Method of making heat sink
a heat sink and heat sink technology, applied in the field of heat sinks, can solve the problems of increased cost of heat sinks, solder and flux, and overheating of electronic components,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
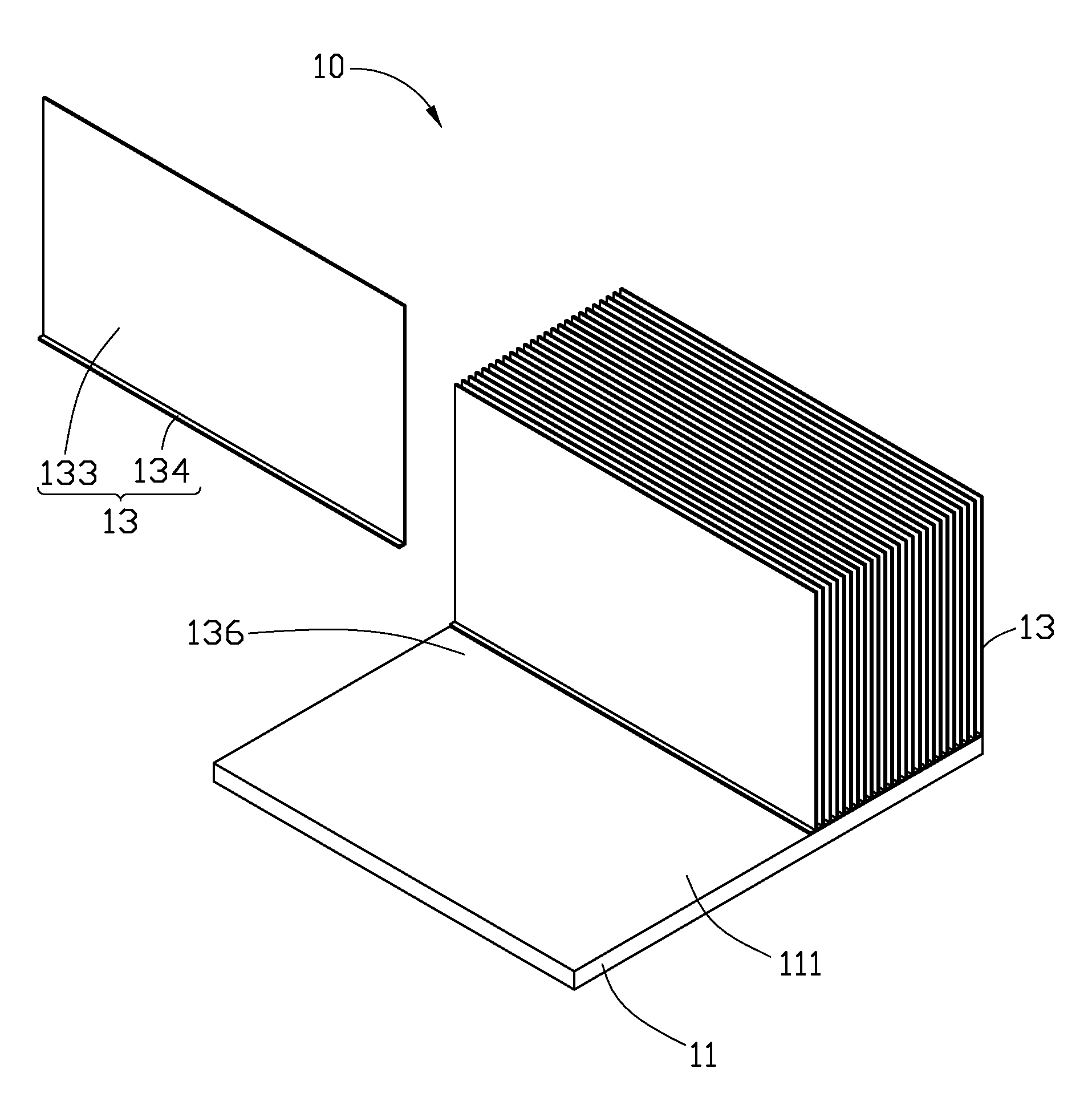
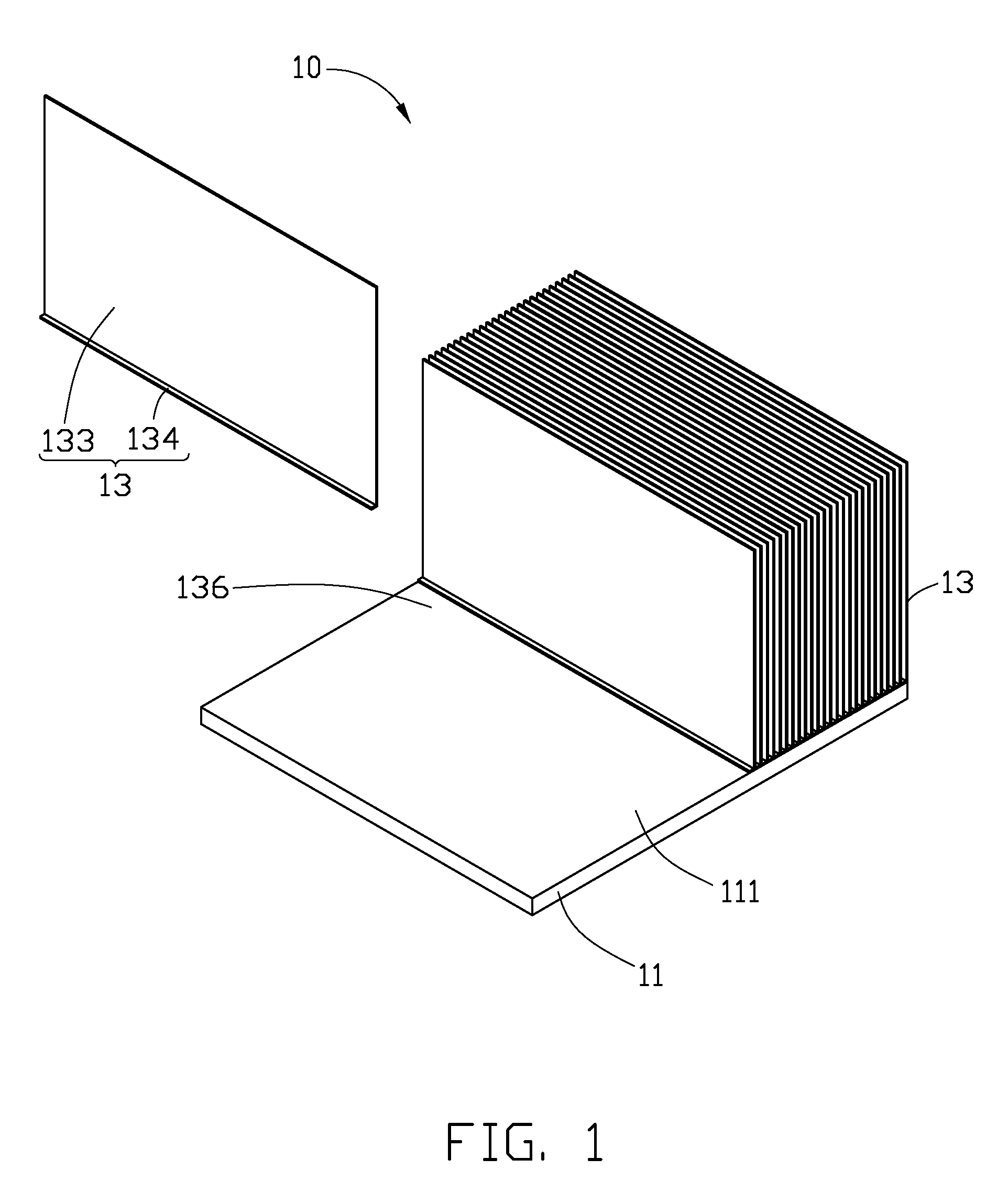
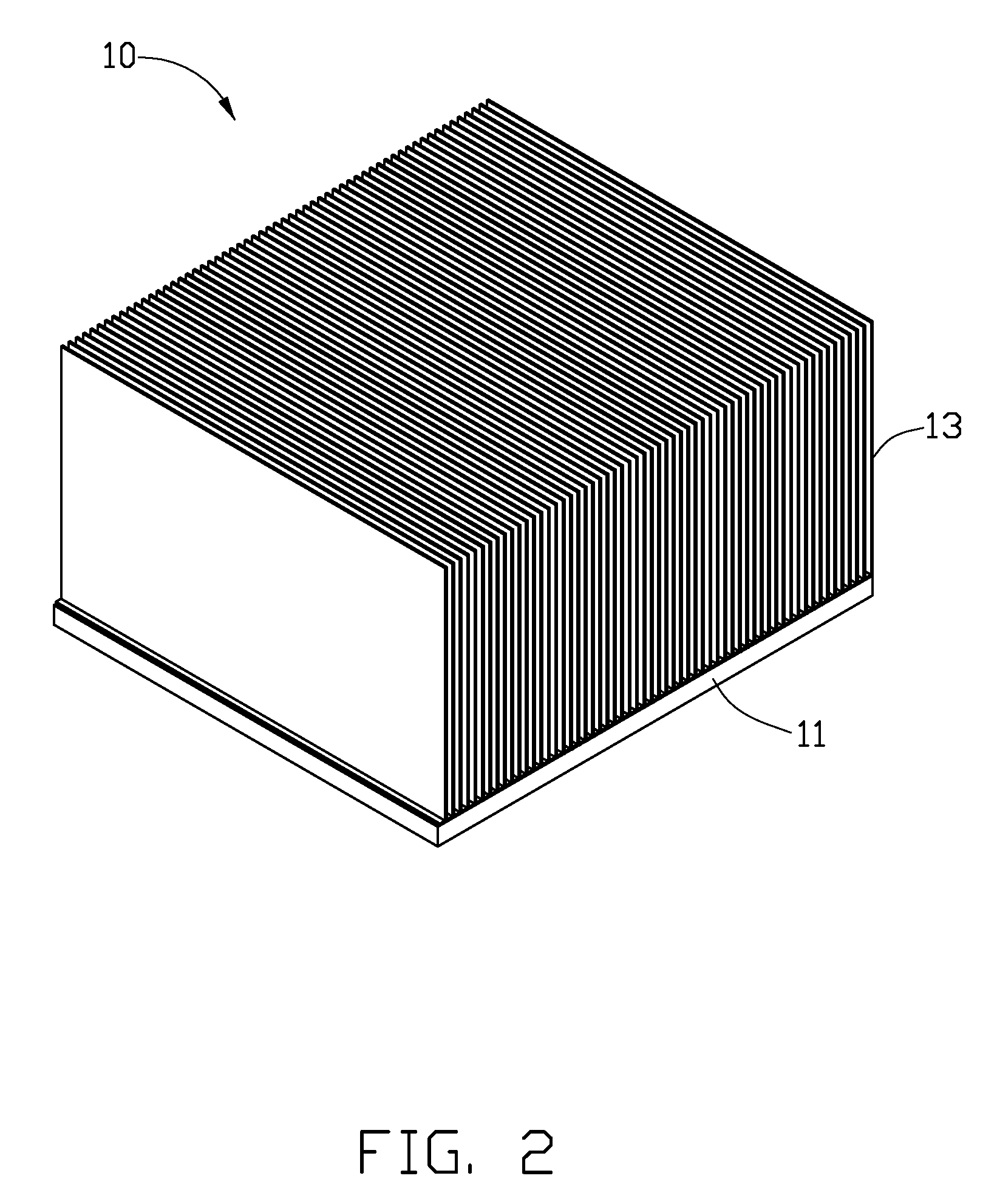
[0014]Referring to FIG. 1, an ultrasonic welding process of a heat sink 10 in accordance with the present invention is shown. Firstly, a base 11 and a plurality of individual fins 13 are provided.
[0015]The base 11 has a rectangular shape. The base 11 is made of copper, which has good thermal conductivity. The base 11 has a contacting surface 111 at a top thereof.
[0016]The fins 13 are made of aluminum, which has good thermal conductivity. Aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity than copper. Each fin 13 has a plate shape, and has a thickness in a range of 0.3˜0.4 mm. Each fin 13 includes a rectangular main body 133, and a flange 134 extending vertically and outwardly from a bottom side of the main body 133.
[0017]During assembly of the heat sink 10, the fins 13 are successively welded to the base 11 by ultrasonic welding method. Specifically, the flange 134 of each fin 13 is welded on the contacting surface 111 of the base 11 by the ultrasonic welding method. When one of the fins 13 ...
second embodiment
[0021]Referring to FIG. 3, an ultrasonic welding process of a heat sink 20 in accordance with the present invention is shown. Firstly, a base 21 and a plurality of individual fins 23 are provided.
[0022]The base 21 has a cylindrical shape. The base 21 is made of copper, which has good thermal conductivity. The base 21 has a circular contacting surface 211 at a circumference thereof.
[0023]The fins 23 are made of aluminum, which has good thermal conductivity. Each fin 23 has a plate shape, and has a thickness in a range of 0.3˜0.4 mm. Each fin 23 includes a main body 233, and a flange 234 extending vertically and outwardly from an inner side of the main body 233. The main body 233 of each fin 23 includes a lower part 237, a middle part 238 and an upper part 239. A length from an inner side towards an outer side of each of the lower part 237, the middle part 238 and the upper part 239 is successively increased, thereby forming two sidesteps at an outer side of the main body 233.
[0024]Du...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cylindrical shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com