Method for manufacturing wire, apparatus for manufacturing wire, and copper alloy wire
a manufacturing apparatus and technology for copper alloy wire, applied in heat treatment apparatus, furnaces, conductors, etc., can solve the problems of high equipment cost, inability to perform the age-treatment of the usual precipitation-type alloy, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the number of processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
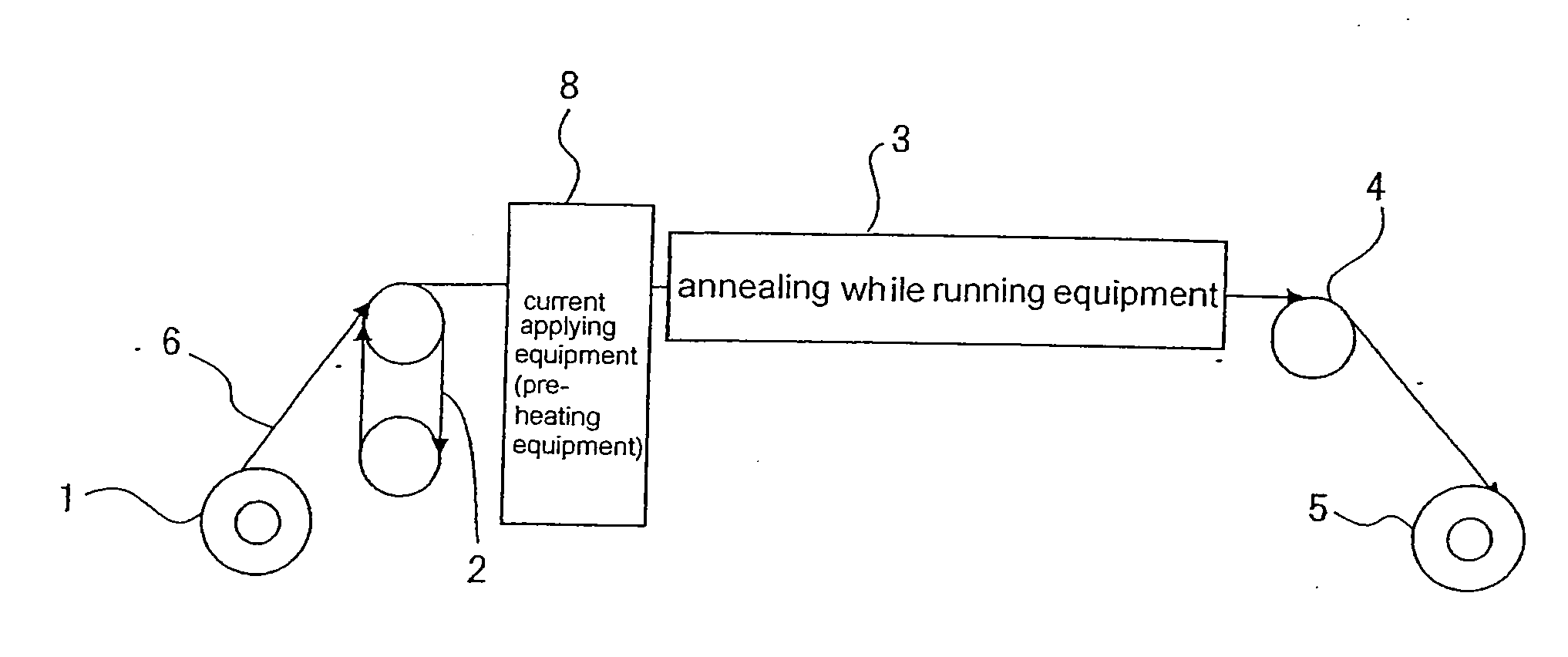
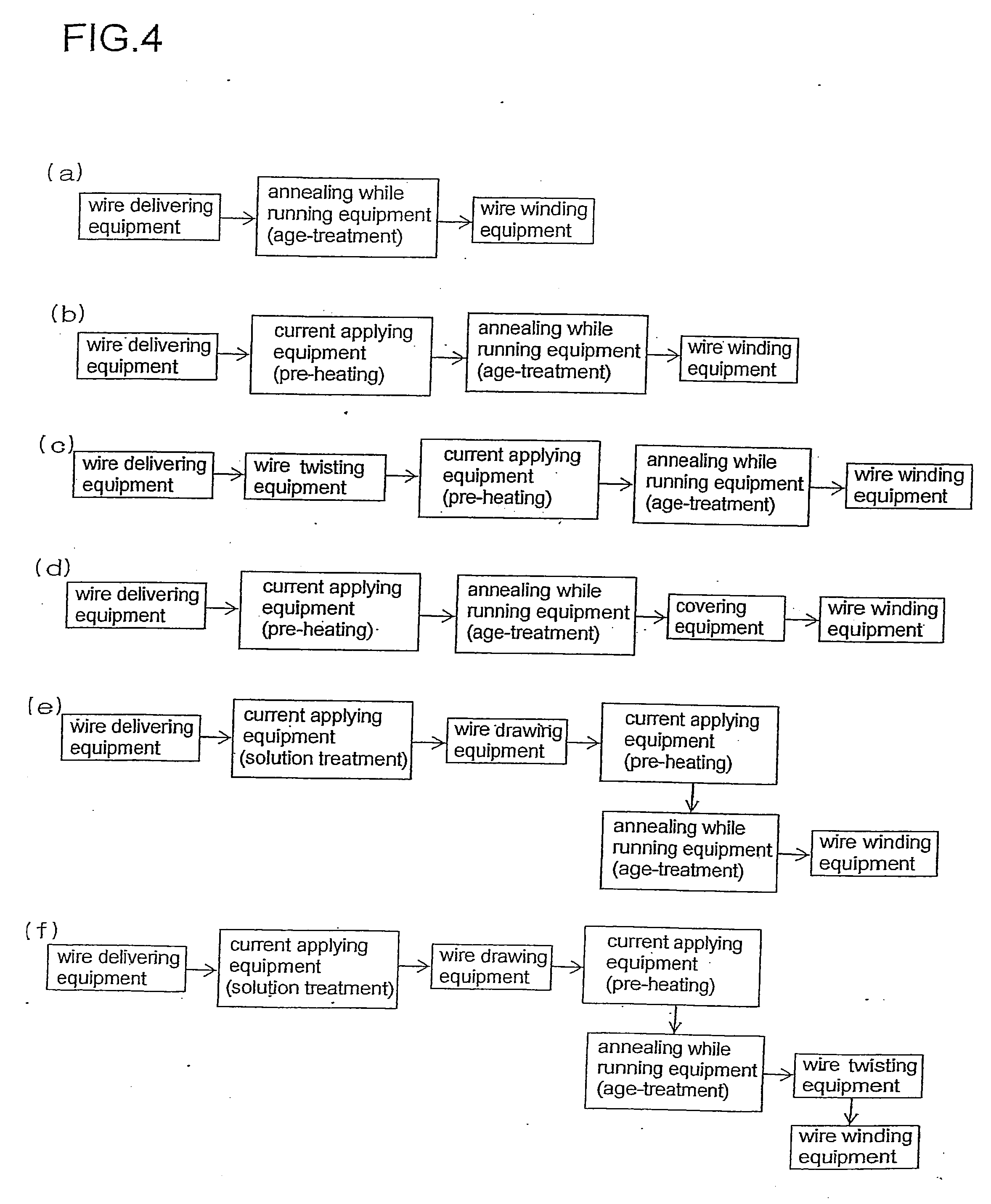
[0197]The alloys Nos. 1 to 38 are subjected to the solution treatment, and then the copper alloy wires having the diameter of 0.1 mm are formed. The copper alloy wires are continuously age-treated under the conditions as shown in Table 2 using the apparatus for manufacturing wire as depicted in FIGS. 3 and 4(b). The results are shown in Table 2. For comparison, the copper alloy wires having the diameter of 0.1 are formed using the above described alloys. The copper alloy wires are age-treated by the conventional method using the batch furnace. More specifically, the wires are heated to the temperature (degrees Celsius) as shown in Table 2, and held at the temperature for a time period of heating time (sec), and then wound by the wire winding equipment. The tensile strength (MPa) and electrical conductivity (% IACS) of the wire in the annealing while running equipment are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2HeatingTensileElectricalAdhesionSampleAlloytimestrengthdonductivityafterNo.No.Temperature...
example 2
[0199]The example with the diameter of the copper alloy wire varied is shown. More specifically, alloy Nos. 16 and 22 as shown in Table 1 are subjected to solution treatment, and then the copper alloy wires having the diameters of 0.03 mm, 0.01 mm, 0.9 mm, 3 mm are formed, respectively. The copper alloy wires are continuously age-treated under the conditions as shown in Table 3 using the apparatus for manufacturing wire as depicted in FIGS. 3 and 4(b).
TABLE 3HeatingTensileElectricalAdhesionSampleAlloyDiametertimestrengthconductivityafterNo.No.(ø mm)Temperature(sec)(MPa)(% IACS)aging51160.0348090063944None52160.150090064545None53160.950090063444None54163.050090062144None55220.0345090050273None56220.147090050573None57220.947090049873None58223.047090048372None
[0200]As is clear from Table 3, all the samples Nos. 51 to 58 (i.e., Cu—Ni—Si alloys No. 16, Cu—Cr alloys No. 22) are subjected to necessary age-treatment without adhesion after age-treatment. More specifically, it is appreciated ...
example 3
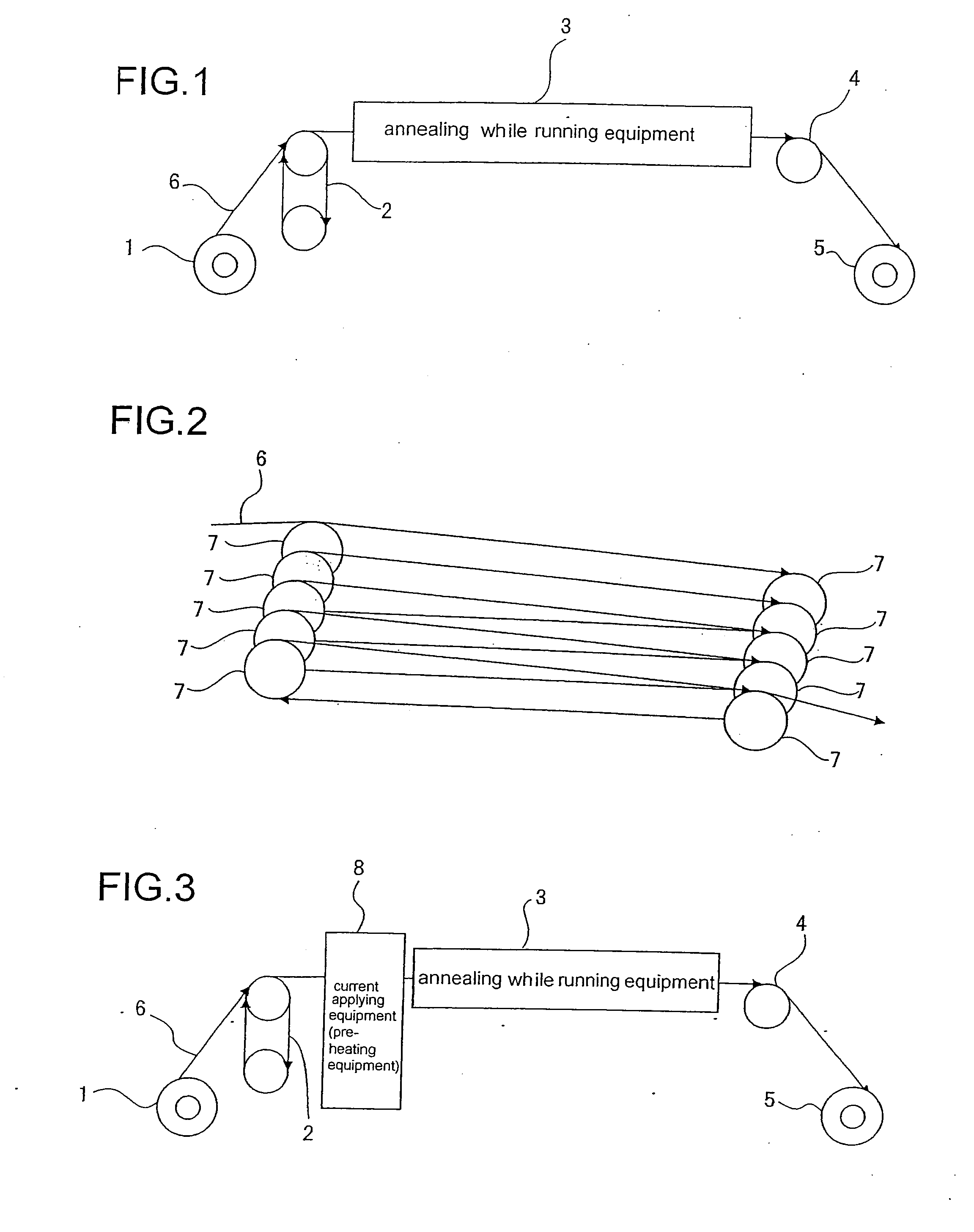
[0201]The same tests as Example 1 are carried out using the apparatus for manufacturing wire as shown in FIGS. 5, 6, and 8(a) in which the wire is heated by applying current while running for age-treatment. The center values of the temperatures of the age-treatment are respectively set to be the temperature as shown in Table 2 in Example 1. The difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature is set to be 40 degrees. For example, the temperature of 500 degrees Celsius in Table 2 means that the center value of the temperature is set to be 500 degrees Celsius, the maximum temperature is set to be 520 degrees Celsius, and the minimum temperature is set to be 480 degrees Celsius.
[0202]As a result, the samples of the present Example which correspond to the samples Nos. 1 to 38 in Table 2 of Example 1 show the same result as those of the samples in Examples 1 in connection with the tensile strength (MPa) and electrical conductivity (% IACS) of the wire in the anneali...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com