Coated Capillary Electrophoresis Tubes and System
a capillary electrophoresis tube and electrophoresis tube technology, which is applied in the direction of coating, instruments, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the sample throughput through the capillary, affecting the reproducibility, and changing the electrosmotic flow velocity of the solution in the capillary, so as to facilitate the increase of the sample flow through the capillary and the density of positive charges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Preparation of Silica Capillary Tubes with a Cross-Linked Coating
[0030]Trimethoxysilylpropyl (polyethyleneimine) (PEI silane) is a linear polyethyleneimine attached to trimethoxy silyl propyl groups. PEI silane was dissolved in methanol to obtain a 5% (v / v) solution of PEI silane in methanol by vortexing for 3 min in a glass vial. A capillary tube was first treated with methanol, then water, and then with 1.0 N Sodium Hydroxide and 1.0 N hydrochloric acid. The capillary was rinsed with deionized water, and afterward with methanol. The PEI silane solution was pumped through the capillary for 12-16 h at room temperature. After this, the capillary was rinsed briefly with methanol. Next, a 10% (v / v) solution of 1,4-Butanediol diglicidylether (BUDGE) in 1,4-Dioxane was pumped through the capillary for 4-6 h at room temperature to cross-link those polymer chains. After this; nitrogen was passed through the capillary while heating it for 1.0 h at 80° C. The capillary was then rinsed thorou...
example ii
Comparison of Electrophoresis Run Profiles for Coated and Uncoated Capillary Tubes
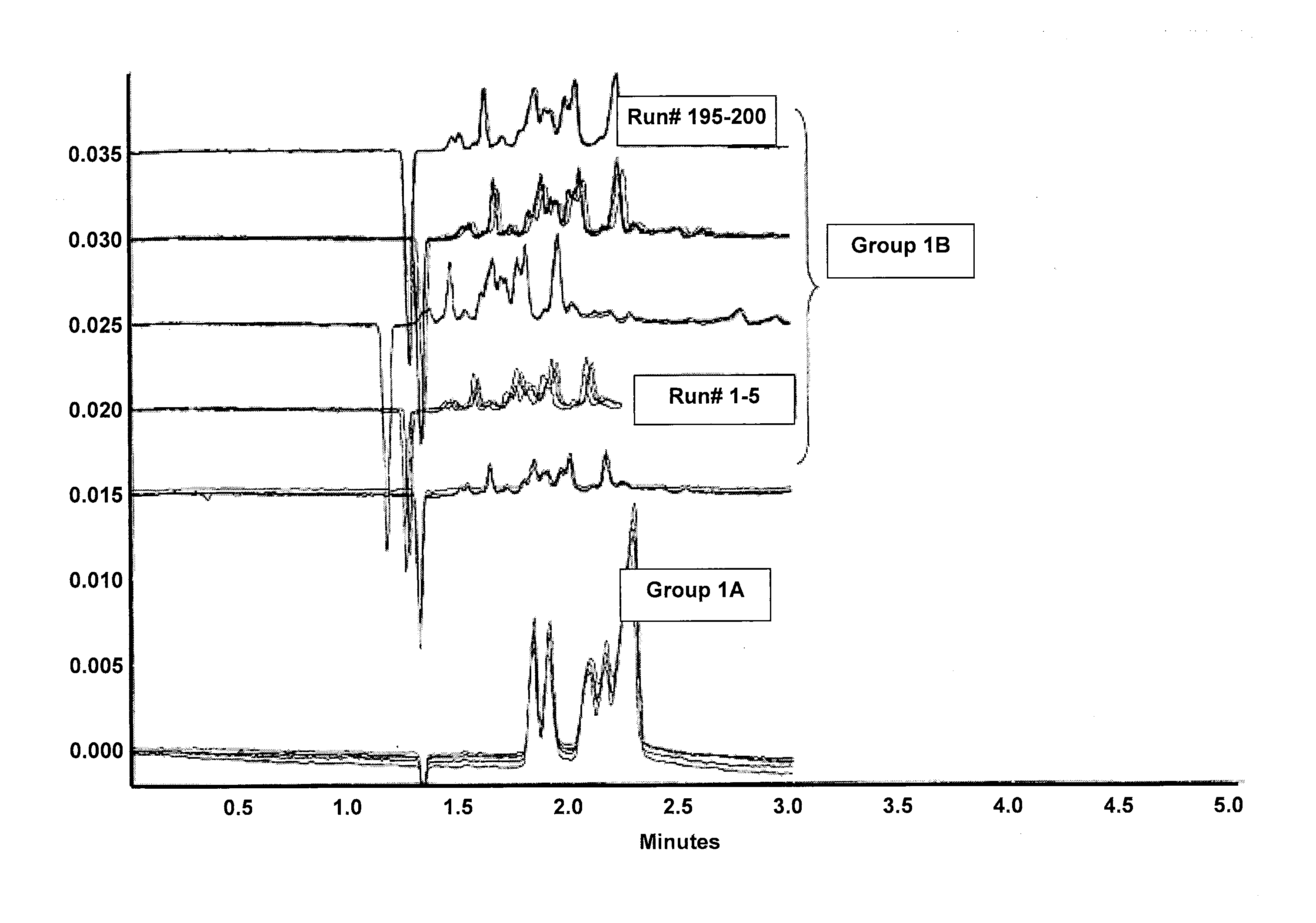
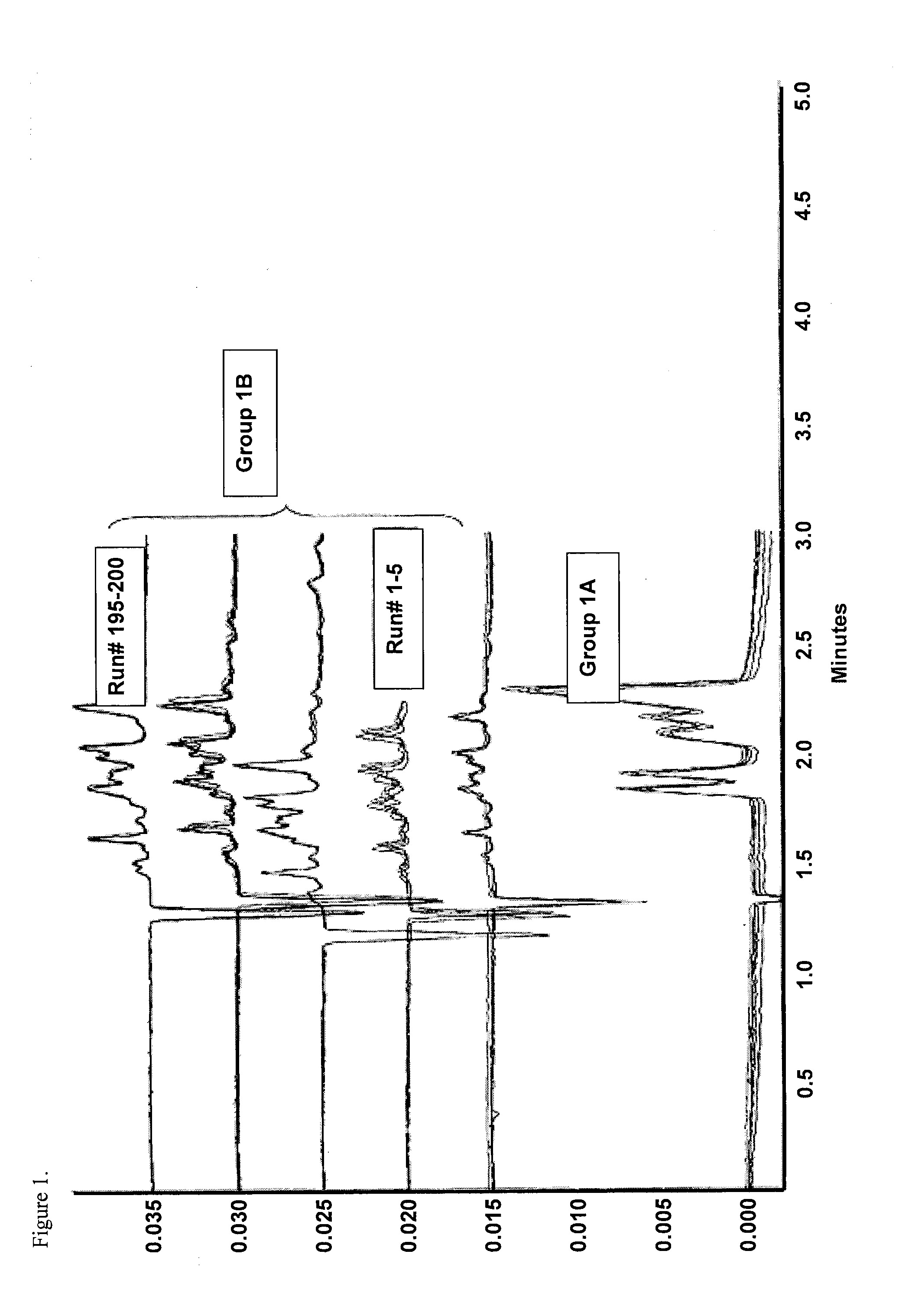
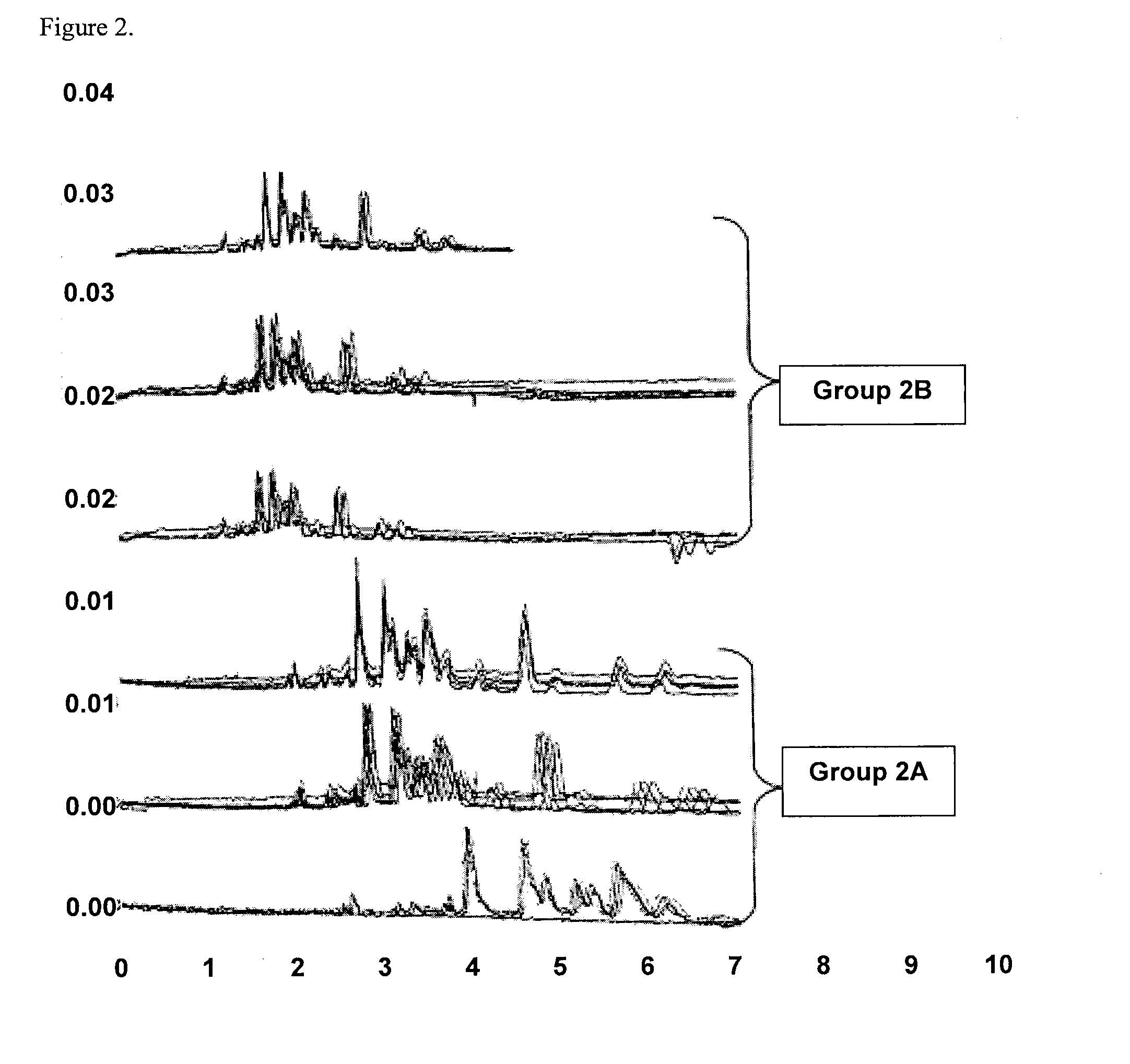
[0031]FIG. 1 illustrates separation profiles obtained from PEI silane and BUDGE coated fused silica capillary tubes. The capillary tubes had a 40 μm internal diameter, a 364 μm outer diameter, a 31 cm total length, and were coated according to example I. Electrophoresis was performed at 400 v / cm field strength on a Beckman Coulter P / ACE MDQ capillary electrophoresis system, available from Beckman Instruments, Inc. (Fullerton, Calif.). Group IA of FIG. 1 shows the electropherograms obtained from the first five runs of five peptide standards. Group 1B in FIG. 1 shows electropherograms obtained up to 200 runs of Horse heart Cytochrome c. The electropherogram shows that migration time of analytes were stable from the first run and thereafter, and that the electrophoretic separation took only 2.3 min to complete. FIG. 2 illustrates separation profiles obtained from bare uncoated fused silica capillary tubes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com