Oral GLP-1 formulations
a technology of oral glp-1 and formulation, which is applied in the field of oral glp-1 formulations, can solve the problems of reducing blood sugar levels, glp-1 may encounter difficulty in traversing the epithelial membrane cells, and the development of oral glp-1 therapeutics is extremely difficult, so as to facilitate the oral delivery of glp-1 and facilitate the bioavailability of glp-1
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Dosing Solutions
[0166] GLP-1 was obtained from Bachem (Torrance, Calif.) as a bulk powder. To prepare stock solutions, GLP-1 was dissolved in deionized water (pH6.5) to obtain a concentration of 8 mg / ml. Stock solutions were kept frozen at −20° C. in 0.5-ml aliquots until used. For dosing solutions, delivery agent was dissolved in deionized water to obtain a final concentration of 200 mg / ml (oral dosing) or 100 mg / ml (intracolonic dosing). The free acid form of delivery agent was converted to the sodium salt by adding one equivalent of sodium hydroxide. Solutions were vortexed, sonicated, and heated, and if necessary, additional sodium hydroxide was added in μl quantities to achieve uniform solubility. A specified quantity of GLP-1 stock was then added to the delivery agent solution to obtain a final concentration of 1 or 0.3 mg / ml (oral) or 0.6 mg / ml (intracolonic). After solubilization and drug addition, solutions were brought to final volume by the addition of dei...
example 2
Preparation of Deliver Agent No. 24 in Published International Application No. 03 / 072195
Preparation of 4-dimethylamino-benzoyl chloride
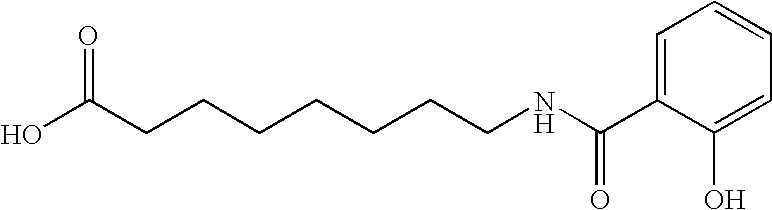
[0171] To a 1000 mL round bottomed flask was added 4-dimethylamino-benzoic acid (50.0 g, 1.0 eq) and THF (600 mL). A solution of thionyl chloride (44.16 mL, 2.0 eq) in tetrahydrofuran was added and the resulting mixture heated to reflux for 4 hours. The excess thionyl chloride and solvent were removed under reduced pressure to yield 4-dimethylamino-benzoyl chloride as a solid, which was used without further purification in the preparation of compound 560.
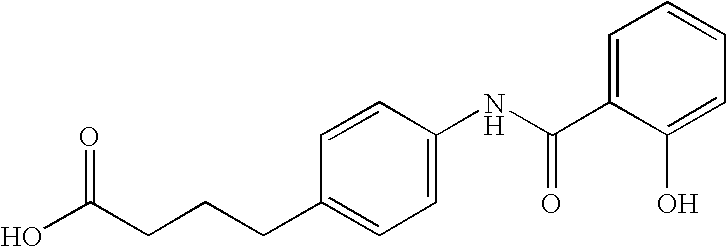
[0172] Preparation of delivery agent 24: To a 1000 mL round bottomed flask was added chlorotrimethylsilane (15.48 mL, 2 eq) in methylene chloride (250 ml). 4-aminobutyric acid (10.0 g, 1 equivalent) was added and the mixture was heated to reflux for 1.5 hours. The resulting solution was cooled to 0° C. (ice bath) and triethylamine (27.21 mL, 3 equivalents) was added drop-wise. A solution of 4-dime...
example 3
Preparation of Deliver Agent No. 8 in Published International Application No. 03 / 072195
[0173]
[0174] Step 1. 4,N-Dimethylbenzenesulphonamide was reacted with ethyl-8-bromooctanoate in DMF under the influence of sodium hydride to obtain 8-[Methyl-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-amino]-octanoic acid ethyl ester
[0175] Step 2. The ester of 8-[Methyl-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-amino]-octanoic acid ethyl ester was hydrolyzed in aqueous sodium hydroxide to obtain 8-[Methyl-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-amino]-octanoic acid
[0176] Step 3. The sulphonamide of 8-[Methyl-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-amino]-octanoic acid was removed under reductive conditions and the resulting amine reacted with hydrogen chloride to obtain (7-Carboxy-heptyl)-methylammonium hydrochloride.
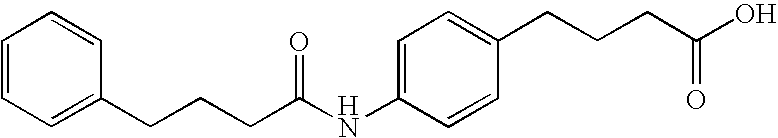
[0177] Step 4. The carboxylic acid of (7-Carboxy-heptyl)-methylammonium hydrochloride was protected in-situ with chlorotrimethylsilane. The resulting trimethylsilyl ester was reacted with 0-acetylsalicyloyl chloride. The protecting groups were removed with ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bioavailability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com