Module for cooling semiconductor device
a semiconductor device and module technology, applied in the field of modules for cooling semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of large amount of heat generated, insufficient heat absorption of peltier devices (tec), and insufficient heat absorption of heat pipes. achieve the effect of improving cooling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
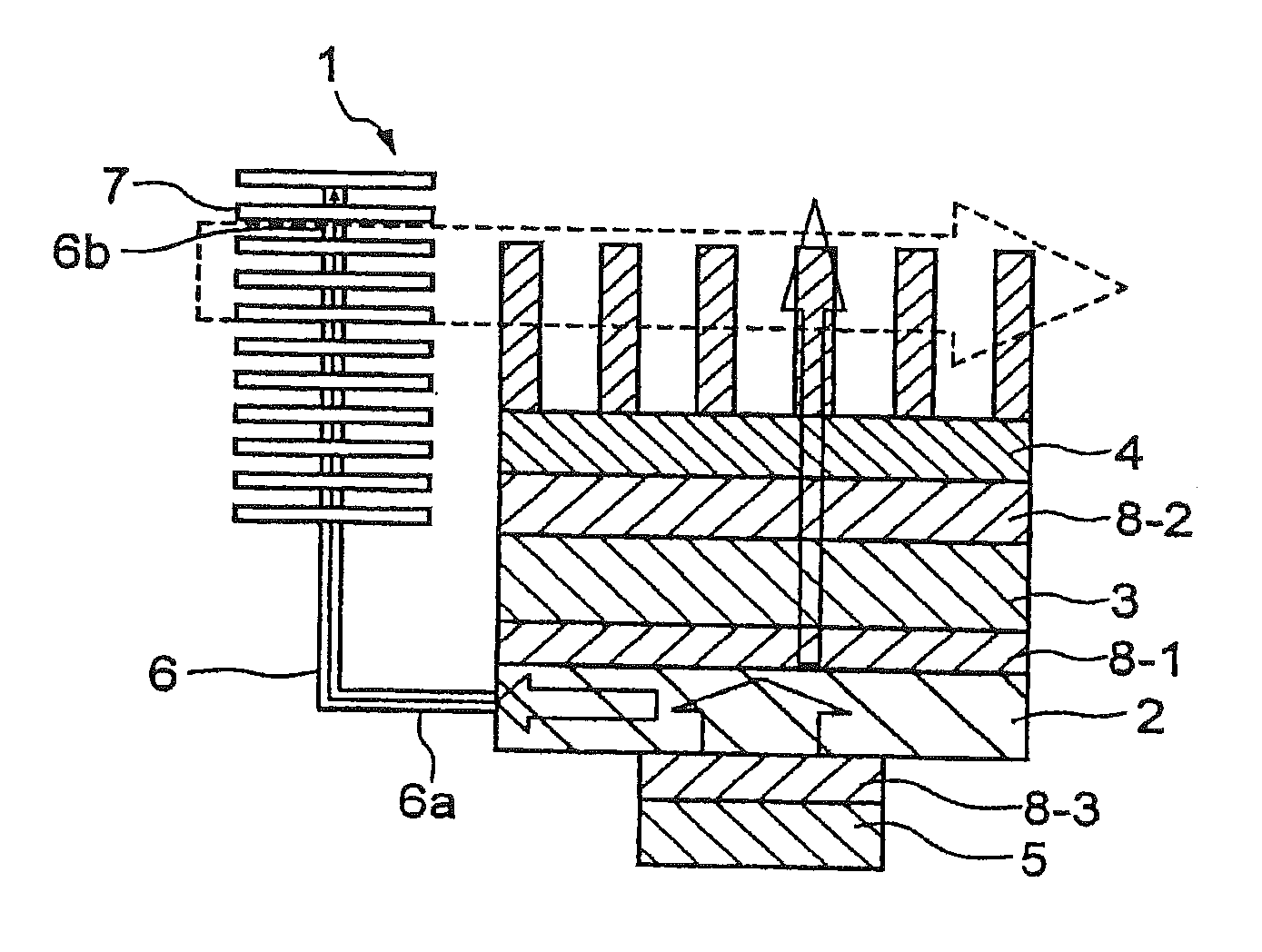
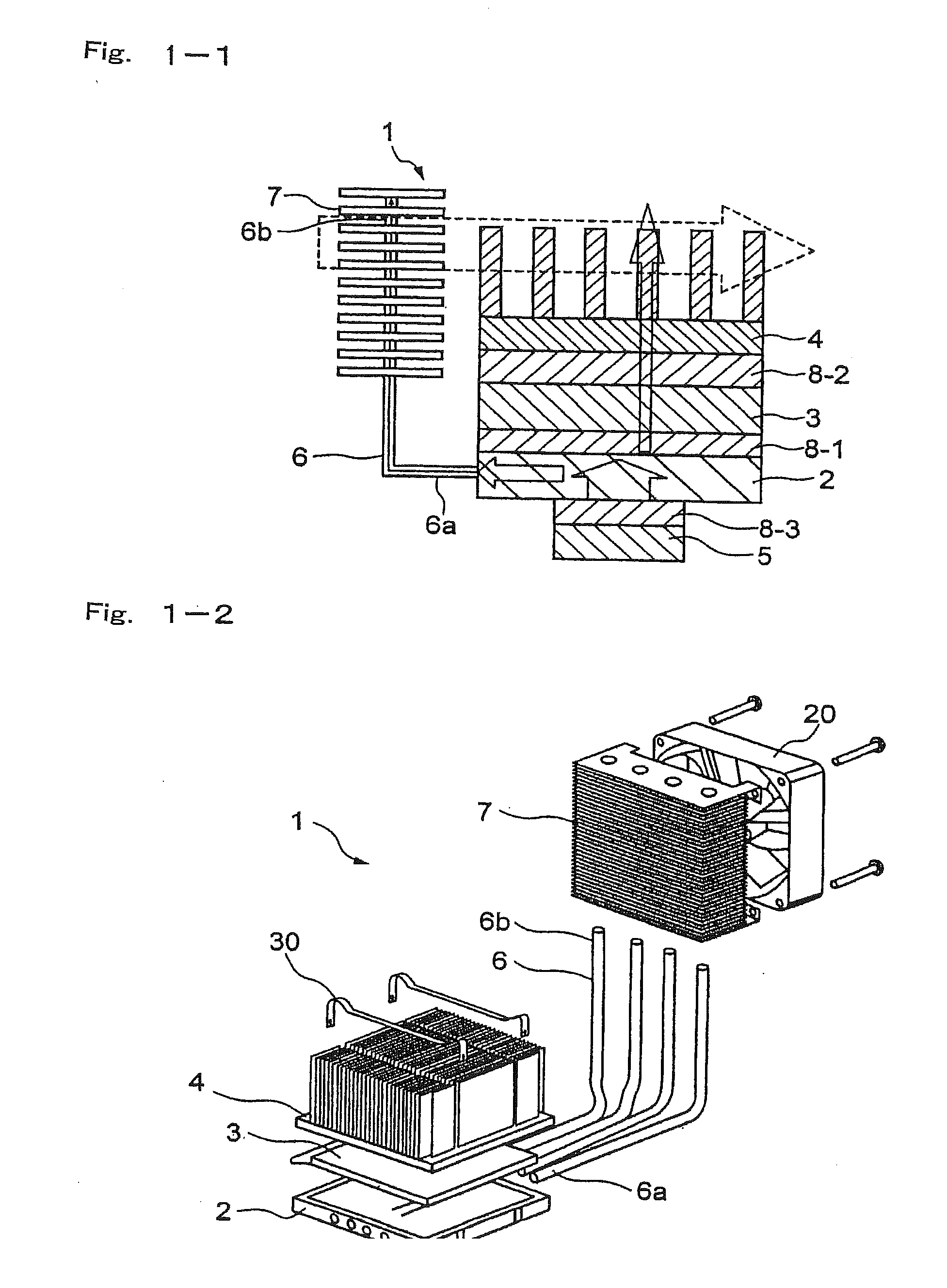
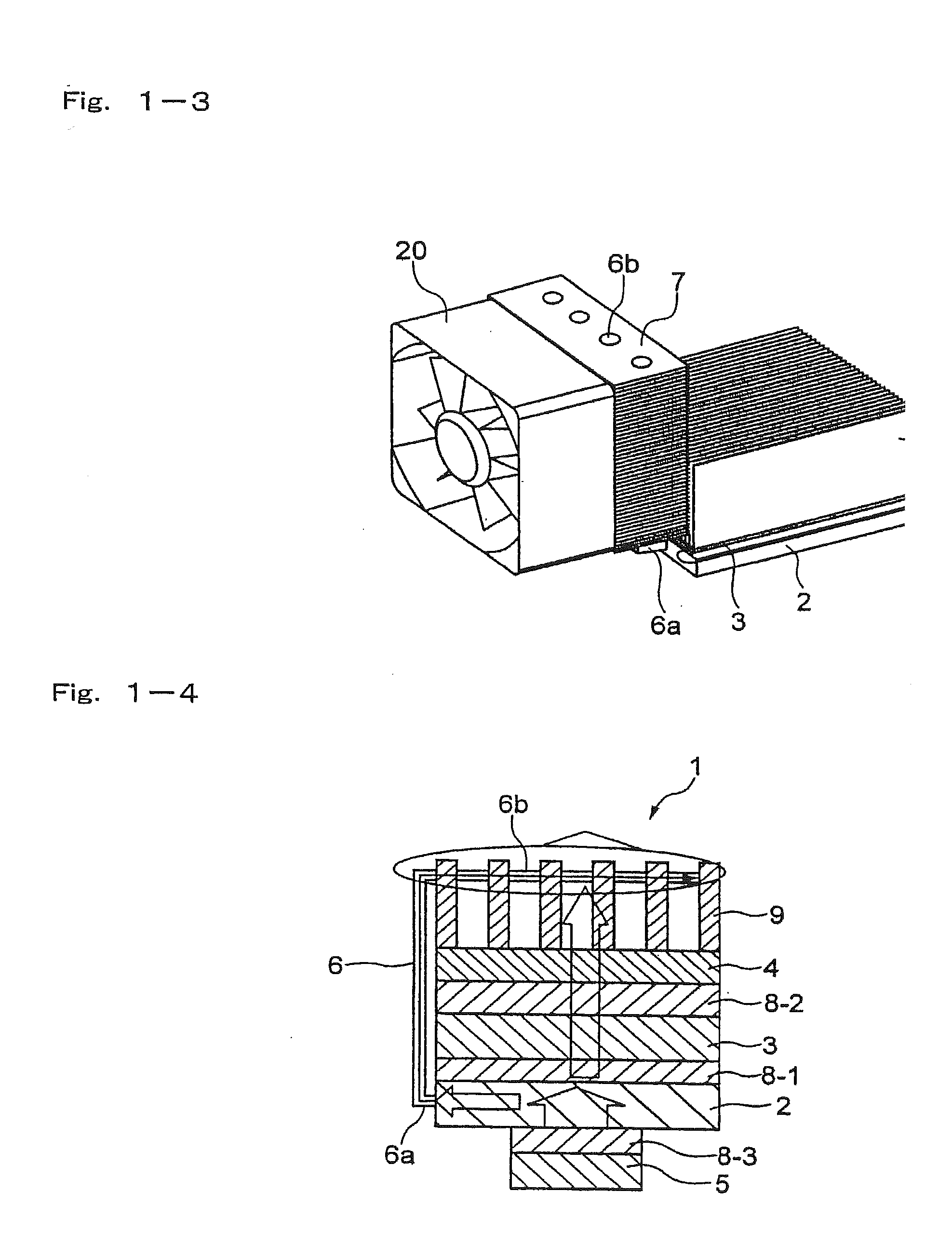
[0126]The module for cooling a heat generating element of the invention as shown in FIG. 2-2 is prepared. More specifically, a heat receiving plate formed by a material having a high thermal conductivity such as aluminum or copper is attached to a heat generating source such as a CPU mounted on a printed board. At least one prescribed recessed portion (for example, a hole) is formed in the heat receiving plate, and an end of a heat transfer device having a low thermal resistance such as a heat pipe is thermally connected to the recessed portion and fixed therein.
[0127]The other end of the heat pipe (heat transfer device) is thermally connected to a prescribed recessed portion (for example, a hole having a prescribed diameter) formed in a heat dissipating plate formed by a material having a high thermal conductivity such as aluminum or copper. The heat pipe is fixed to the above recessed portion of the hear receiving plate and the heat dissipating plate by soldering, crimping or the ...
example 2
[0141]The module for cooling a heat generating element of the invention as shown in FIG. 2-4 is prepared. The module is substantially the same as the module for cooling a heat generating element as shown in FIG. 2-2 except that the heat receiving plate is arranged so as to be parallel to the heat dissipating plate. In FIG. 2-4, the first heat sink is placed at the lower side of the heat dissipating plate, however, the first heat sink may be placed at the upper side of the heat dissipating plate and the second heat sink may be place at the lower side of the heat dissipating plate.
[0142]In addition, the module for cooling a heat generating element of the invention as shown in FIG. 2-5 is prepared. More specifically, the heat receiving plate is arranged so as to be parallel to the heat dissipating plate, and furthermore, the third heat sink is attached to the heat receiving plate in addition to the first heat sink and the second heat sink as described with reference to FIG. 2-4. The th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com