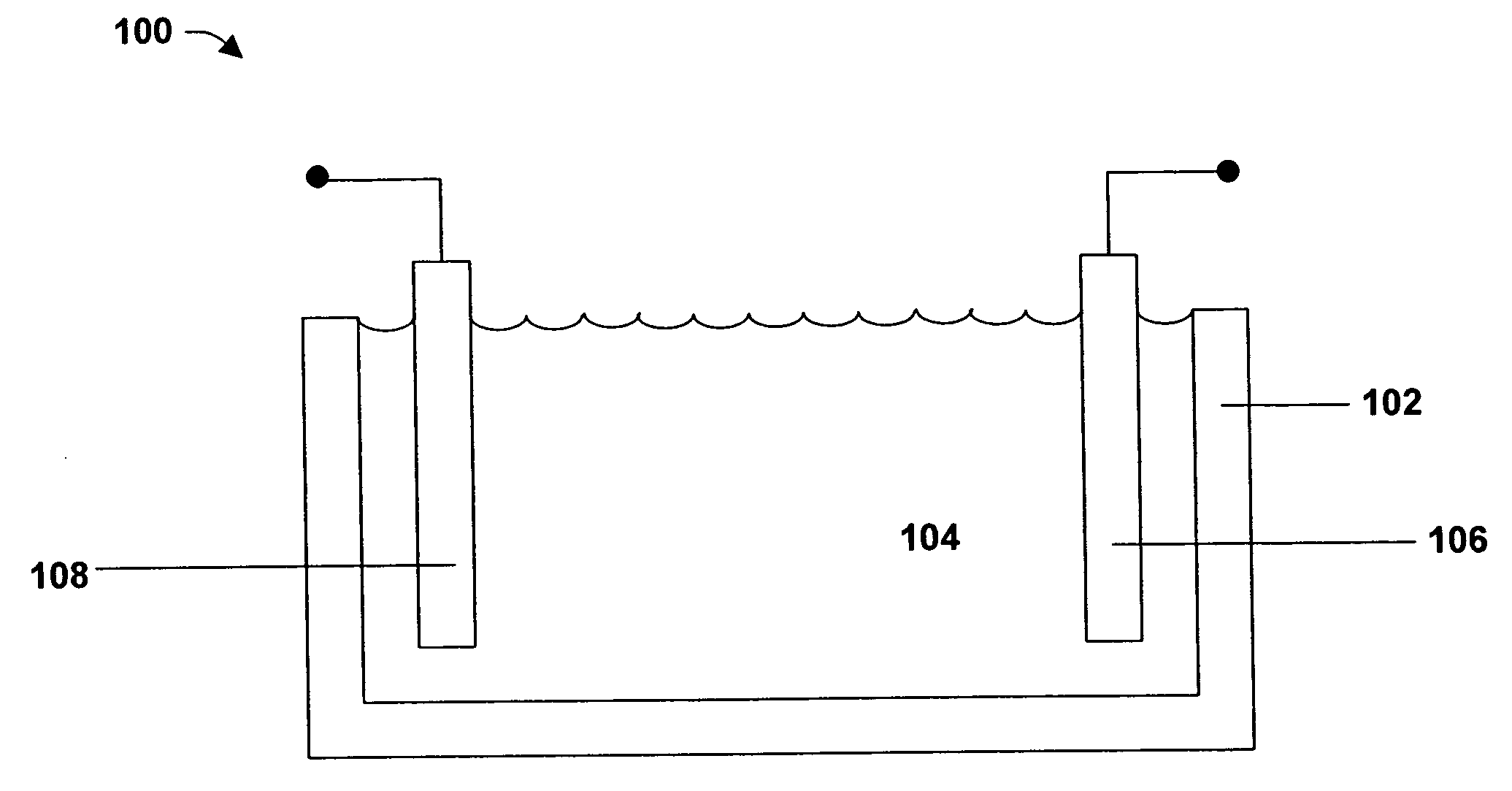
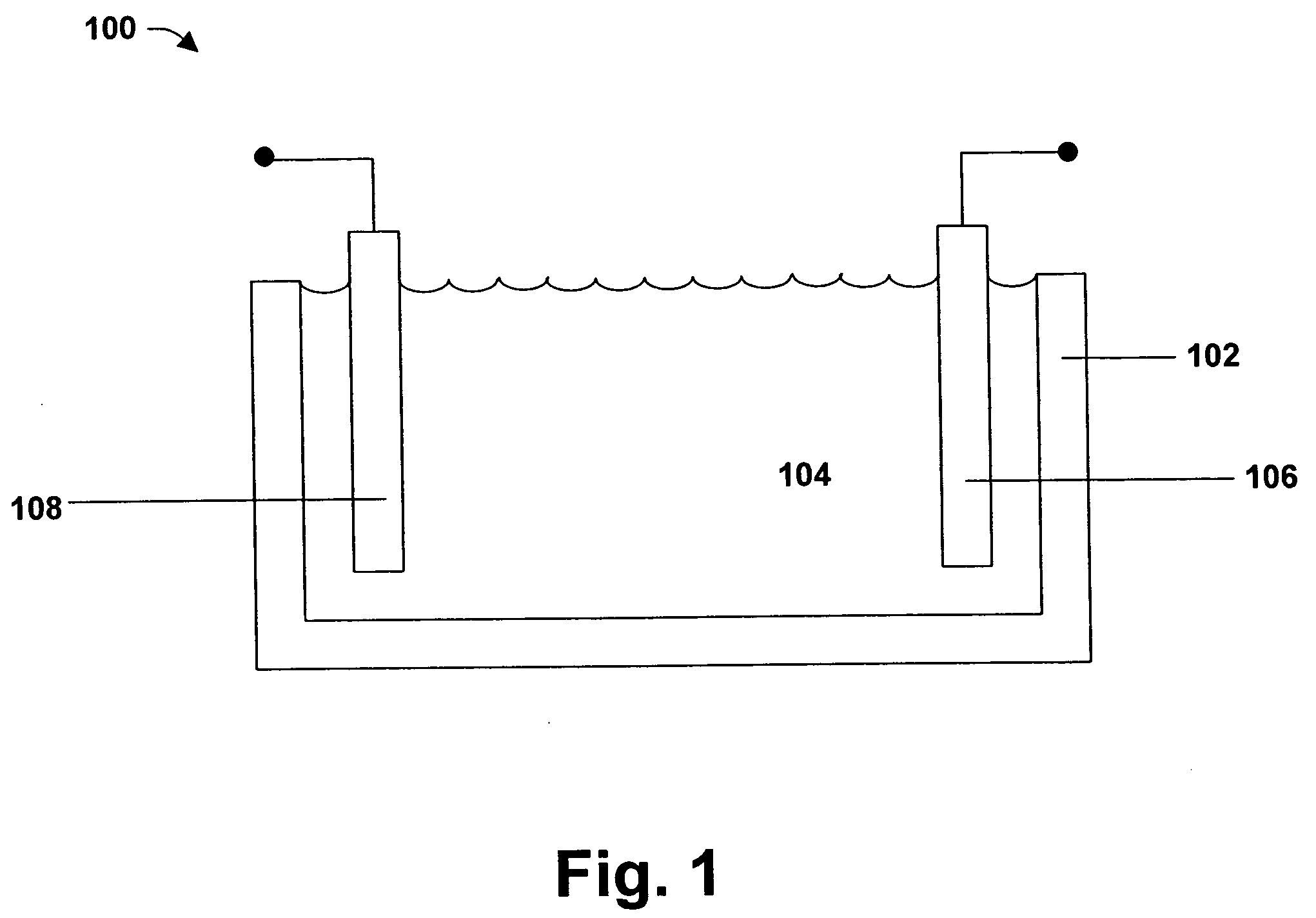
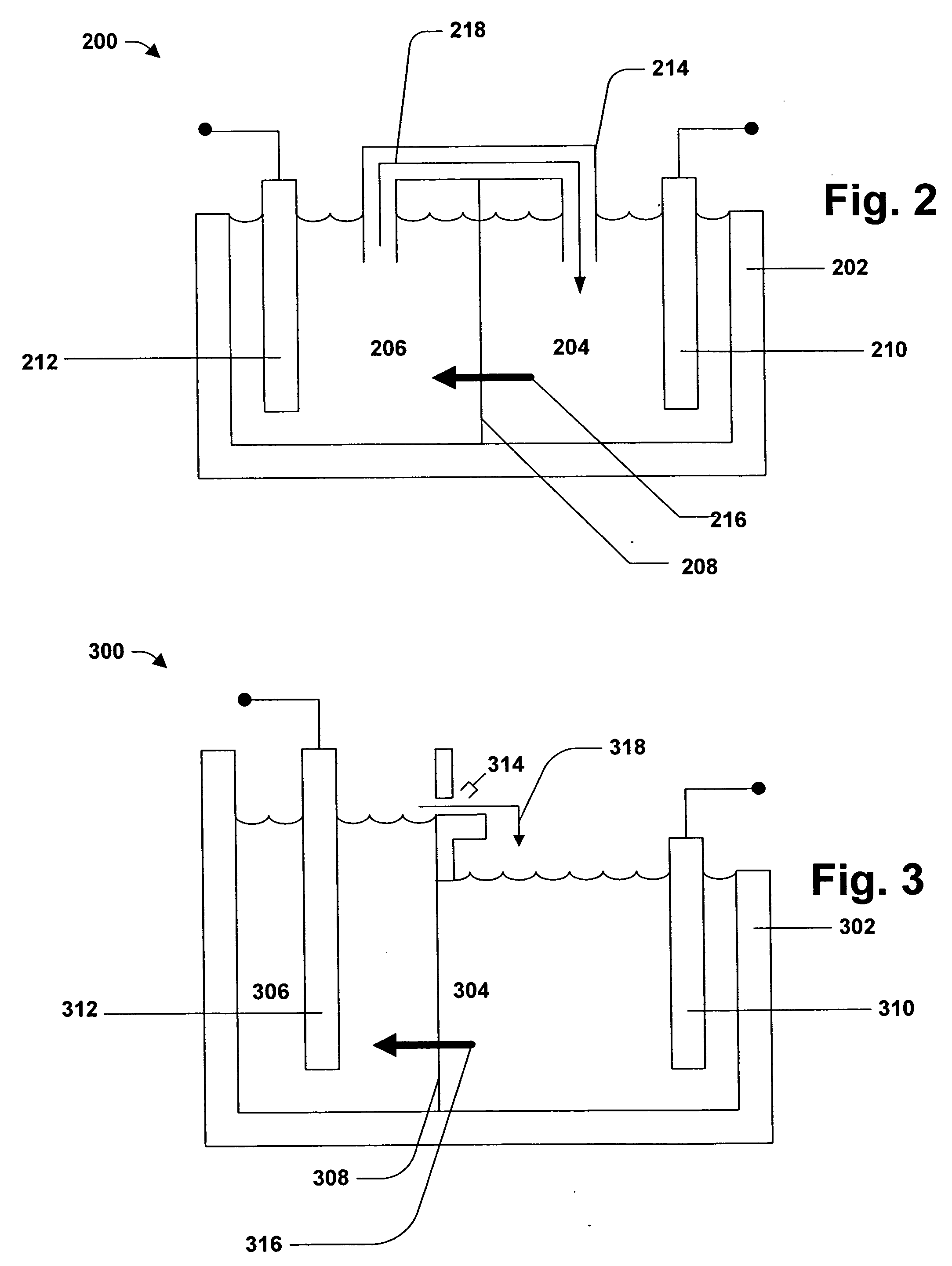
[0011] The subject invention can be employed for tin alloy electroplating. Generally speaking, electroplating involves metal in ionic form migrating in solution from a positive to a negative electrode. An electrical current passing through the solution causes substrates at the cathode to be coated by the metal (tin and alloy metal(s)) in solution. That is, in most embodiments, the substrate to be plated is the cathode.
[0012] The electroplating bath or catholyte and anolyte (for simplicity, the term electroplating bath is used to encompass single compartment and multiple compartment systems, multiple compartment systems including at least one catholyte and at least one anolyte) are aqueous solutions. In this connection, the electroplating bath contains water. However, the electroplating bath may optionally contain one or more co-solvents. Such co-solvents include water-miscible solvents such as alcohols, glycols, alkoxy alkanols, ketones, and various other aprotic solvents. Specific...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current carrying capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com