Patents
Literature
351results about How to "Increase temperature difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
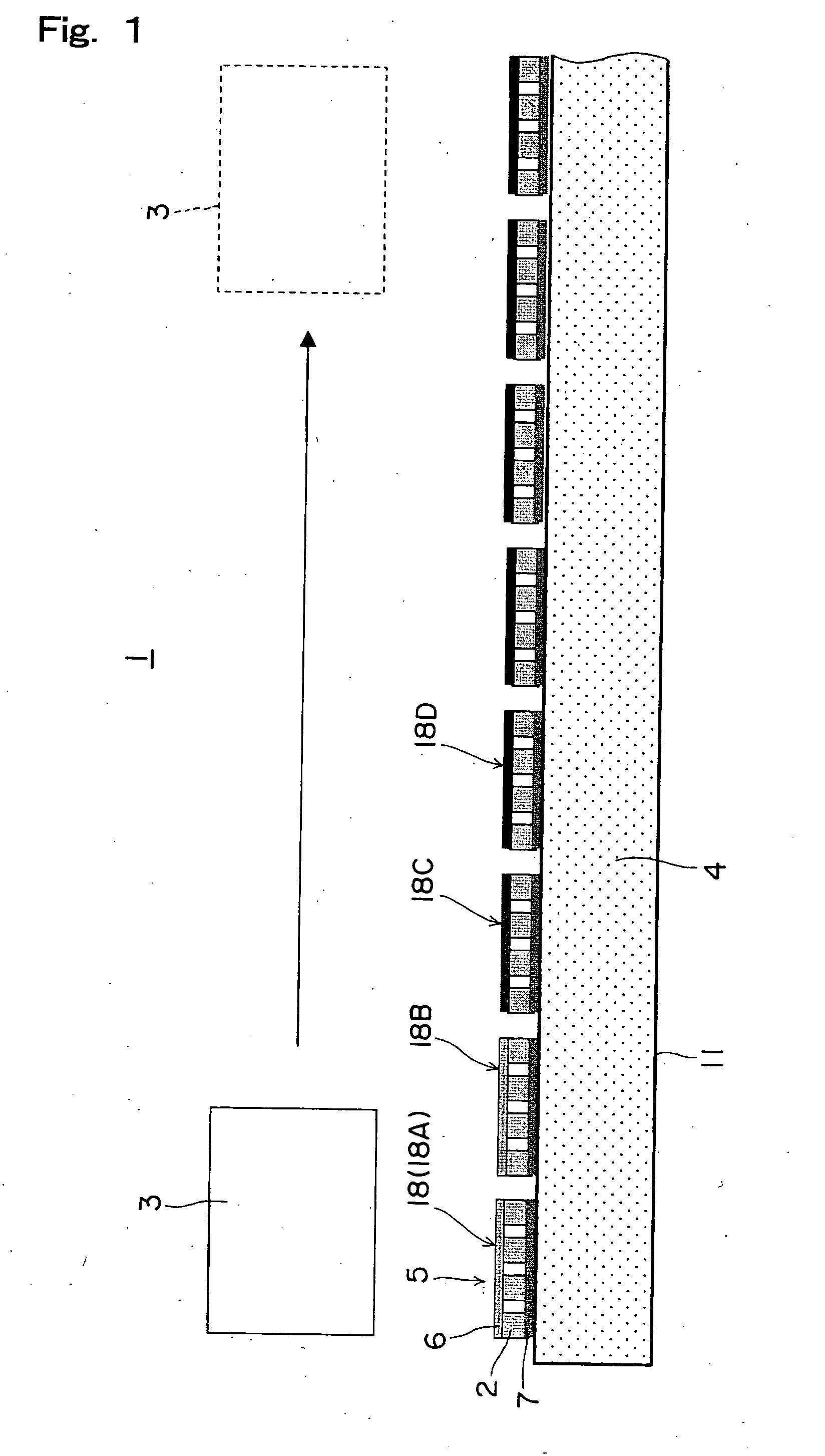
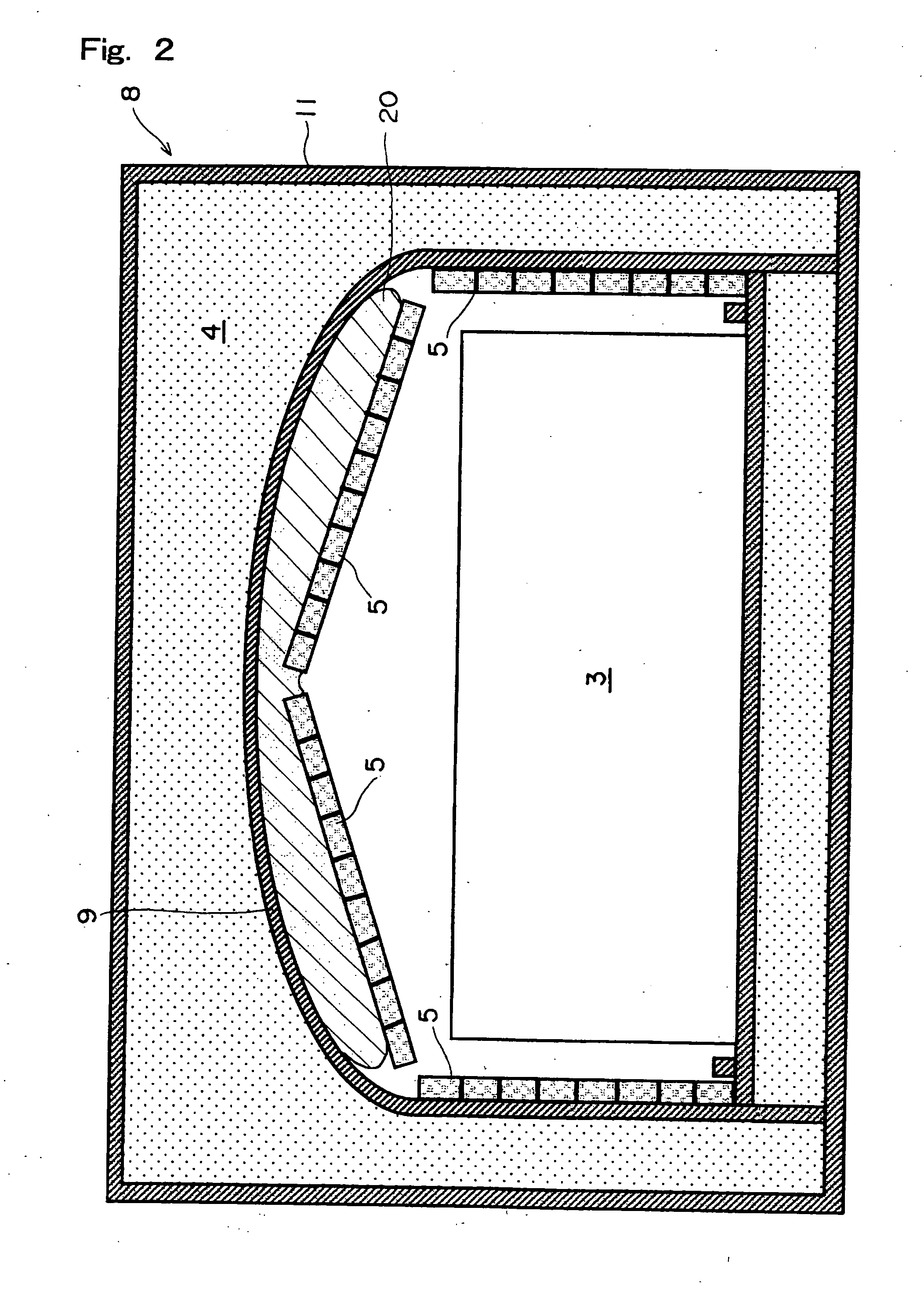
Energy storage and generation
InactiveUS20090282840A1Maximize useMinimize changesSolidificationLiquefactionPropellerProcess engineering
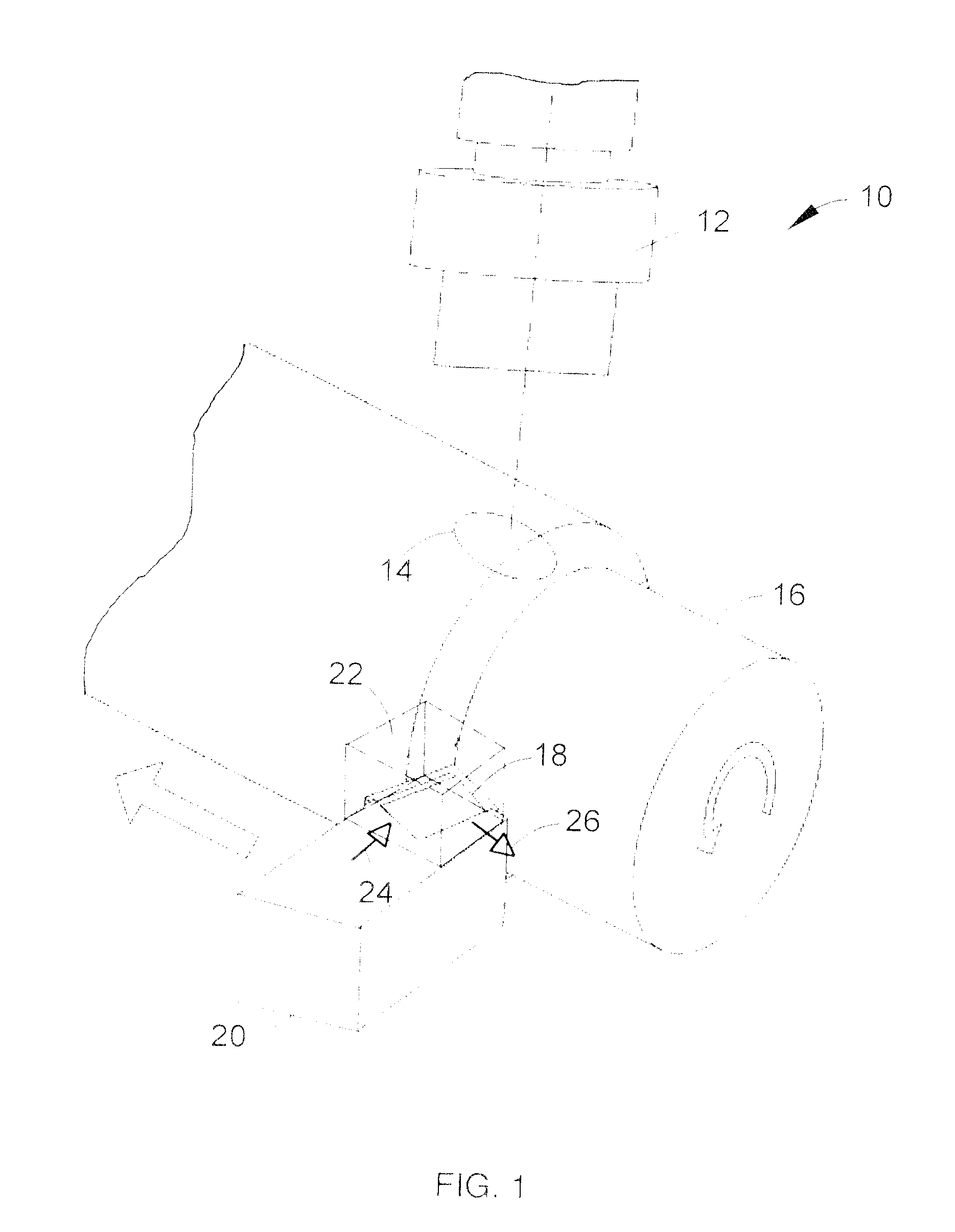
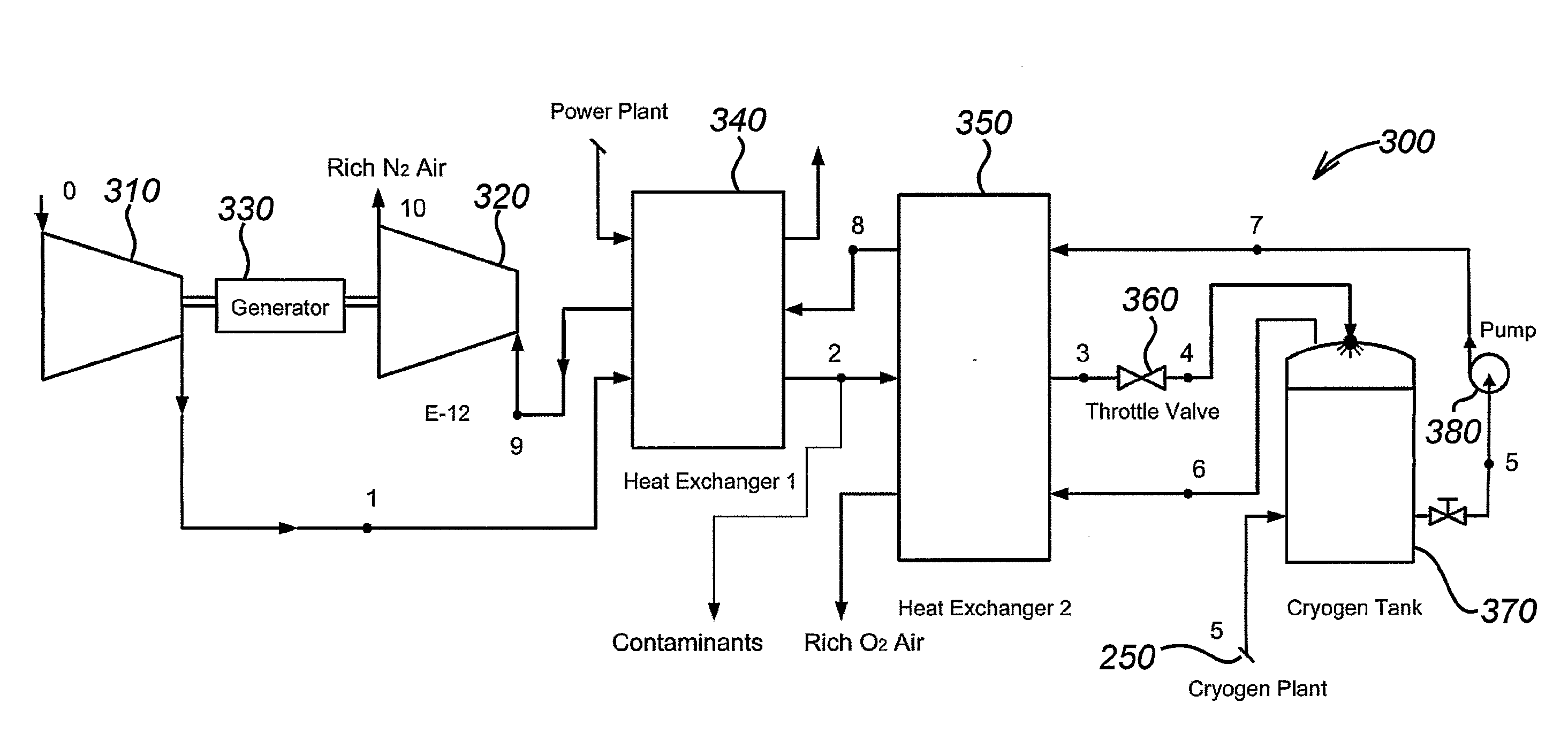
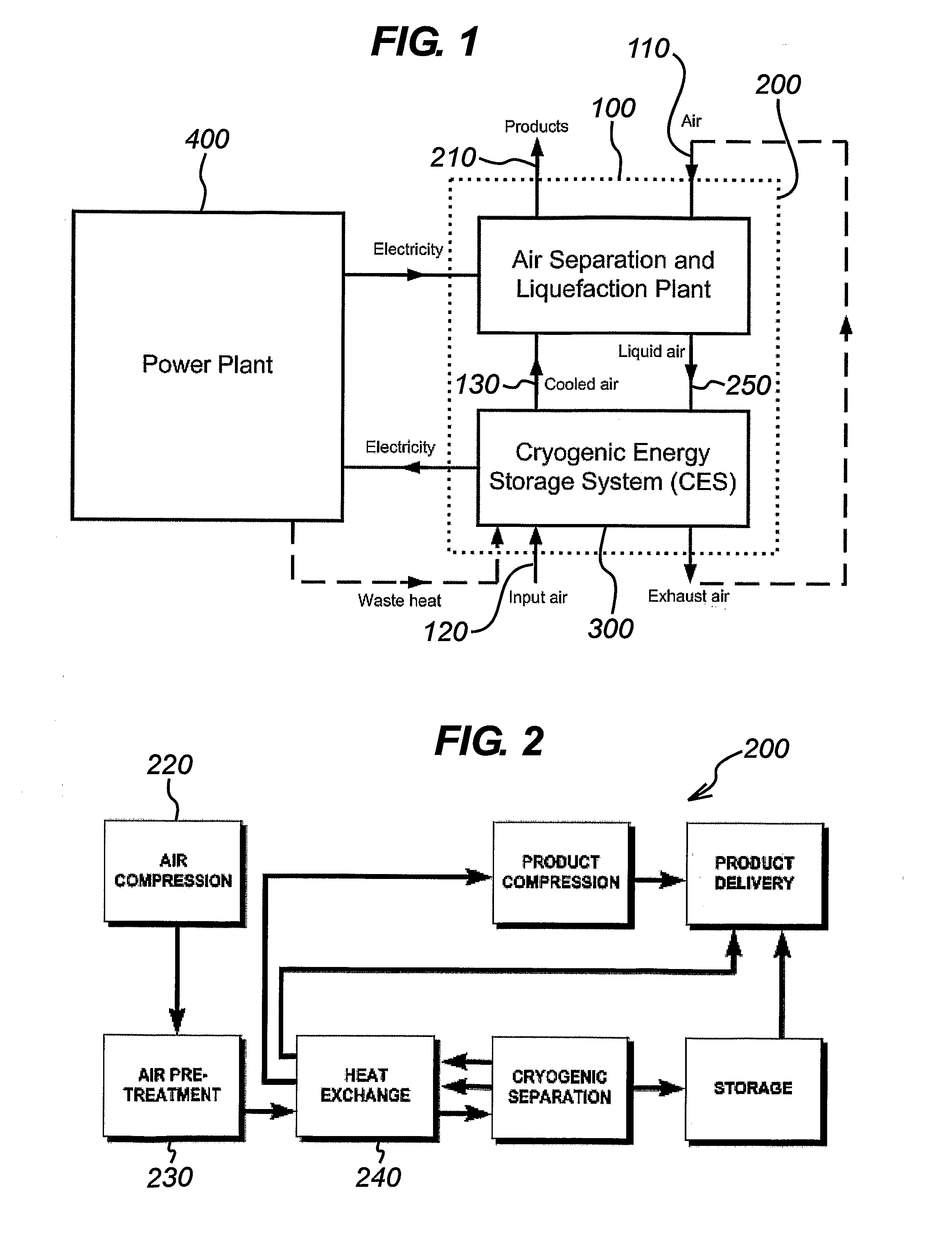
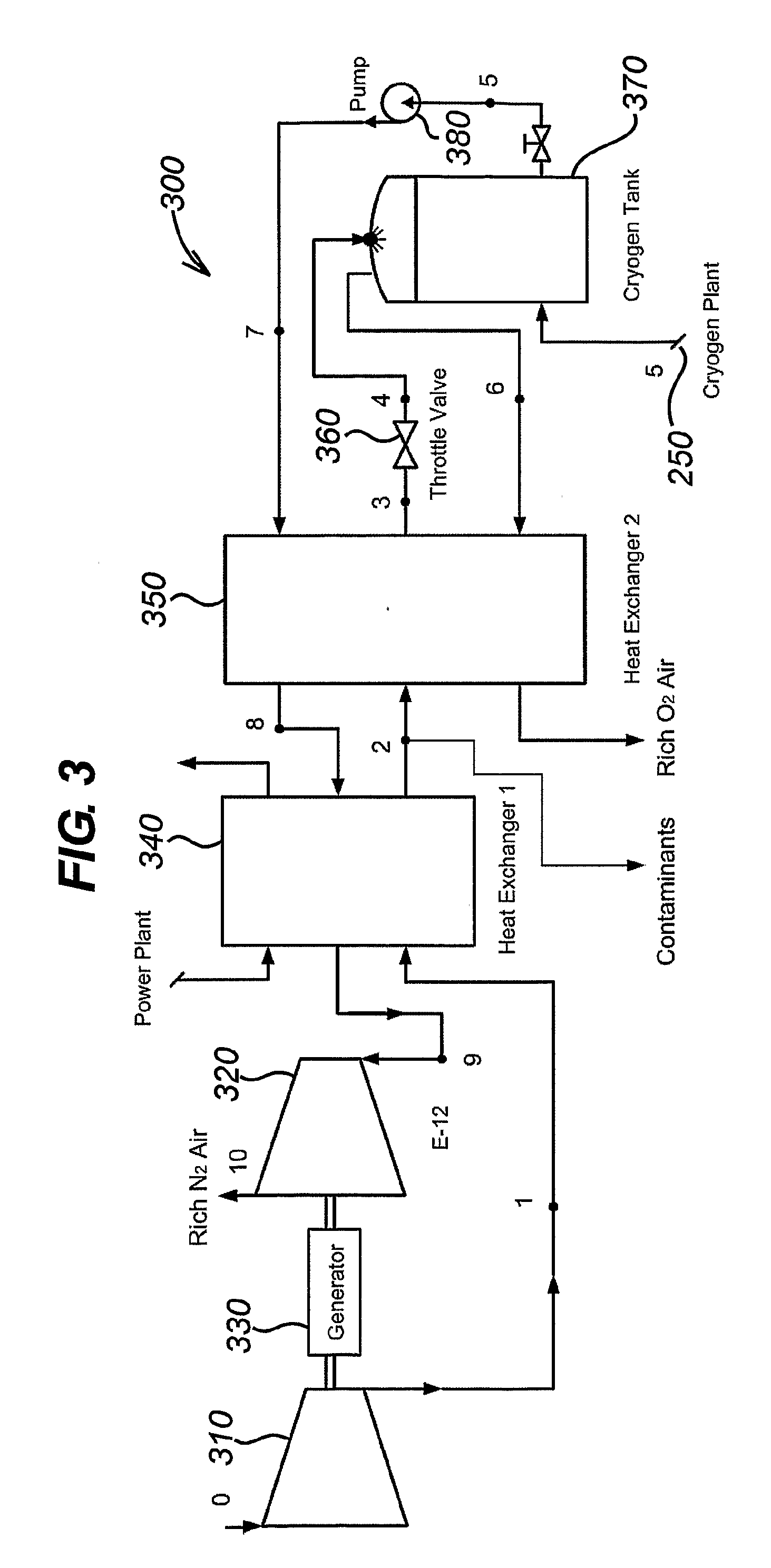
The present invention concerns systems for storing energy and using the stored energy to generate electrical energy or drive a propeller (505). In particular, the present invention provides a method of storing energy comprising: providing a gaseous input, producing a cryogen from the gaseous input; storing the cryogen; expanding the cryogen; using the expanded cryogen to drive a turbine (320) and recovering cold energy from the expansion of the cryogen. The present invention also provides a cryogenic energy storage system comprising: a source of cryogen; a cryogen storage facility (370); means for expanding the cryogen; a turbine (320) capable of being driven by the expanding cryogen; and means (340, 350) for recovering cold energy released during expansion of the cryogen.
Owner:HIGHVIEW ENTERPRISES LTD
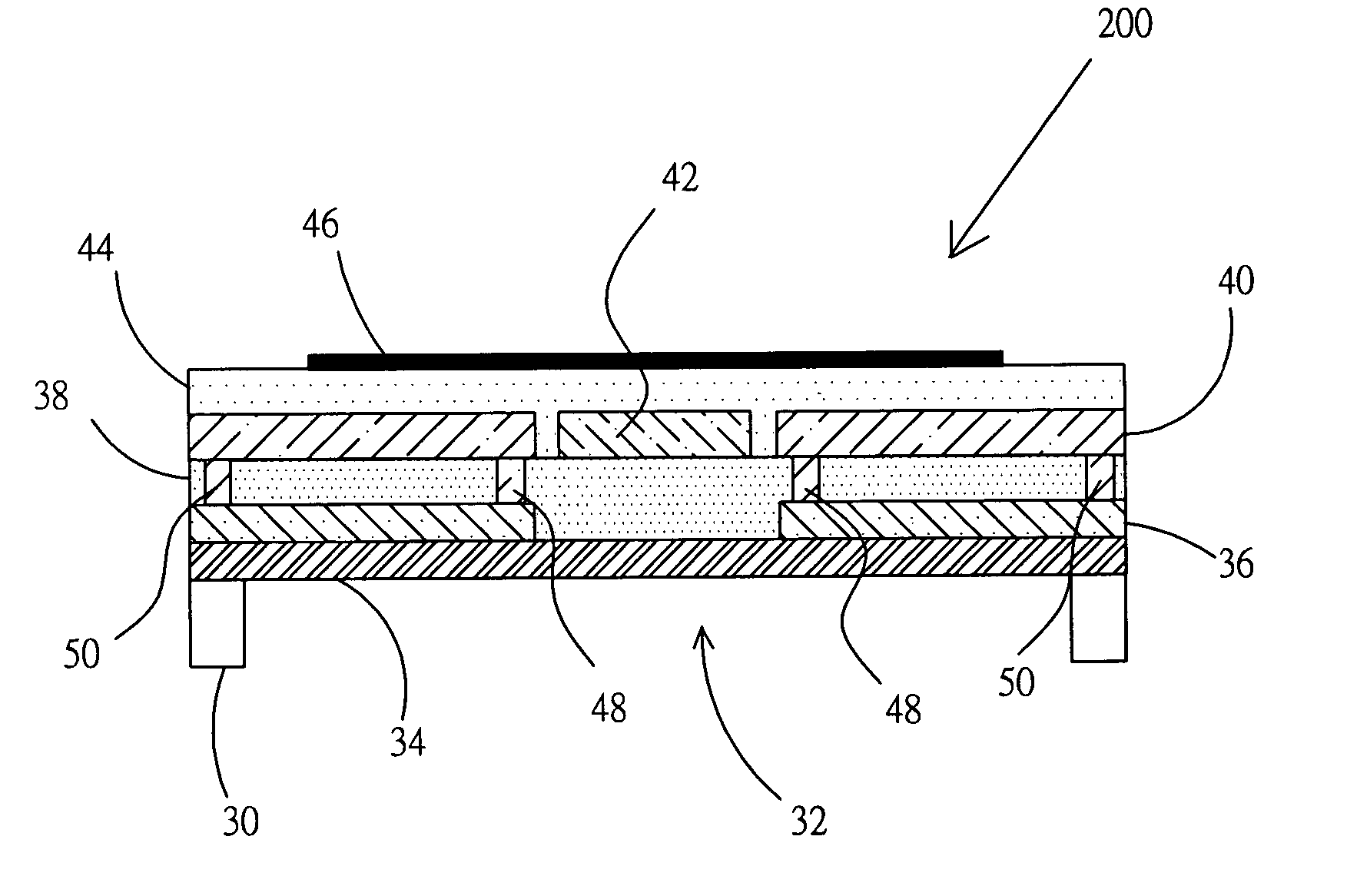
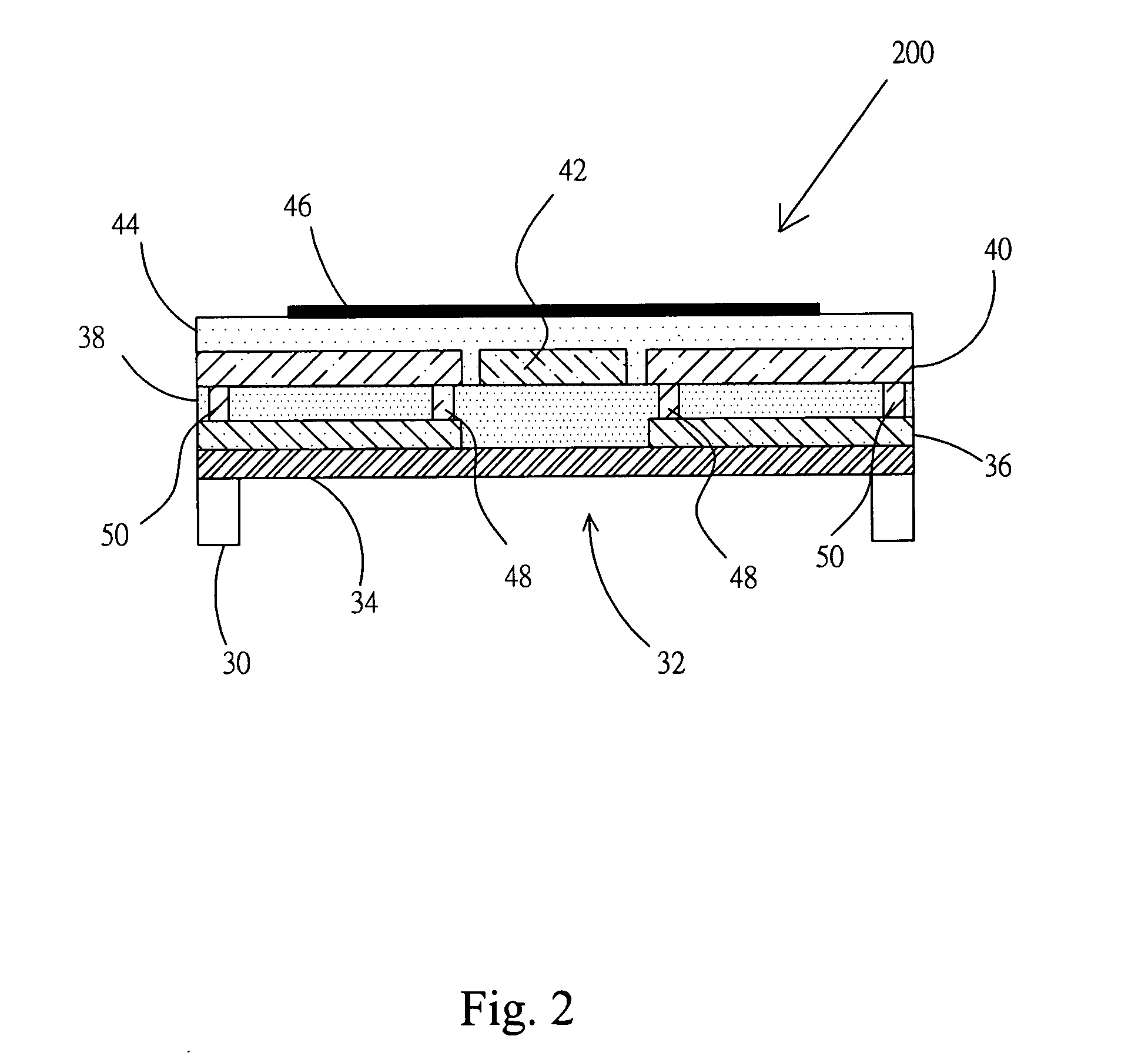
Module for cooling semiconductor device
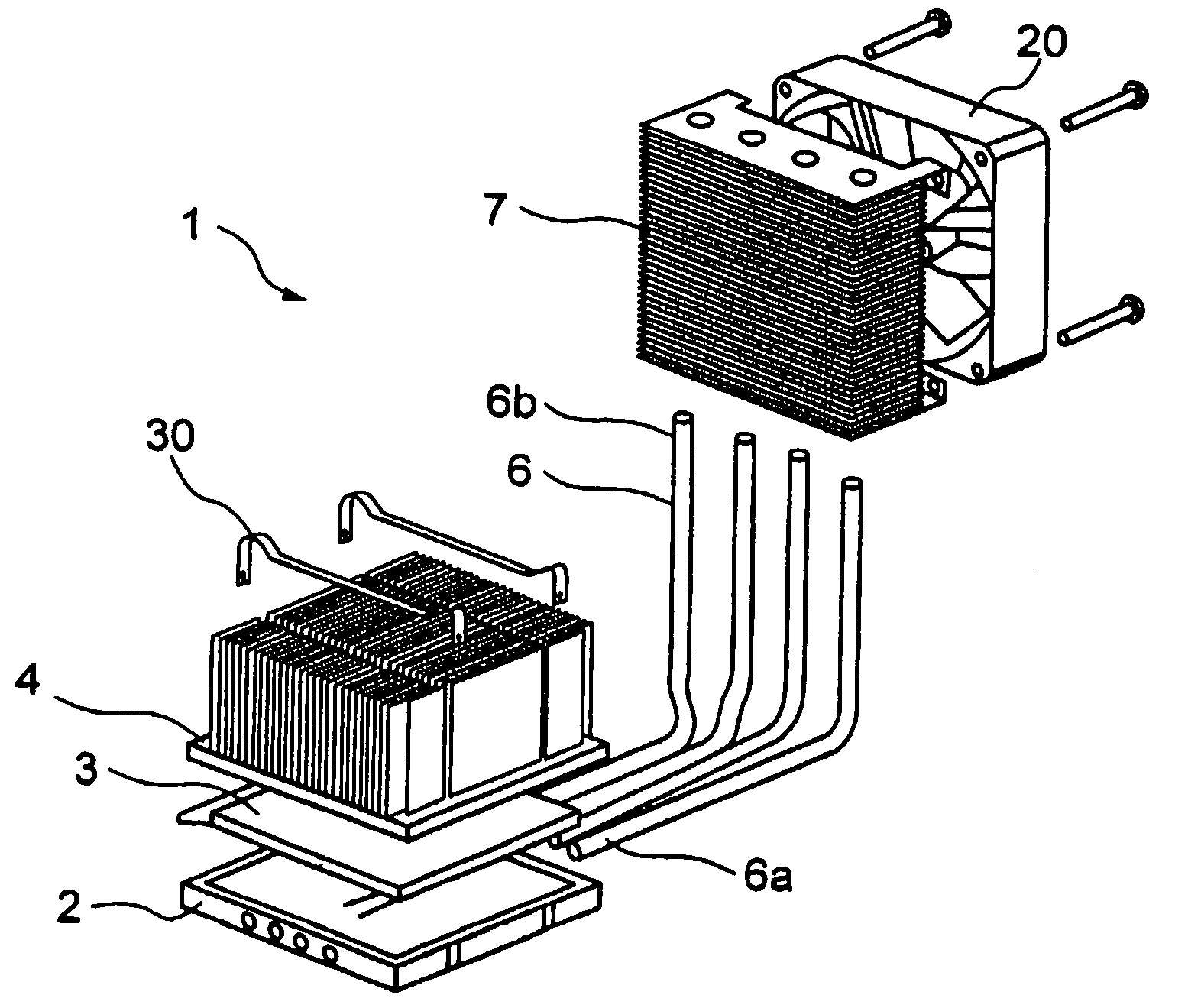
InactiveUS20050257532A1Improve cooling efficiencyReduce heat gainDomestic cooling apparatusIndirect heat exchangersThermoelectric coolingDevice material
A module for cooling a heat generating element comprising a heat receiving plate thermally connected to at least one heat generating element; a heat transfer device one end portion of which is thermally connected to the heat receiving plate and other end portion of which is thermally connected to a heat dissipating plate; a thermoelectric cooler one face of which is thermally connected to one face of the heat dissipating plate; a first heat sink thermally connected to other face of the heat dissipating plate; and a second heat sink thermally connected to other face of said thermoelectric cooler.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
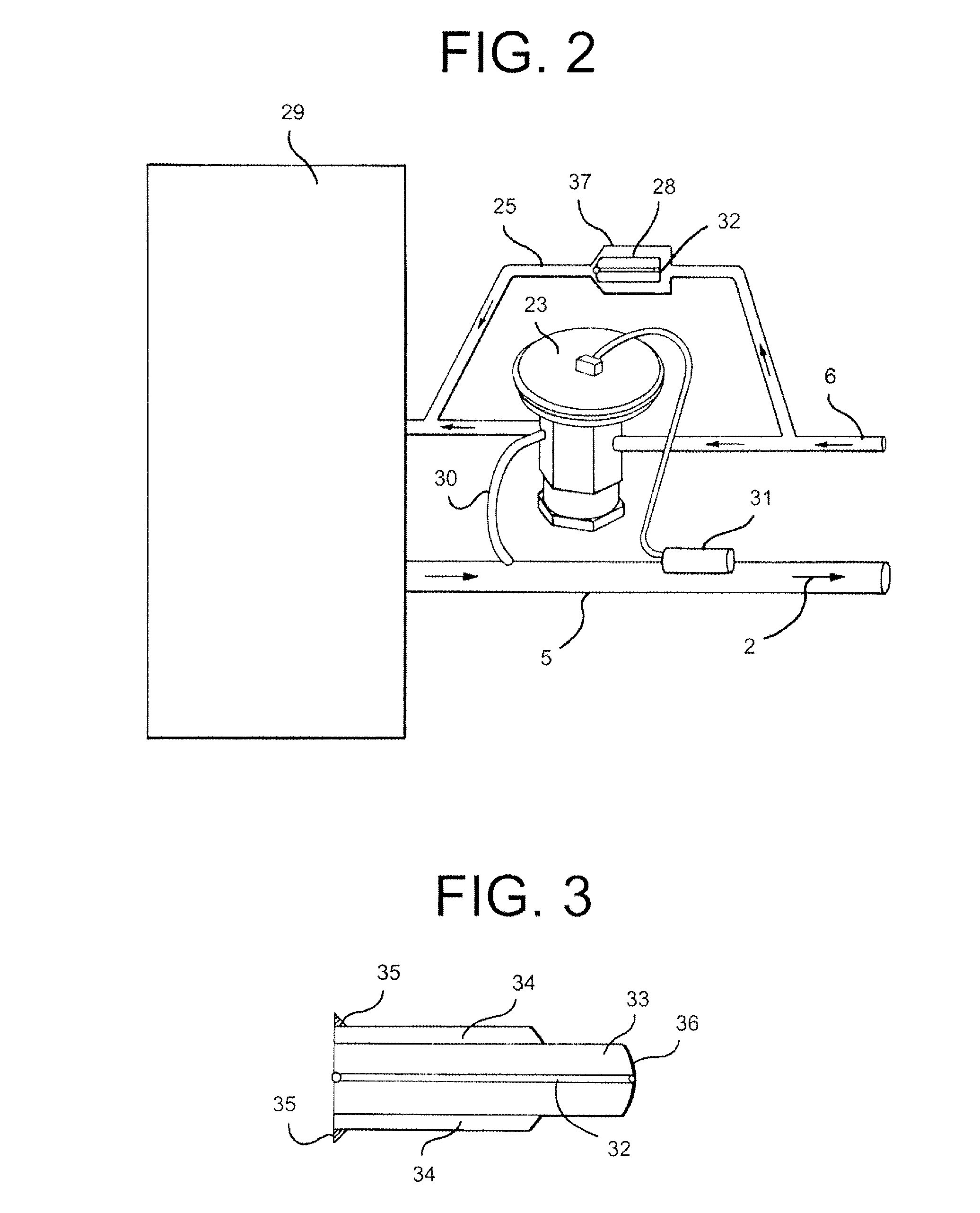
Contact heat-transferring cooking system with an electric hotplate
InactiveUS6150636AImprove heat transfer performanceIncrease temperature differenceCooking-vessel materialsDomestic stoves or rangesCouplingVolumetric Mass Density
A contact heat-transferring electric hotplate (11) is provided, which is made from nonoxidic ceramic, particularly silicon nitride. Its very thin hotplate body (14) in the form of a disk is installed in self-supporting manner in a hob plate, e.g. by bonding, and has an extremely flat surface or which is adapted to the cooking vessel shape, which creates such a small gap with respect to said vessel that a coupling is possible even with higher power densities with only a temperature difference of a few degrees. The heating means (17) is also in contact with or directly connected to the underside of the hotplate body (14).
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
Thermoelectric power generator with intermediate loop
InactiveUS7608777B2Performance maximizationIncrease temperature differenceThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectMachines/enginesHeat fluxNuclear engineering
A thermoelectric power generator is disclosed for use to generate electrical power from heat, typically waste heat. An intermediate heat transfer loop forms a part of the system to permit added control and adjustability in the system. This allows the thermoelectric power generator to more effectively and efficiently generate power in the face of dynamically varying temperatures and heat flux conditions, such as where the heat source is the exhaust of an automobile, or any other heat source with dynamic temperature and heat flux conditions.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
Parallel flow reactor having improved thermal control
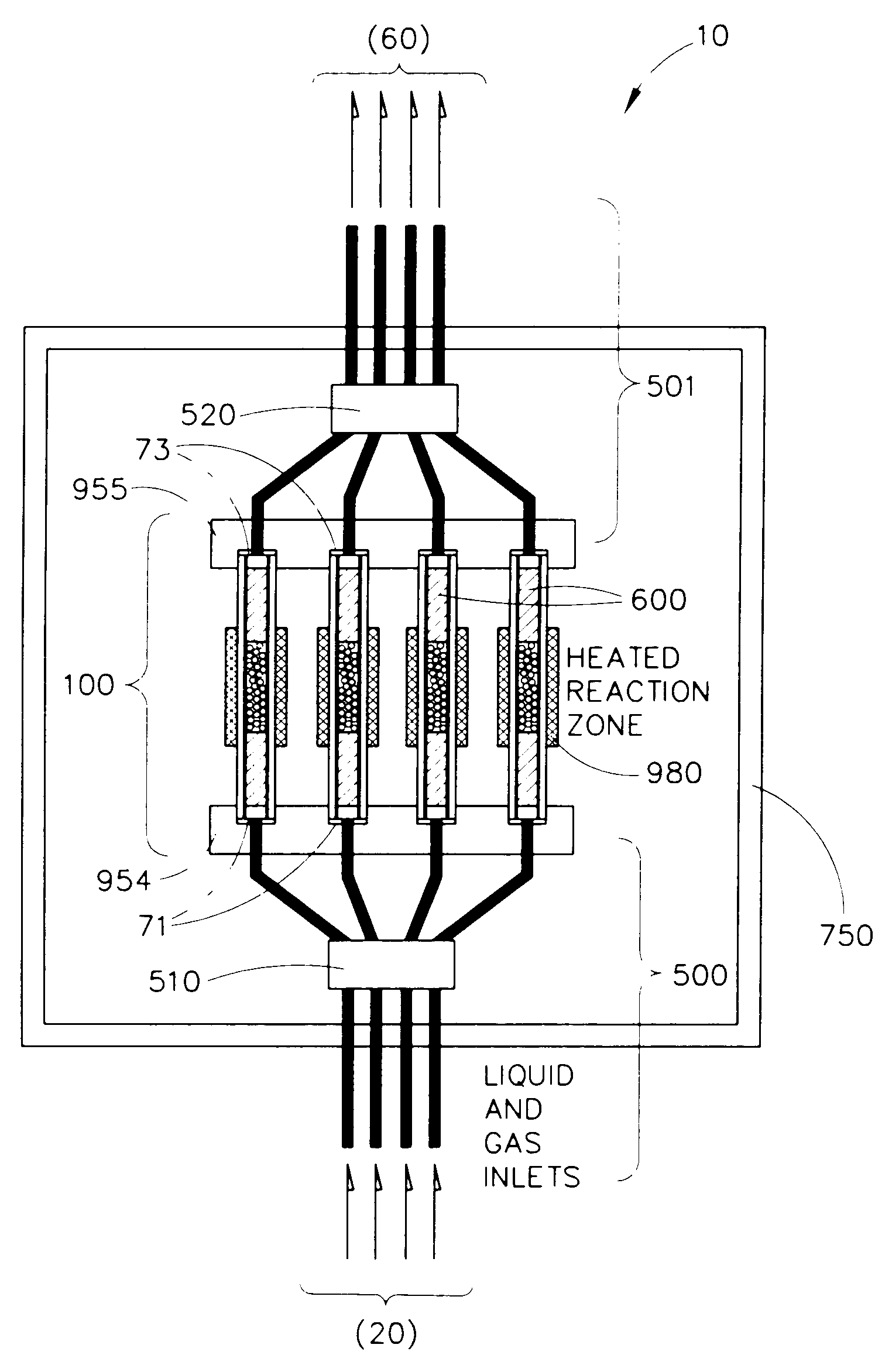
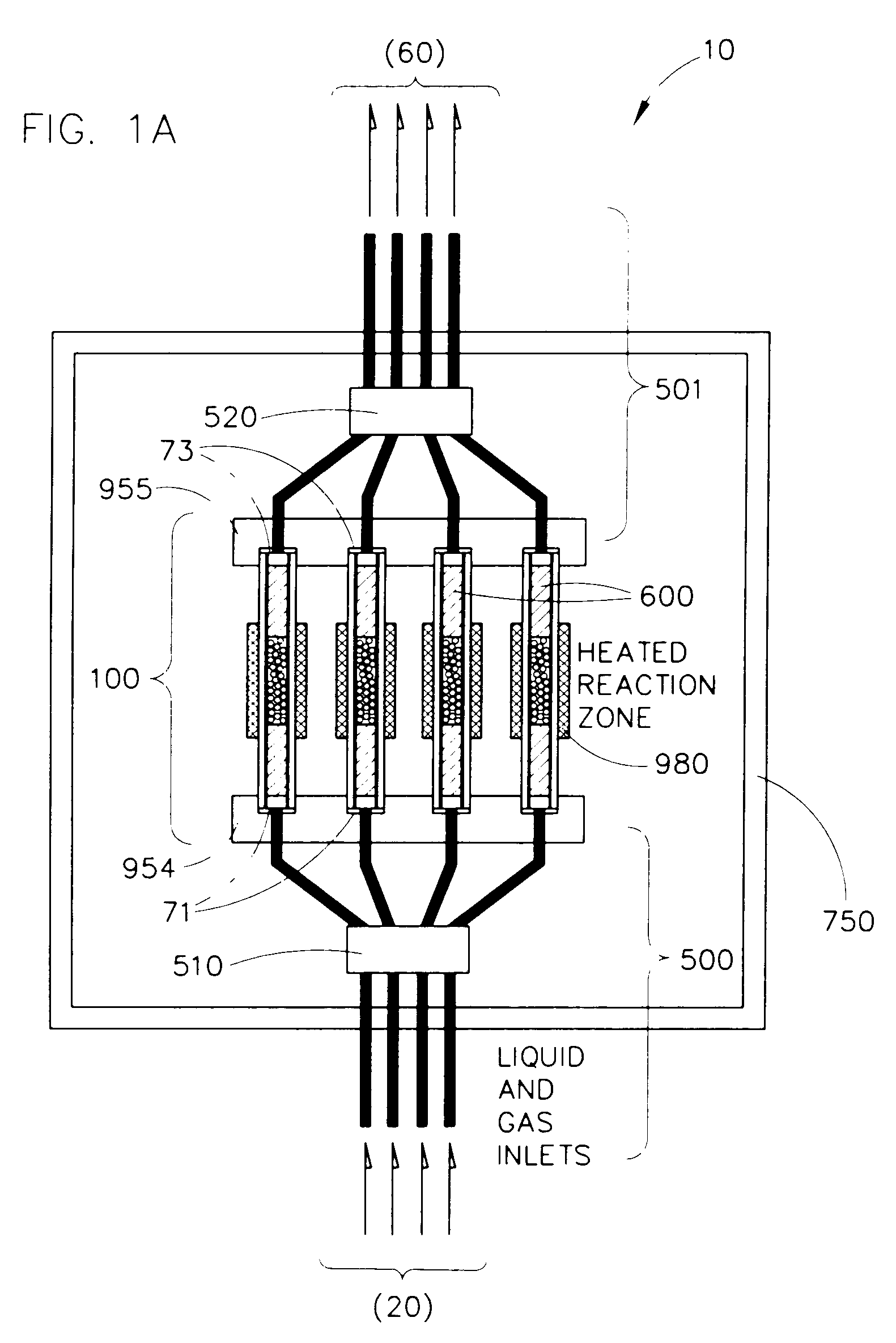
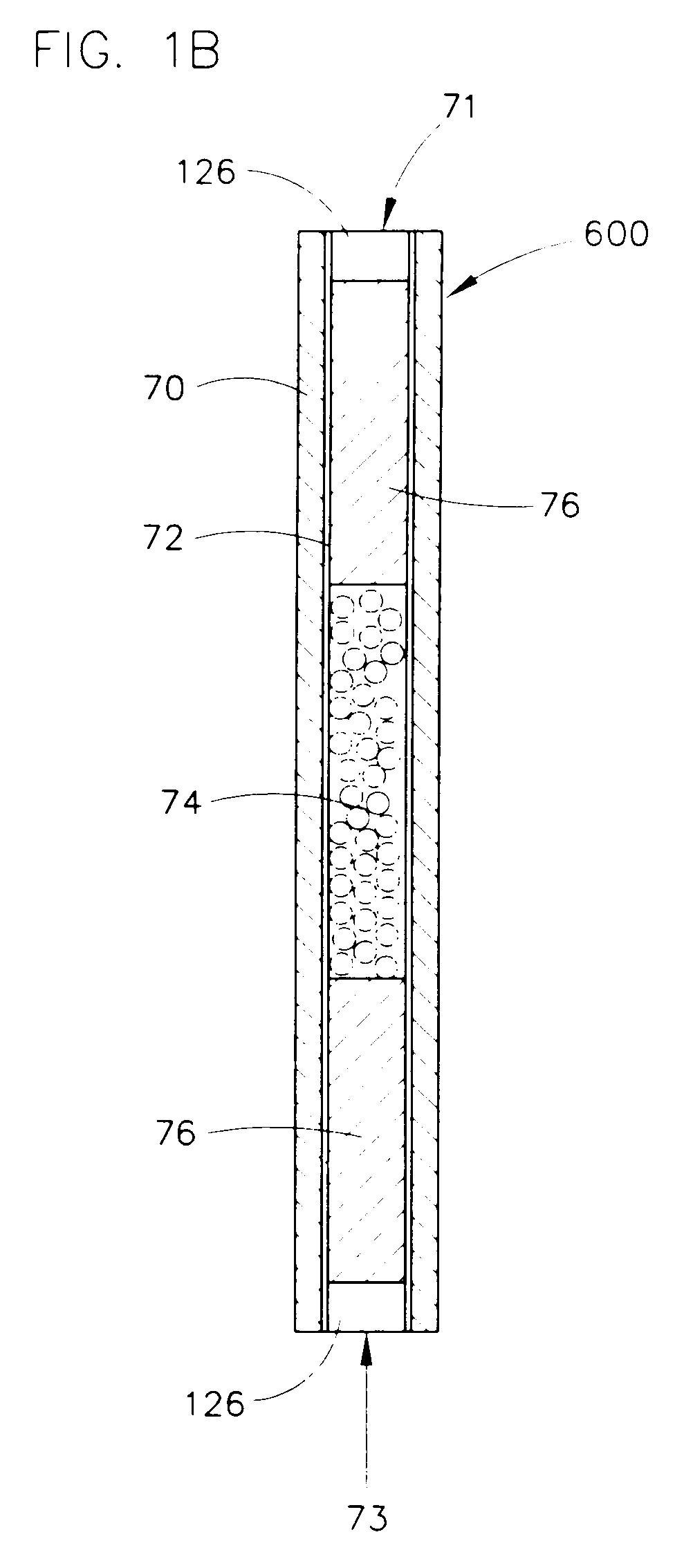
InactiveUS7118917B2Efficient identificationEfficiency optimizationSequential/parallel process reactionsLighting and heating apparatusChemical treatmentThermal isolation
Parallel flow chemical processing systems, such as parallel flow chemical reaction systems are disclosed. These systems are adapted to simultaneously and independently vary temperature between separate flow channels, preferably by employing separate, individual heating elements in thermal communication with each of four or more parallel flow reactors. The flow reactors are preferably isolated from each other using a thermal isolation system comprising fluid-based heat exchange. In preferred embodiments, the axial heat flux can be fixedly or controllably varied.
Owner:FREESLATE
Heat spreader for emissive display device
InactiveUS7160619B2Increase temperature differenceTube/lamp screens manufactureStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceGraphite
A heat spreader for an emissive display device, such as a plasma display panel or a light emitting diode, comprising at least one sheet of compressed particles of exfoliated graphite having a surface area greater than the surface area of that part of a discharge cell facing the back surface of the device.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
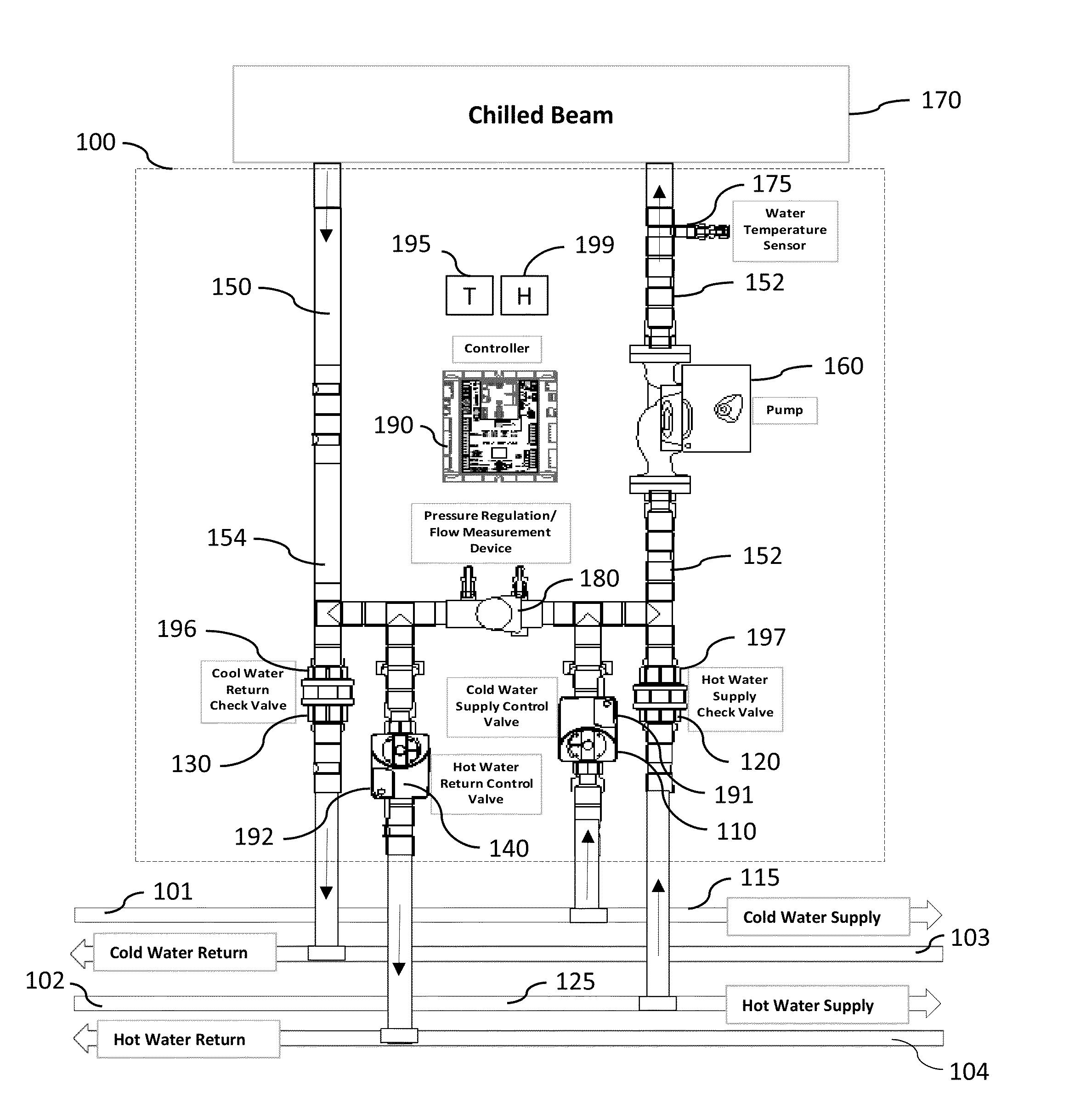
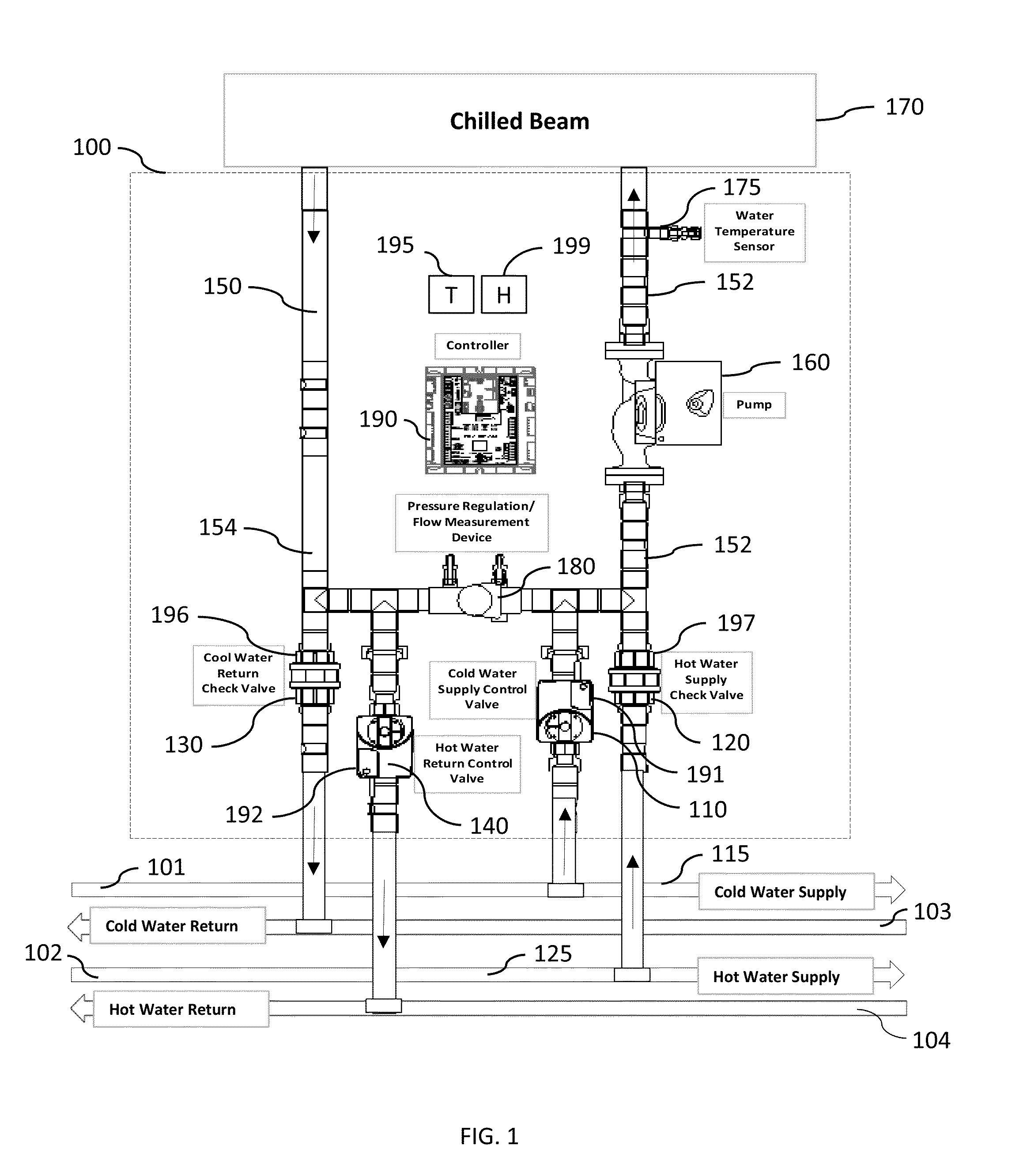
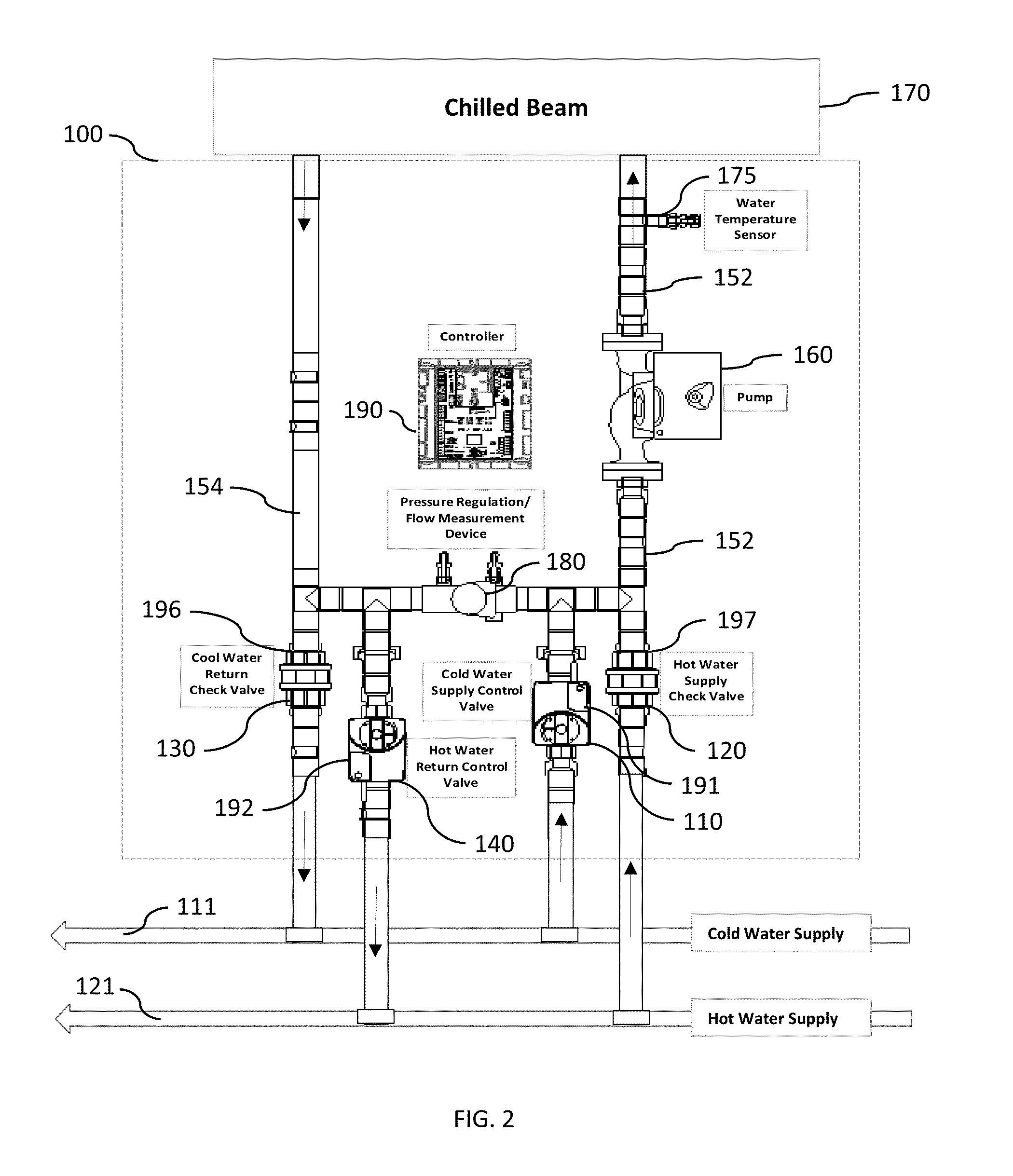
Chilled beam pump module, system, and method
ActiveUS20130199772A1Improve performanceSimple design and installationTemperatue controlHeat exchange apparatusWarm waterComputer module
Chilled-beam zone pump modules for controlling zones of a chilled-beam heating and air conditioning system, multiple-zone chilled beam air conditioning systems for cooling multiple-zone spaces, and methods of controlling chilled beams in multi-zone air conditioning systems. Embodiments include a pump serving each zone that both recirculates water within the module and chilled beam and circulates water in and out of a chilled or warm water distribution system through valves to control temperature. Different embodiments provide heating as well as cooling, use check valves to reduce the number of control valves required, adjust the temperature of the beam to avoid condensation, change pump speed to save energy or increase capacity, can be used in two- or four-pipe systems, allow for lower installation cost, provide better performance or control, improve reliability, overcome barriers to the use of chilled beams, or a combination thereof.
Owner:SEMCO INC
Heat spreader for emissive display device
InactiveUS7150914B2Increase temperature differenceTemperature differenceTube/lamp screens manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyDisplay deviceGraphite
A heat spreader for an emissive display device, such as a plasma display panel or a light emitting diode, comprising at least one sheet of compressed particles of exfoliated graphite having a surface area greater than the surface area of that part of a discharge cell facing the back surface of the device.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for cooling integrated circuit chips using recycled power
InactiveUS20080229759A1Lower operating temperatureRecycling wasted energy within the computer systemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesComputerized systemCooling power
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that cools integrated circuit (IC) chips within a computer system. During operation, the system converts heat generated by a heat-generating-device within the computer system into thermoelectric power. The system then supplies the thermoelectric power to an IC chip as a cooling power to reduce the operating temperature of the IC chip, thereby recycling wasted energy within the computer system.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Thermoelectric Conversion System and of Increasing Efficiency of Thermoelectric Conversion System
InactiveUS20080023056A1Control quantityKeep soundnessThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentEmissivityTemperature difference
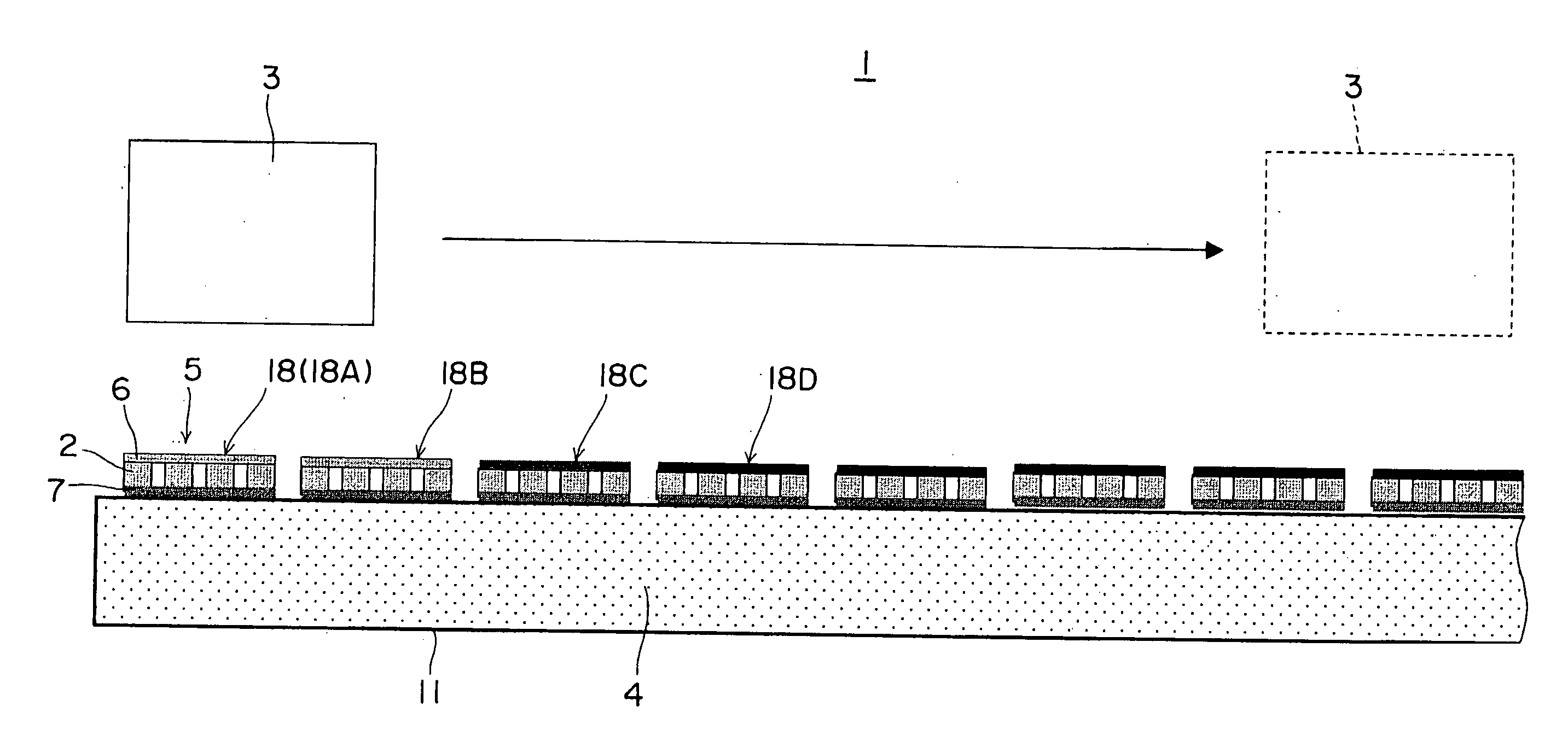
The present invention relates to a thermoelectric conversion system for receiving heat by radiation from a heat source and an efficiency improving method of the thermoelectric conversion system, the system including at least one thermoelectric conversion module 5 having at least a pair of thermoelectric elements 2, a heat receiving zone 6 placed not to contact a heat source 3 for receiving heat by radiation from the heat source 3 and a radiating zone 7 positioned on an opposite side to the heat receiving zone 6 and cooled by a coolant 4, generating electric power by a temperature difference between the heat receiving zone 6 and the radiating zone 7, a continuous or divided heat receiving surface 18 formed by one or a plurality of surfaces facing the heat source 3 of the heat receiving zone 6, and each of the heat receiving surface 18 is given a different quantity of heat from the heat source 3, the system comprising the heat receiving surface 18 has a plurality of different emissivities according to the quantity of heat received from the heat source 3.
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY +1
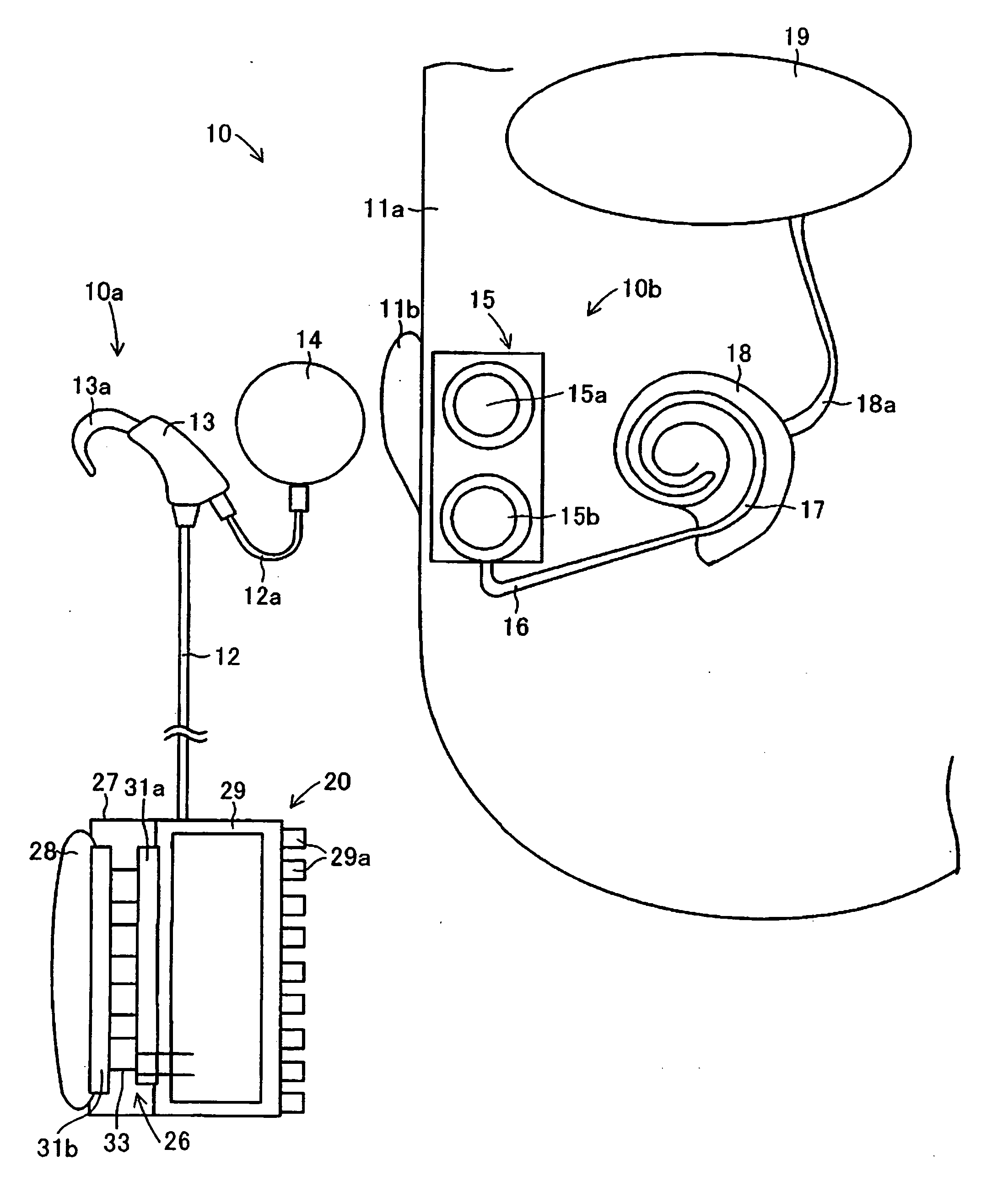
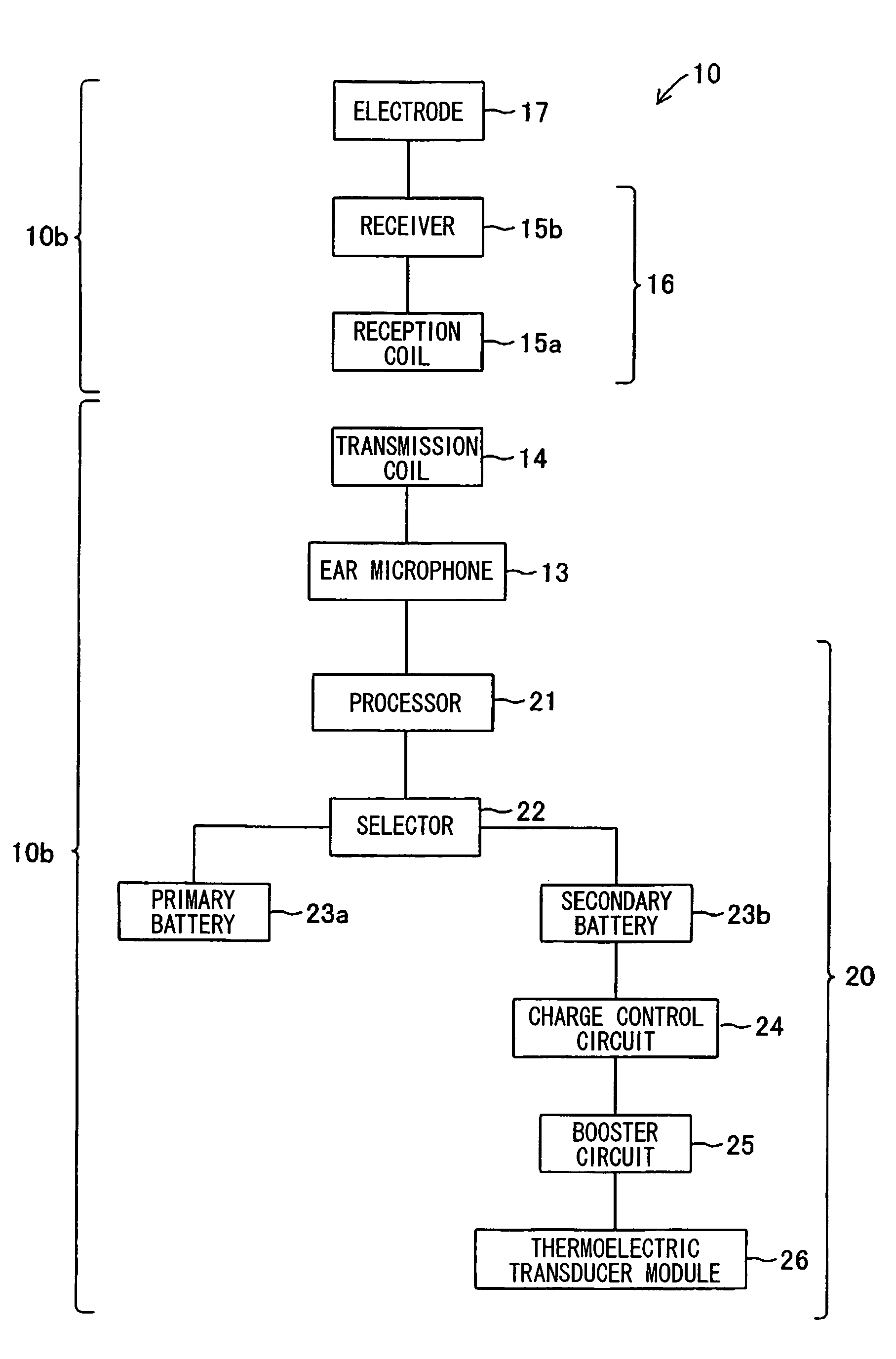
Artificial inner ear and thermoelectric generator therefor
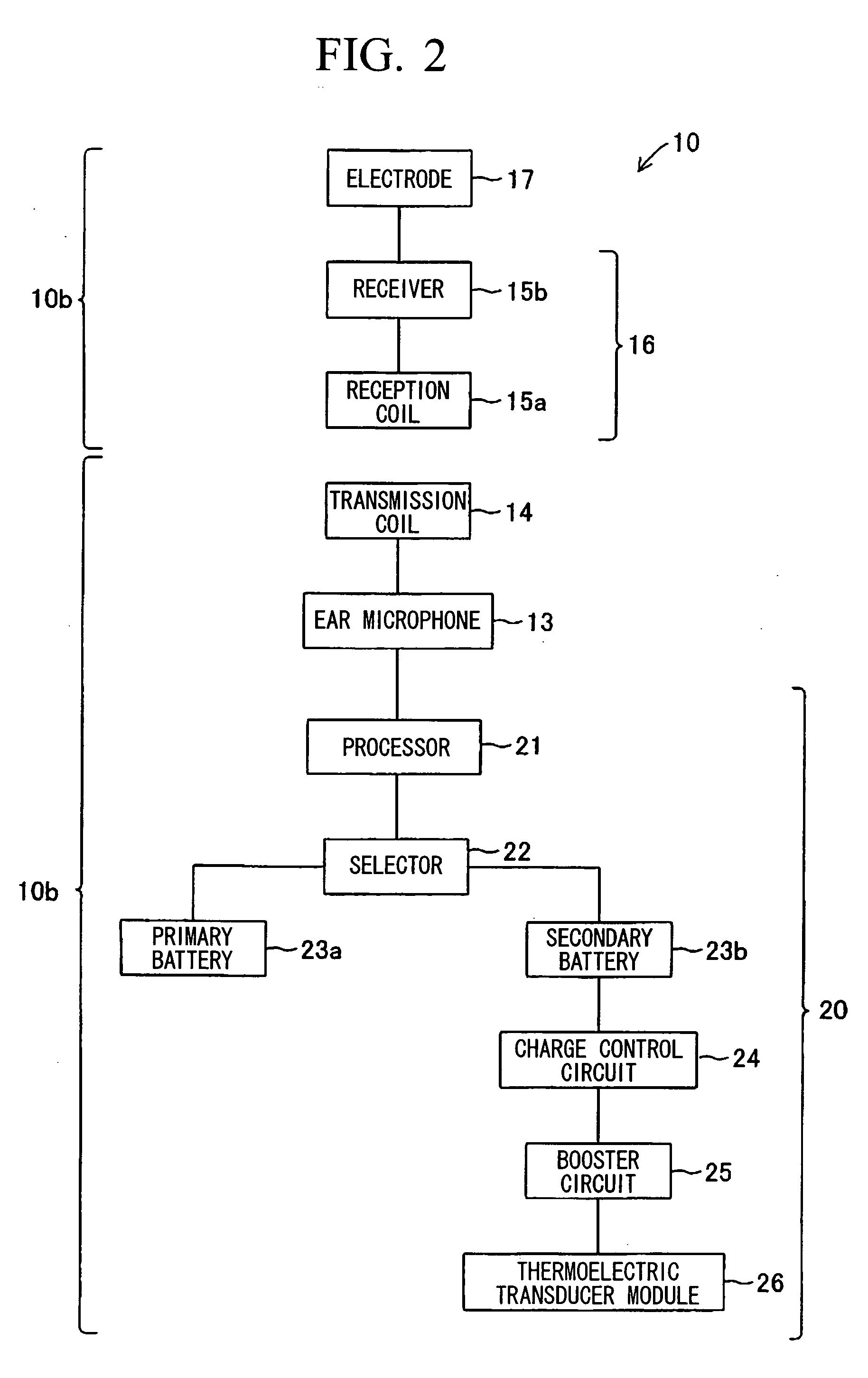
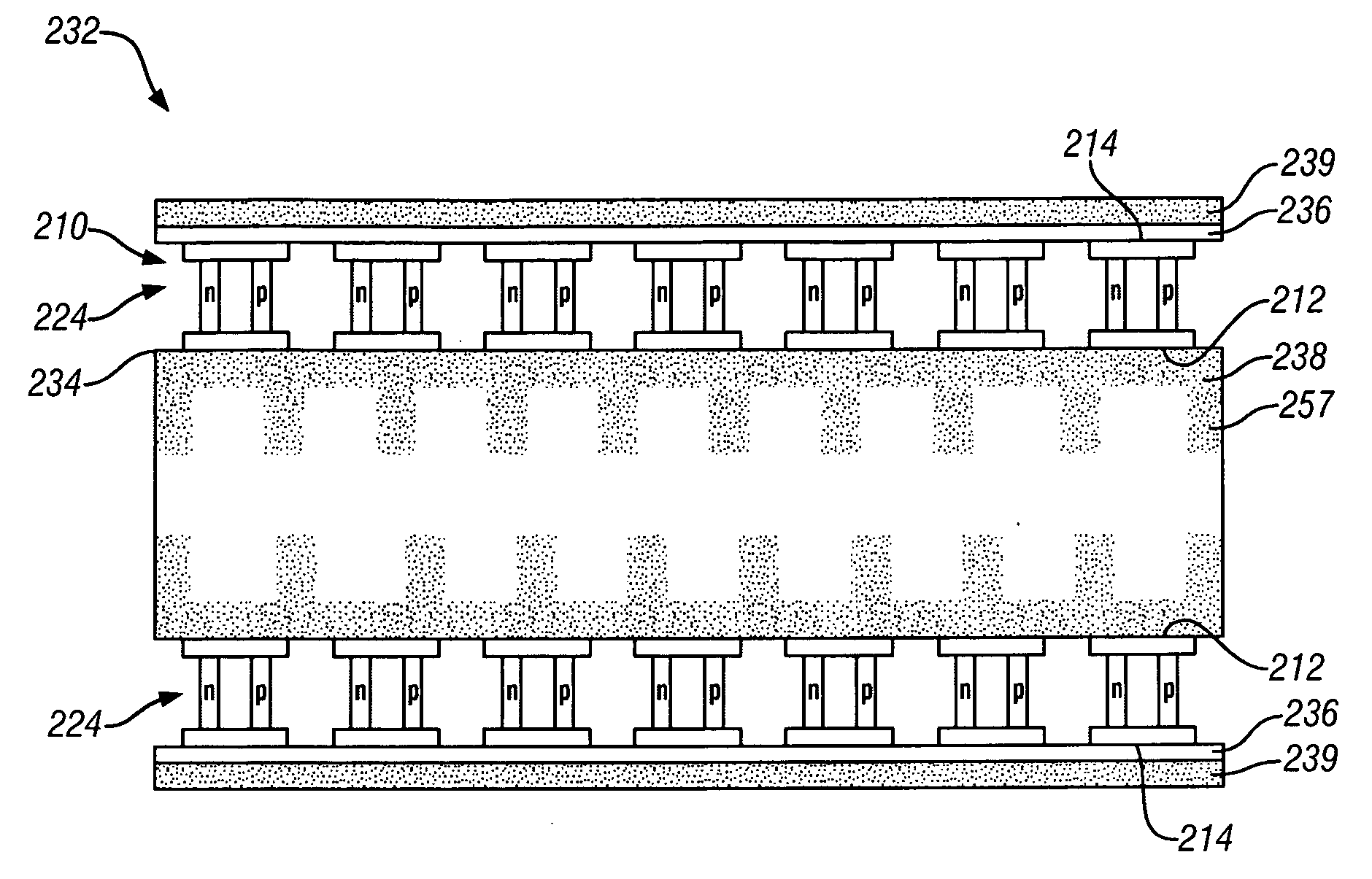
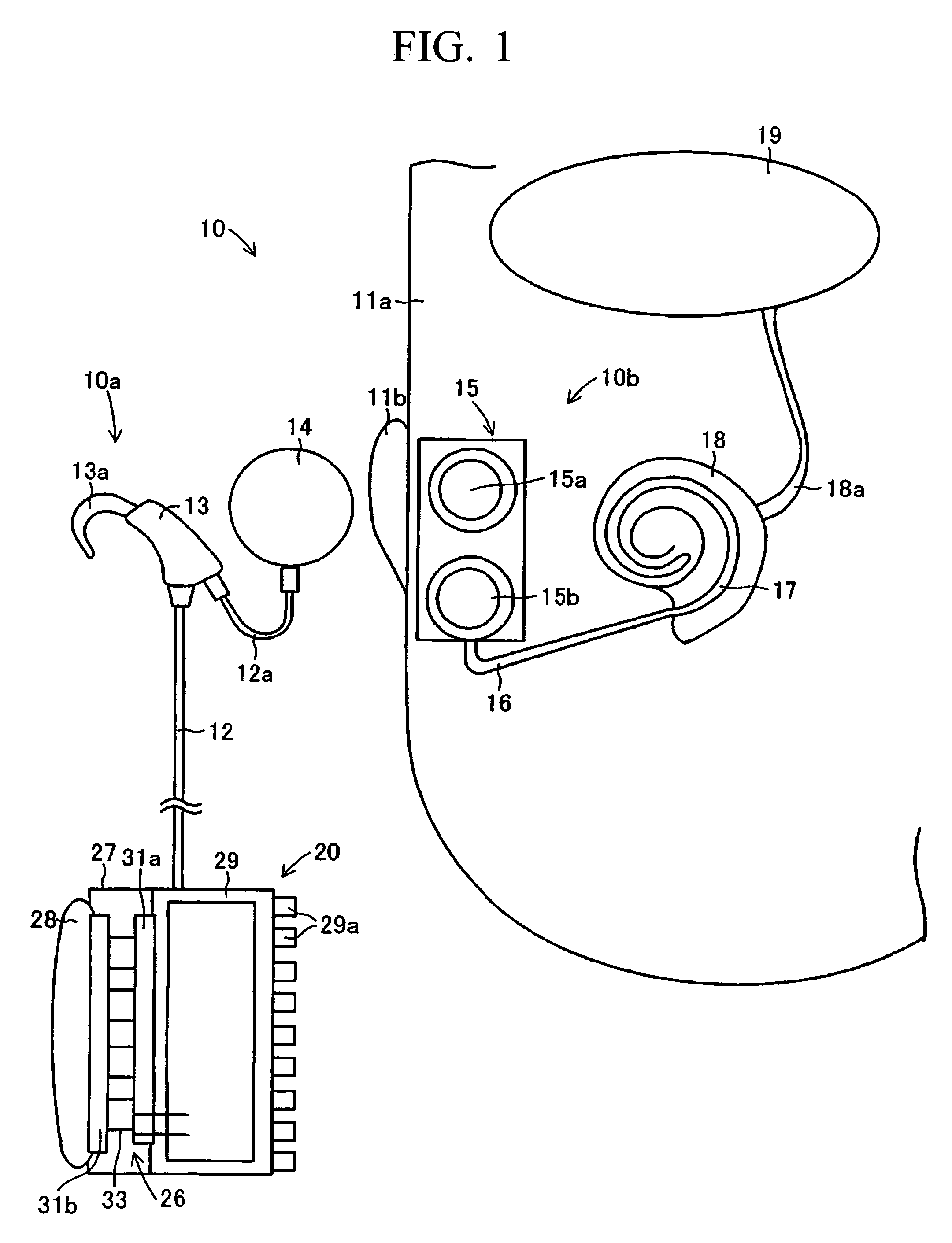
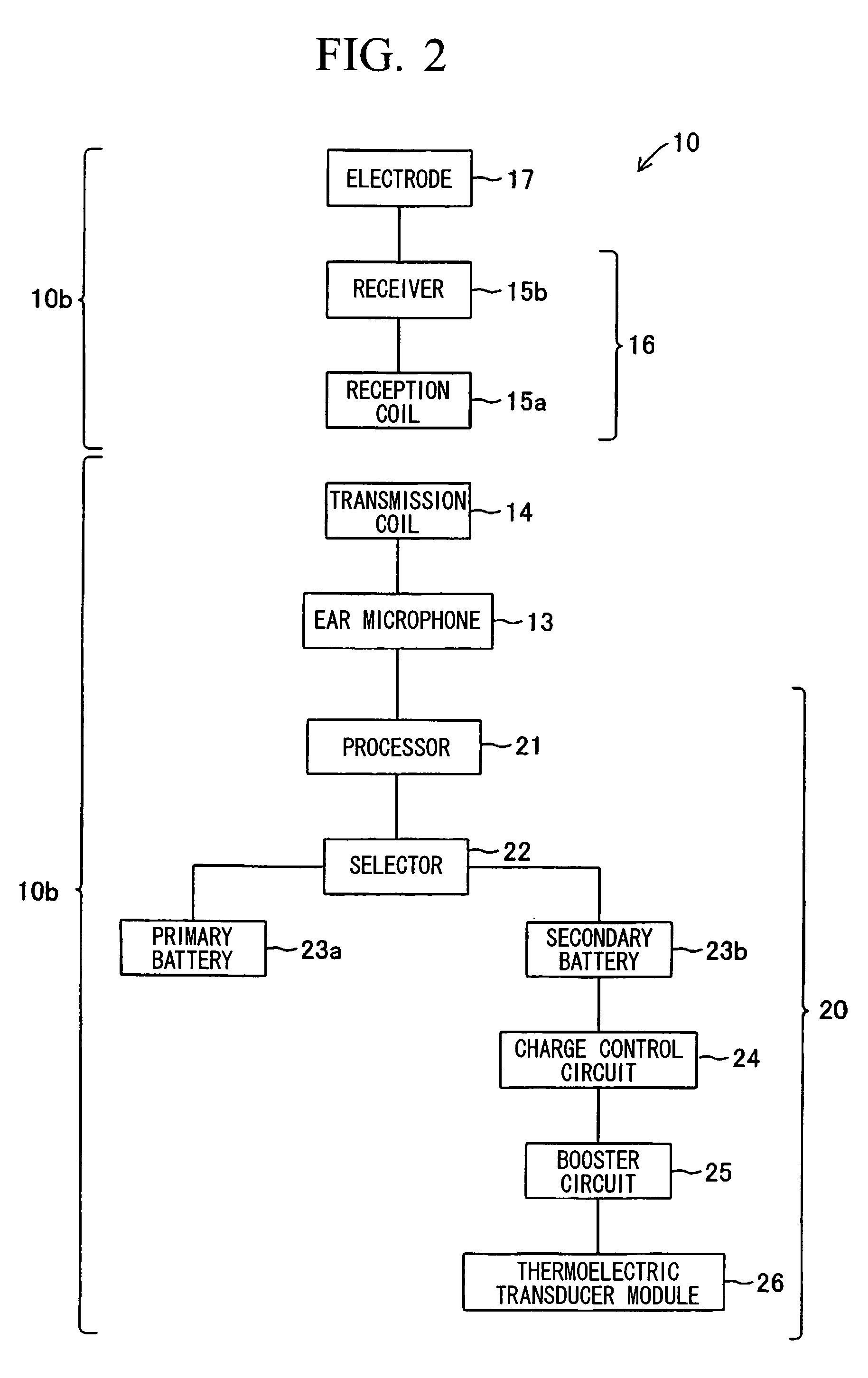
InactiveUS20060169314A1Generate large amountImprove heat transfer efficiencyElectrotherapyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricitySpeech Processor
An artificial inner ear includes a speech processor that operates based on electricity generated by a thermoelectric transducer module, in which numerous thermoelectric elements join between oppositely arranged upper and lower substrates each having numerous electrodes. A heat absorption layer composed of a heat conductive material such as a resin, rubber, and metal is attached to the upper substrate of the thermoelectric transducer module. The heat absorption layer has deformability in shape in conformity with a prescribed part of the human body and is heated using human body temperature so as to cause a temperature difference between the upper and lower substrates, thus generating electricity in the thermoelectric transducer module. A heat-dissipation member composed of aluminum can be attached to the lower substrate so as to increase the temperature difference.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Efficient and light weight thermoelectric waste heat recovery system
InactiveUS20100186422A1Increase profitHigh electrical outputAir-treating devicesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectOn boardEngineering
One embodiment includes an on-board thermoelectric vehicle system for generating electrical energy using a heated fluid stream, including at least one thermoelectric device having a high temperature junction and a low temperature junction, and a body of high conductivity foam shaped and located to increase heat transfer from the heated fluid stream to the high temperature junction or to increase heat transfer from the low temperature junction of the thermoelectric device.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Fuel system inerting
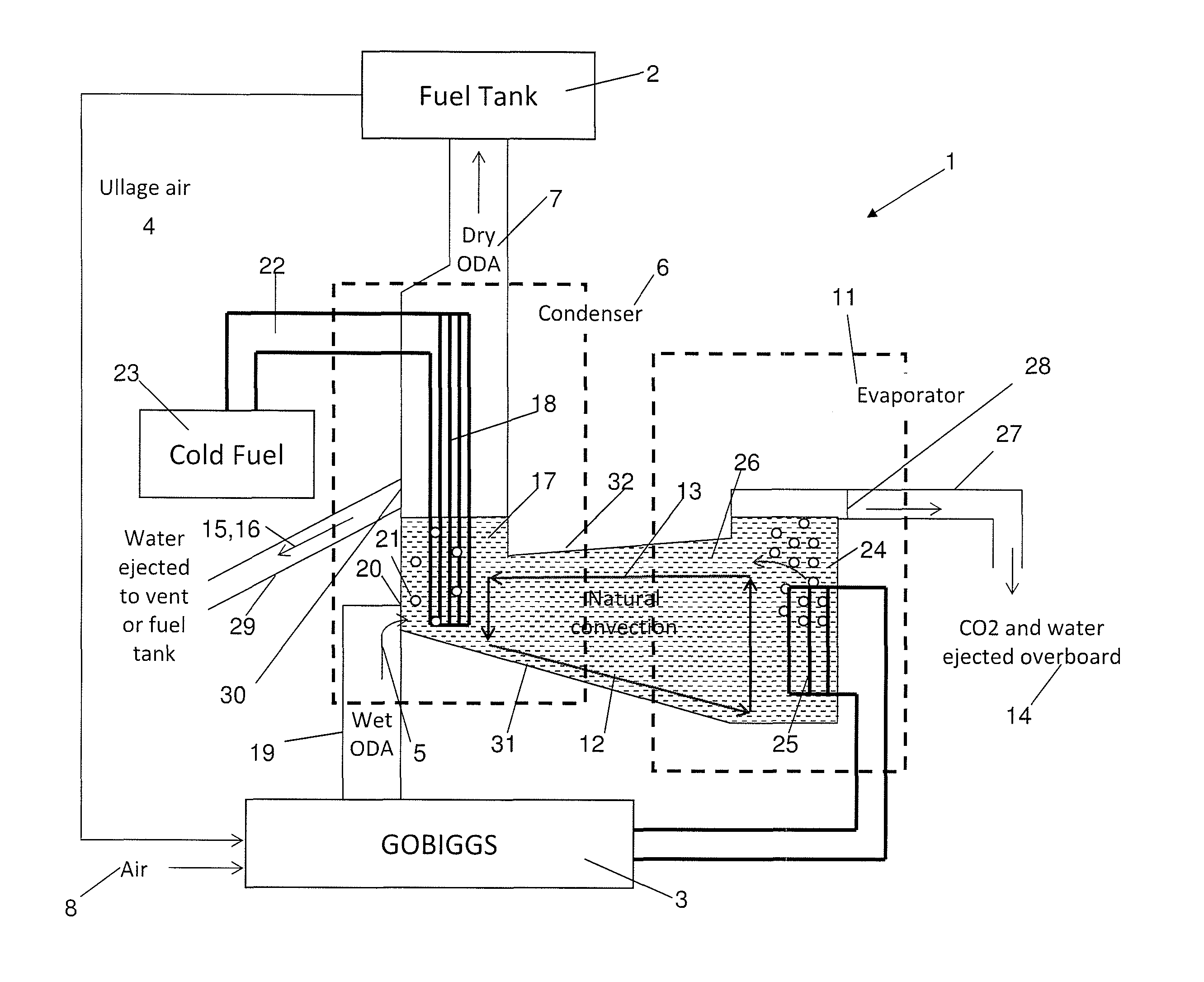
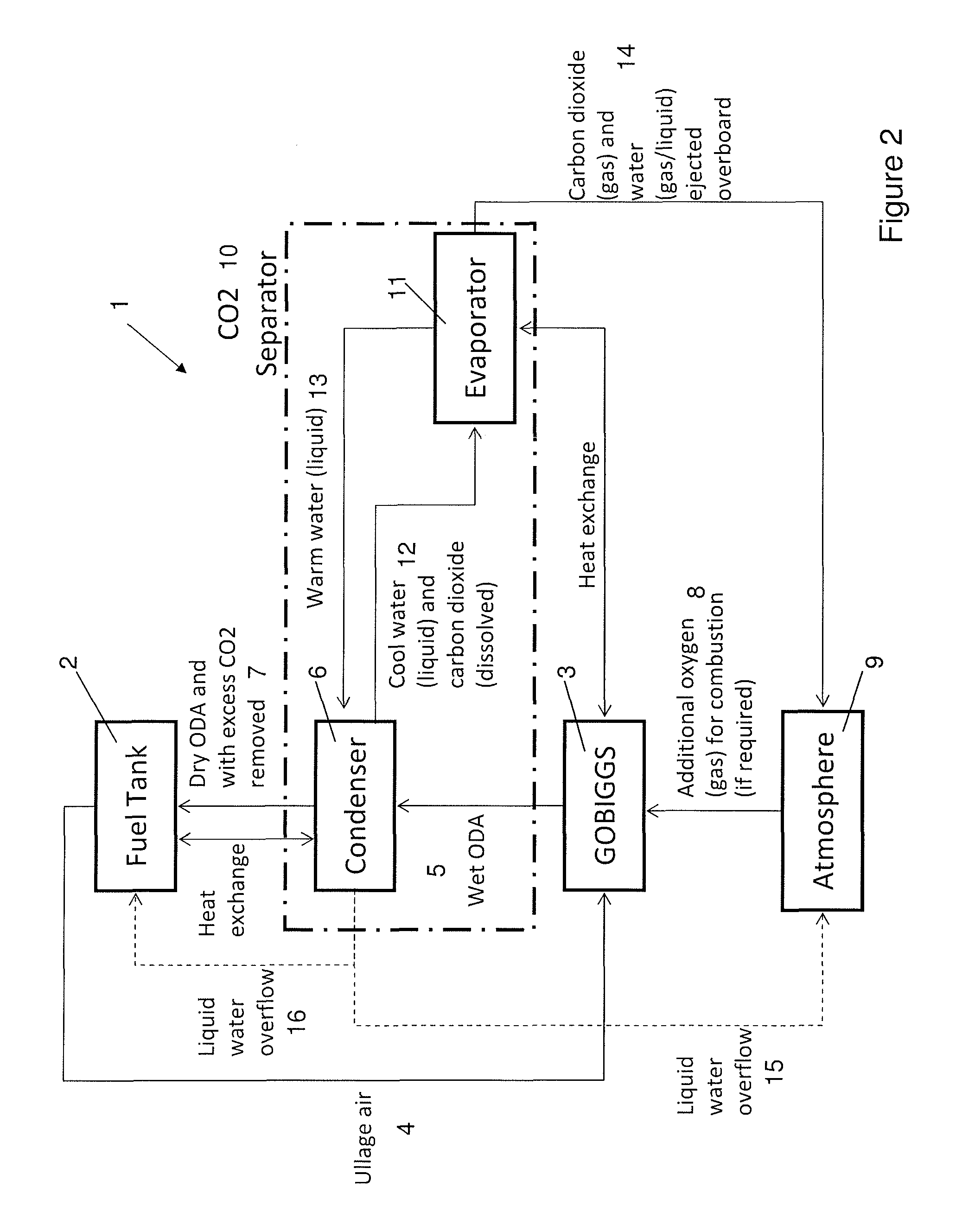
ActiveUS8828344B2Reduce contentTemperature differentialOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid degasificationProcess engineeringOxygen
A fuel system comprising a fuel tank, a catalytic inerting device for producing oxygen depleted air (ODA) by reaction of fuel vapor from the fuel tank with air, and a separator device for separating carbon dioxide from the ODA gas before feeding the carbon dioxide depleted ODA gas to the fuel tank so as to render the fuel tank ullage atmosphere inert. Also, a method of reducing the carbon dioxide content of oxygen depleted air (ODA) produced by a catalytic inerting device for inerting a fuel tank ullage atmosphere, the method comprising separating carbon dioxide from the ODA gas before feeding the carbon dioxide depleted ODA gas to the fuel tank. The system may be installed in an aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Detection and recognition of objects by multispectral sensing
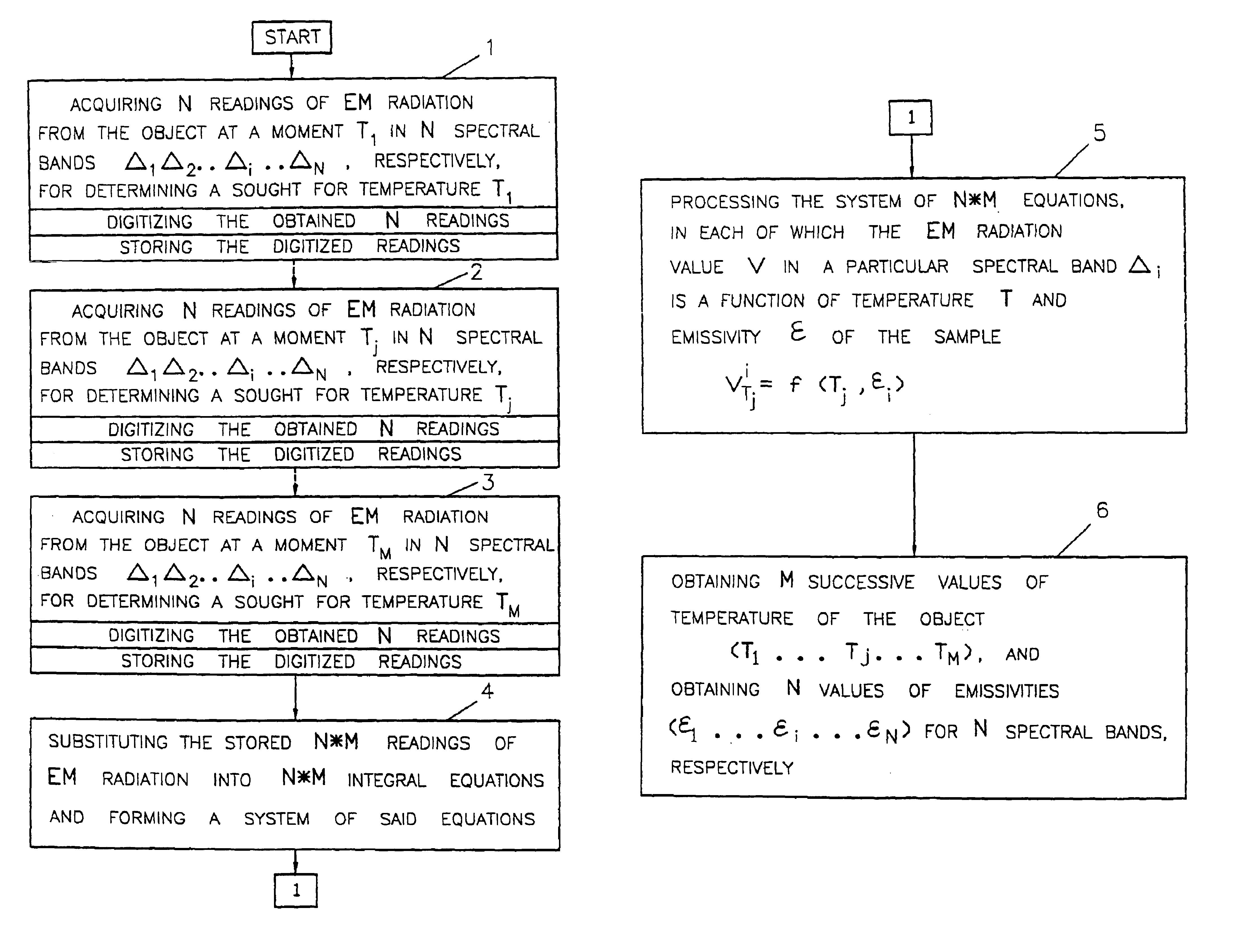
InactiveUS6837617B1Accurate temperature valueIncrease temperature differenceRadiation pyrometryPhotometryEmissivitySpectral bands
A method and a system for determining temperature and / or emissivity of an object by remote sensing are described. Based on the concept of temperature and emissivity determination, there are also developed a method and a system for the detection and recognition of an object that includes a plurality of sub-objects. The method for the detection and recognition of an object comprises acquiring, inter alia, electromagnetic radiation data of electromagnetic radiation emitted from a selected region in at least two spectral bands, recording and storing the required electromagnetic radiation data, deriving descriptive maps constituted by pixels of the selected region from the stored data and classifying the pixels of said descriptive maps of said selected region by pattern recognition processor means.
Owner:ISRAEL AEROSPACE IND
Rocket motor joint construction including thermal barrier
InactiveUS6446979B1Function increaseImprove propertiesEngine sealsPower plant exhaust arrangementsFiberPorosity
A thermal barrier for extremely high temperature applications consists of a carbon fiber core and one or more layers of braided carbon fibers surrounding the core. The thermal barrier is preferably a large diameter ring, having a relatively small cross-section. The thermal barrier is particularly suited for use as part of a joint structure in solid rocket motor casings to protect low temperature elements such as the primary and secondary elastomeric O-ring seals therein from high temperature gases of the rocket motor. The thermal barrier exhibits adequate porosity to allow pressure to reach the radially outward disposed O-ring seals allowing them to seat and perform the primary sealing function. The thermal barrier is disposed in a cavity or groove in the casing joint, between the hot propulsion gases interior of the rocket motor and primary and secondary O-ring seals. The characteristics of the thermal barrier may be enhanced in different applications by the inclusion of certain compounds in the casing joint, by the inclusion of RTV sealant or similar materials at the site of the thermal barrier, and / or by the incorporation of a metal core or plurality of metal braids within the carbon braid in the thermal barrier structure.
Owner:NASA
Thermoelectric power generator with intermediate loop
InactiveUS20090139556A1Performance maximizationTemperature controlThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentHeat fluxNuclear engineering
A thermoelectric power generator is disclosed for use to generate electrical power from heat, typically waste heat. An intermediate heat transfer loop forms a part of the system to permit added control and adjustability in the system. This allows the thermoelectric power generator to more effectively and efficiently generate power in the face of dynamically varying temperatures and heat flux conditions, such as where the heat source is the exhaust of an automobile, or any other heat source with dynamic temperature and heat flux conditions.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
Heat spreader for emissive display device
InactiveUS20070042188A1Increase temperature differenceTemperature differenceTube/lamp screens manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyDisplay deviceGraphite
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
Cooler for electronic devices
InactiveUS7044202B2Improve cooling effectIncrease temperature differenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCold airPath length
A cooler for electronic devices provides cool air to the inlet sides of the heat sink by using a radial blower with blades located around air outlets of the heat sink. This blower is driven by a brushless DC electric motor. The motor has an opening in the center allowing for the transfer of incoming air to the center of the heat sink. The rotors outer circumferential arrayed poles are rigidly secured to the frame of the radial blower. The stator of the motor is rigidly secured to the heat sink and has an opening in its center. The stator comprises circumferential arrayed coils on circuit board material. When the current flows through the stator coils, the coils acquire a magnetic polarity. The poles of the rotor and stator coils attract and repel depending on the polarities. The cool air comes simultaneously from opposite sides of the heat sink. For this reason the heat sink has a divider located approximately in the middle of the heat sink fins. The blades of the radial blower are located around the air outlets on the heat sink. Because the ambient air is drawn in from both sides of the heat sink the air path length through the heat sinks channels is effectively halved. This results in an increased cooling ability for the heat sink because of the increase in temperature differentials.
Owner:ADVANCED ROTARY SYST
Thermoelectric Generator for Implants and Embedded Devices
InactiveUS20090292335A1Reliable powerIncrease temperature differenceElectrotherapyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectCold plateBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a TEG device comprising a first unit comprising a thermopile unit and a second unit comprising a cold plate and / or a radiator. One of the first and second units is adapted for being embedded or implanted into a body, while the other of the first and second units is adapted for being placed at the outer surface of the body, i.e. in a fluid. The first and second units are adapted for being thermally connected to each other through the surface between the body and the fluid when in use.
Owner:STICHTING IMEC NEDERLAND
High-efficiency hybrid ocean temperature difference power generating system
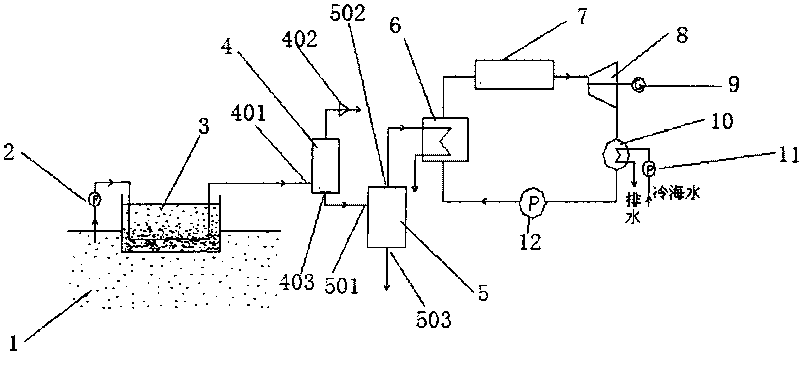
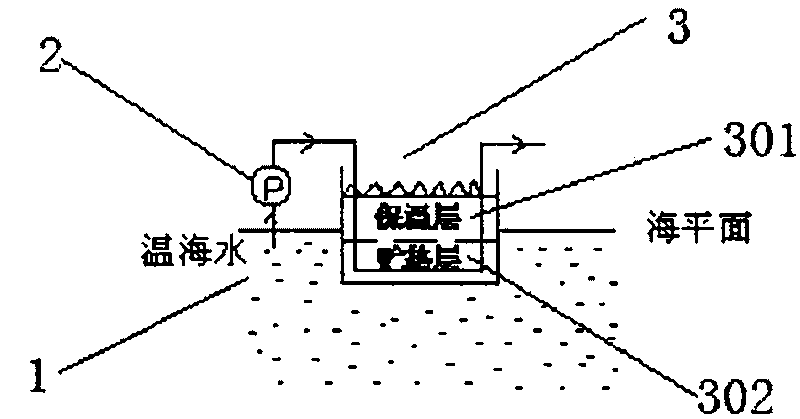
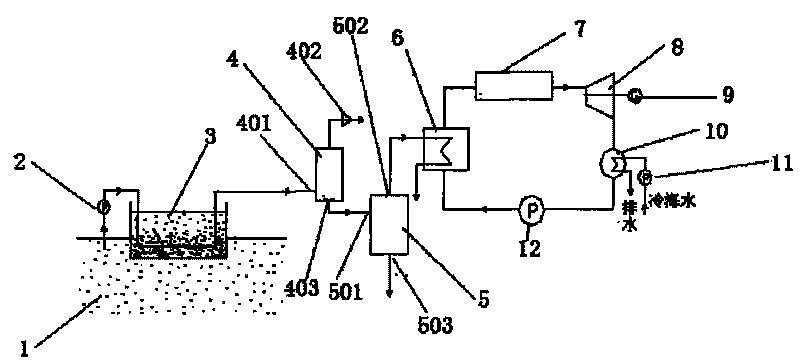
InactiveCN101737282AIncrease temperatureIncrease temperature differenceSolar heating energyMachines/enginesSeawaterSolar thermal collector
The invention discloses a high-efficiency hybrid ocean temperature difference power generating system. When the system works, warm sea water is pumped by a warm water pump to pass through a solar pond, and heated by solar radiation; the heated sea water enters a degasser for degassing, enters a flash evaporator for flash evaporation, and then enters a focusing solar thermal collector to continuously raise the temperature; and overheated steam enters a steam turbine for doing work in an expanding way; cold sea water is pumped into a condenser by a cold sea water pump; and the cold sea water with raised personal temperature flows back to the sea to continuously cycle. The system is suitable for coastal towns, islands and marine engineering, and achieves the effects of saving electric energy, and making full use of ocean resources.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
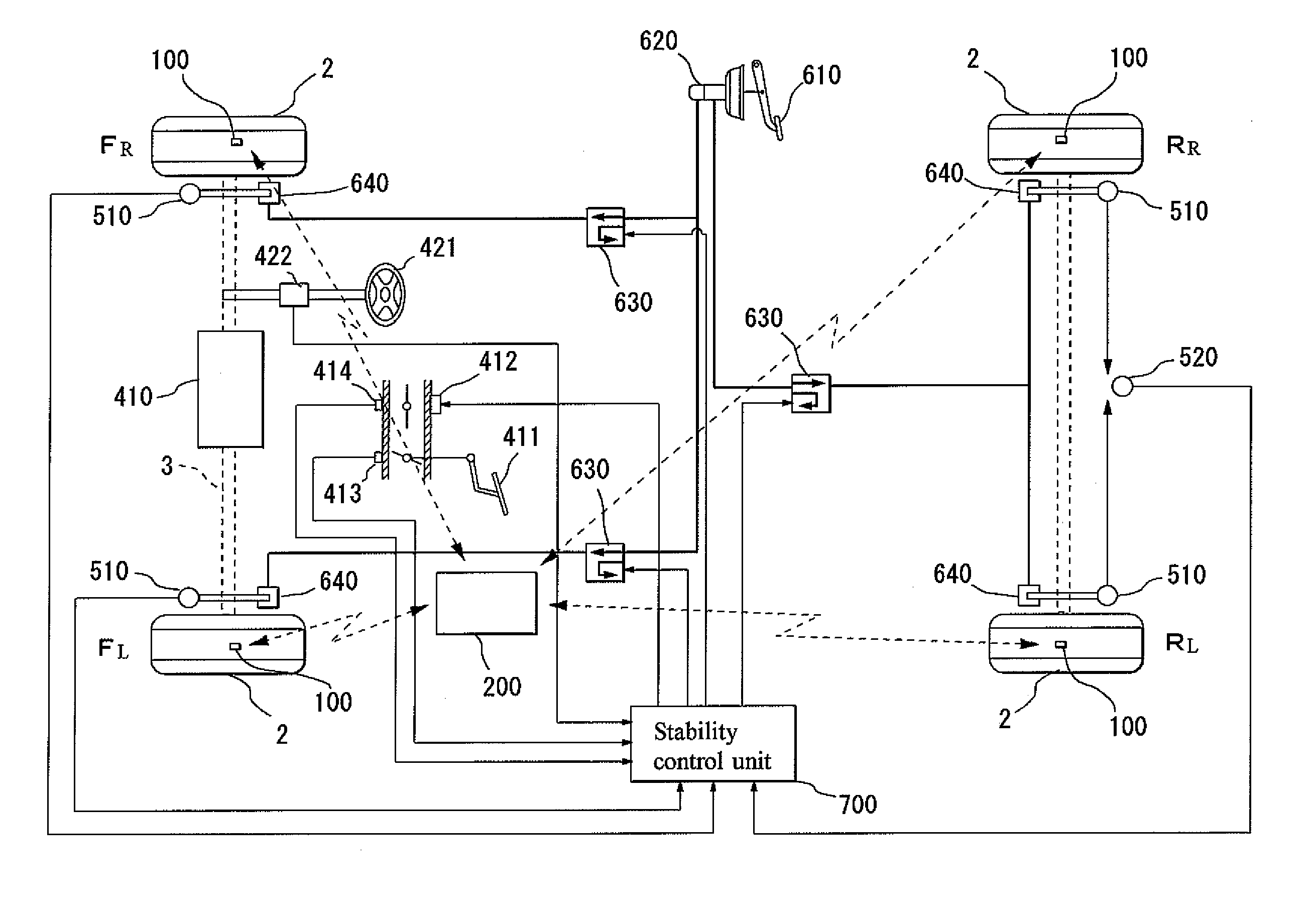
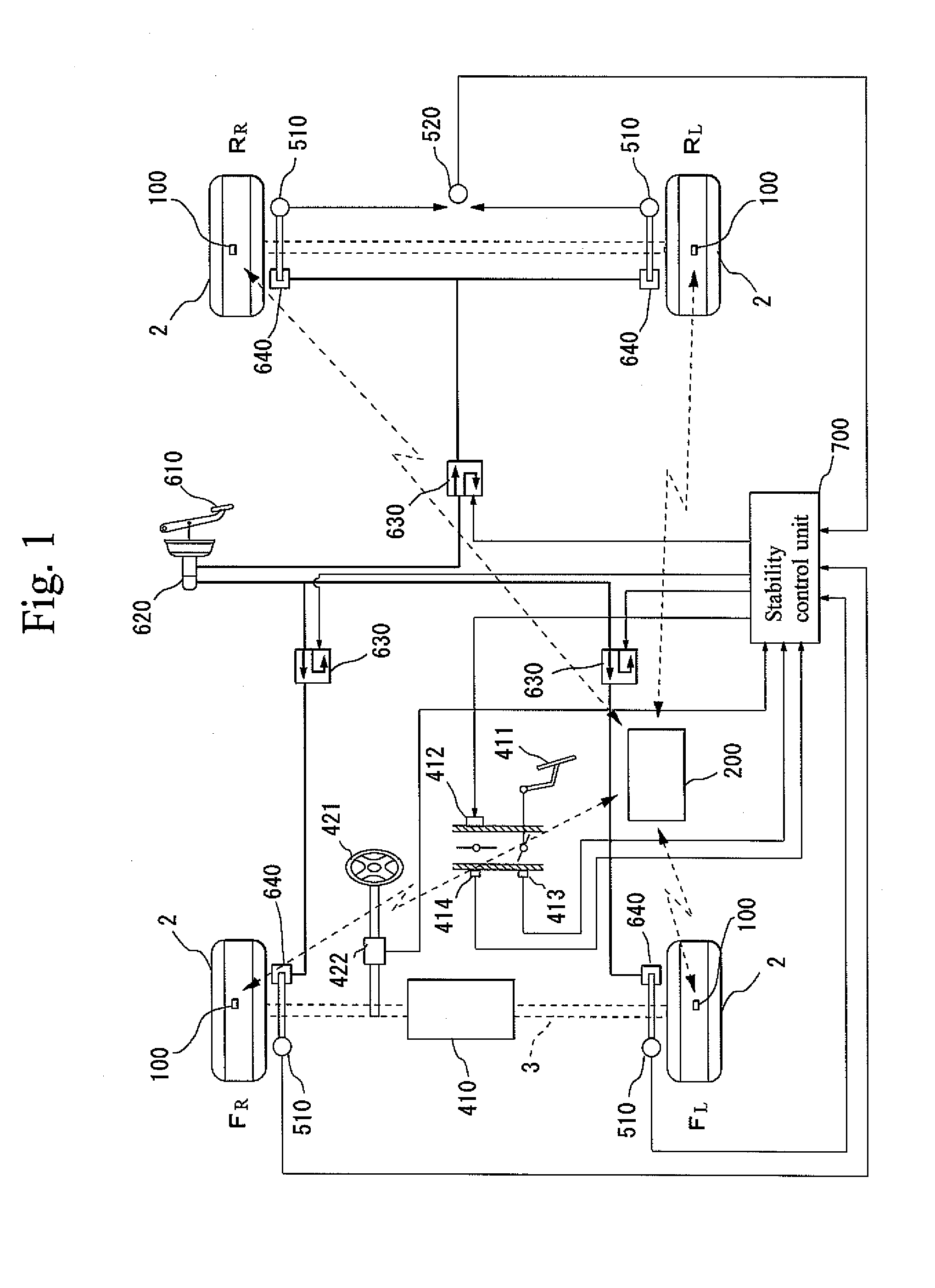
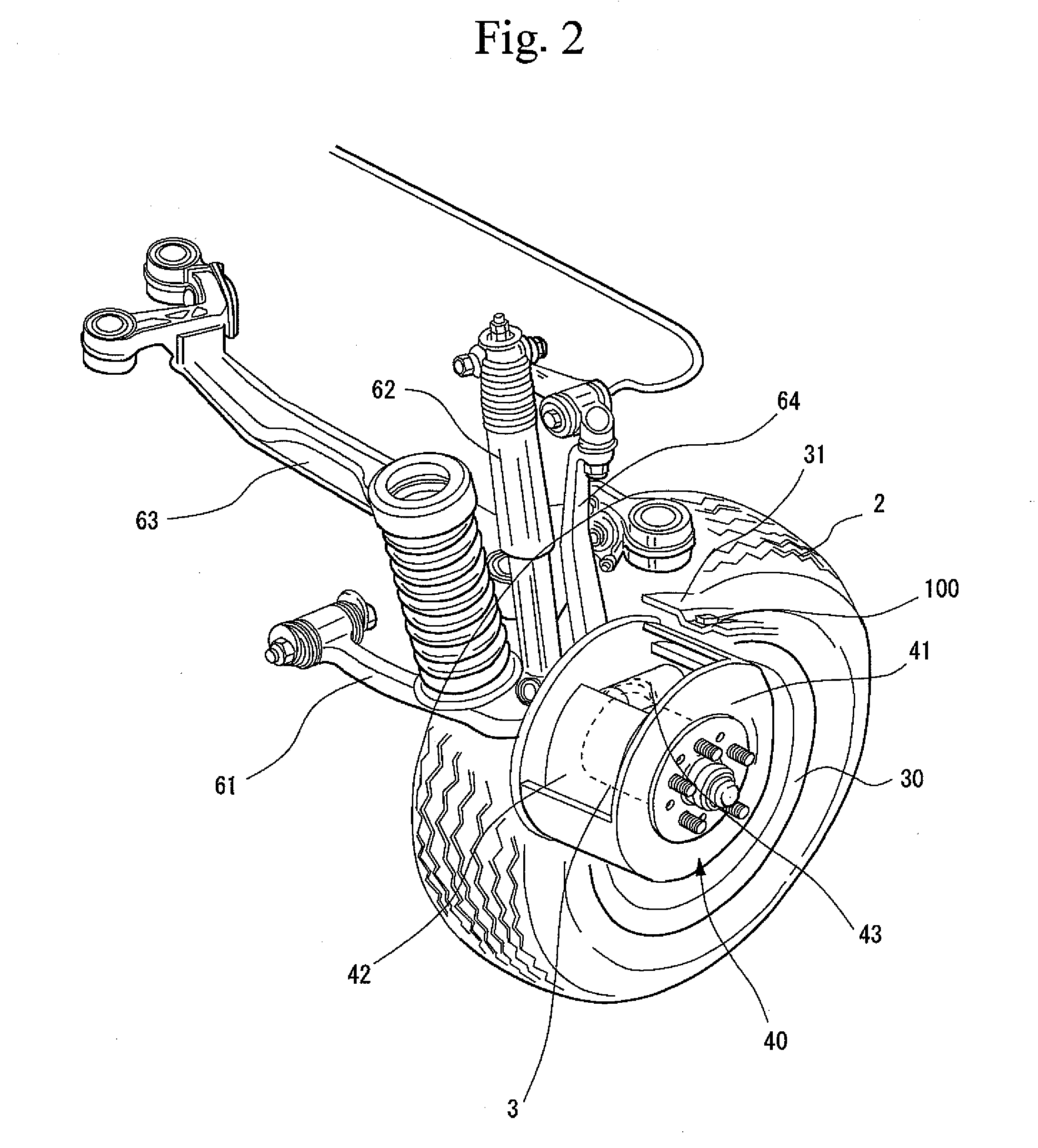
Vehicle Abnormality Detection Method and Device Thereof and Sensor Unit Thereof
InactiveUS20080018445A1Increase frictional resistanceIncrease temperature differenceThermometer detailsSuspensionsAutomotive engineeringVehicle brake
There is provided a vehicle abnormality detection method detecting an abnormal state in which a high temperature occurs due to maladjustment of a vehicle bearing mechanism section or vehicle brake mechanism section, and a device thereof and a sensor unit thereof. By use of the sensor unit 100 mounted in a rim 31, an air temperature within a tire 2 is sensed as a first temperature and a temperature (second temperature) of the rim 31 is sensed as a temperature related to at least one of a temperature of the vehicle bearing mechanism section and a temperature of the vehicle brake mechanism section 40. Then a temperature difference between the first and second temperatures is calculated and when the temperature difference is a predetermined value or more, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the vehicle bearing mechanism section or vehicle brake mechanism section 40. The abnormality is thus detected.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Machining apparatus and process
InactiveUS20110048183A1High temperature differentialHigh removal rateAuxillary equipmentWorkpiecesTitaniumEngineering
A machining process and apparatus capable of increasing removal rates achievable when machining titanium and its alloys. The process includes heating a portion of a workpiece with a laser beam, cryogenically cooling a cutting tool with a cryogenic fluid without flowing the cryogenic fluid onto the workpiece, and machining the heated portion of the workpiece with the cutting tool. The apparatus includes a cutting tool, a device for heating a portion of a workpiece with a laser beam prior to being machined with the cutting tool, and a device for cryogenically cooling the cutting tool with a cryogenic fluid without flowing the cryogenic fluid onto the workpiece. The cryogenic fluid is circulated around the cutting tool to achieve a temperature differential between the workpiece and the cutting tool that is capable of improving removal rates and extending tool life at cutting speeds of, for example, above 100 m / min.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
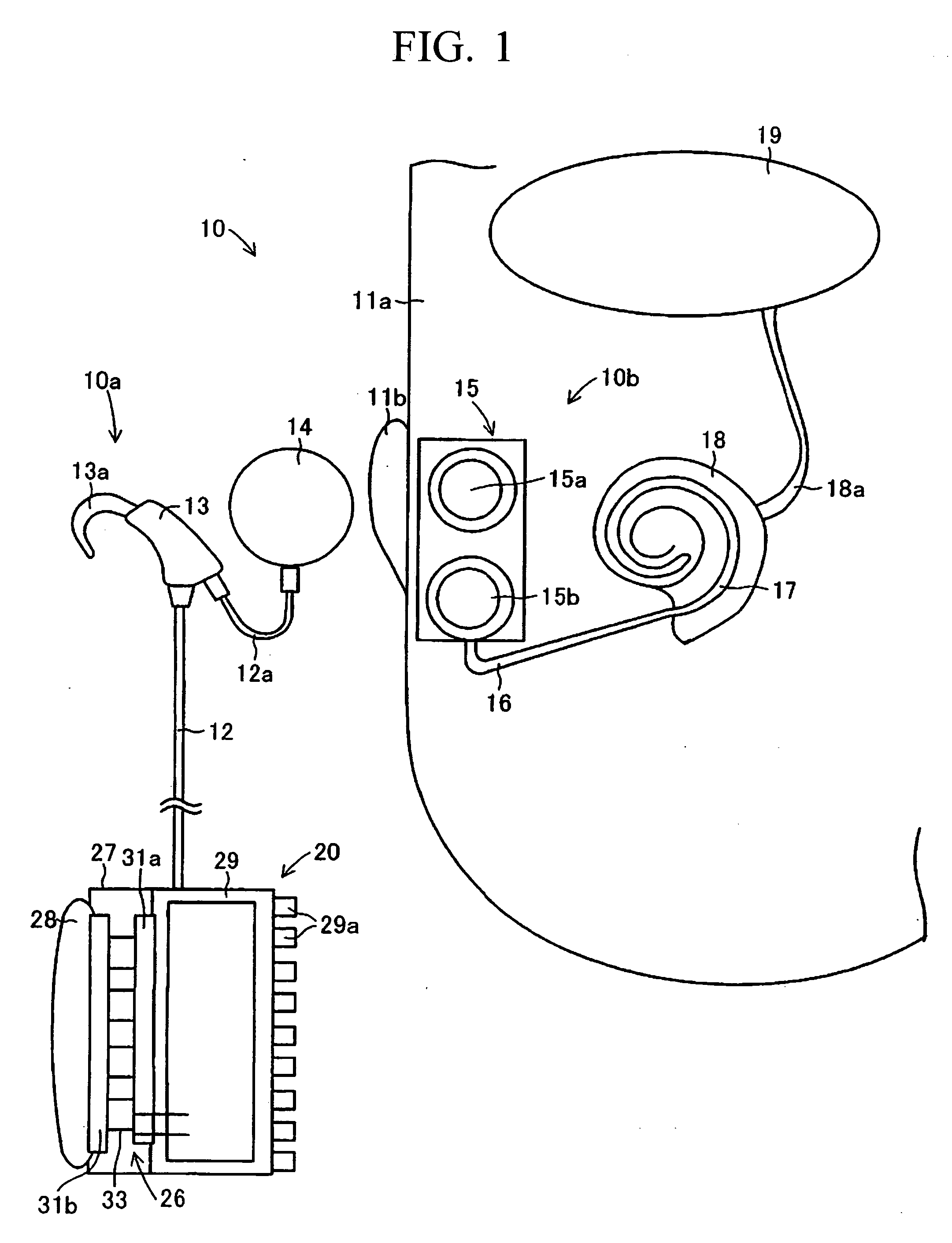
Artificial inner ear and thermoelectric generator therefor
InactiveUS7532937B2Generate large amountImprove heat transfer efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectHuman bodySpeech Processor
An artificial inner ear includes a speech processor that operates based on electricity generated by a thermoelectric transducer module, in which numerous thermoelectric elements join between oppositely arranged upper and lower substrates each having numerous electrodes. A heat absorption layer composed of a heat conductive material such as a resin, rubber, and metal is attached to the upper substrate of the thermoelectric transducer module. The heat absorption layer has deformability in shape in conformity with a prescribed part of the human body and is heated using human body temperature so as to cause a temperature difference between the upper and lower substrates, thus generating electricity in the thermoelectric transducer module. A heat-dissipation member composed of aluminum can be attached to the lower substrate so as to increase the temperature difference.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
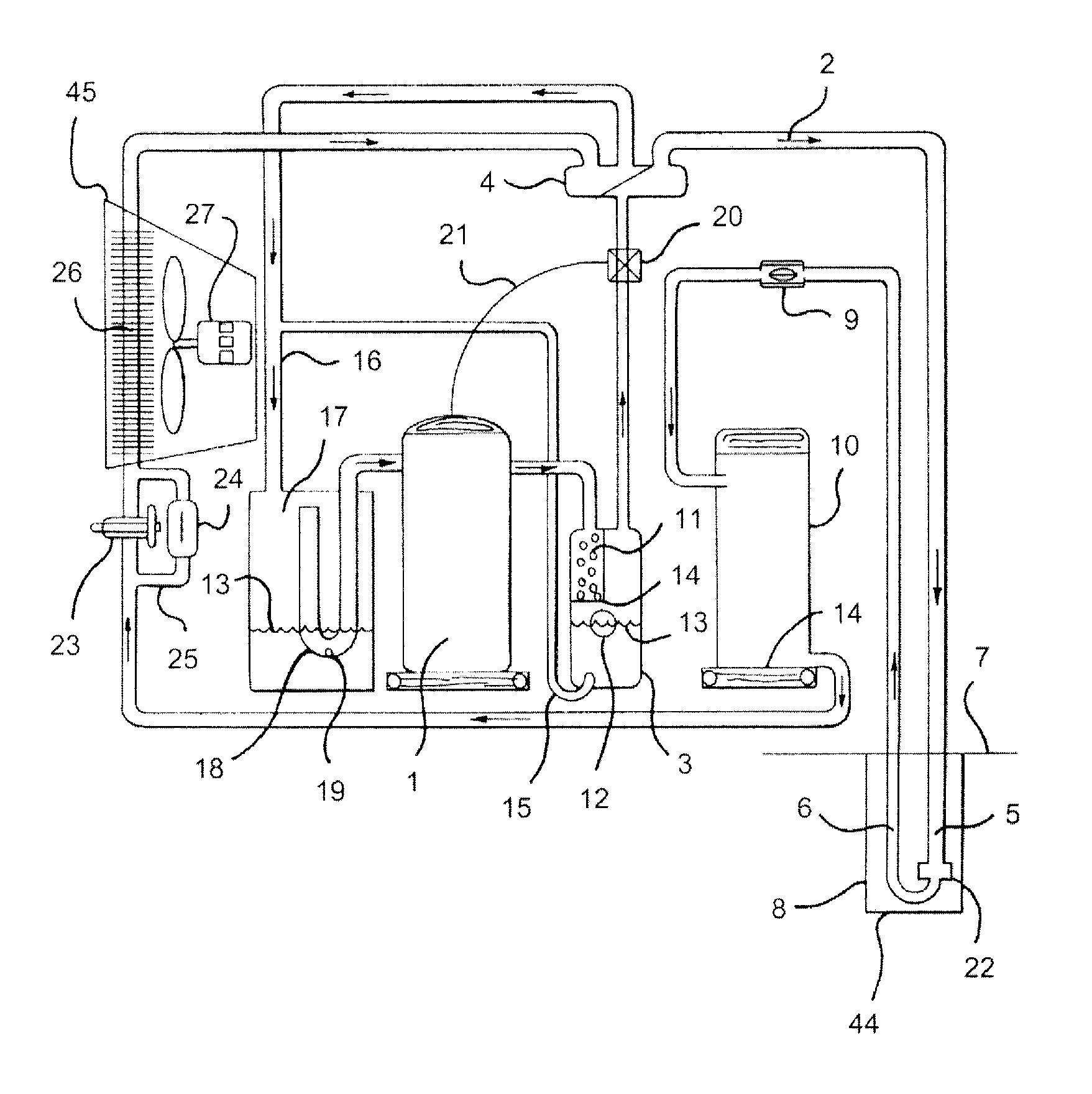
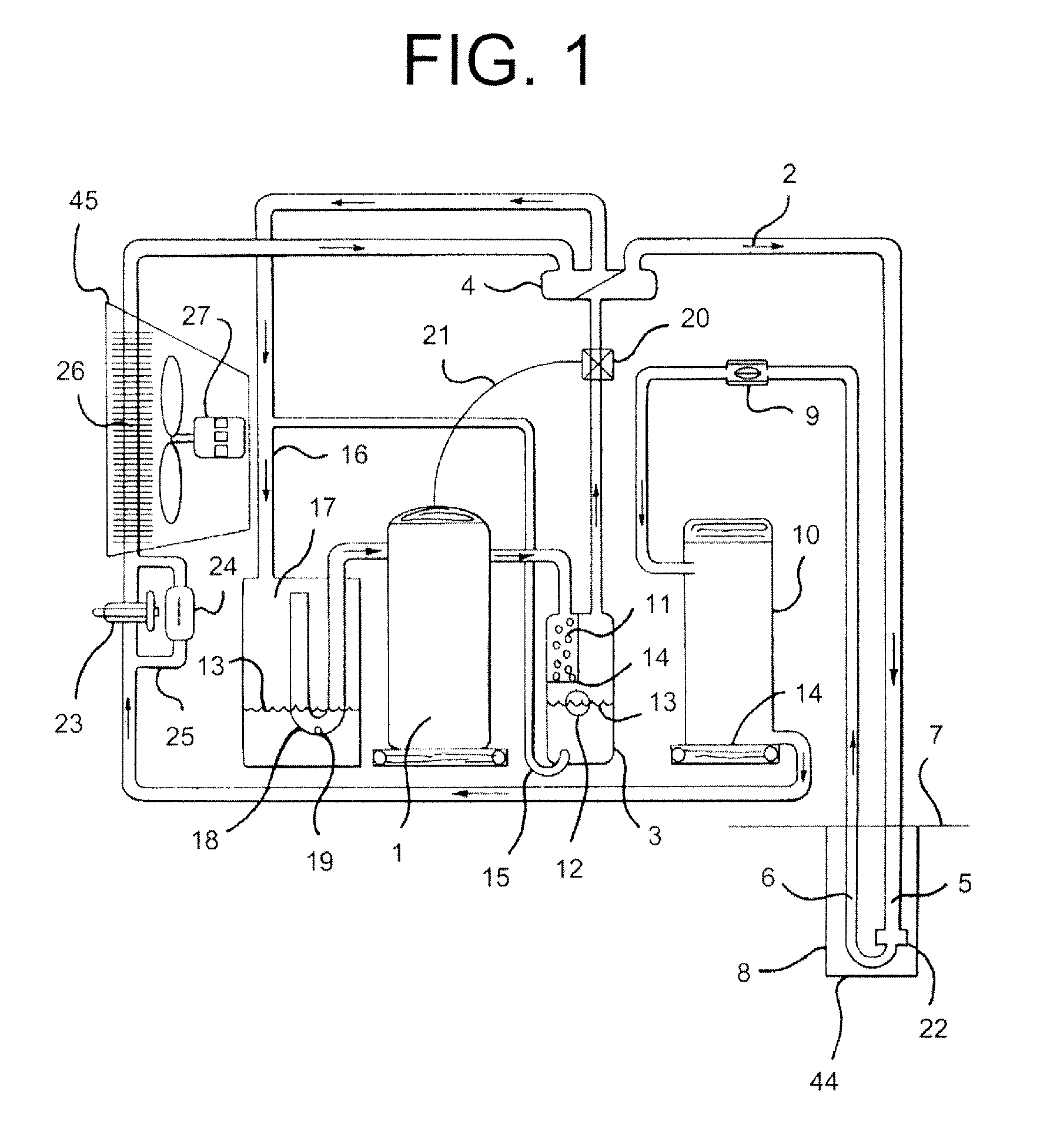
Refrigeration apparatus
ActiveUS20100300141A1Low flow resistanceIncrease flow rateCompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cyclePlate heat exchangerEngineering
An air-conditioning apparatus uses carbon dioxide as a refrigerant, and includes comprises a two-stage-compression-type compression mechanism, a heat source-side heat exchanger, an expansion mechanism, a usage-side heat exchanger, and an intercooler. The intercooler uses air as a heat source. The intercooler is configured and arranged to cool refrigerant flowing through an intermediate refrigerant tube that draws refrigerant discharged from the first-stage compression element into the second-stage compression element. The intercooler is integrated with the heat source-side heat exchanger to form an integrated heat exchanger, with the intercooler disposed in an upper part of the integrated heat exchanger.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Module for cooling semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100269517A1Improve cooling efficiencyReduce heat gainDomestic cooling apparatusIndirect heat exchangersThermoelectric coolingEngineering
A module for cooling a heat generating element comprising a heat receiving plate thermally connected to at least one heat generating element; a heat transfer device one end portion of which is thermally connected to the heat receiving plate and other end portion of which is thermally connected to a heat dissipating plate; a thermoelectric cooler one face of which is thermally connected to one face of the heat dissipating plate; a first heat sink thermally connected to other face of the heat dissipating plate; and a second heat sink thermally connected to other face of said thermoelectric cooler.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
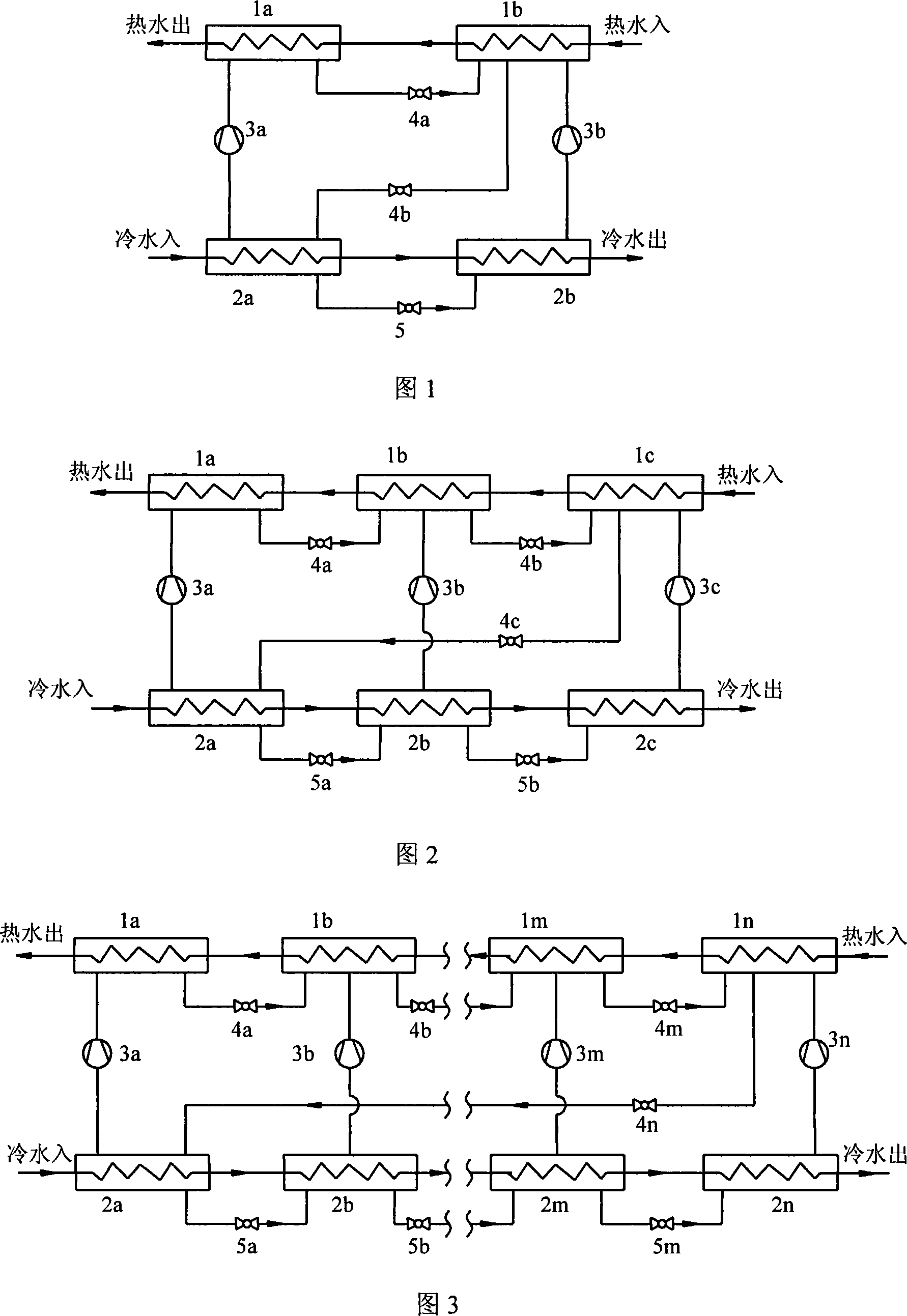
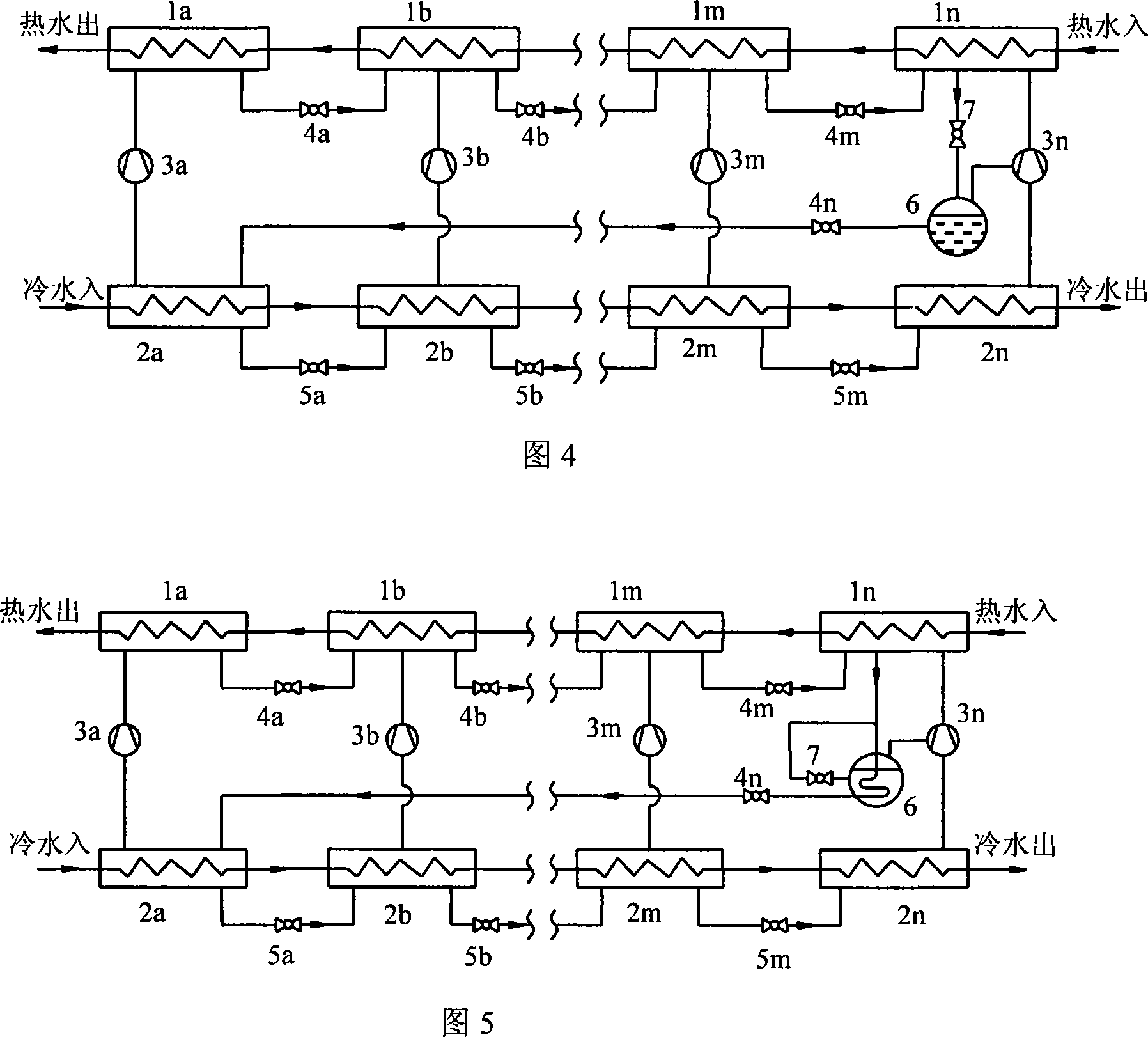
Multistage-cascaded compression type heat pump set under large temperature difference
InactiveCN101093116AIncrease temperature differenceSmall heat transfer temperature differenceCompression machines with several condensersCompression machines with several evaporatorsTemperature differenceRefrigerant
This invention relates to a multi-stage serial large temperature-difference compression thermal pump set composed of multiple stages of condensers, evaporators, a compressor and a related throttle device and connection pipelines, in which the waterway systems of the condensers of each stage and evaporators are serial to form a connected in-out system of waterway, pipelines of cold-producing medium of the adjacent condensers are serial by the throttle device, the condenser of the last stage is connected with the evaporator of the first stage by the compressor to form a channel of cold-producing medium.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-Faceted Designs for a Direct Exchange Geothermal Heating/Cooling System
ActiveUS20080173425A1Improve heat transfer performanceDecrease overall system operational efficiency levelHeat pumpsOther heat production devicesGeothermal heatingAir handler
A direct exchange heating / cooling system with at least one of a reduced compressor size, with a 500 psi high pressure cut-off switch, with a 98% efficient oil separator, with extra oil, operating at a higher pressure than an R-22 system, with receiver design parameters for efficiency and fox capacity, with geothermal heat exchange line set design parameters, with special heating / cooling expansion device sizing and design, with a specially sized air handler, and with a vapor line pre-heater.
Owner:WIGGS B RYLAND
Structure of thermopile sensor
InactiveUS20050034749A1Improve Sensing PerformanceSimple structureThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsInsulation layerSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to an improved structure of a thermopile sensor, which is to employ a membrane to cover a substrate that has a cavity. Besides, a plurality of thermoelectric elements is formed on the membrane extending outwards from the central side of the membrane and is composed of two different materials connected in series. The material of the element can be a composite of metal material and semiconductor material, and an insulation layer partitions the two materials; therefore, the two materials are connected in series through a contact hole. In addition, the contact hole formed at the central side of the membrane is called hot junction, whereas the contact hole formed at the side of the substrate is called cold junction. Moreover, to enhance the sensing performance of the thermopile sensor, a heat-conducting layer is formed at the center of the membrane, and after the heat-conducting layer is covered with another insulation layer, an absorption film is formed. The invention changes the temperature difference distribution by adding in a heat-conducting layer so as to enhance the sensing performance.
Owner:OPTO TECH
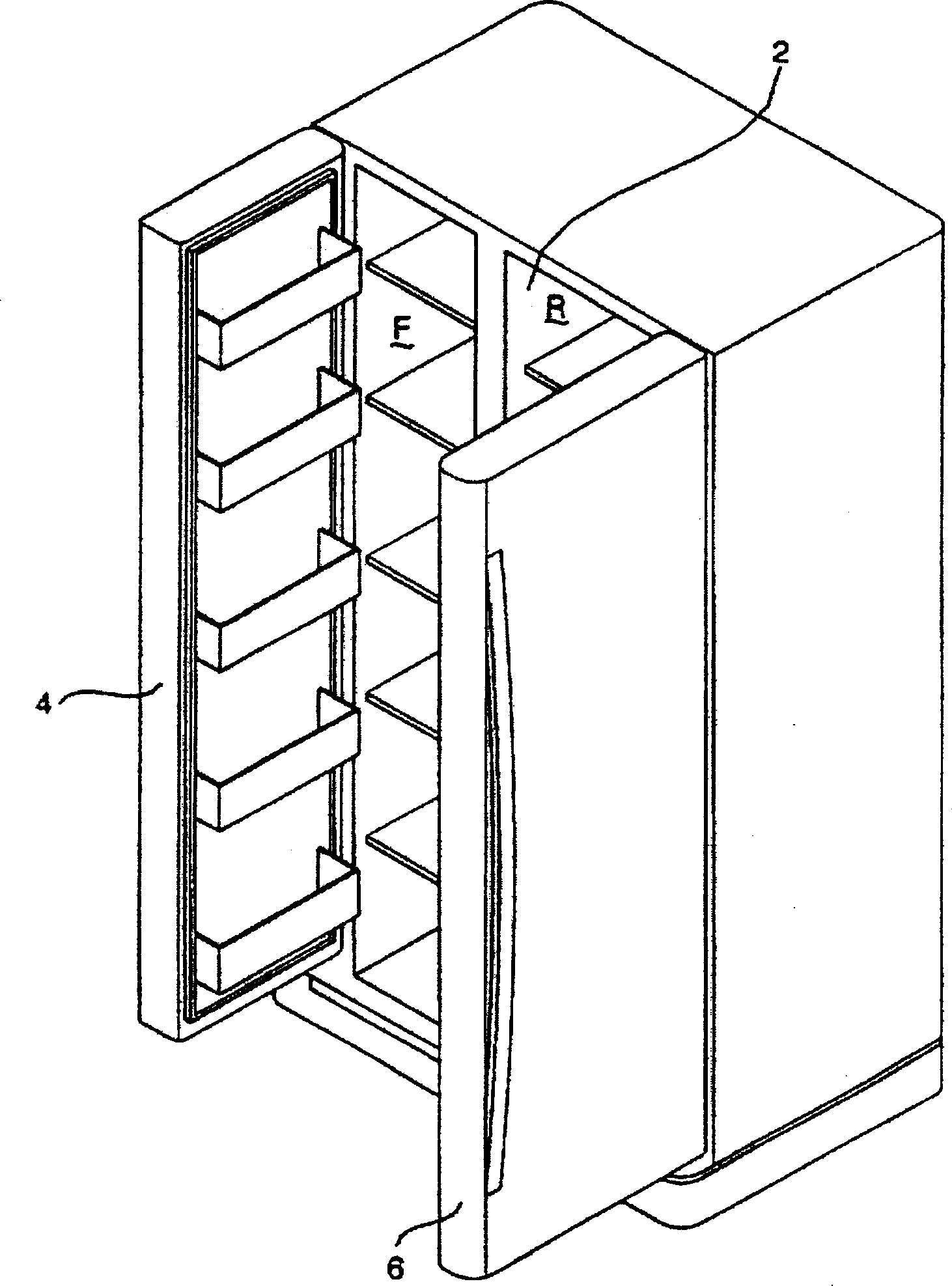
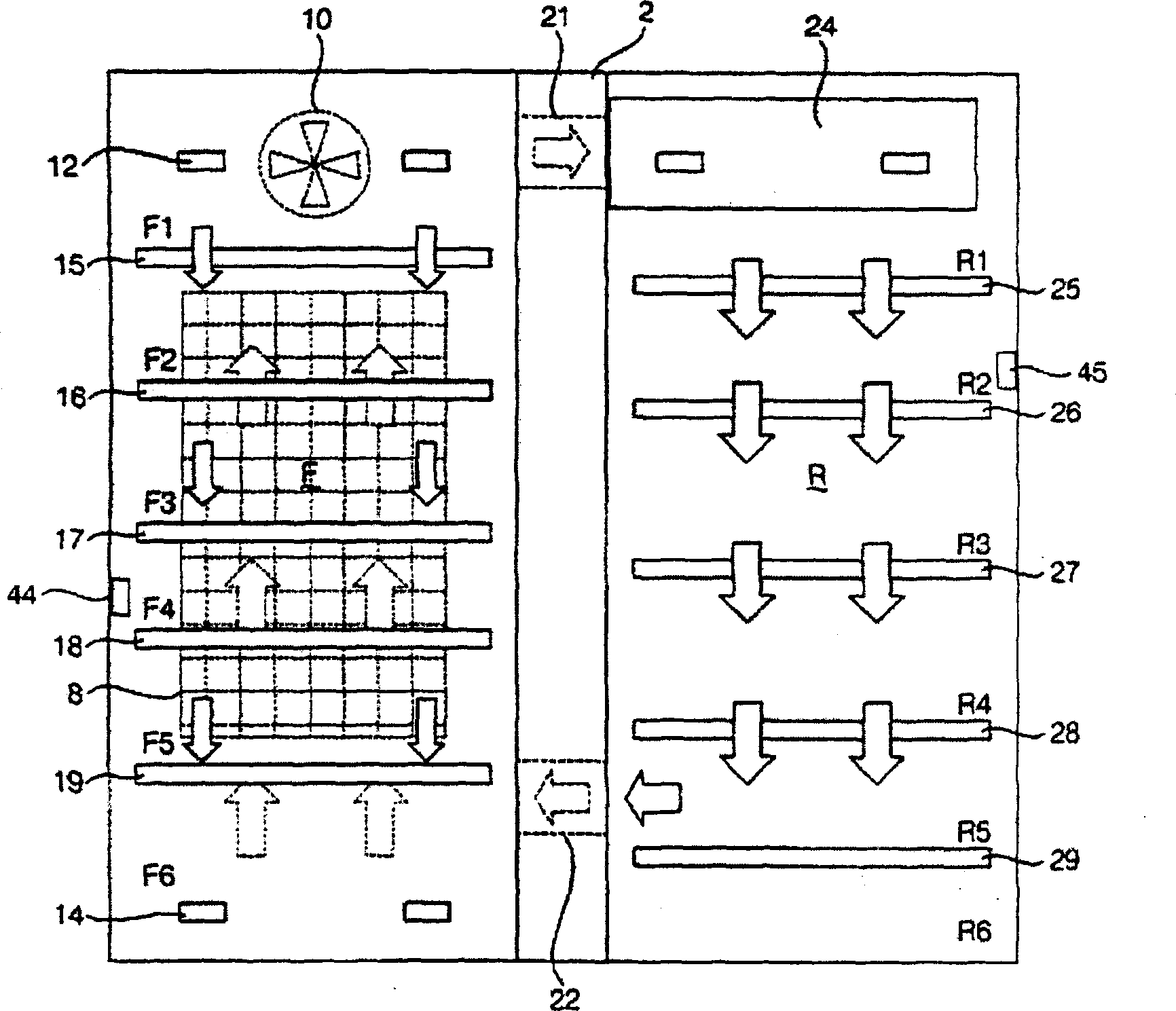
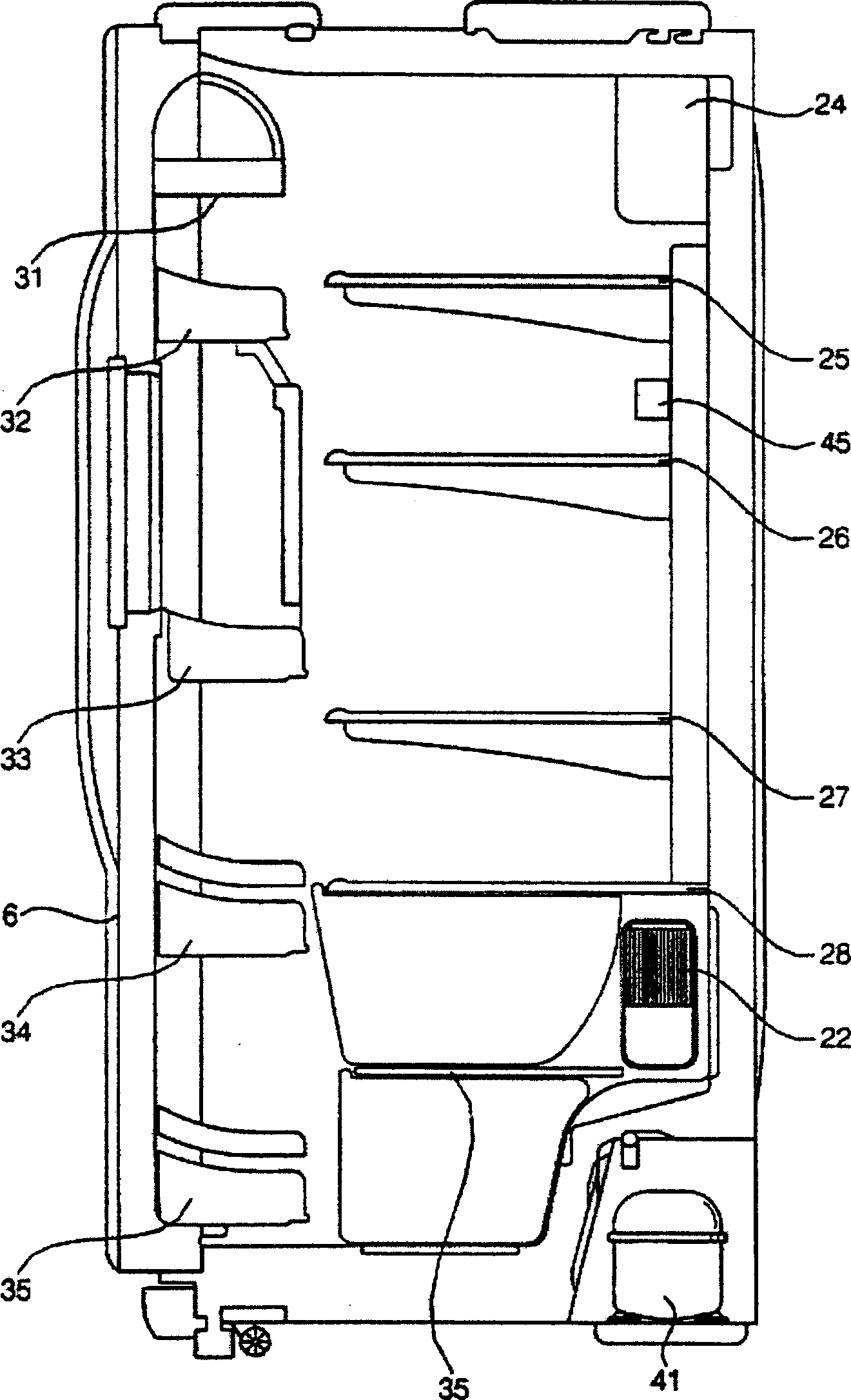
Temperature control method of refrigerator
InactiveCN1534263AIncrease temperature differenceIncrease electric powerDomestic refrigeratorsRefrigeration componentsTemperature controlCold air
Disclosed is a temperature control method for a refrigerator which can minimize a deviation in refrigerant compartment temperature while minimizing the power consumption of the refrigerator. The temperature control method includes the steps of (A) comparing a sensed temperature of a freezing compartment with a predetermined maximum freezing compartment temperature and a predetermined minimum freezing compartment temperature, respectively, thereby controlling a compressor and a circulating fan to be turned on or off such that the sensed freezing compartment temperature is ranged between the predetermined maximum and minimum freezing temperatures, (B) comparing, following the step (A), a sensed temperature of a refrigerating compartment defined with a plurality of refrigerating chambers therein, with a predetermined maximum refrigerating compartment temperature and a predetermined minimum refrigerating compartment temperature, respectively, thereby controlling a damper to be opened or closed and the circulating fan to be turned on or off such that the sensed refrigerating compartment temperature is ranged between the predetermined maximum and minimum refrigerating temperatures, and (C) discharging cold air into at least one of the refrigerating chambers when the damper is closed, and the compressor and the circulating fan are turned on.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
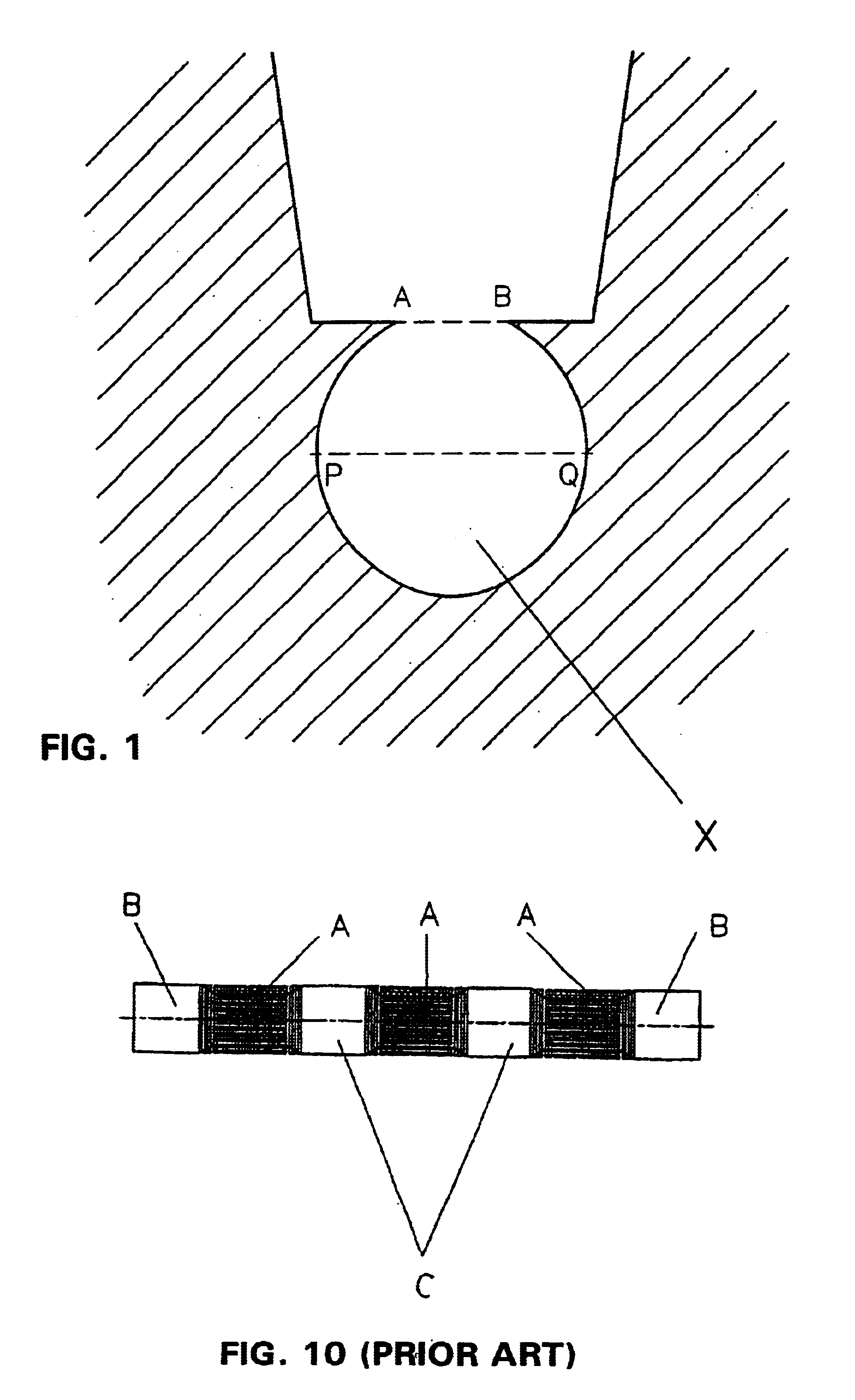
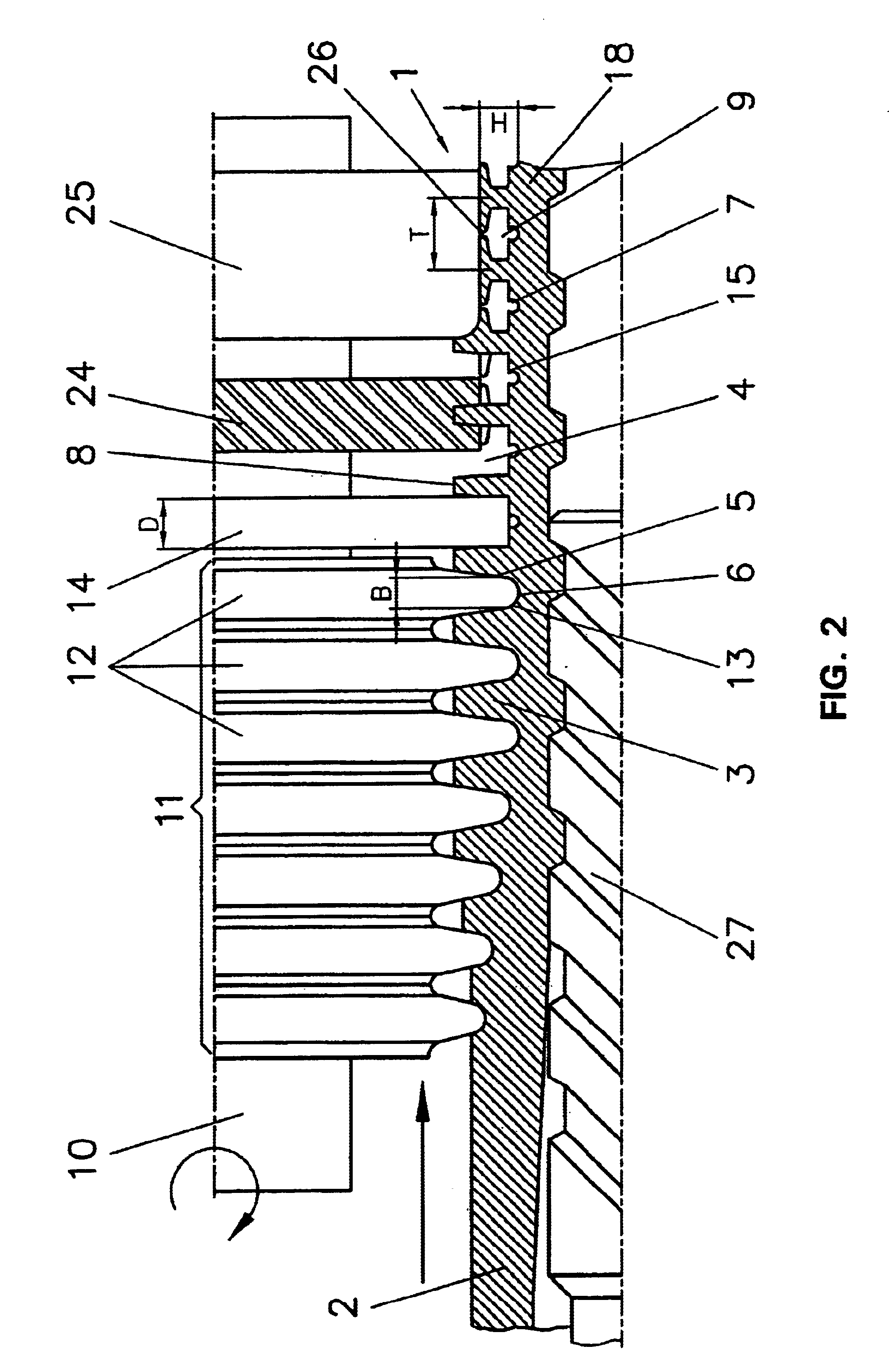
Heat transfer tube and a method of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS6913073B2Increase temperature differenceAccelerate evaporationCorrosion preventionCoatingsMechanical stabilityEvaporation
A metallic heat transfer tube, in particular for the evaporation of liquids from pure substances or mixtures on the outside of the tube. Fins are integrally formed on the outside of the tube. Recesses are arranged in the area of the base of the primary grooves and extend between the fins. The recesses are in the form of re-entrant secondary grooves. The mechanical stability of the tube is not negatively influenced because material is primarily removed from the fin flanks toward the base of the groove so that the re-entrant secondary grooves are radially open.
Owner:WIELAND WERKE AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com