Two-phase liquid cooling system with active venting
a liquid cooling system and active venting technology, applied in the direction of domestic cooling apparatus, semiconductor/solid-state device details, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of cooling system cooling fluid boiling point, cooling system cooling fluid loss, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the performance and reliability of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Two-Phase Cooling System with Active Venting
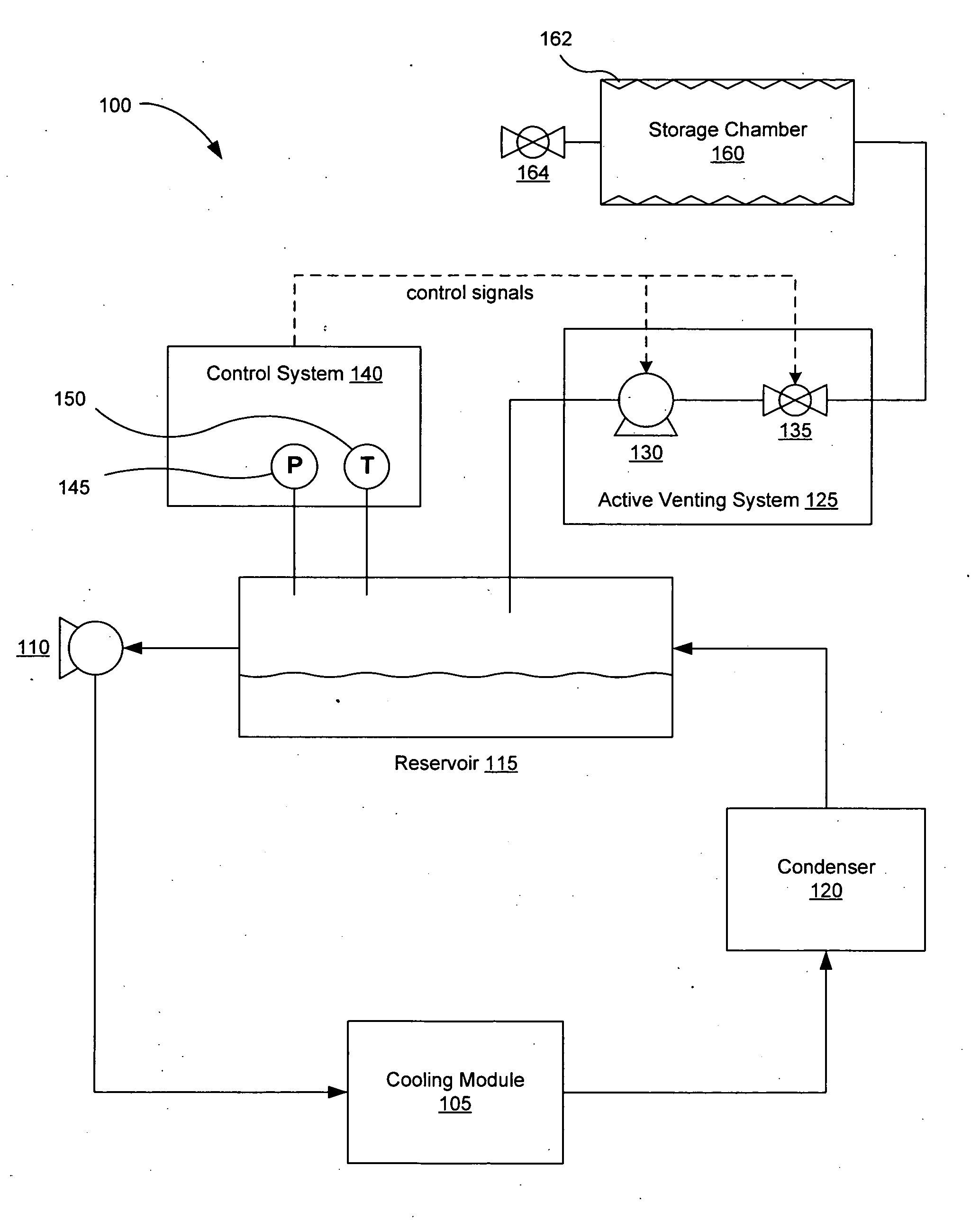
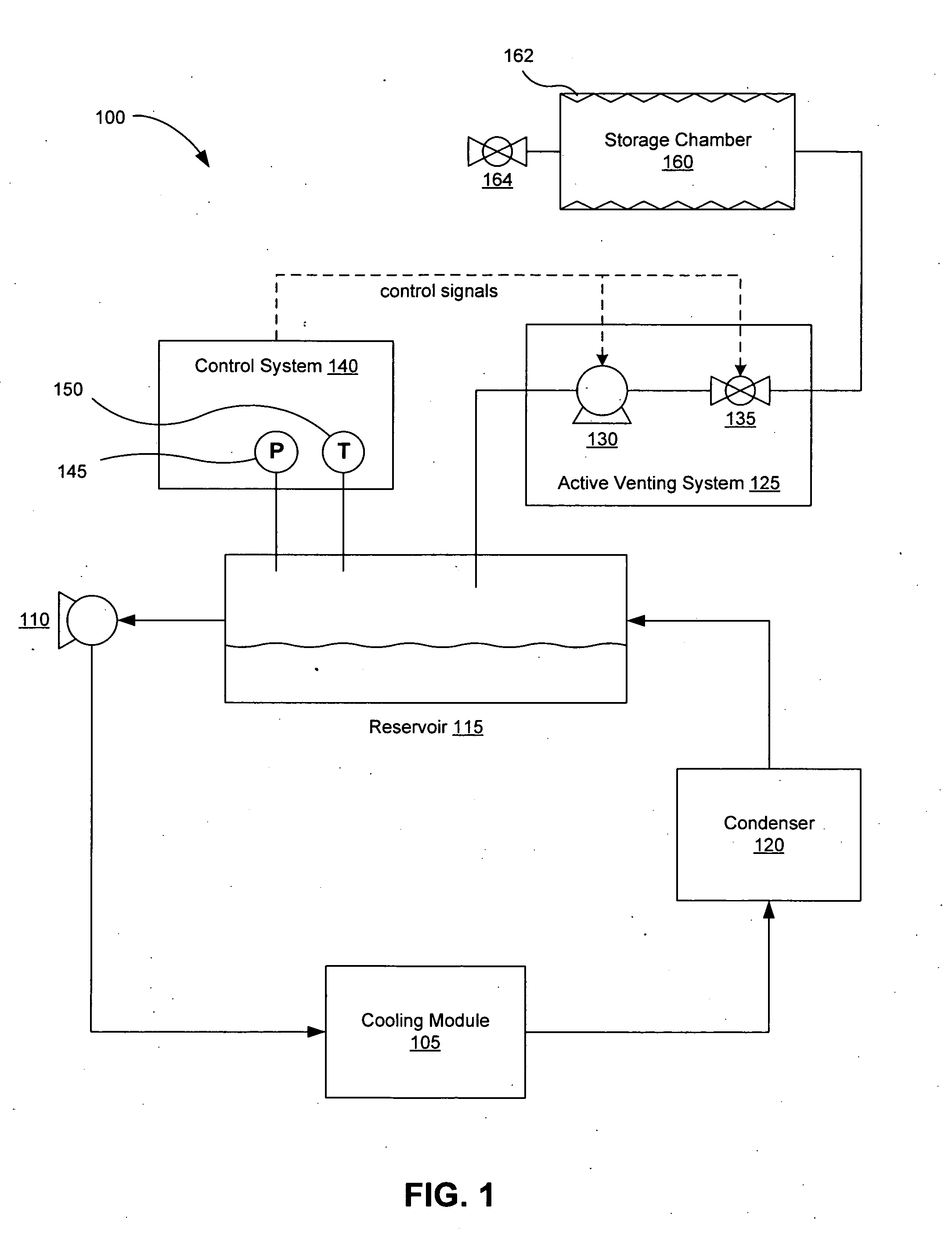
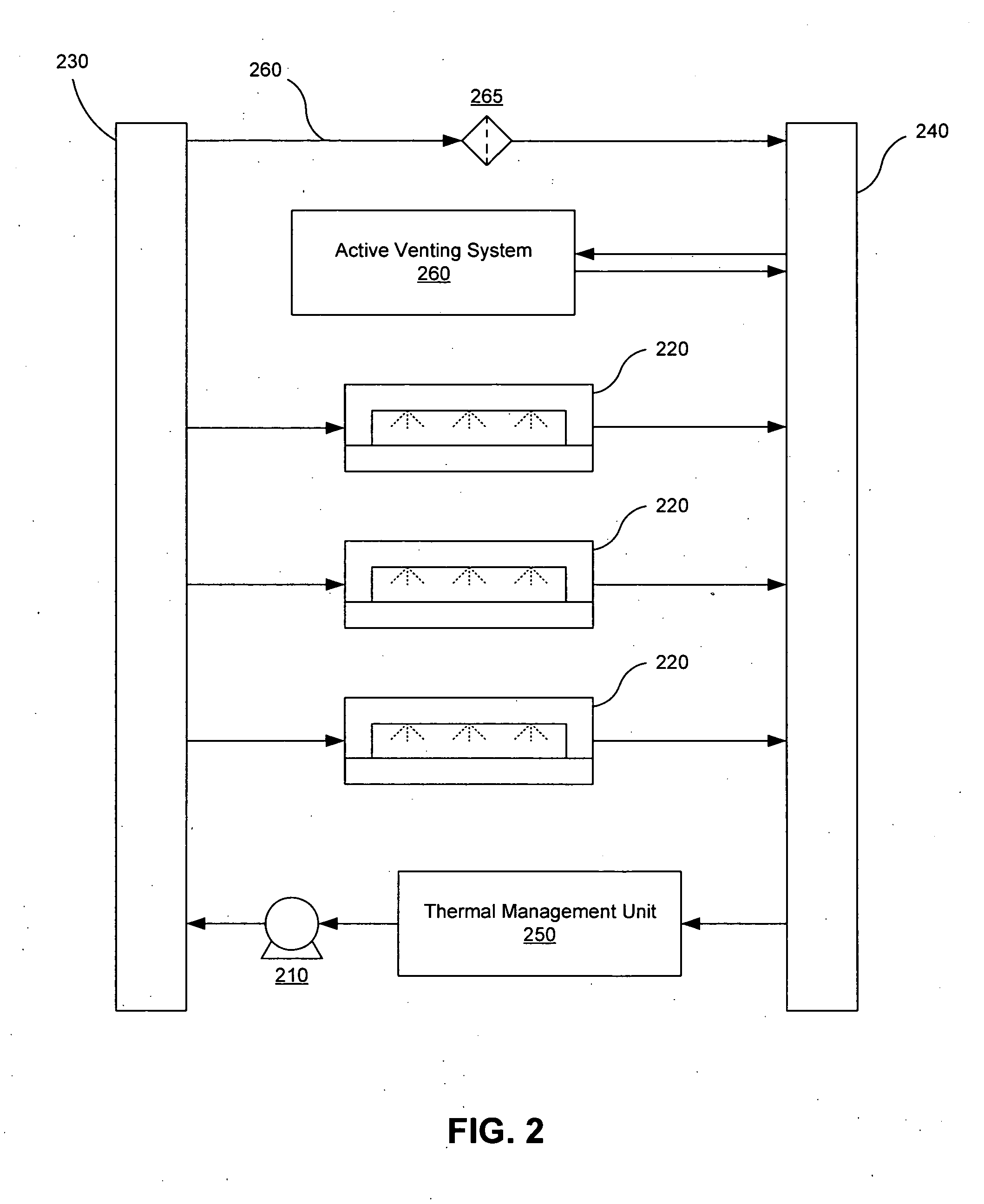
[0028]FIG. 1 illustrates one embodiment of a two-phase liquid cooling system 100 with active venting capabilities. The liquid cooling system 100 includes at least one cooling module 105, a pump 110, a reservoir 115, and a condenser 120. The pump 110 pressurizes a supply of liquid coolant from the reservoir 115 and delivers the liquid coolant to the cooling module 105. The cooling module 105 places the liquid coolant in thermal contact with a heat producing device (not shown), such as but not limited to computer processors, blade servers, circuit boards, memory, video cards, power devices, and the like. In the cooling module 105, heat from the heat producing device transforms at least a portion of the liquid coolant into a vapor phase fluid. The cooling fluid is transferred to a condenser 120, which removes heat and condenses the vapor phase fluid back into the liquid phase and delivers it to a reservoir 115. The liquid coolant can then b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com