Method for improving cartilage repair and/or preventing cartilage degeneration in a joint
a cartilage repair and joint technology, applied in the field of medical treatment, can solve the problems of limited regeneration capacity of cartilage, enormous amount of intensive and repetitive forces on articular cartilage, etc., and achieve the effect of improving cartilage repair and/or slowing down cartilage degeneration, and preventing further cartilage degeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Injection of a Gel in Hoffa's Fat-Pad for Controlled Release of Pro Chondrogenic Factors
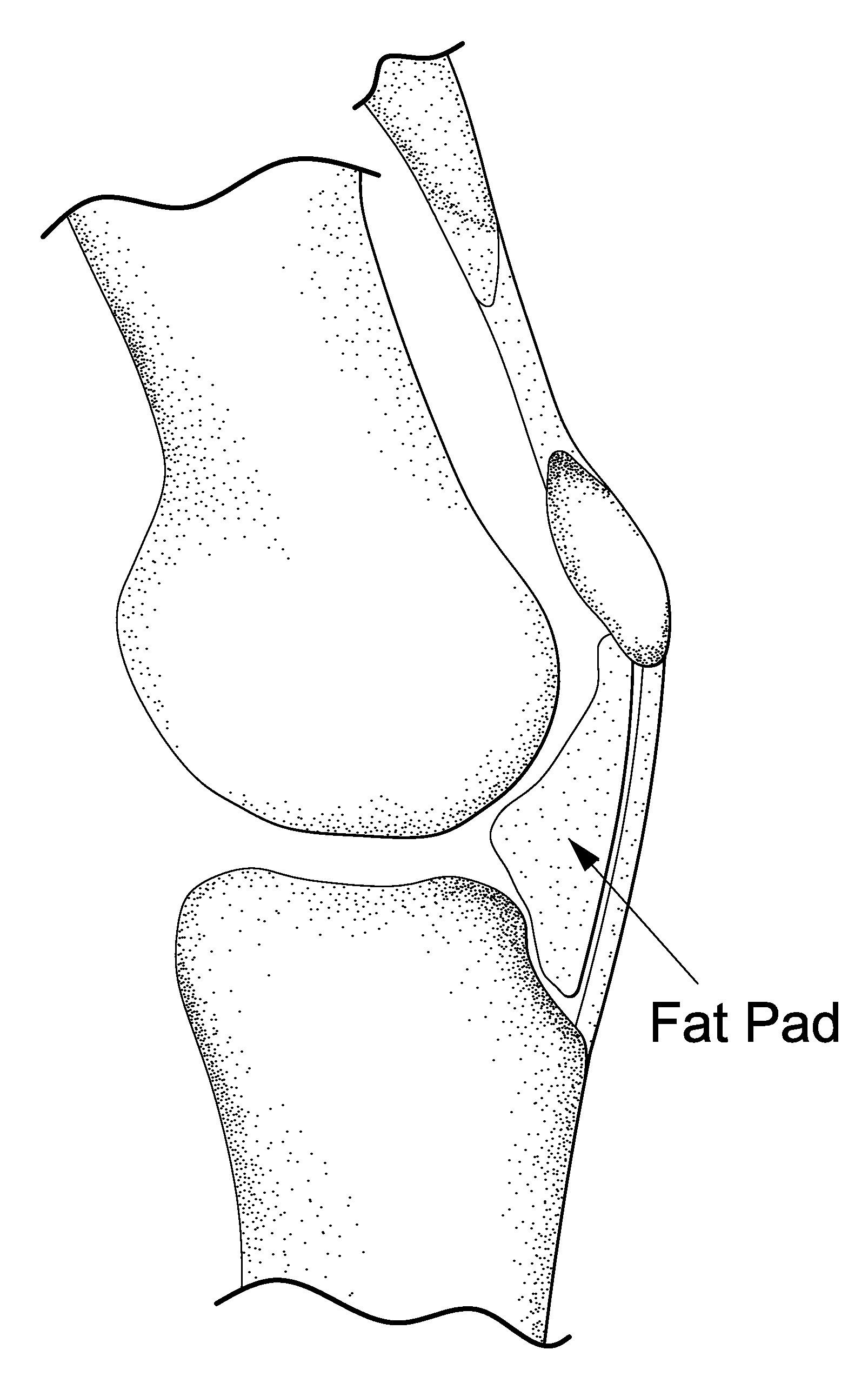
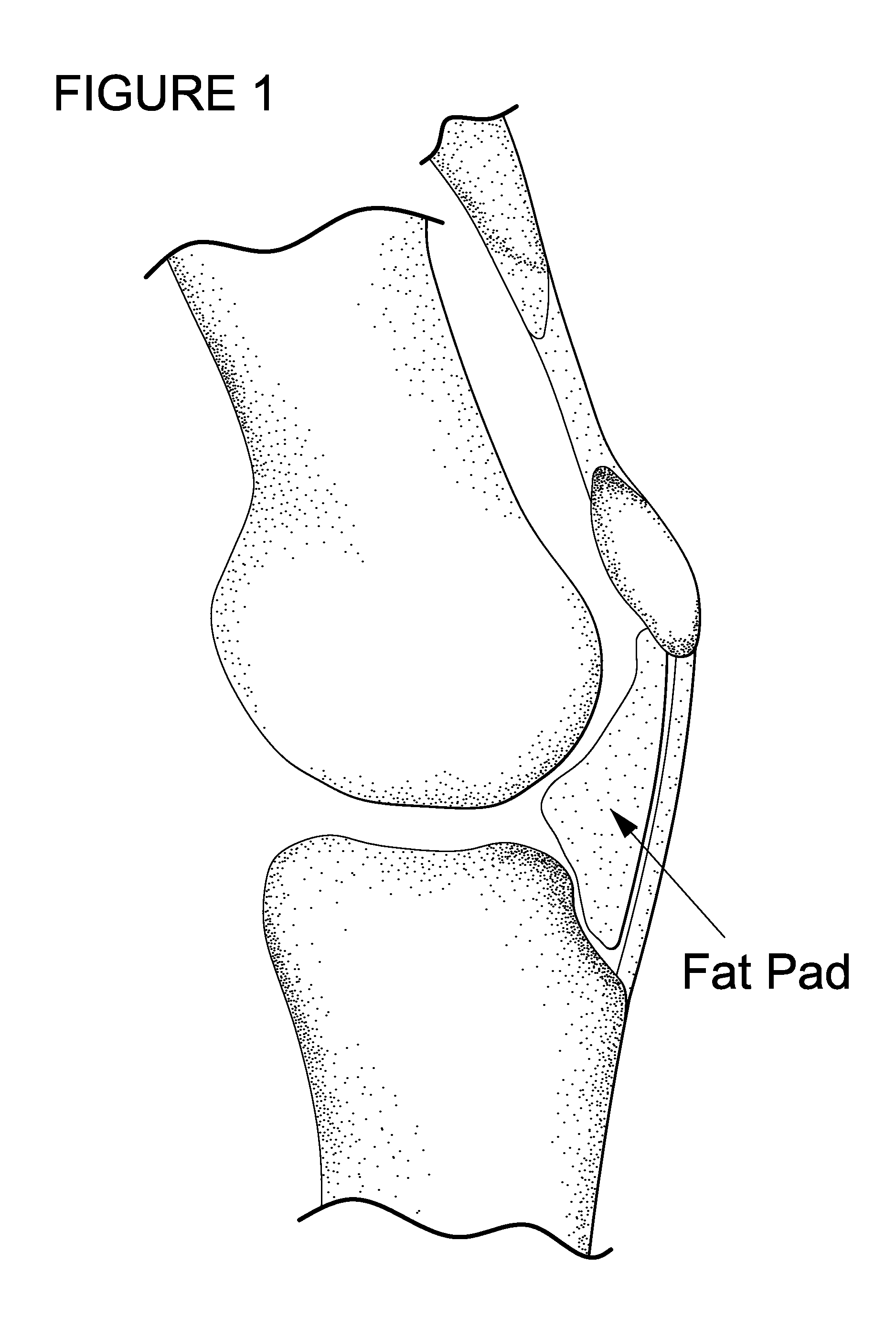
[0102]Rat model: Dutch laws on animal experimentation were strictly followed throughout the study and the experimental animal protocol was approved by the Maastricht University committee for animal experiments. After induction of general anaesthesia, both knees of Wistar rats were shaved and prepared for aseptic surgery. The centre of the patella tendon was identified. A 28 G needle with a 1 ml syringe was used to penetrate the centre patella tendon. Directly after the patella tendon was penetrated, approximately between 0.1 and 0.2 ml of the Bio-Gel containing iodine based contrastagent (Visipaque®) was injected in Hoffa's fat-pad (HFP). Since the gel was mixed with X-ray contrast, the side of injection was examined by fluoroscopy.
example 2
Ex Vivo Injection and Release from Hoffa's Fatpad
[0103]It is advantageous that injection in HFP is feasible, a certain amount can be injected, the injected gel is contained in Hoffa's fatpad, and a certain release is maintained in time. For this purpose we injected different amounts of a radiopaque contrast agent in human HFPs. The HFP could easily be reached through the patellar tendon. An amount of 10 cc could be injected in HFP. Within HFP the contrast agent was not contained in one depot but distributed equally through the fatpad (FIG. 2). For an ex vivo approach HFPs were collected after TKA. The freshly harvested HFPs were injected with bromophenol blue in InGell™. These studies show that at 37° C. gel formation was instantaneous, and the dye is maintained in InGell™ (FIG. 2D). In contrast, injections of the colour dye or contrast agent without the Bio-Gel showed immediate and complete dispersion throughout the Hoffa, with no containment of the additives at all (FIG. 2A-C). Di...
example 3
Histological Evaluation
[0104]Five days and 30 days post-injection the rats were sacrificed and whole knee joints were fixed in 4% buffered formalin and decalcified in 10% EDTA for histology. After embedding in paraffin 7 μm sections were cut and stained with hematoxylin / eosin or with safarin 0 / fast green.
[0105]Both fluoroscopy and histology showed that after penetration of the patella tendon a Bio-Gel could easily and reproducibly be injected in Hoffa's fatpad. Histology and fluoroscopy showed retention of the Bio-Gel in Hoffa's fatpad even after 30 days follow-up. The human cadaver study confirmed this finding; after 1000 flexion / extension cycles the Bic-Gel remained in Hoffa's fatpad.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com