Surface-emitting laser light source using two-dimensional photonic crystal
a laser light source and photonic crystal technology, applied in lasers, semiconductor lasers, active medium materials, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the efficiency of laser beams
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
(1) First Embodiment
One Example of the First Aspect of the Surface-Emitting Laser
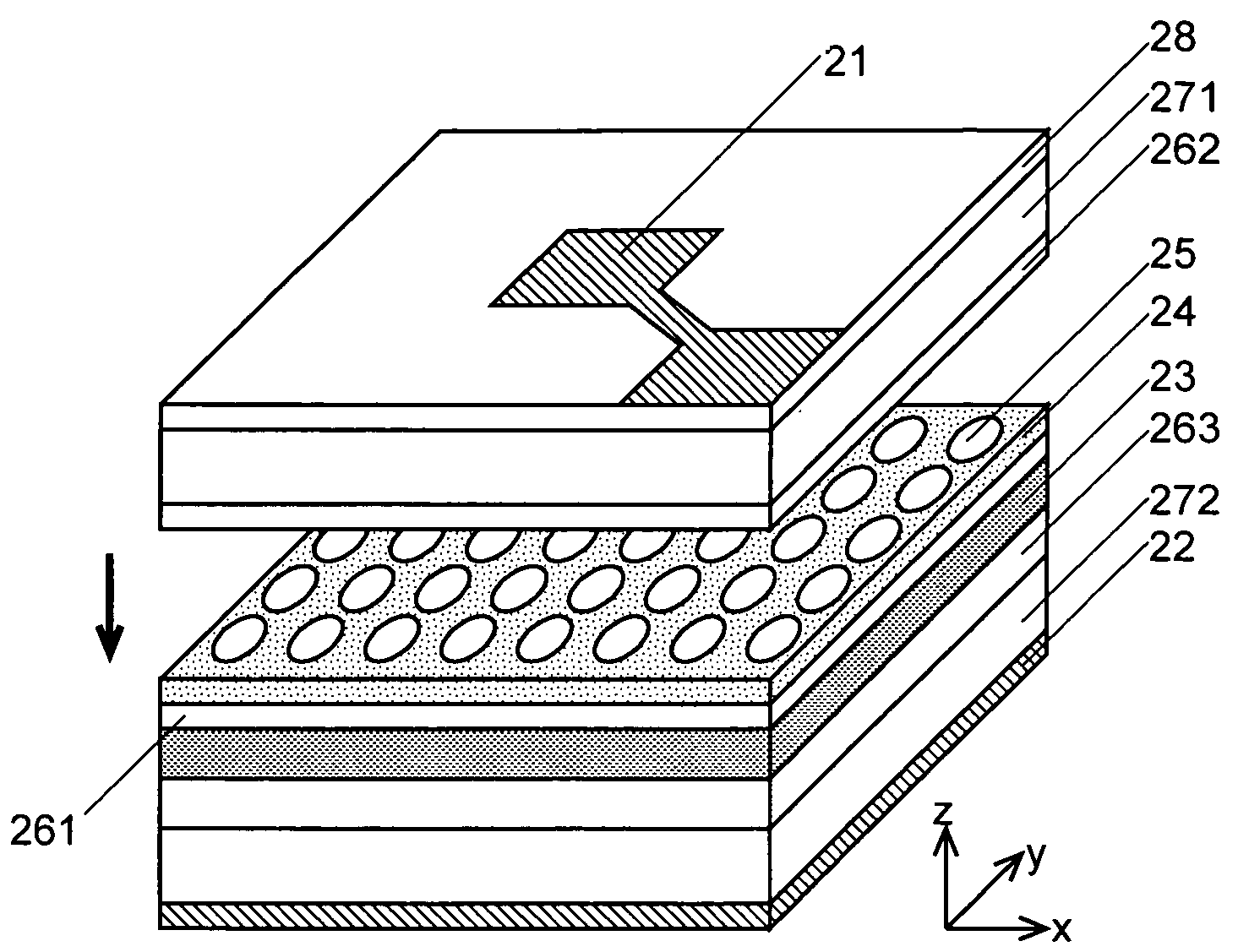
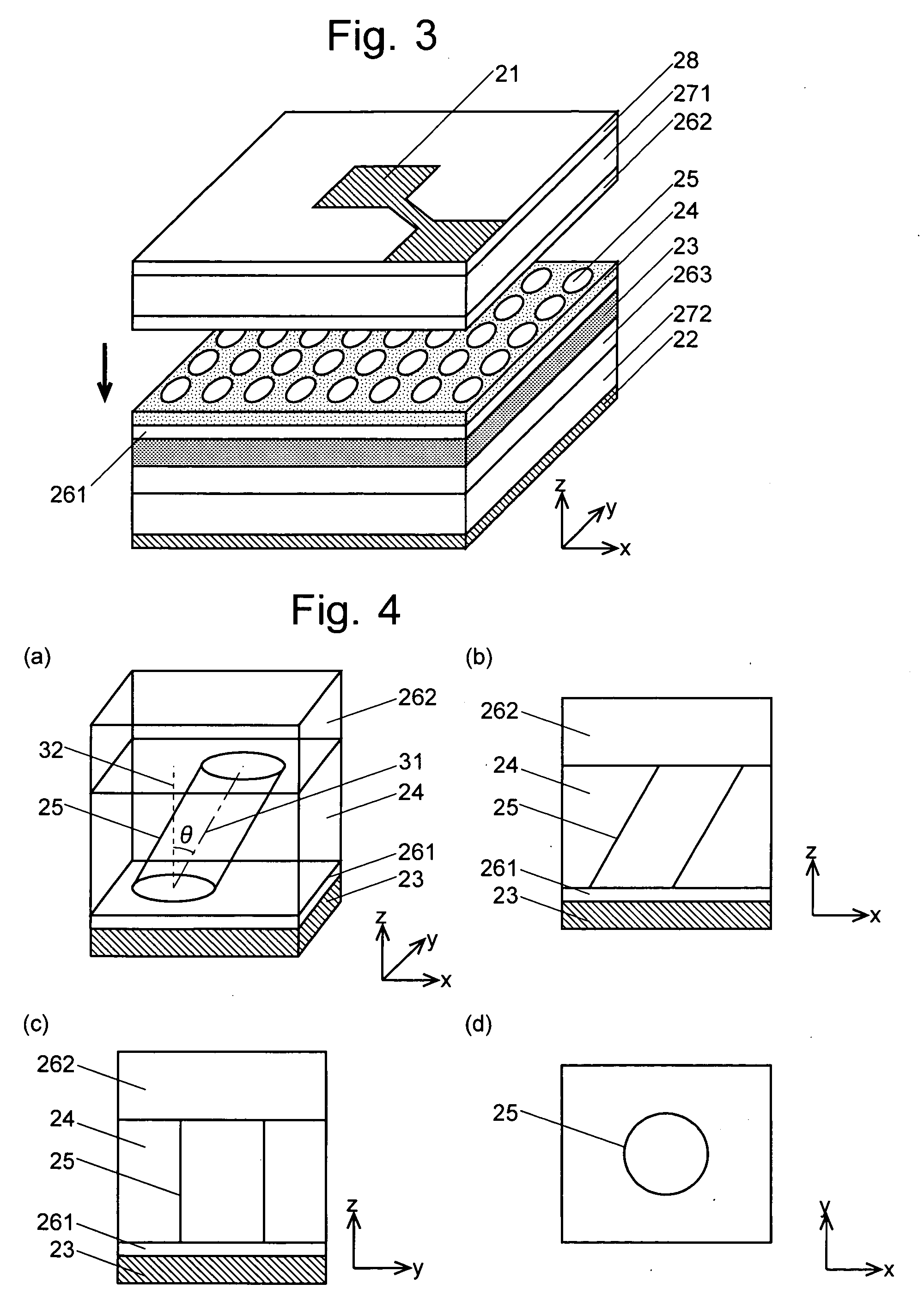
[0092]As a first embodiment of the laser light source according to the present invention, one example of the first aspect of the surface-emitting laser light is explained referring to FIGS. 3 to 5.
[0093]In the laser light source of the present embodiment as shown in FIG. 3, an active layer 23 made of Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs) / Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and having multiple quantum wells (MQW) is provided between an anode 21 and a cathode 22. A two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 24 made of p-type GaAs is formed on the active layer 23 via a spacer layer 261, which is also made of p-type GaAs. The two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 24 includes a plate member having holes 25 periodically arranged in a square lattice pattern. The shape of the holes 25 is described later. In the example of FIG. 3, the spacer layer 261 and the two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 24 are integrally created as a sin...
second embodiment and third embodiment
(2) Second Embodiment and Third Embodiment
Other Examples of the First Aspect of the Surface-Emitting Laser
[0100]Next, the second and third embodiments of the laser light source according to the present invention are explained referring to FIGS. 6 and 7. The laser light sources in these embodiments have a structure similar to that of the laser light source of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 3 with the exception of the shape of the holes.
[0101]FIG. 6 shows the shape of a hole 45 in the second embodiment and FIG. 7 shows the shape of a hole 55 in the third embodiment. In both FIGS. 6 and 7, (a) is a perspective view, (b) is a protection view to the x-z plane, (c) is a projection view to the y-z plane, and (d) is a sectional view (or plan view) on the surface of the two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 24 disposed on the spacer layer 262. As in the case of FIG. 3, a large number of holes having the same shape are actually arranged in a square lattice pattern in the two-dimensional ...
fourth embodiment
(4) Fourth Embodiment
Second Aspect of the Surface-Emitting Laser
[0110]As a fourth embodiment of the present invention, FIGS. 13 to 19 are used to explain an example of the second aspect of the surface-emitting laser. FIG. 13 is a perspective view showing a laser light source of the present embodiment. This laser light source has a structure similar to that of the laser light source of the first embodiment except for a two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 74. The structure of the two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 74 is now explained.
[0111]FIG. 14(a) is a top view of the two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 74. The two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 74 is created from a slab-shaped matrix body made of p-type GaAs with a thickness of 130 nm in which modified refractive index region groups 75 are arranged in a square lattice pattern with a period of 285 nm. FIGS. 14(b) and 14(c) are a top view and a longitudinal sectional view of one of the modified refractive index region ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com