Methods and Compositions for Cellular Reprogramming
a cellular reprogramming and composition technology, applied in drug compositions, immunological disorders, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problems of intimal migration and proliferation of smc over the length of the damaged blood vessel, clinical pathological features of ap disease, and comparable inhibition of normal cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
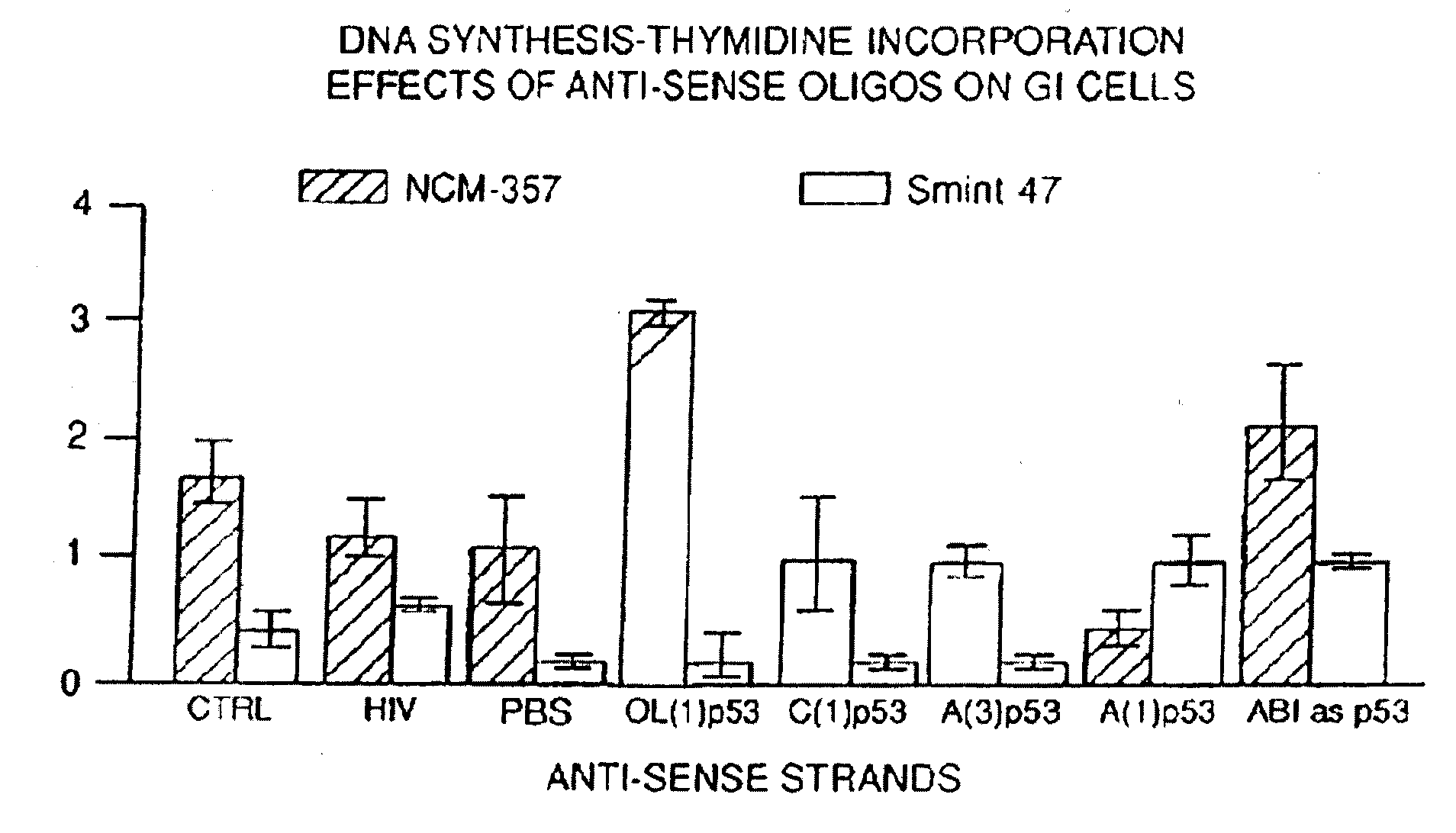
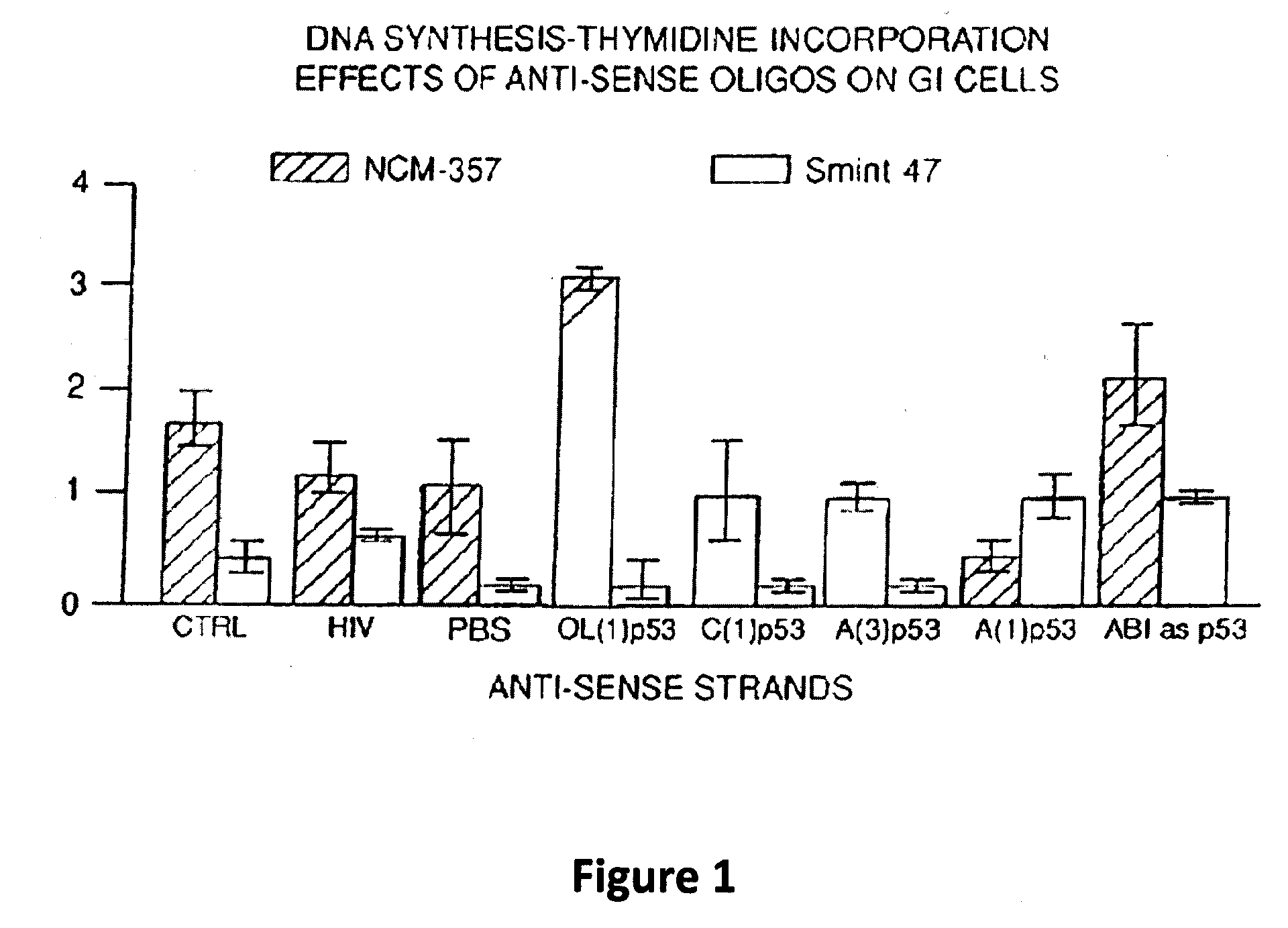
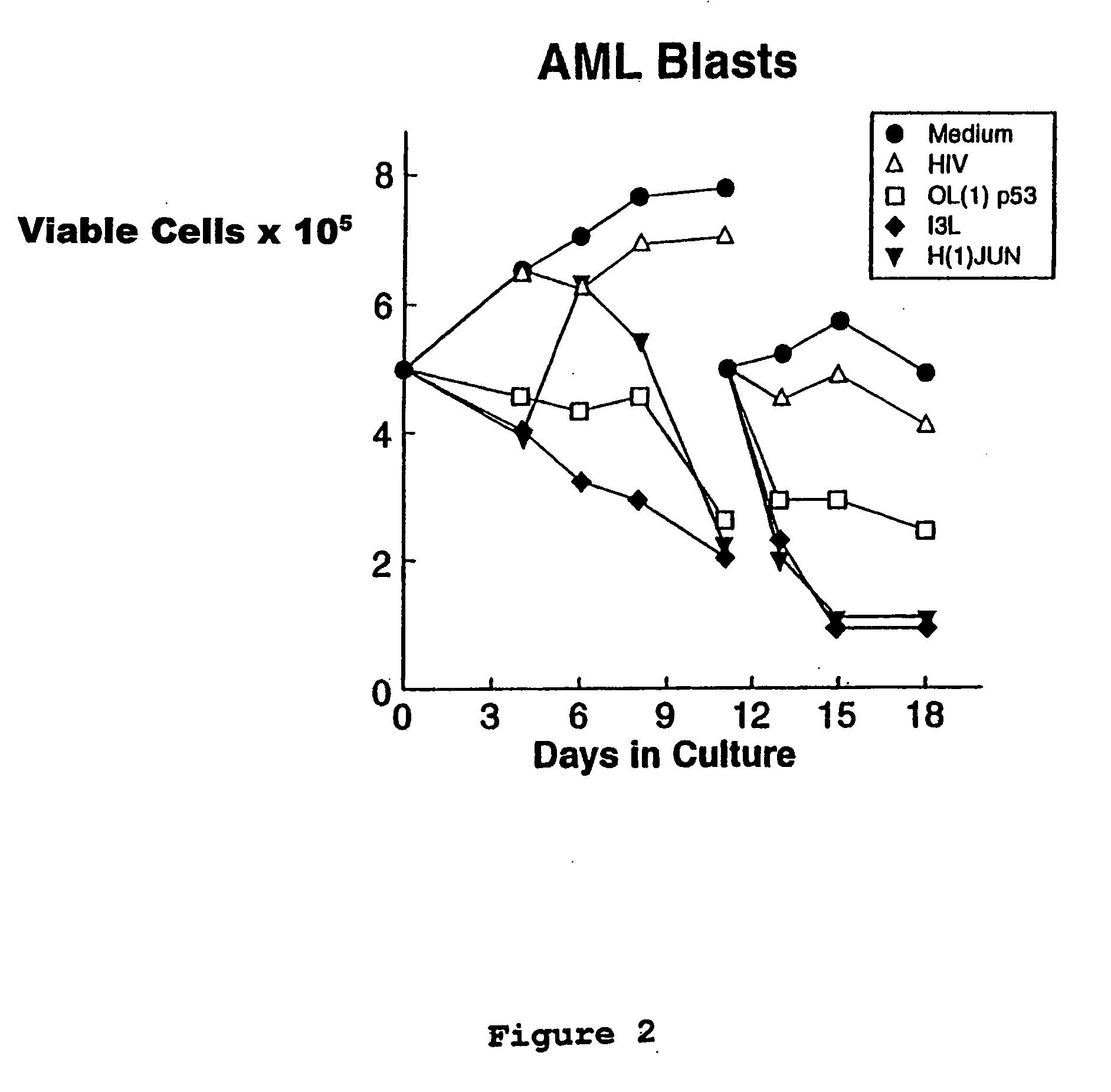
[0224]In vitro comparisons of the relative activity levels of the four p53 antisense ODNs (SEQ ID NOS. 1-4) showed that OL(1)p53 (SEQ ID NO.4) was consistently the most active in terms of producing anti-tumor effects. Freshly obtained acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blast cells, as well as ovarian, colon, lung and brain cancer specimens, were tested. In nearly every experiment in which the four p53 antisense ODNs were evaluated simultaneously on such tumor specimens, the OL(1)p53 antisense ODN exhibited the most potent activity. Activity was determined as a reduction in viable cell counts and by reduced capacity of treated cells to grow in methyl cellulose as colonies in colony forming assays, compared to cells treated with control ODNs. The results with fresh AML blast cells have been published (Bayever et al., Leukemia and Lymphoma 12: 223-231,1994). These data were consistent with the notion that the secondary selection method would yield ODN sequences with a greater probability of ...
example 2
[0225]Having discovered a method for selecting highly active antisense ODNs, the present inventor designed a series of antisense ODNs against two other gene targets in order to further test and confirm the value of the selection method herein disclosed. The MDR1 gene that encodes P-glycoprotein, and the gene encoding the multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) were selected for these studies. The protein products of these genes constitute molecular pumps that have been implicated in the production of the multidrug resistance phenotype in cancer cells. Hence, antisense ODNs with the capacity to block the expression of these genes would be expected to increase the sensitivity of treated multidrug resistant tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents such as vincristine, doxorubicin and VP-16. The entire MDR1 gene has been cloned and sequenced, while only the MRP cDNA has been cloned and sequenced. consequently, there is a much larger number of functional sites that can be targeted on...
example 3
[0232]As was done for the MDR1 gene transcripts in Example 2, the primary selection method was also used to design antisense ODNs to target selected regions within the MRP cDNA gene transcript, based on what is known in the literature about the functions of the various regions of the transcript (Cole et al., Science 258: 1650, 1992). Functional sites targeted included the 5′-cap site, the 5′-untranslateu leader and the translational start site. In addition, other antisense ODNs Io were selected using the secondary selection method described above.
[0233]Relative antisense ODN activity among the various MRP antisense ODNs was determined in exactly the same manner as was described in Example 2 above for analysis of the MDR1 antisense ODNs, except that the MRP antisense ODNs were tested on the MRP-expressing, multidrug-resistant A427 human lung cancer cell line (Giard et al., J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 51: 1417, 1973), Table XVI summarizes the prototype MRP antisense ODNs tested in these stu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| lipophilic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com