Methods for selecting protease resistant polypeptides
a protease resistant polypeptide and protease technology, applied in the field of protease resistant polypeptide selection, can solve the problems of limited efficacy of agents that have potential in vivo use (e.g., ) and achieve the effects of improving or relatively high melting temperature (tm), enhancing stability, and facilitating prophylaxis and diagnosis of diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example a
Lead Selection & Characterisation of domain antibodies to human TNFR1
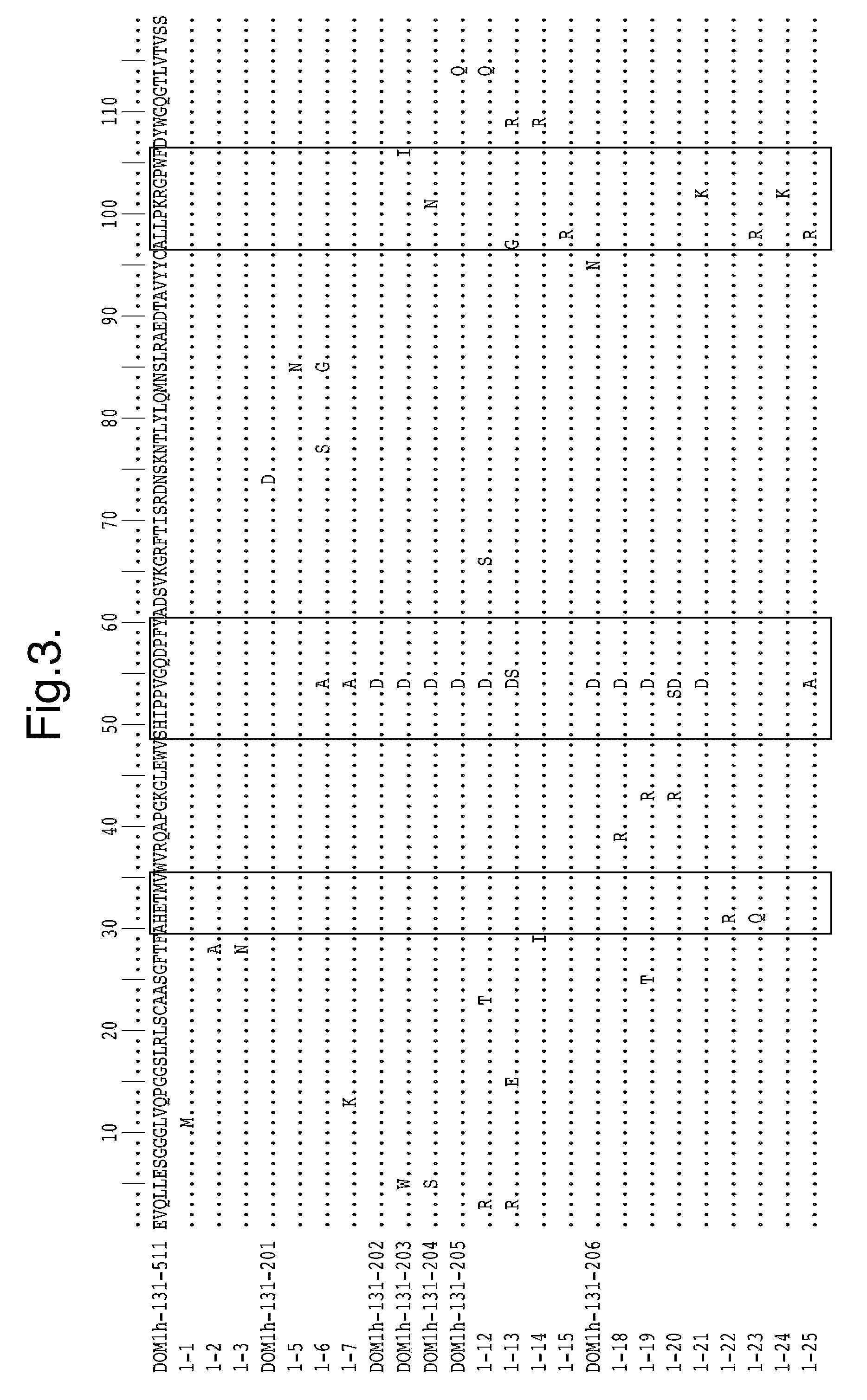
[0306]Domain antibodies generated were derived from phage libraries. Both soluble selections and panning to passively absorbed human TNFR1 were performed according to the relevant standard methods. Human TNFR1 was purchased as a soluble recombinant protein either from R&D systems (Cat No 636-R1-025 / CF) or Peprotech (Cat no. 310-07) and either used directly (in the case of passive selections) or after biotinylation using coupling via primary amines followed by quality control of its activity in a biological assay and analysis of its MW and extent of biotinylation by mass spectrometry. Typically 3 rounds of selection were performed utilising decreasing levels of antigen in every next round.
[0307]Outputs from selections were screened by phage ELISA for the presence of anti-TNFR1 binding clones. DNA was isolated from these phage selections and subcloned into a expression vector for expression of soluble dAb fragments. ...
example 1
Phage Vector pDOM13
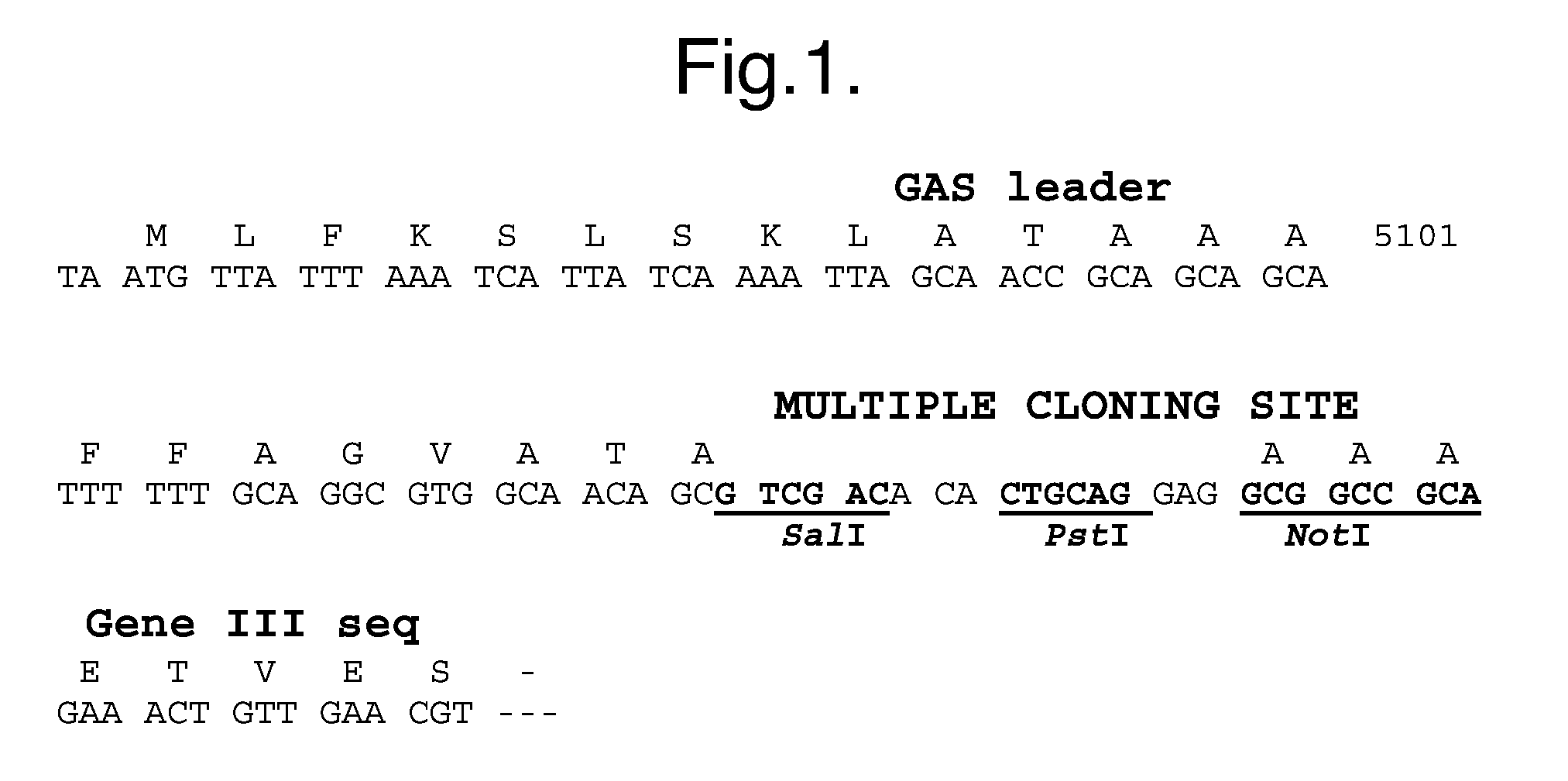
[0341]A filamentous phage (fd) display vector, pDOM13 was used. This vector produces fusion proteins with phage coat protein III. The multiple cloning site of pDOM13 is illustrated in FIG. 1. The genes encoding dAbs were cloned as SalI / NotI fragments.
example 2
Test Protease Selections on Phage-Displayed Domain Antibodies (dAbs) with a Range of Resistance to Trypsin
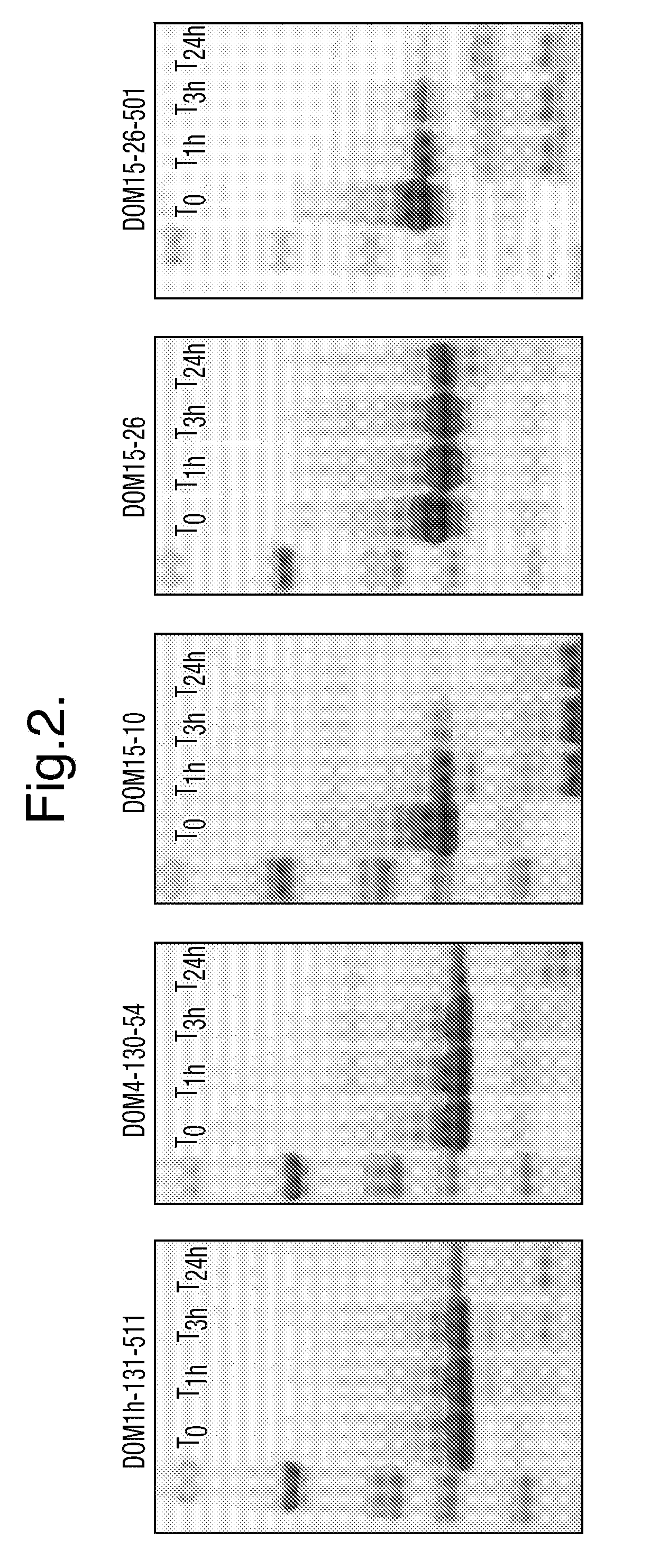
[0342]The genes encoding dAbs DOM4-130-54 which binds IL-1R1, DOM1h-131-511 which binds TNFR1, and DOM15-10, DOM15-26 and DOM15-26-501, which bind VEGFA, were cloned in pDOM13 and phages displaying these dAbs were produced according to standard techniques. Phages were purified by PEG precipitation, resuspended in PBS and titered.
[0343]The above dAbs displayed a range of ability to resist degradation by trypsin when tested as isolated proteins. Resistance to degradation was assessed as follows: dAb (1 mg / ml) in PBS was incubated with trypsin at 40 μg / ml at 30° C., resulting in a molecular ratio of 25:1 dAb:trypsin. Samples (30 μl) were taken immediately before addition of trypsin, and then at T=1 hour, 3 hours, and 24 hours. Protease activity was neutralized by addition of Roche Complete Protease Inhibitors (2×) followed by immersion in liquid nitrogen and storage on dry ice. 15 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com