Laser safety system
a laser and safety technology, applied in the field of laser safety systems, can solve the problems of laser radiation damage to an unprotected human eye, potential harm to both people and equipment, and considerable physical damage to the eye, so as to achieve the effect of safely safe positioning a laser system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
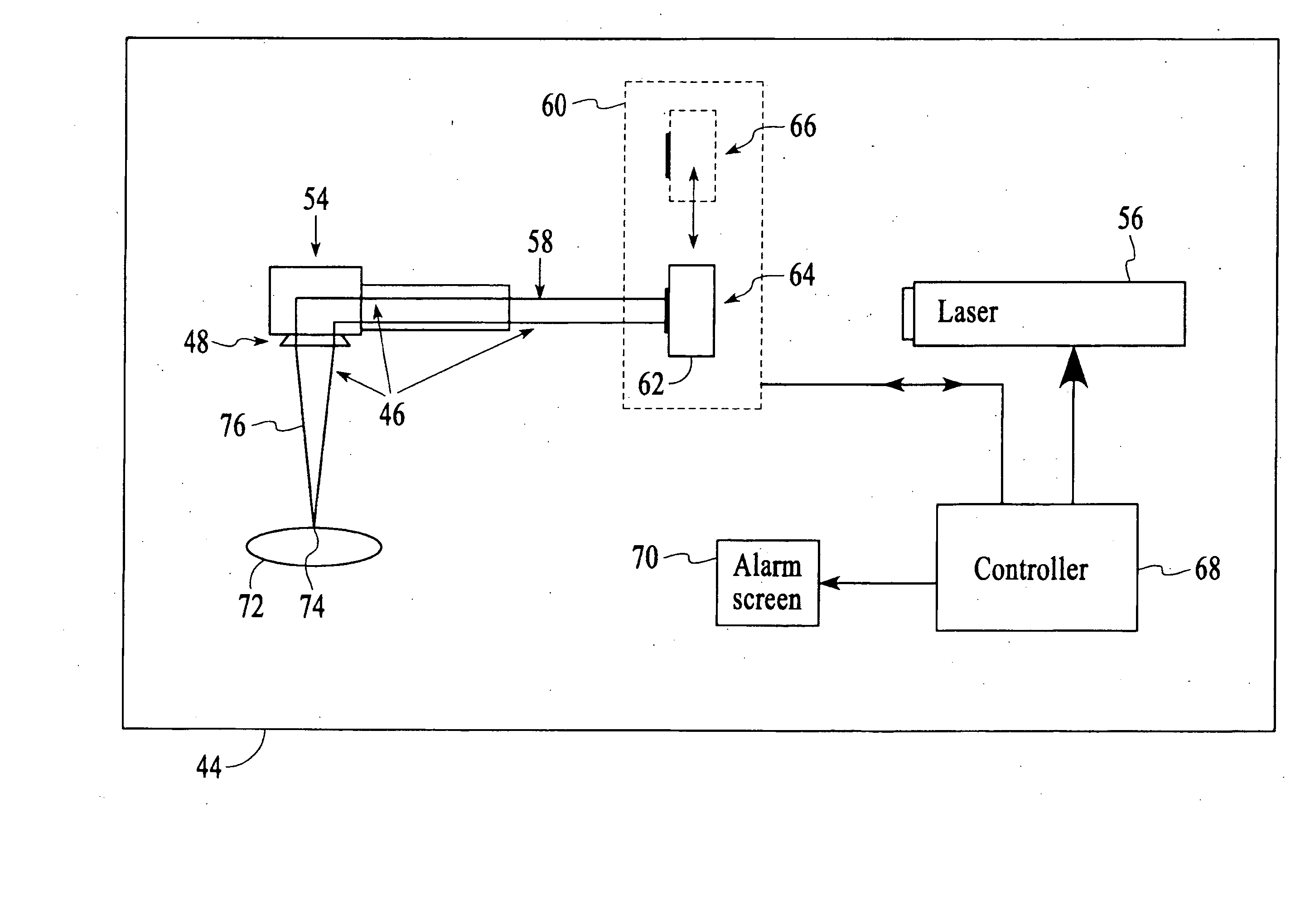
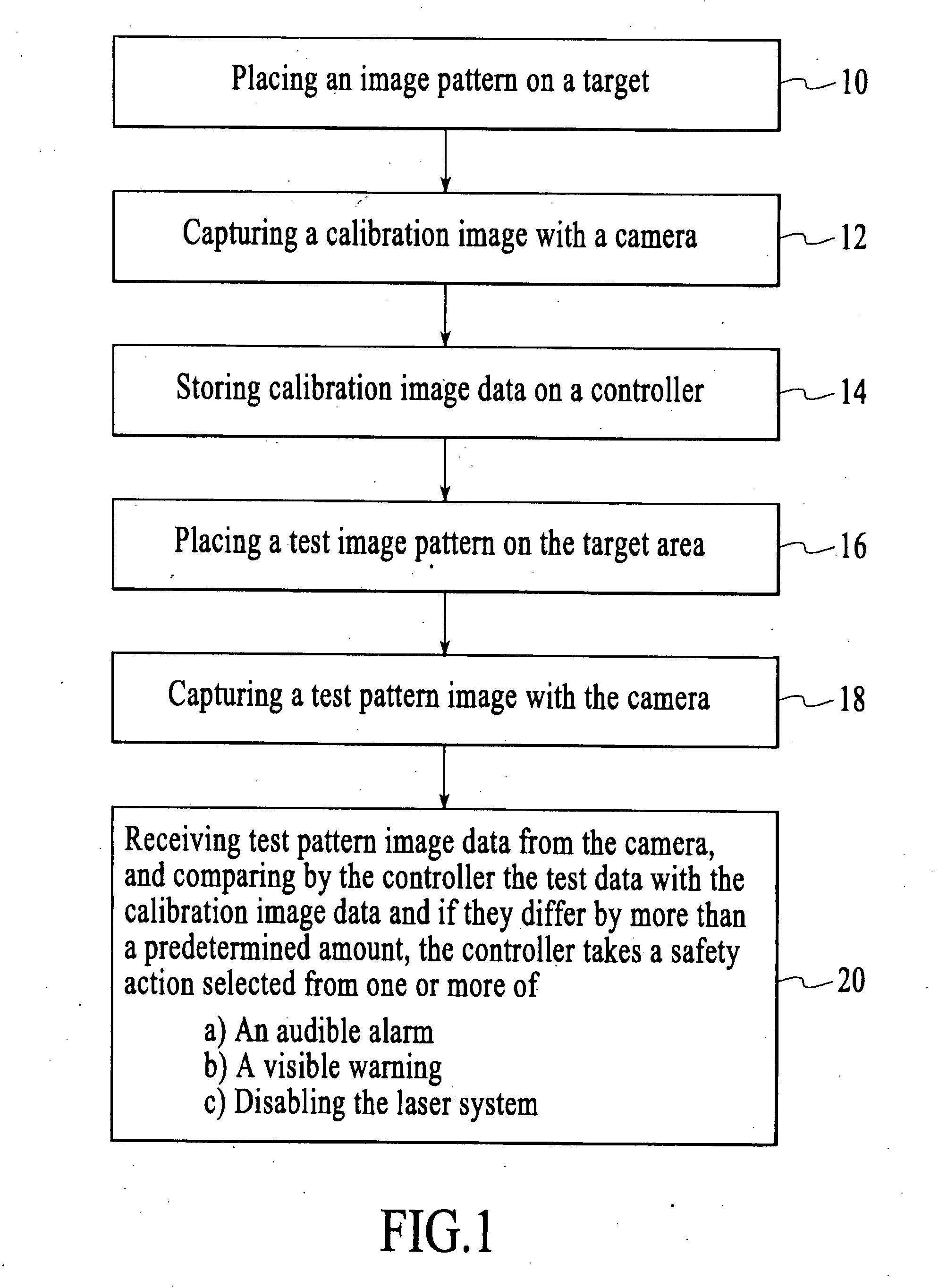
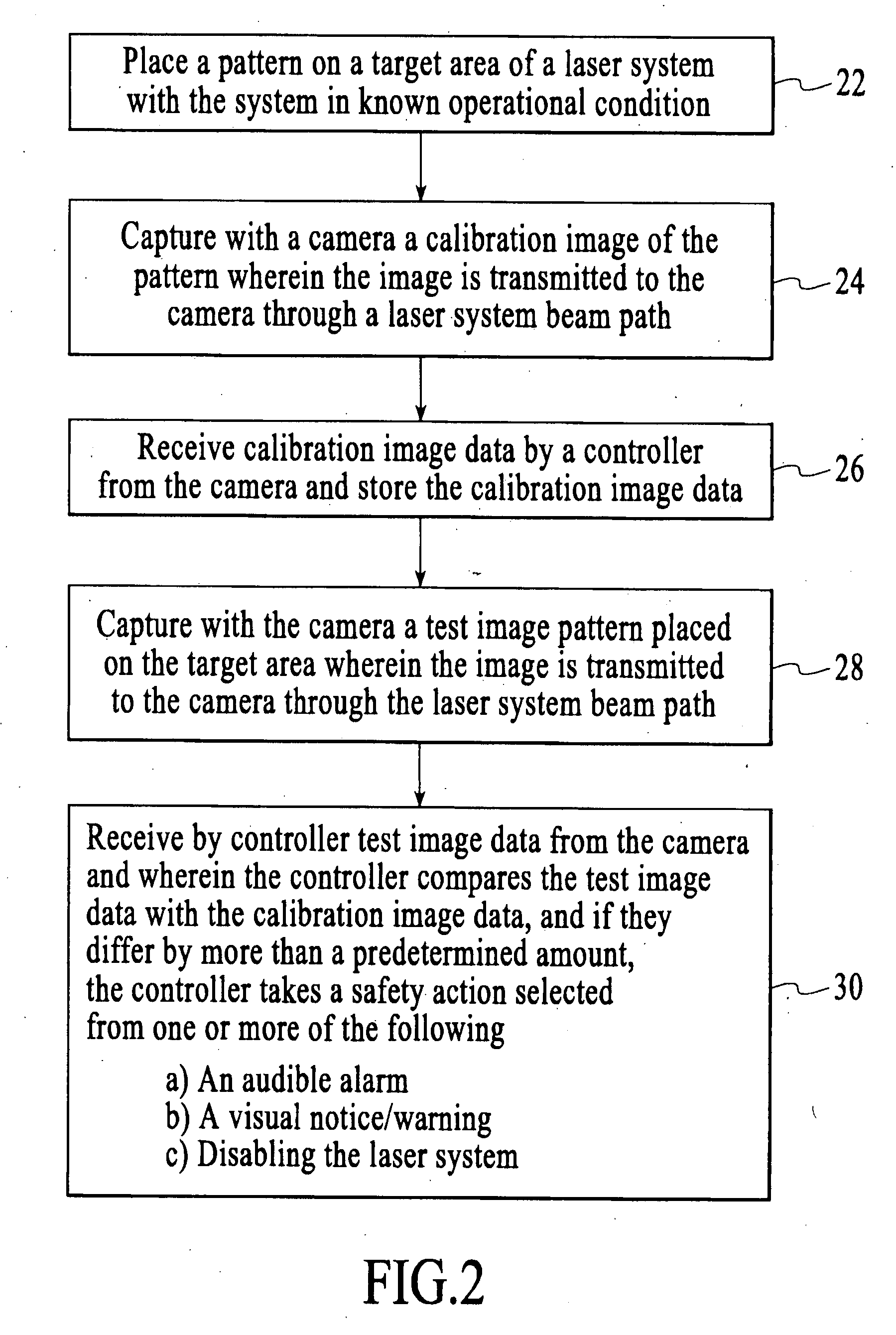
[0051] A method of the present invention is illustrated generally in reference to FIG. 1 of the drawing. A safety system is described for the purpose of reducing the possibility of a laser beam being misdirected and causing damage to persons or property. According to block 10, a calibration image pattern is placed on a target area of a laser system. The term “image pattern” will refer to any form of visible pattern, including a printed or scribed pattern, picture, etc. The image pattern can also be a non-material image, such as a projected light image for example. The adjective “calibration” in “calibration image pattern” is used to indicate that at this point in the method, the system has been determined to be in acceptable working condition, and the image data to be collected at this point referred to as image calibration data is to be used as a reference for future image data, termed “test data” or “image test data” taken prior to operation of the system. The calibration procedur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com