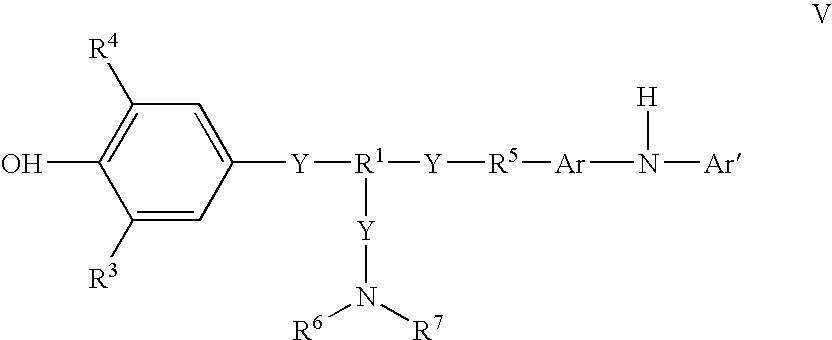
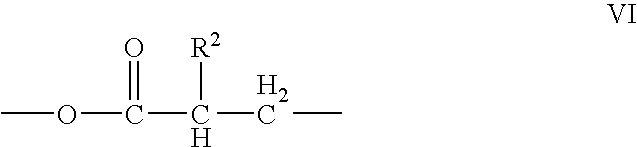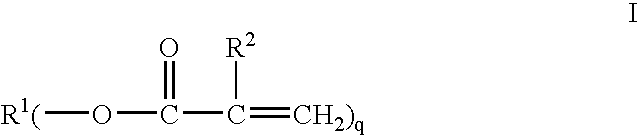Compound and method of making the compound
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method of Making a Compound
[0054]An exemplary process for making an compound of the present application was carried out as follows:
[0055]Step 1: A 1-liter 4-neck flask equipped with nitrogen sub-surface was charged with 236.8 g of trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA), 300 g methanol, and 0.8 g of laural mercaptan. To this solution 192.8 g of bis(2-ethylhexylamine) was added dropwise over 4 hr period and then allowed to stir at room temperature for 3 hrs. The temperature was then raised to 65° C. to distill methanol and finally vacuum stripped and filtered over Celite. A total of approximately 424 g of product was isolated. % N=2.74%
[0056]Step 2: A 500 mL flask was charged with 149 g of process oil, 64 g of 2,6-di-tert butylphenol and 1 g of potassium hydroxide. The mixture was heated to about 120° C. and then mild vacuum was applied to remove about 1.3 ml of distillate. Vacuum was removed and the mixture was then heated to 140° C. 161 g of the product isolated from step 1 was then...
example 2
Method of Making an Compound
[0058]Another exemplary process for making a compound of the present application was carried out as follows.
[0059]A 500 ml flask was charged with 74 g of TMPTA and 240 g of butanol. The flask was equipped with nitrogen sub-surface and reflux condenser and heated to about 80° C. 46 g of NPPDA was added in portions over 30 min and the mixture was then heated to reflux for 8 hrs. 51.5 g of 2,6-di-tert butylphenol and 0.7 g potassium hydroxide were added and the mixture was again held at reflux for 7 hrs. The reflux condenser was replaced with a distillation apparatus and the mixture was heated to 145° C., during which almost 200 ml butanol was removed. The mixture was cooled to 65° C. and 60.3 g of bis(2-ethylhexyl)amine was added dropwise over a 2 hr period. The mixture was held at 65° C. for 3 hrs and then vacuum stripped. 7 g of talc was added and stirred for 30 minutes, followed by filteration through paper to remove solids. The filtered product had 4.22...
example 3
Evaluation of Engine Oils Containing the Compound of Example 1 in the Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test (TEOST MHT-4)
[0060]The TEOST MHT-4 is a standard lubricant industry test for the evaluation of the oxidation and carbonaceous deposit-forming characteristics of engine oils. The test is designed to simulate high temperature deposit formation in the piston ring belt area of modern engines. The test utilizes a patented instrument (U.S. Pat. No. 5,401,661 and U.S. Pat. No. 5,287,731; the disclosure of each patent is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety) with the MHT-4 protocol being a relatively new modification to the test. Details of the test operation and specific MHT-4 conditions have been published by Selby and Florkowski (Selby et al.) in a paper entitled, “The Development of the TEOST Protocol MHT as a Bench Test of Engine Oil Piston Deposit Tendency” presented at the 12th International Colloquium Technische Akademie Esslingen, Jan. 11-13, 2000. Wilfried ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com