Catalytic anti-factor VIII allo-antibodies
a technology of catalytic anti-factor and alloantibody, which is applied in the field of catalytic anti-factor viii alloantibodies, can solve the problems of life-threatening and crippling haemorrhagic disease, deficiency or deficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the catalytic rate of thrombin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Affinity-Purification of Anti-Factor VIII Antibodies
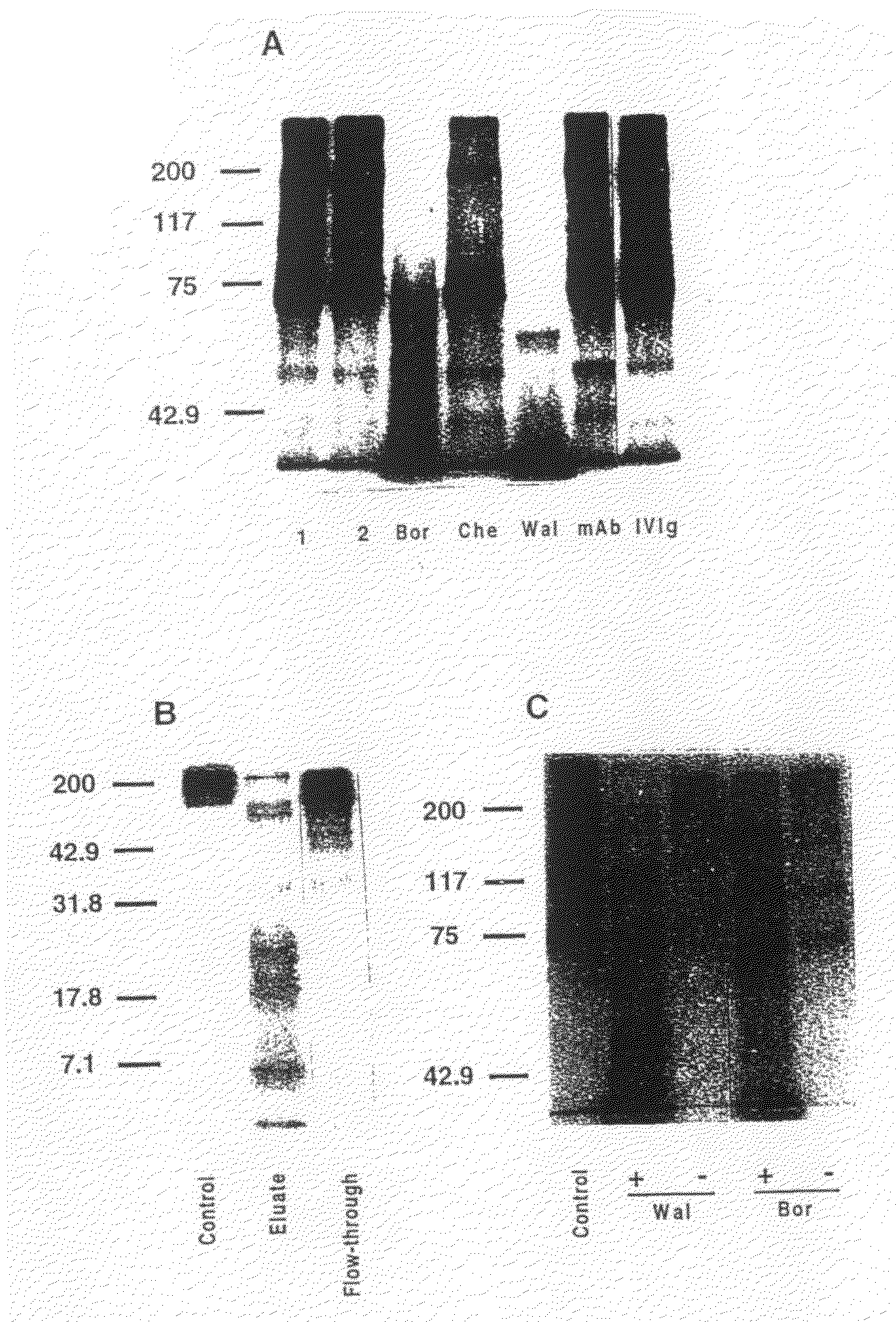
[0067]Antibodies were isolated from plasma by ammonium sulphate precipitation. Antibodies reactive with Factor VIII were then affinity-purified on a CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B matrix to which immuno-purified commercial human plasma-derived Factor VIII had been coupled (25000 U / 3 g of gel). The flow-throughs of the columns were collected. After extensive washing with PBS pH 7.4, anti-Factor VIII antibodies were eluted using 0.2 M glycine pH 2.8, dialysed against PBS and concentrated with Centriprep. Flow-throughs and eluates were aliquoted and stored at −20° C. until use. F(ab′)2 fragments of anti-Factor VIII antibodies were prepared as previously described.
[0068]The concentration of anti-Factor VIII IgG was 130, 20 and 280 μg per 10 mg of IgG applied to the column in the case of patients Bor, Che and Wal, respectively, (i.e., 143±130 μg / mI of unfractionated plasma), which is in agreement with previous observations.
example ii
Factor VIII-Neutralising Activity
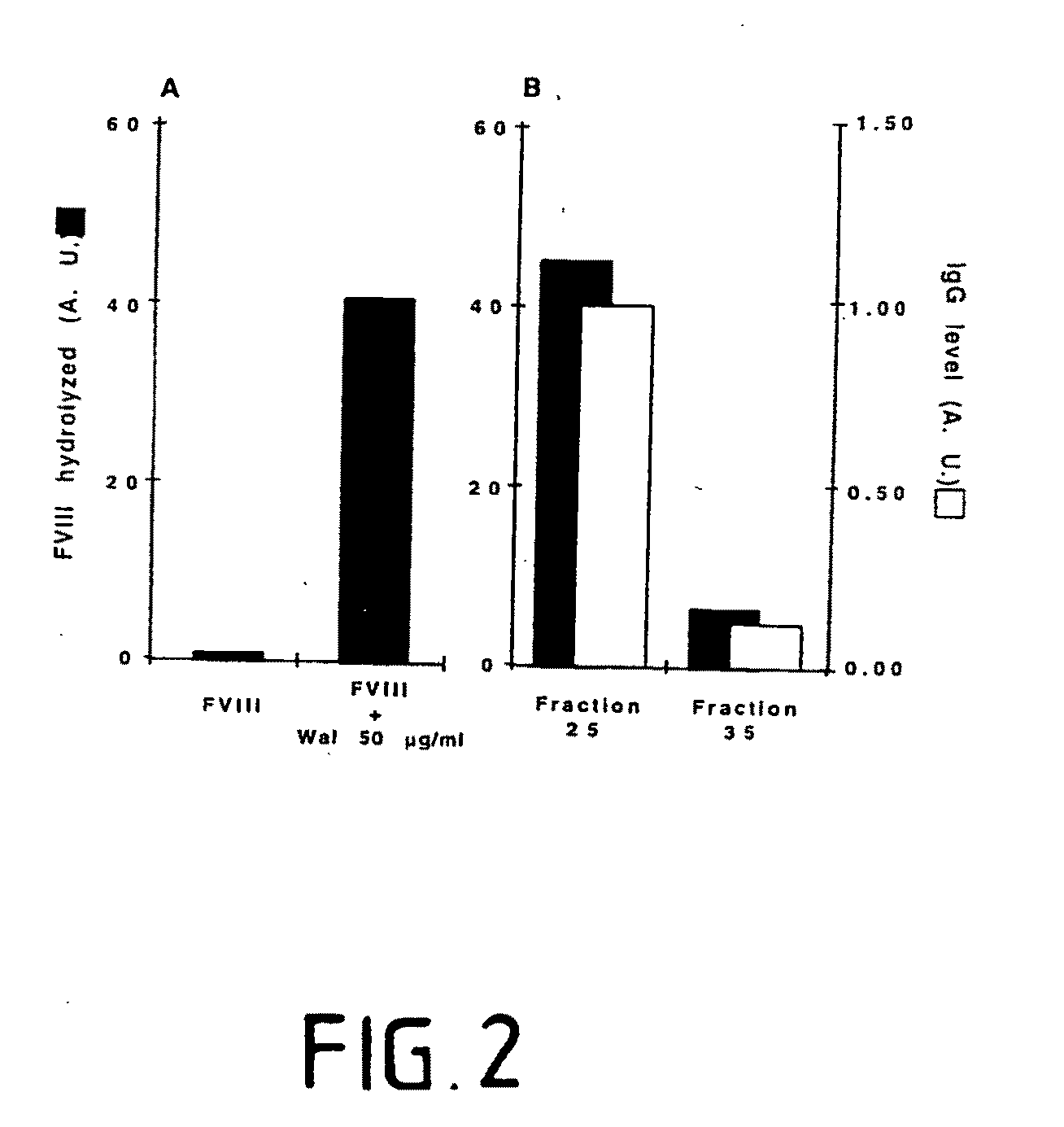
[0069]The Factor VIII-neutralising activity of anti-Factor VIII antibodies was determined by the method of Kasper et al. and expressed as Bethesda units (BU) (ref). BU were defined as the inverse of the concentration of IgG which causes 50% inhibition of Factor VIII procoagulant activity. Residual Factor VIII activity was measured in a one-stage assay by determination of the activated partial thromboplastin time using human plasma depleted of Factor VIII (Behring) as substrate and human placental Pathromtin® (Behring) as activators. Heated plasma or immunopurified anti-Factor VIII IgG to be tested, were incubated with pooled citrated human plasma for 2 h at 37° C. The clotting time of four serial dilutions of a reference plasma pool (Immuno AG, Wien) was compared with the clotting time of three dilutions of each sample to be tested. Dilutions were carried out in Owren-Koller buffer (Diagnostica Stago). Inter-assay variation ranged between 1 and 2.5%....
example iii
Assay for Hydrolysis of Factor VIII
[0071]Commercial human recombinant Factor VIII was labelled with 125I to a specific activity of 11.6 nCi / μg, by using the iodogen method. [125I]-Factor VIII (1.5 to 150 ng) was incubated in 50 μl of 50 mM tris-HCI pH 7.7, 100 mM glycine, 0.025% Tween-20 and 0.02% NaN3 alone or with 17 to 1667 nM of immuno-purified anti-Factor VIII IgG for 5 min to 10 hours at 38° C. Human monoclonal anti-digoxin IgG M061 (mAb) and normal unfractionated human polyclonal IgG (IVIg, Sandoglobulin®), were used as negative controls. Samples were mixed 1:1 with Laemmli's buffer without mercaptoethanol, and were subjected to SDS electrophoresis without boiling, after loading 20 μl of each sample per lane. Samples were run in parallel on 7.5% and 15% SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions, after loading 20 μl of each sample per lane. Migration was performed at room temperature using a mini-PROTEAN II system at 25 mA / gel, until the dye front reached the bottom of the gel. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com