Pharmaceutical dosage forms fabricated with nanomaterials for quality monitoring
a nano-material and dosage form technology, applied in the direction of material heat development, instruments, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the application of nano-materials, affecting the quality of nano-materials,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
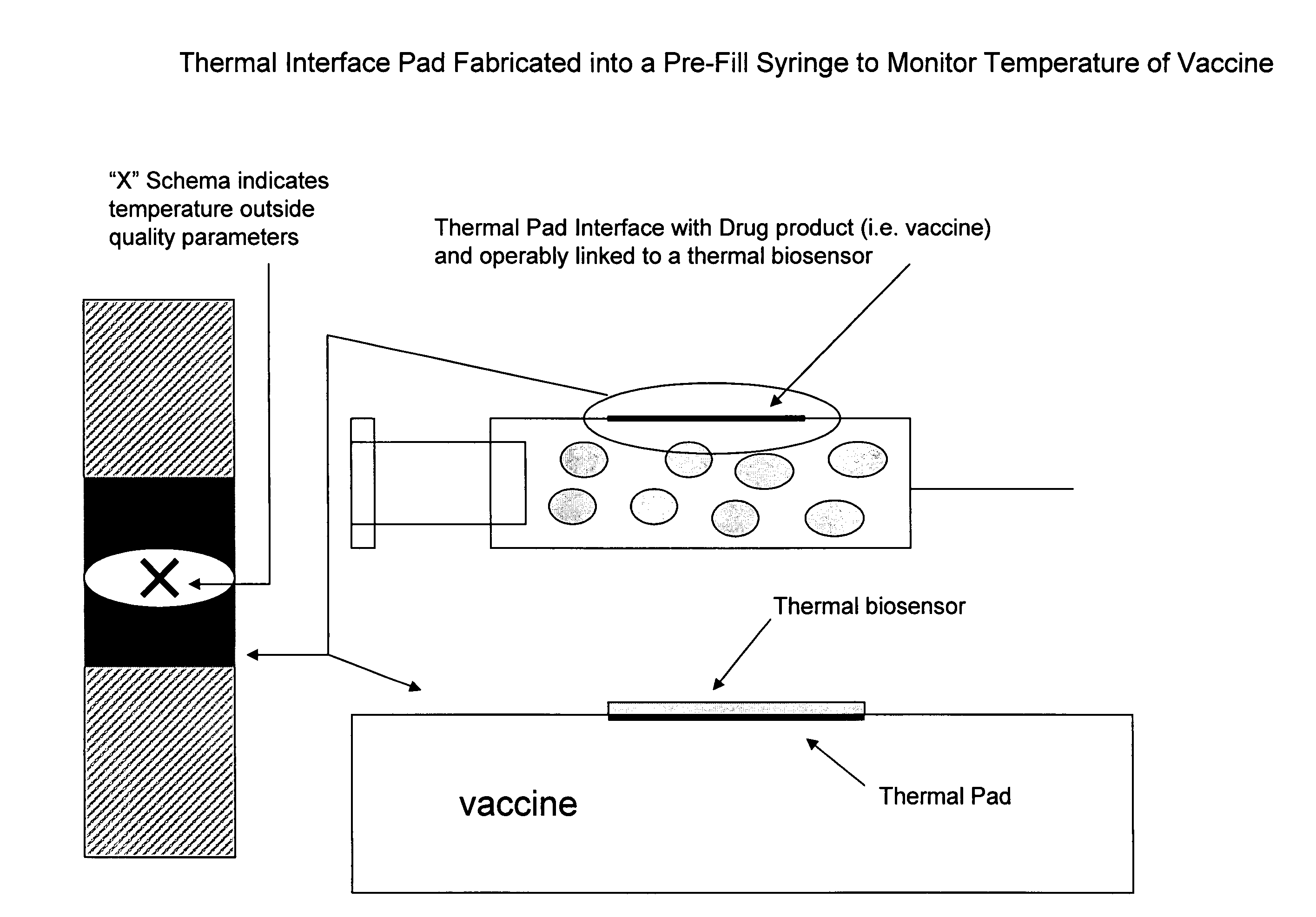
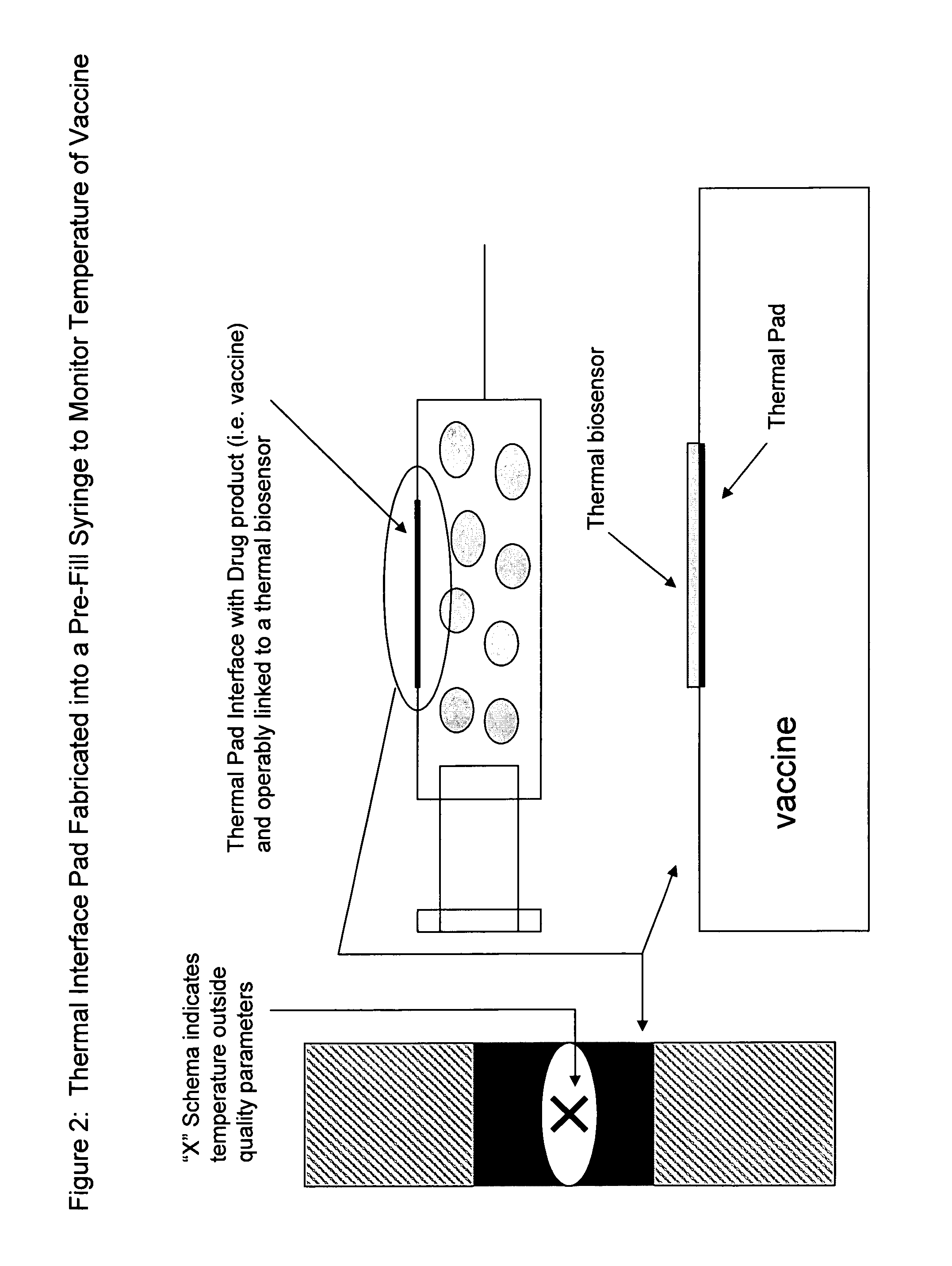
Thermally Conductive Nanomaterials Fabricated into Pre-Filled Syringes
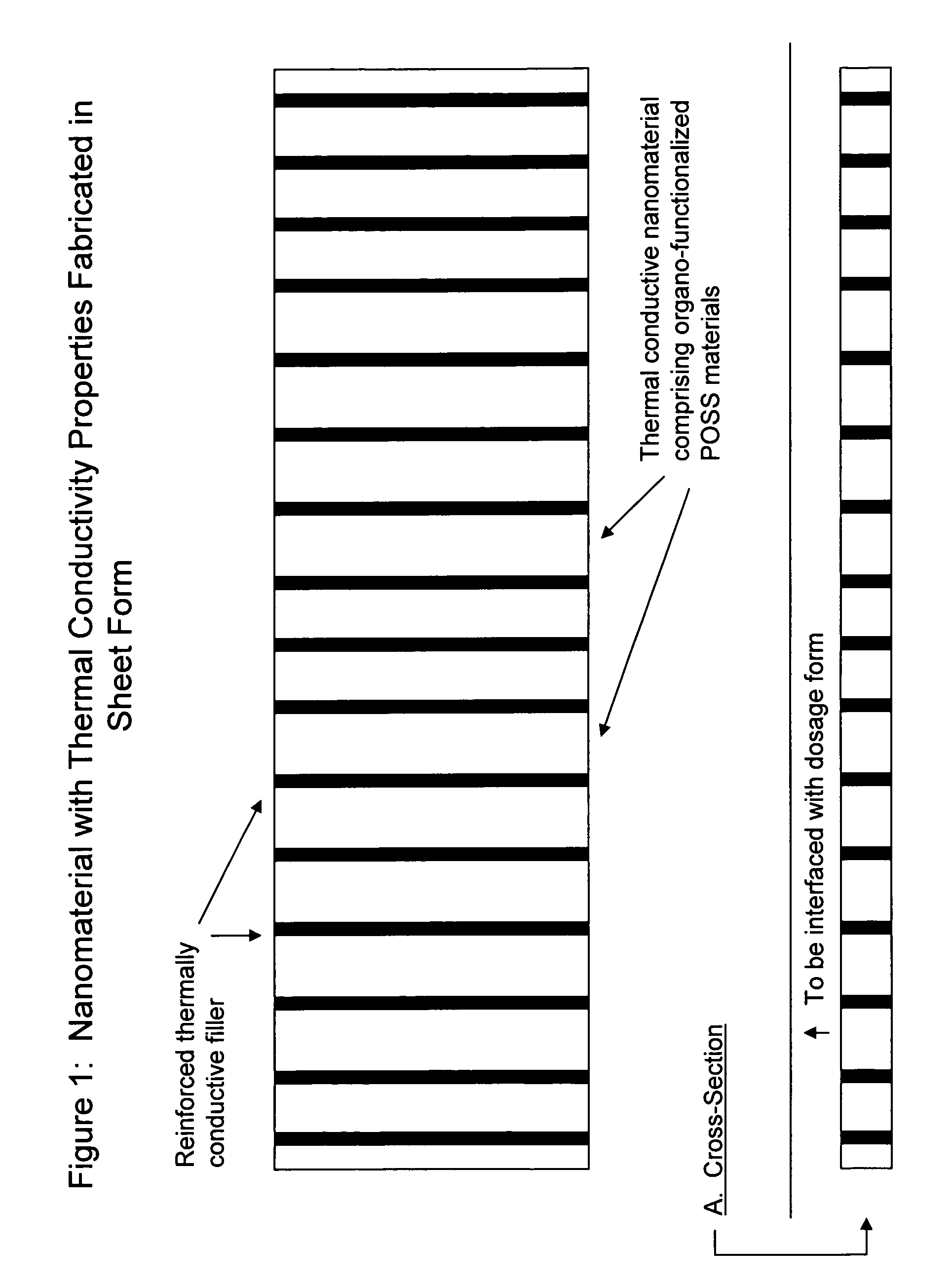
[0206]The nanomaterial with enhanced thermal conductivity is generated by methods known in the art. The nanomaterial is formed into sheets providing an interface between the thermal pad and the drug product and providing an interface between the thermal pad and a thermal biosensor. (FIG. 1). In one embodiment, the nanomaterial is fabricated into a pre-filled syringe. The thermal biosensor monitors temperature of the drug product enclosed therein (e.g. a vaccine). When the temperature falls outside the pre-set parameter(s) a schema notifies the end-user (e.g. doctor, patient, nurse, etc.) and the dosage form is discarded or corrective action is taken. (FIG. 2).
[0207]In one embodiment, the monitoring and quality assessment achieves a step of supply chain management whereby drug product quality and shelf-life are increased. Costs are reduced over time.
[0208]In a further embodiment, the monitoring and quality assessme...
example 2
Quality Monitoring of Drug Product Using Nanomaterials with Enhanced Luminescent Properties
[0209]The nanomaterial with enhanced luminescent properties is generated by methods known in the art. Dosage forms fabricated with the nanomaterials are produced by standard methods and a drug product is enclosed therein. Sensors monitor such properties as pH, temperature, degradation, potency, solubility, and other properties affecting drug product efficacy. When the pre-set property falls outside the quality parameter(s) a schema notifies the end-user (e.g. doctor, patient, nurse, etc.) and the dosage form is discarded or corrective action is taken. In one embodiment, the schema comprises a color change in the dosage form. In one embodiment, the schema comprises a symbol display on the dosage form. In one embodiment, the schema comprises a word display on the dosage form. (FIG. 3).
example 3
Optically Enhanced Nanomaterials Fabricated into Dosage Forms Enclosing Emulsions
[0210]The nanomaterial with enhanced optical properties is generated by methods known in the art. The nanomaterial is formed into graded index lens whereby the thickness of the lens is uniform providing an optimal interface between the contact lens the dosage form and the optical fiber. (FIG. 4). In one embodiment, the nanomaterial is fabricated into a dosage form enclosing an emulsion.
[0211]An emulsion is a mixture of two or more immiscible (unblendable) substances. One substance (the dispersed phase) is dispersed in the other (the continuous phase).
[0212]Emulsions tend to have a cloudy appearance, because the many phase interfaces scatter light that passes through the emulsion. Emulsions are unstable and thus do not form spontaneously. Energy input through shaking, stirring, homogenizers, or spray processes are needed to form an emulsion. Over time, emulsions tend to revert to a stable state. Addition...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase transition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com