Heat dissipation substrate for electronic device
a technology for electronic devices and heat dissipation substrates, which is applied in the direction of heat management of led devices, transportation and packaging, and metal adhesion improvement of insulation substrates, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of high temperature of led devices, and negative impact on luminous intensity and service life, etc., to improve thermal conductivity of systems, improve the bonding with fluorine-containing polymers, and improve the effect of thermal conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
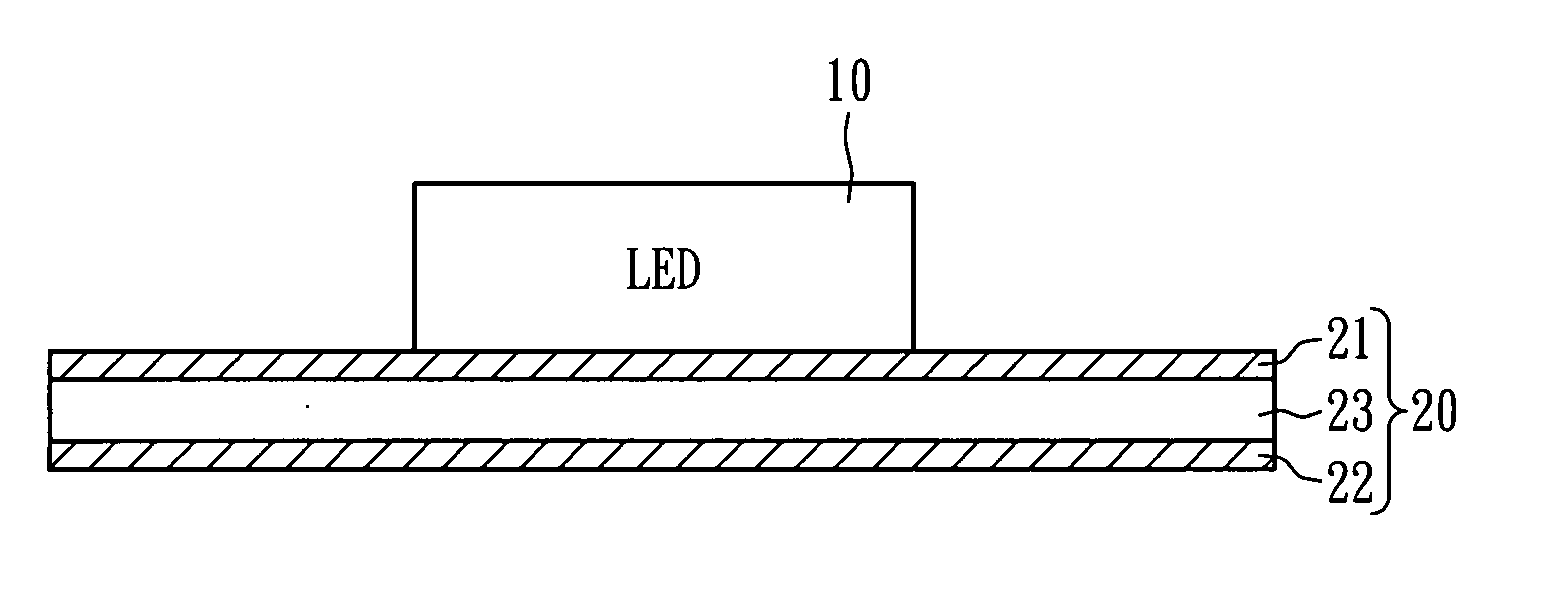
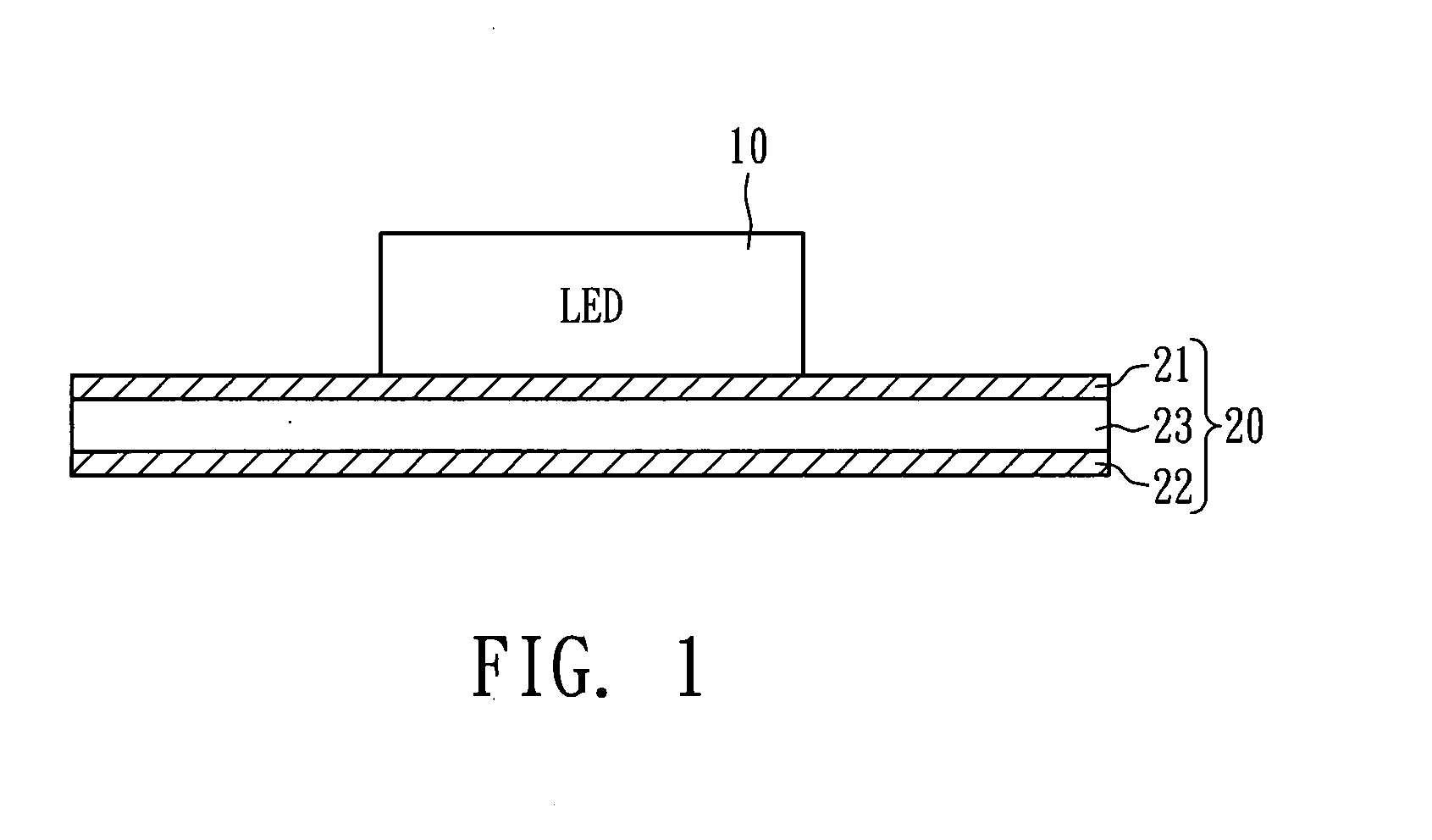
[0016]Referring to FIG. 1, an LED device 10 is carried by a heat dissipation substrate 20. The heat dissipation substrate 20 includes a first metal layer 21, a second metal layer 22, and a thermally conductive polymer dielectric insulating layer 23 stacked between the first metal layer 21 and the second metal layer 22. The LED device 10 is disposed on the surface of the first metal layer 21, and the interfaces between the first and second metal layers 21 and 22 and the thermally conductive polymer dielectric insulating layer 23 are physically contacted, wherein at least one interface is a micro-rough surface. The micro-rough surface has a plurality of nodular projections with a grain size mainly in a range of 0.1-100 μm, thereby increasing the tensile strength therebetween.
[0017]The method of fabricating the heat dissipation substrate 20 is described as follows. The feeding temperature of a batch-type blender (HAAKE-600P) is set to be 20° C. higher than the melting point (Tm) of the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness Rz | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com