Hybrid carbon nanotube reinforced composite bodies
a carbon nanotube and composite body technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of high hardness, compressive strength and wear resistance, high toughness and impact strength, and achieve the effect of reducing the hardness and impact strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
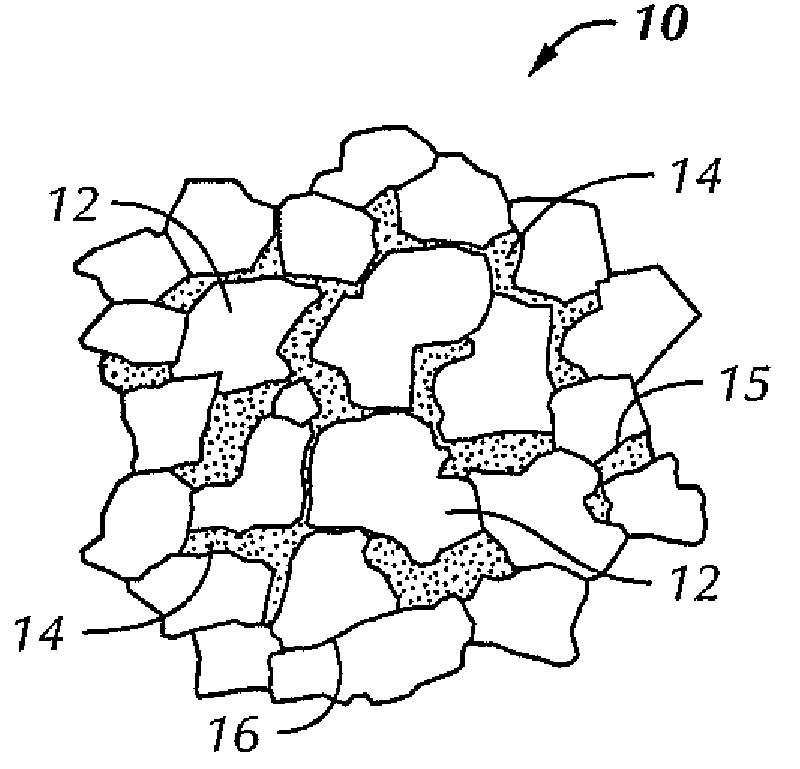
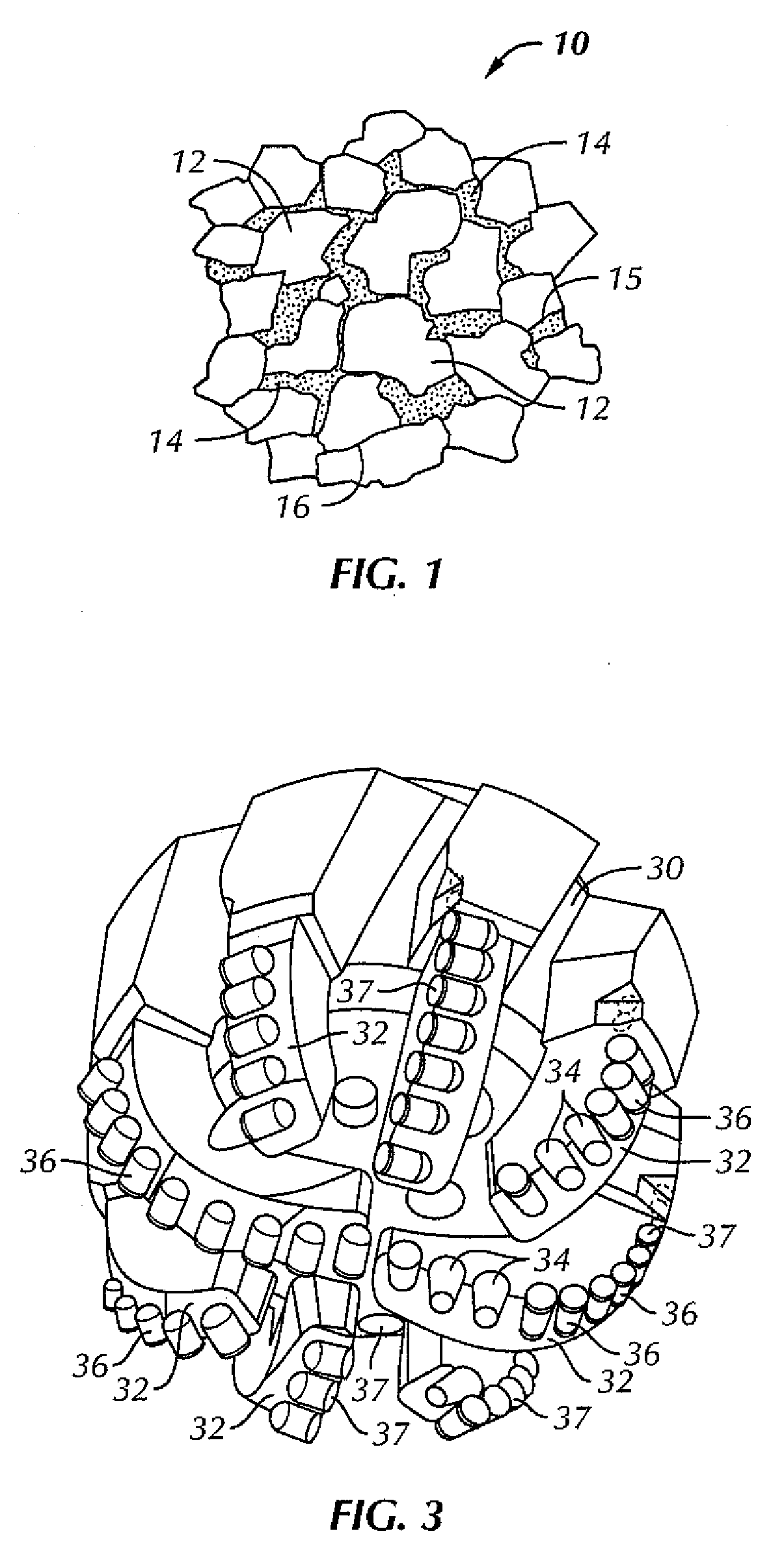
[0027]In one aspect, embodiments disclosed herein relate to composite or matrix bodies used in components of downhole cutting tools, including drill bits, mining picks, core bits, etc. In particular, embodiments relate to composite bodies having formed from tungsten carbide particles surrounded by a ductile metal matrix binder with a reinforcing nanotubular material.
[0028]In addition, embodiments of the present disclosure provide composite bodies which are formed from such tungsten carbides infiltrated by suitable metals or alloys as infiltration binders. Such a composite body may have high transverse rupture strength and toughness while maintaining wear and erosion resistance. Embodiments of the present disclosure are based, in part, on the determination that the life of a composite bit body is related to the body's strength (also known as transverse rupture strength), toughness, and resistance to erosion.
[0029]FIG. 1 illustrates the conventional microstructure of cemented tungsten...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com