Prevention of ovarian cancer by administration of a vitamin D compound
a technology of vitamin d and ovarian cancer, which is applied in the field of prevention of ovarian cancer by administering vitamin d compounds, can solve the problems of no established pharmaceutical approach to the prevention of ovarian cancer, increased risk of identified genetic mutations such as brca1, and inadequate calcification of cartilage and bone, so as to prevent the development of epithelial ovarian cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
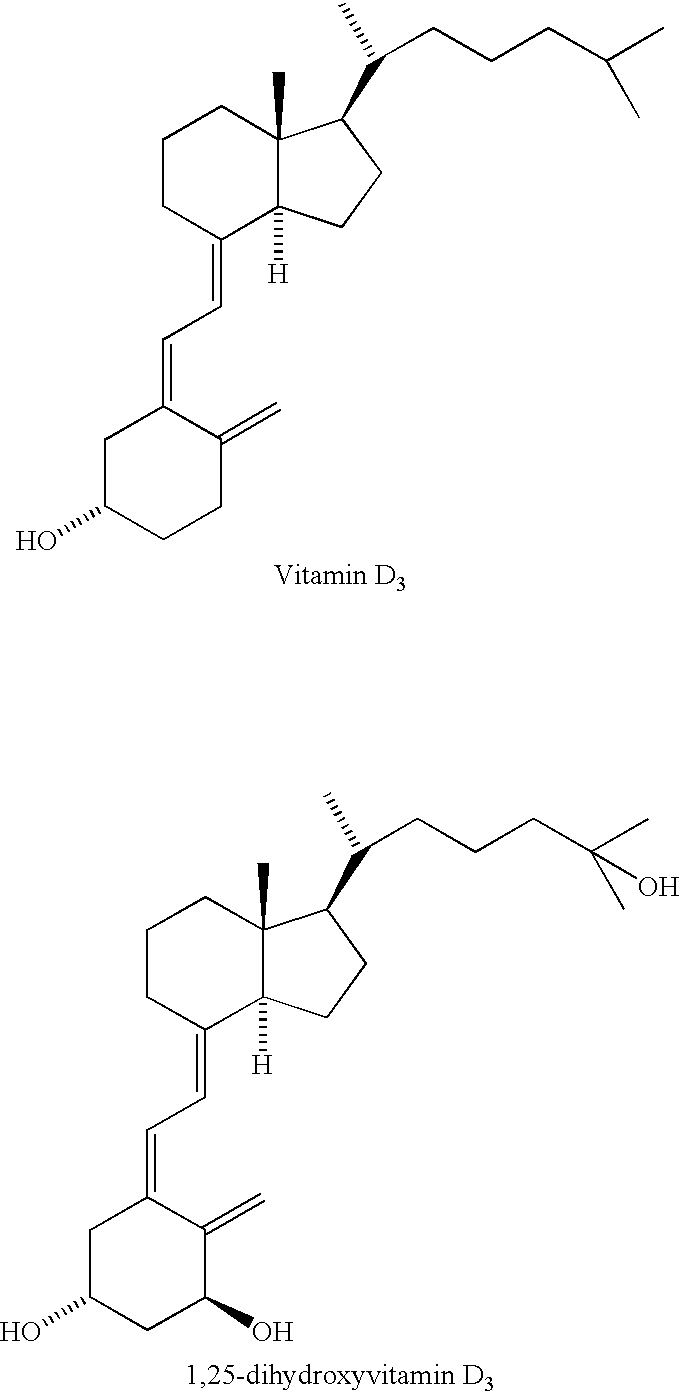
[0048] Example 1 addresses the effect of administration of Vitamin D on human ovarian epithelial cells. According to this example, a cell culture derived from normal ovarian epithelial cells was plated in 24 well plates at a concentration of 100,000 cells per well. After 24 hours, the wells were treated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 at a 100 nM concentration or control medium, and allowed to incubate for 96 hours. All experiments were carried out in triplicate. After 96 hours, cell lysates were extracted from each of the wells, and the cytoplasmic fraction was normalized for cell number and analyzed for DNA-histone complexes indicative of apoptosis using a cell death ELISA (Boehringer Mannheim). A significant (300%) increase in apoptosis (p=0.01) was measured in the human ovarian epithelial cells treated with Vitamin D as compared with the controls.
example 2
[0049] A spontaneously transformed yet non-malignant epithelial cell culture derived from normal human ovarian epithelial cells was plated in pronectin coated 6-well dishes at a concentration of 250,000 cells per well. The cells were allowed to plate and then grow to 70% confluence. The wells were then washed, and the medium was replaced with phenol red free, dextran charcoal treated medium containing 2% fetal calf serum, and treated with 500 ng / ml of 24,25 (OH)2D3 for 72 hours. The cells were harvested, centrifuged, and the resultant cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer. DNA was precipitated using the Puregene DNA Isolation Kit (Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, Minn.). Equal amounts of DNA were then subjected to electrophoresis on a horizontal 1.5% agarose gel containing ethidium bromide and visualized under UV illumination. On electrophoresis, DNA laddering (the hallmark of apoptosis) was observed in cells treated with 24,25 Vitamin D3, but not in the control, untreated cells...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com