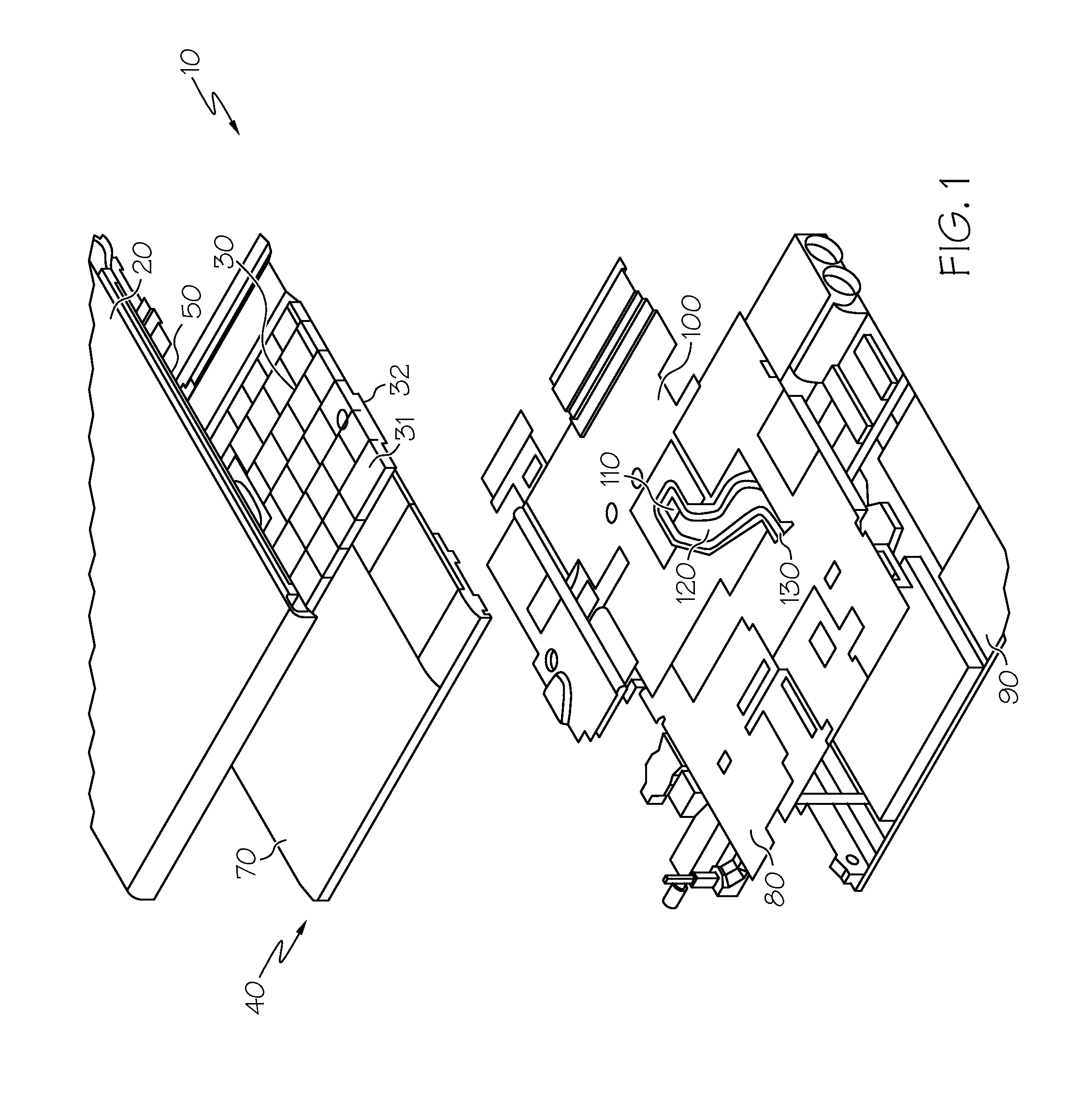
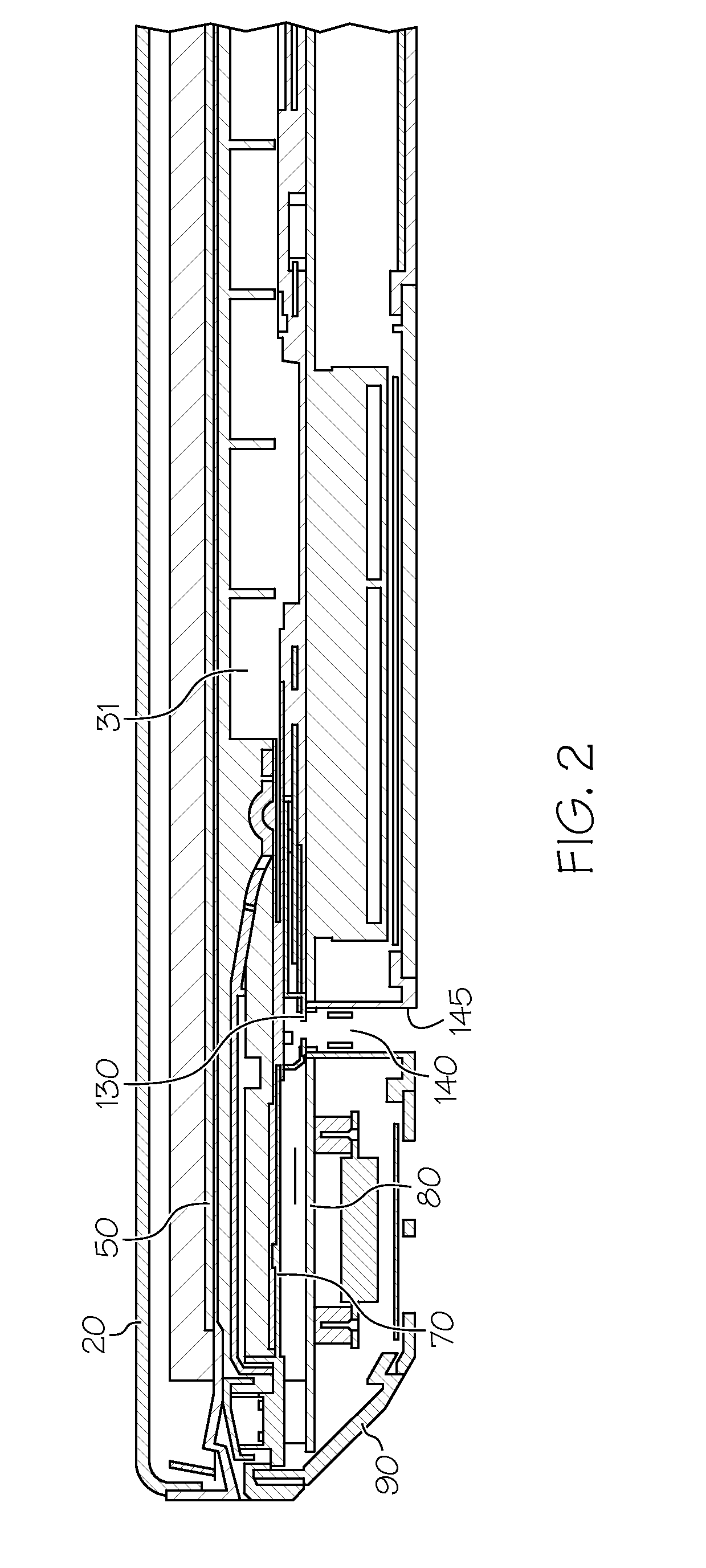
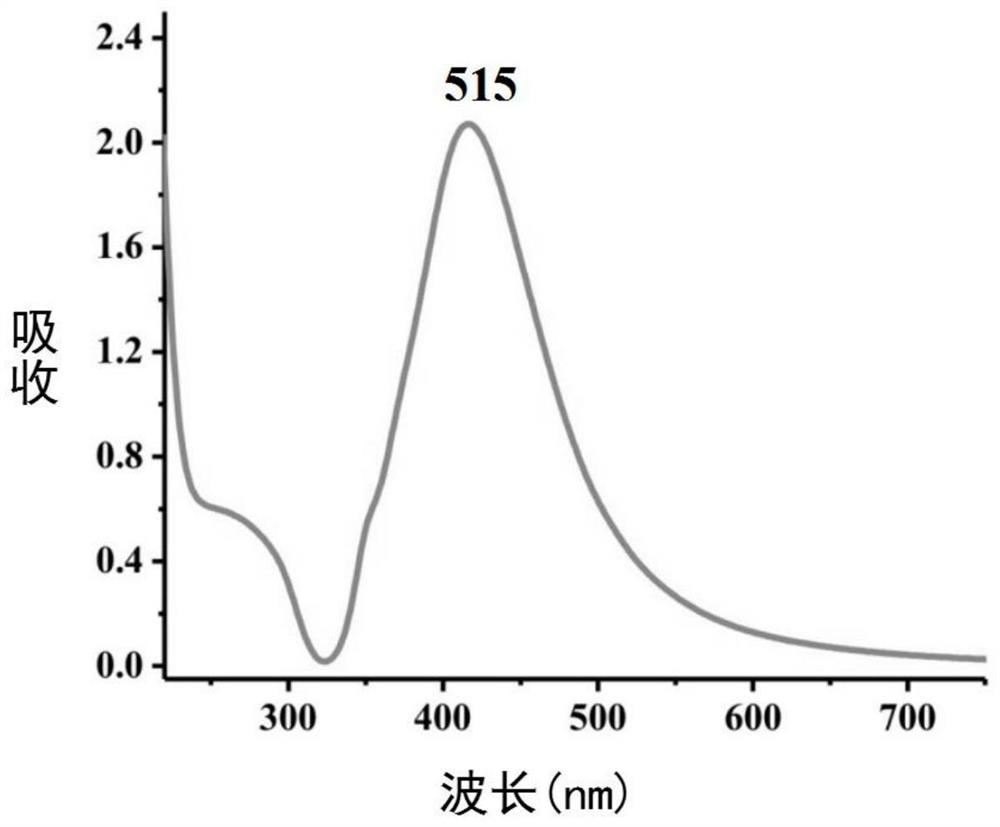
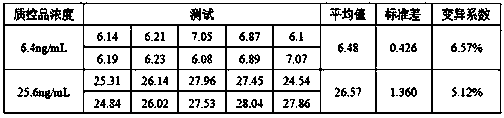
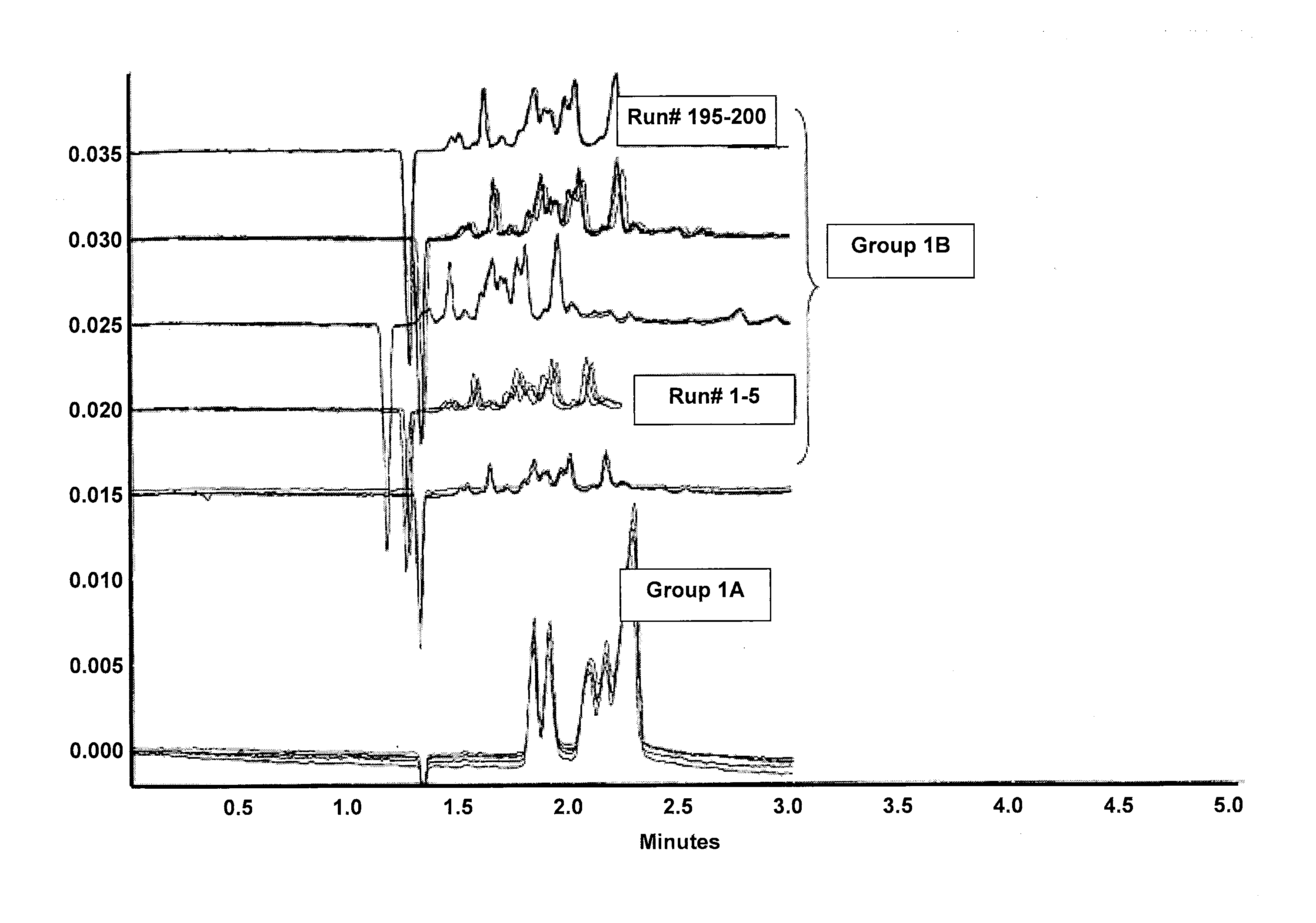
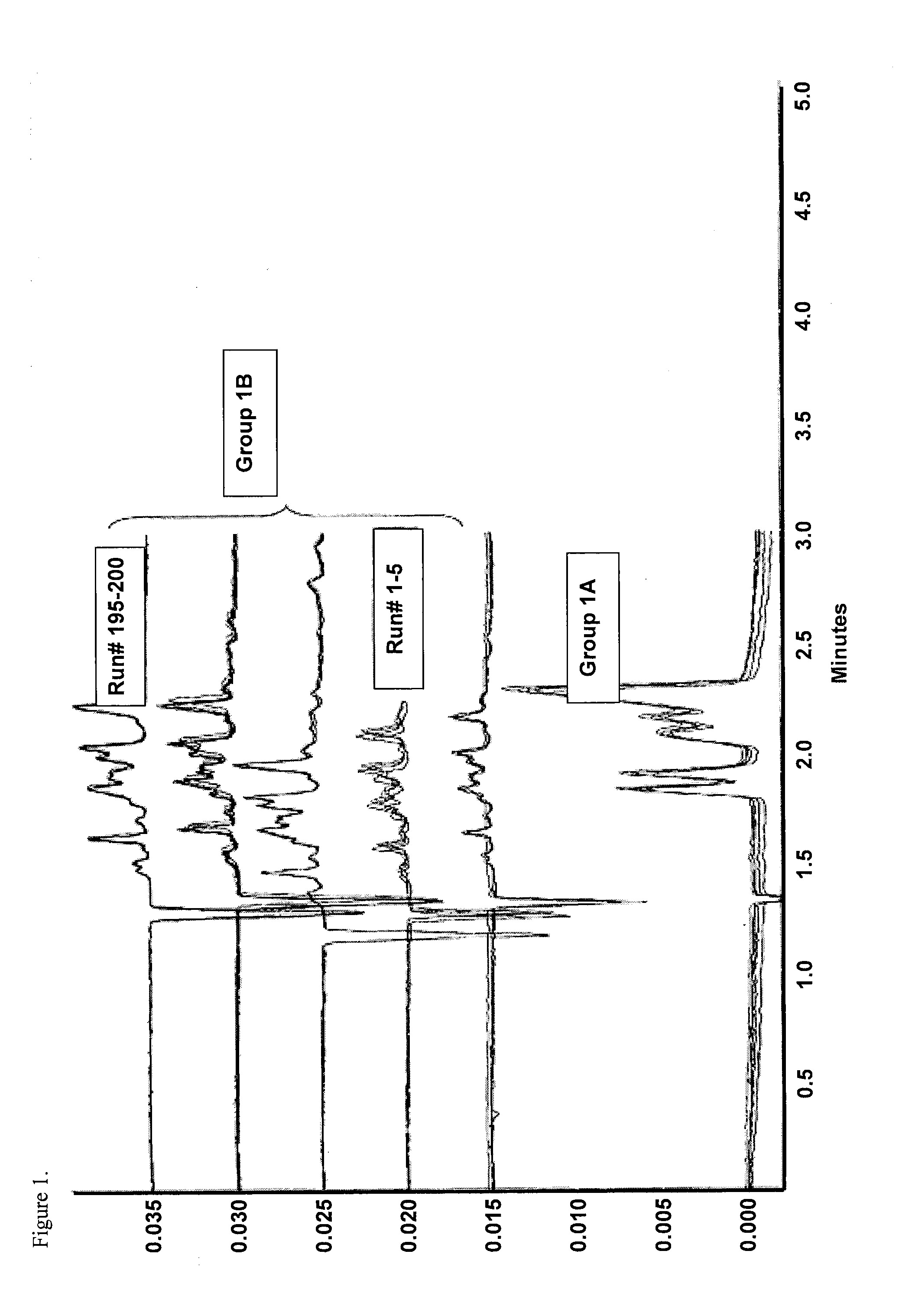
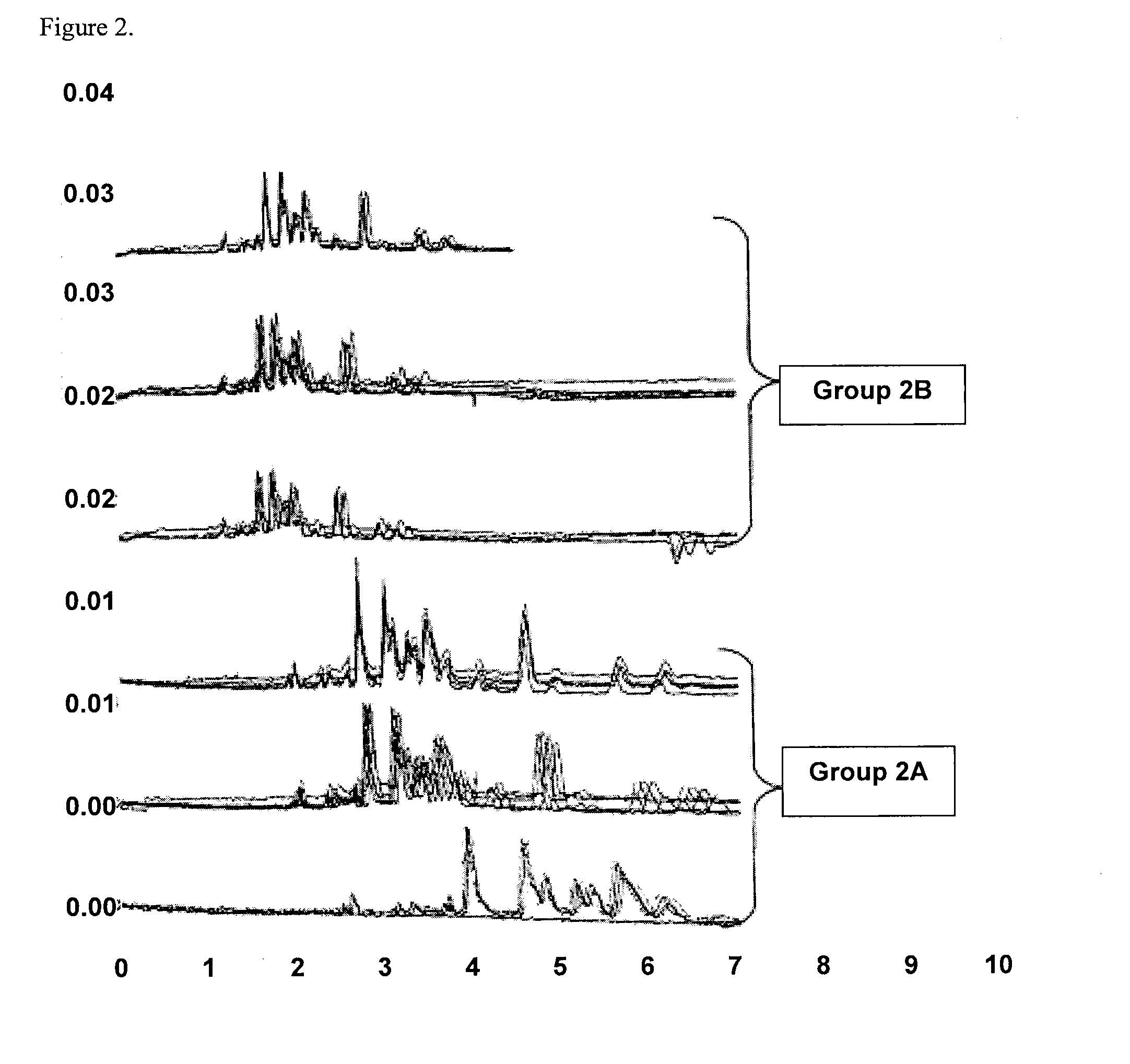
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Capillary surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In fluid mechanics and mathematics, a capillary surface is a surface that represents the interface between two different fluids. As a consequence of being a surface, a capillary surface has no thickness in slight contrast with most real fluid interfaces.
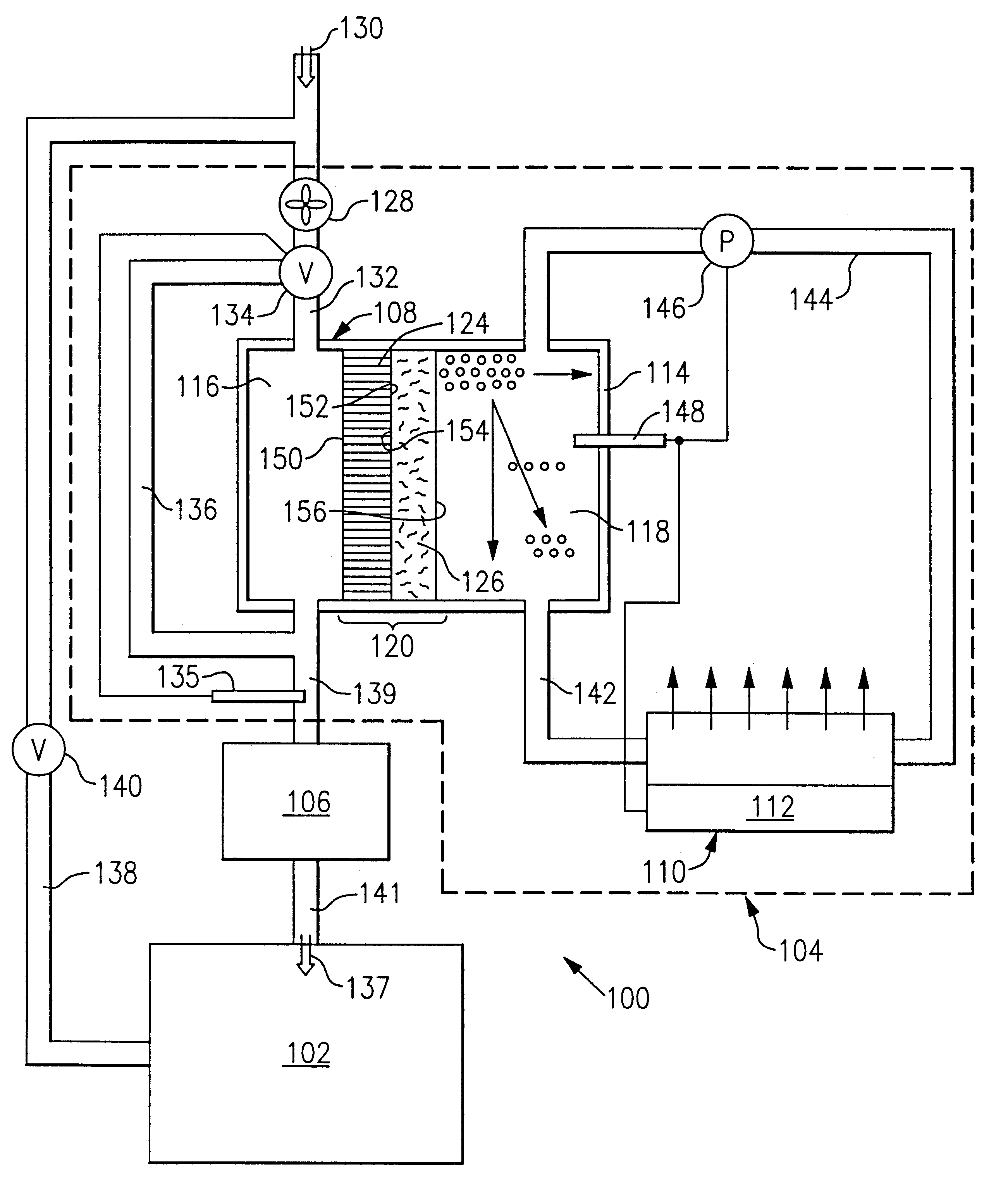
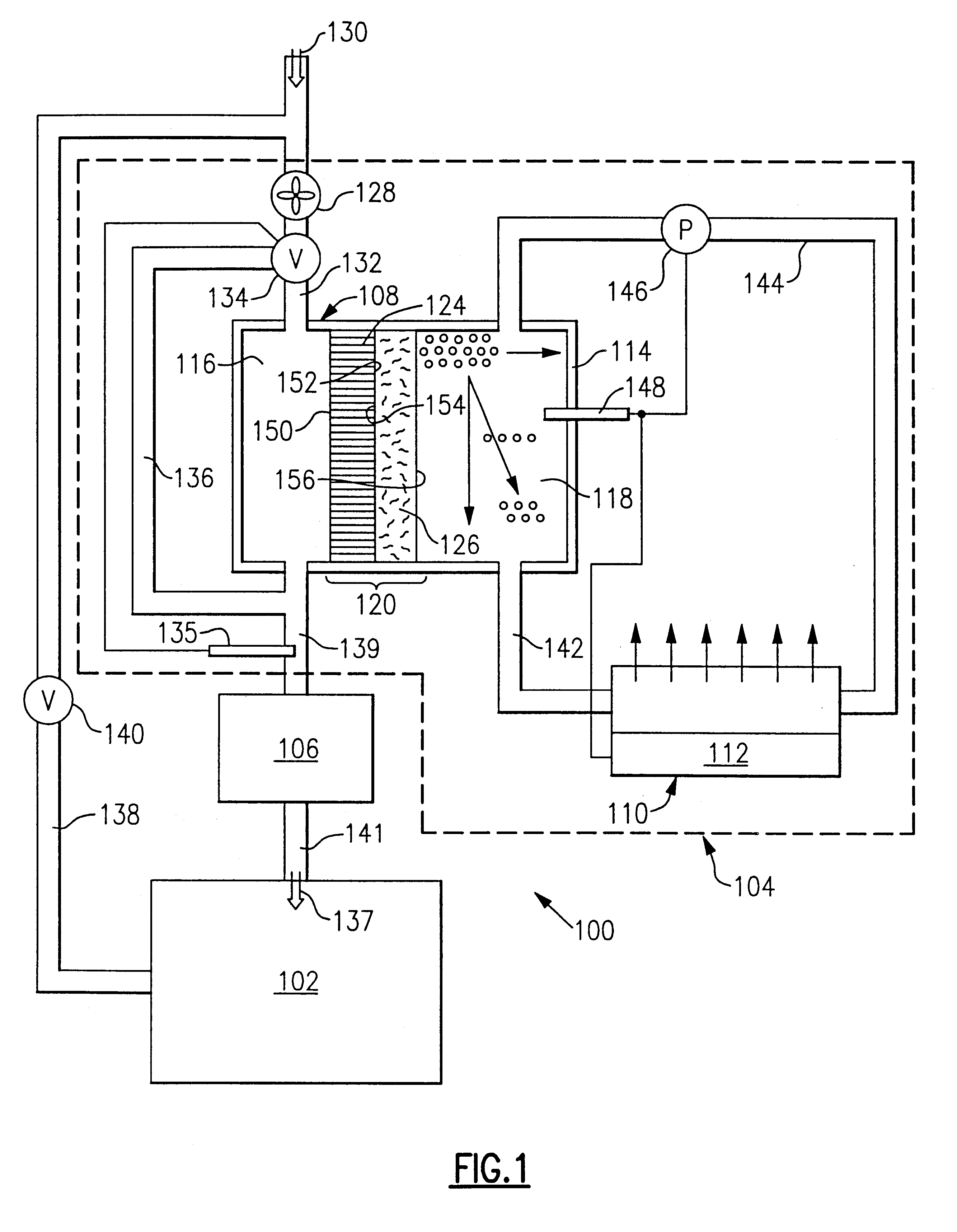
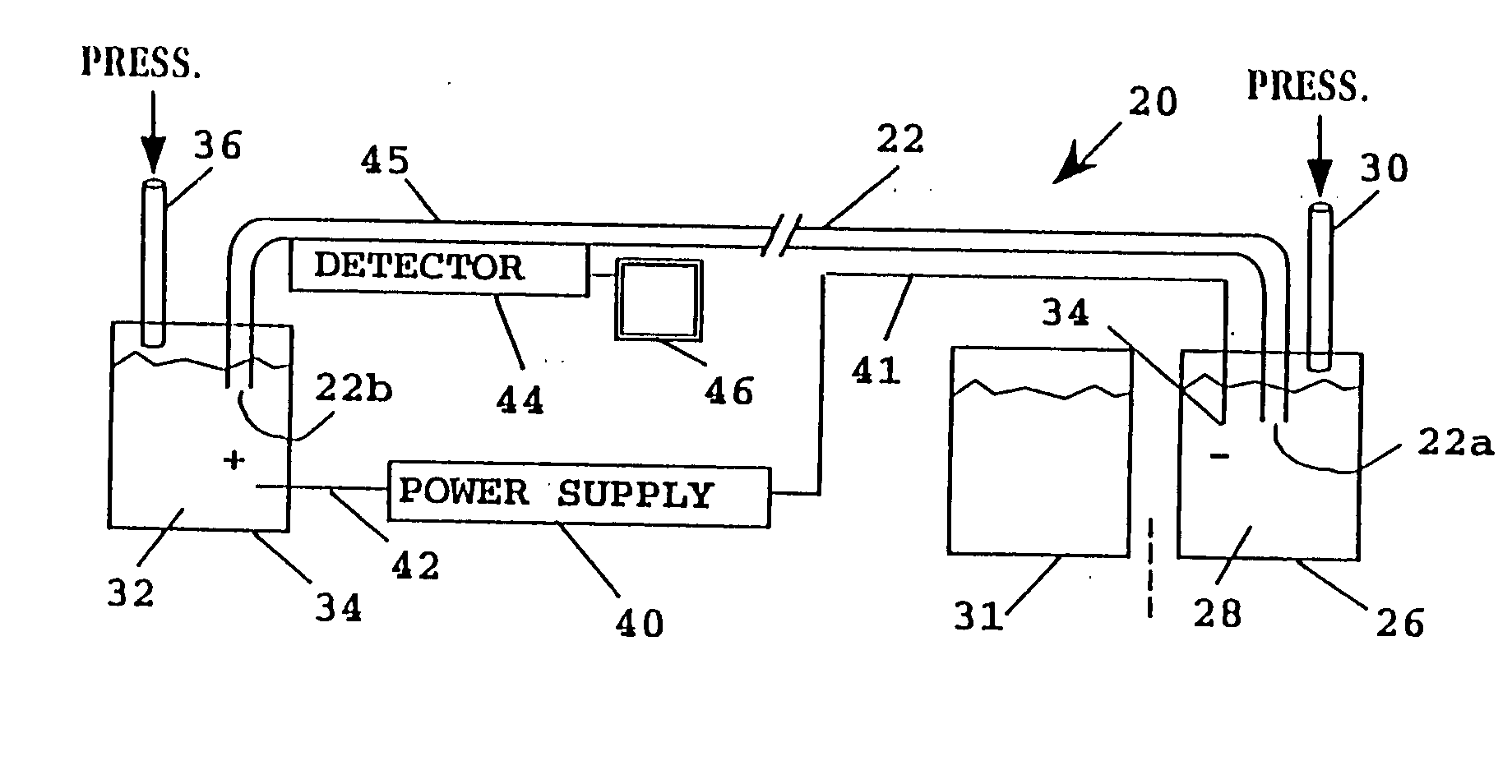
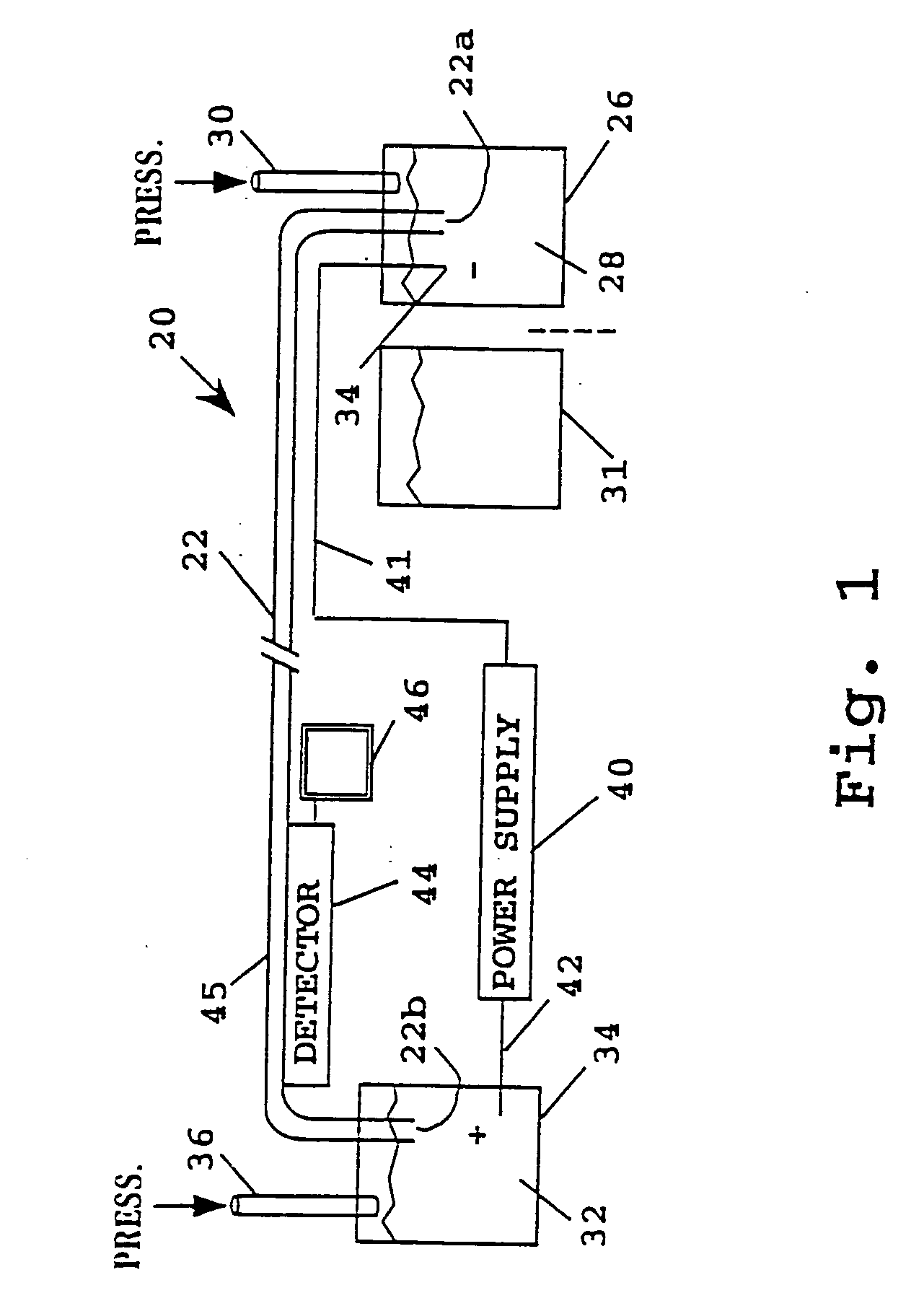
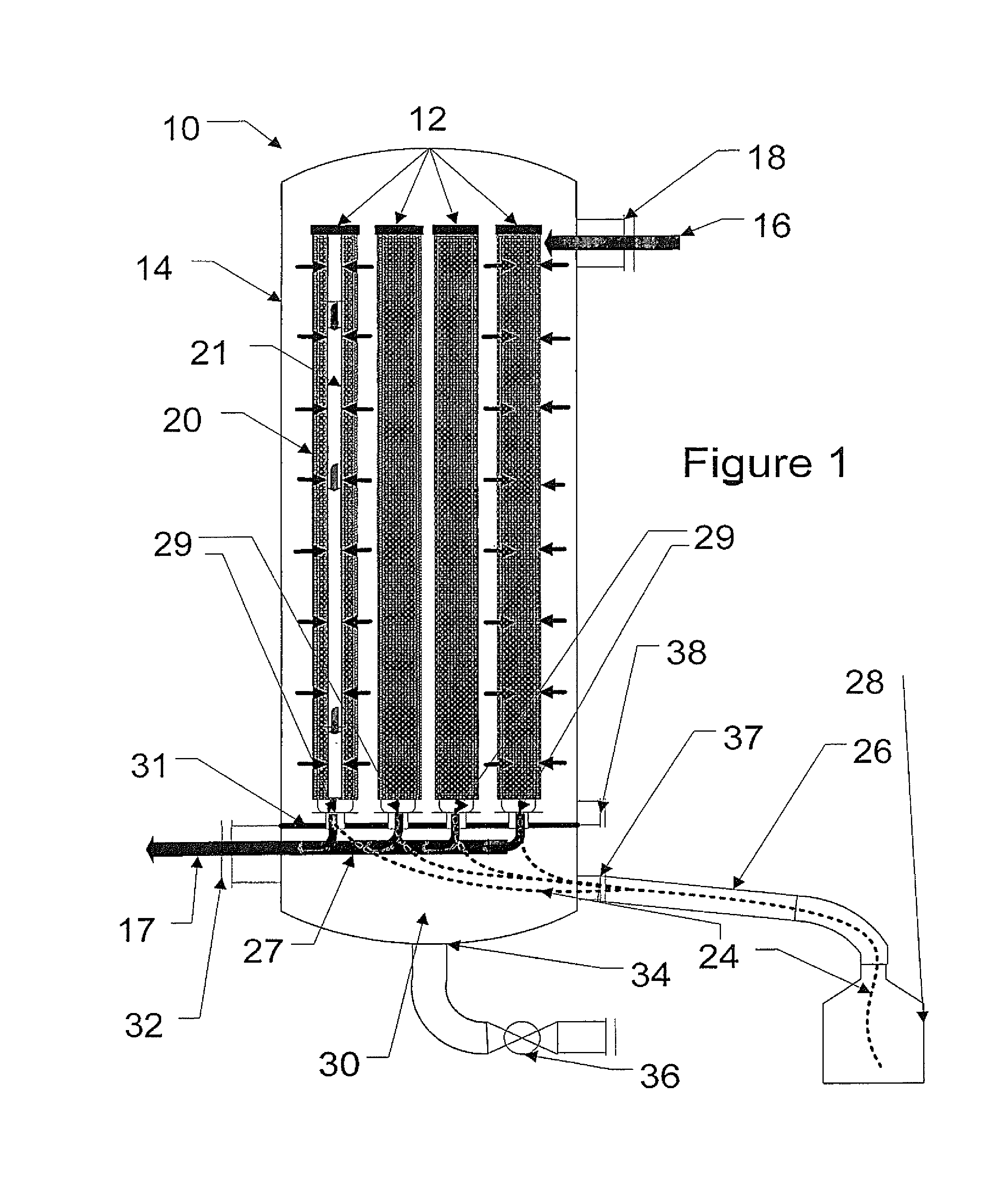
Dehumidification process and apparatus using collodion membrane
InactiveUS6497749B2High gradientAvoid flowSemi-permeable membranesLighting and heating apparatusWater concentrationGlycerol
Owner:ARTHUR S KESTEN
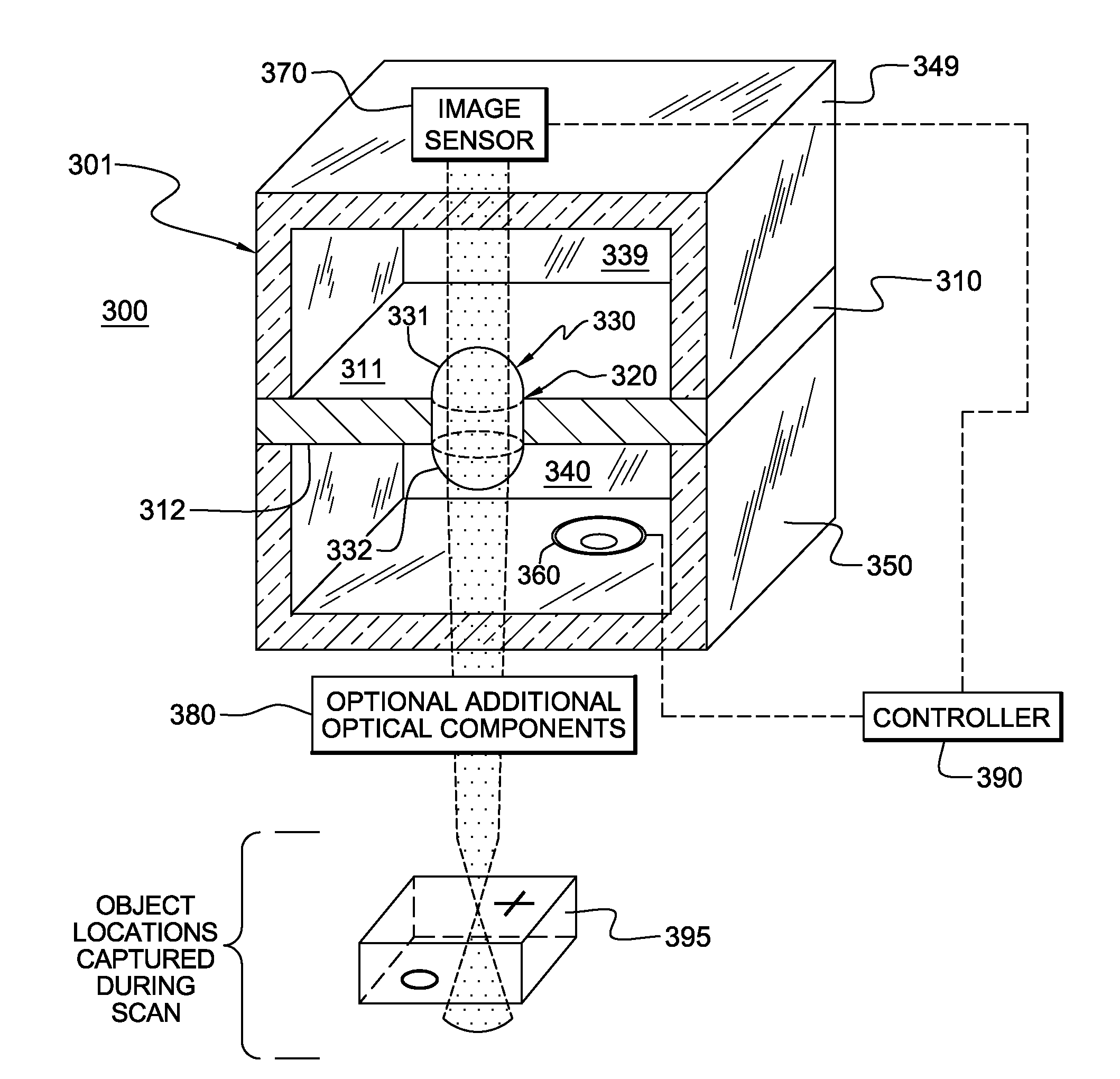
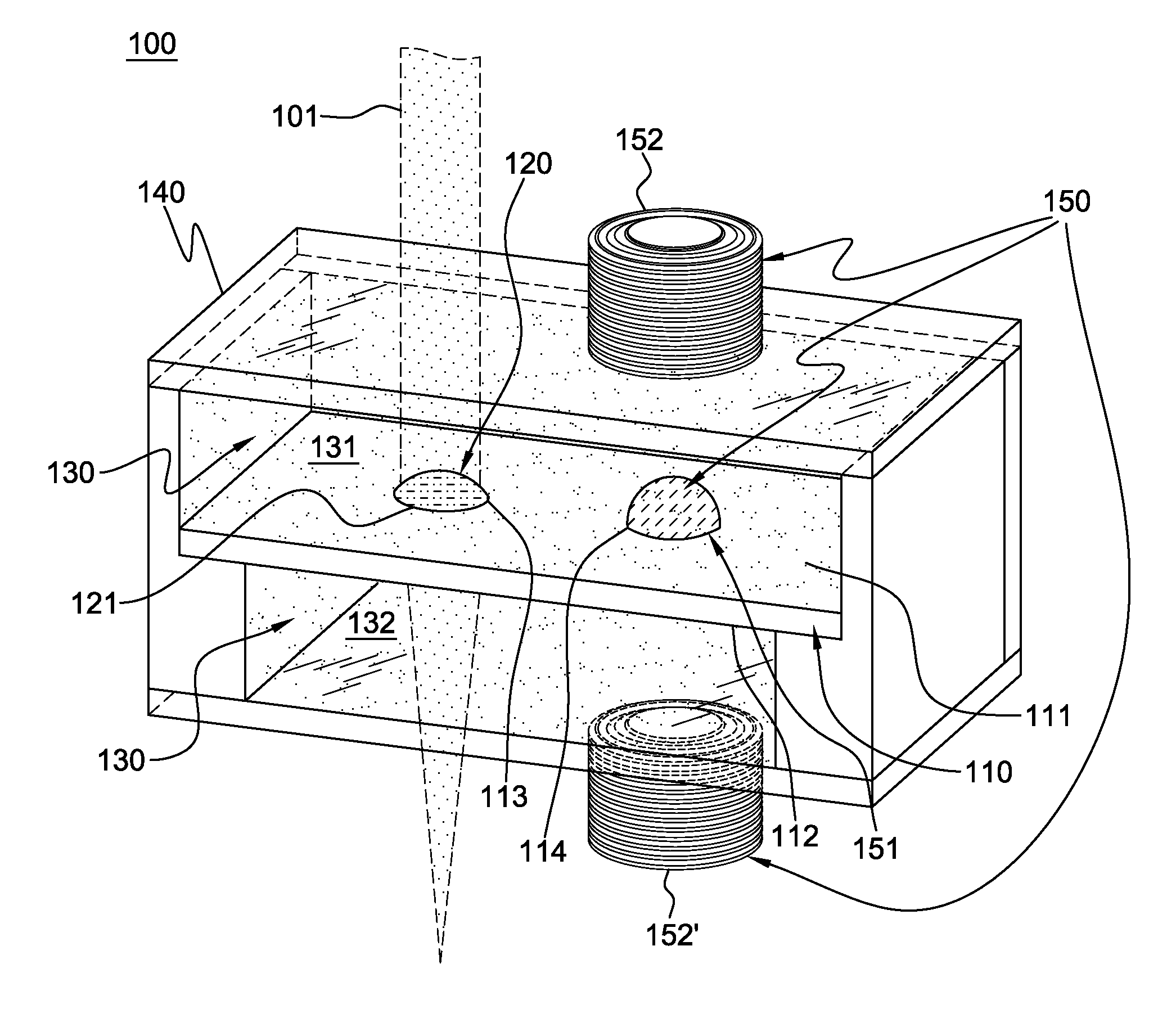
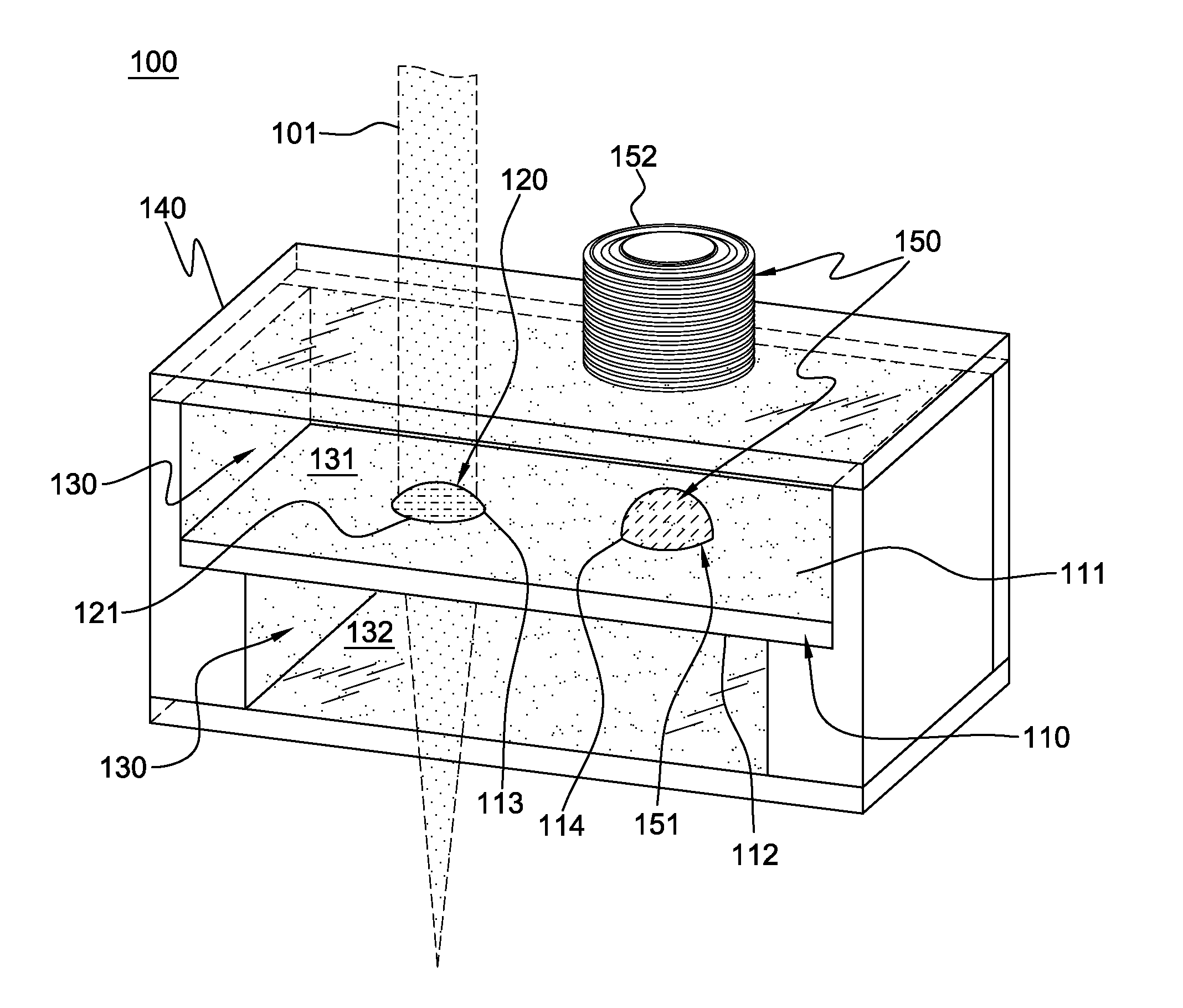
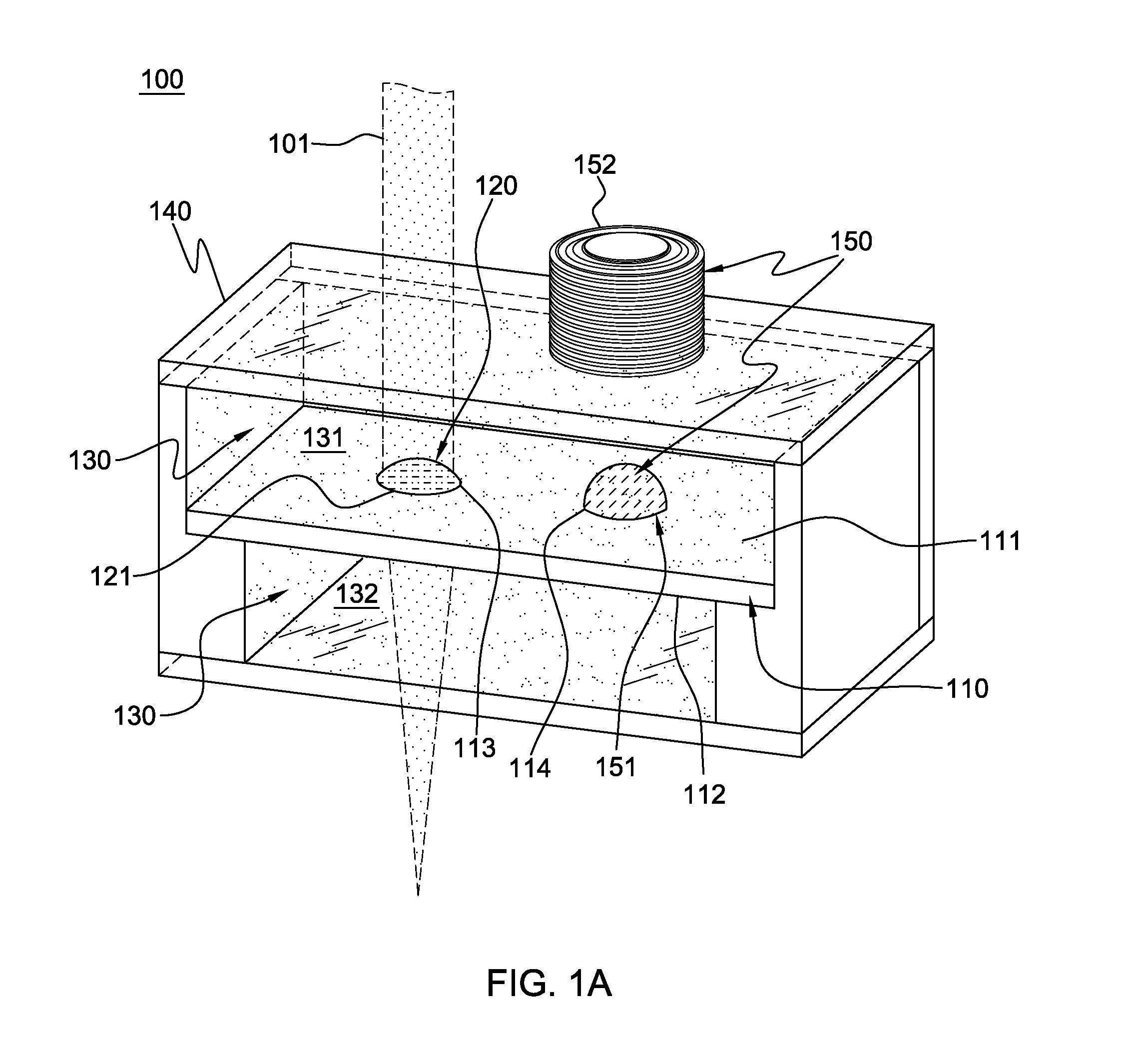
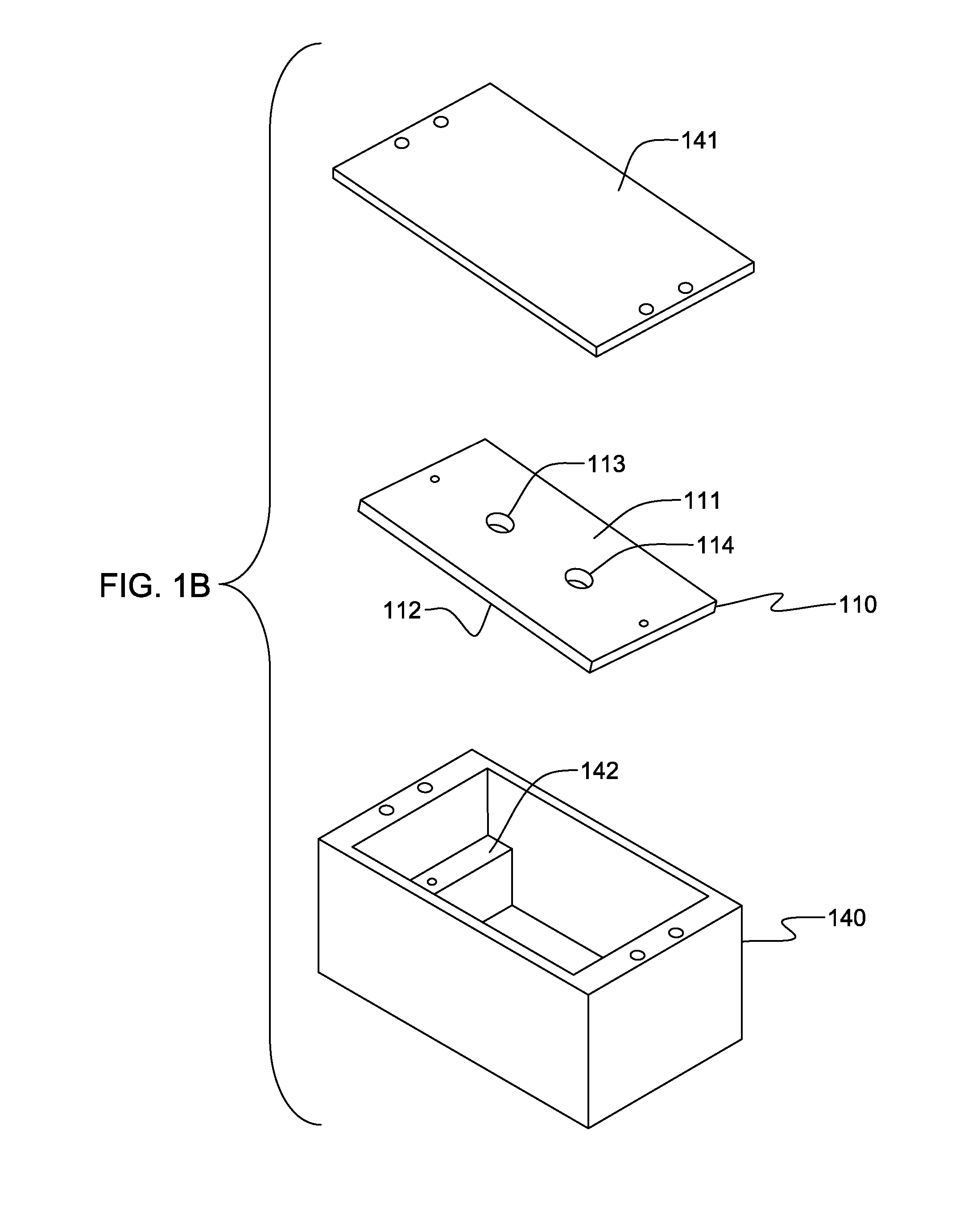
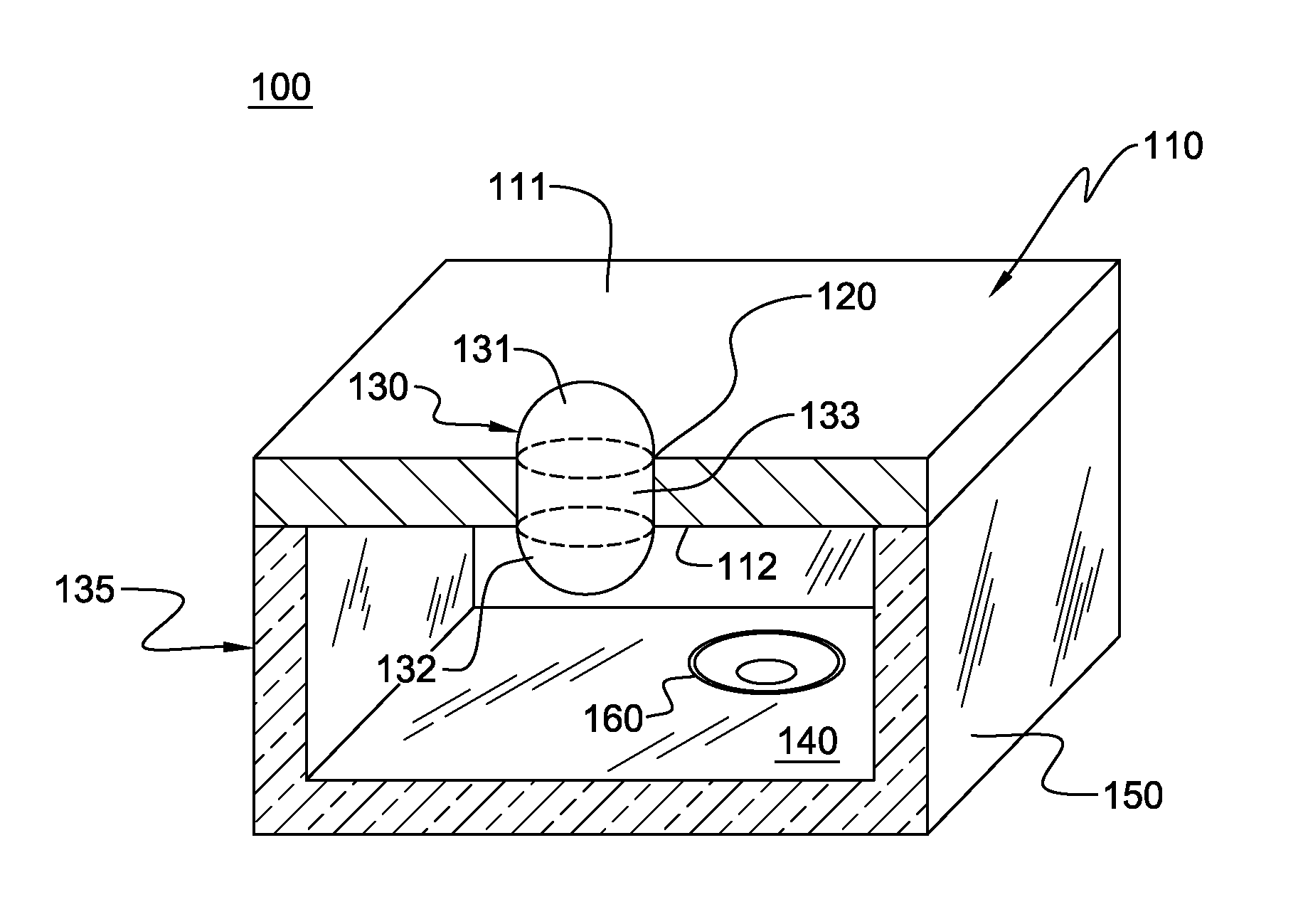
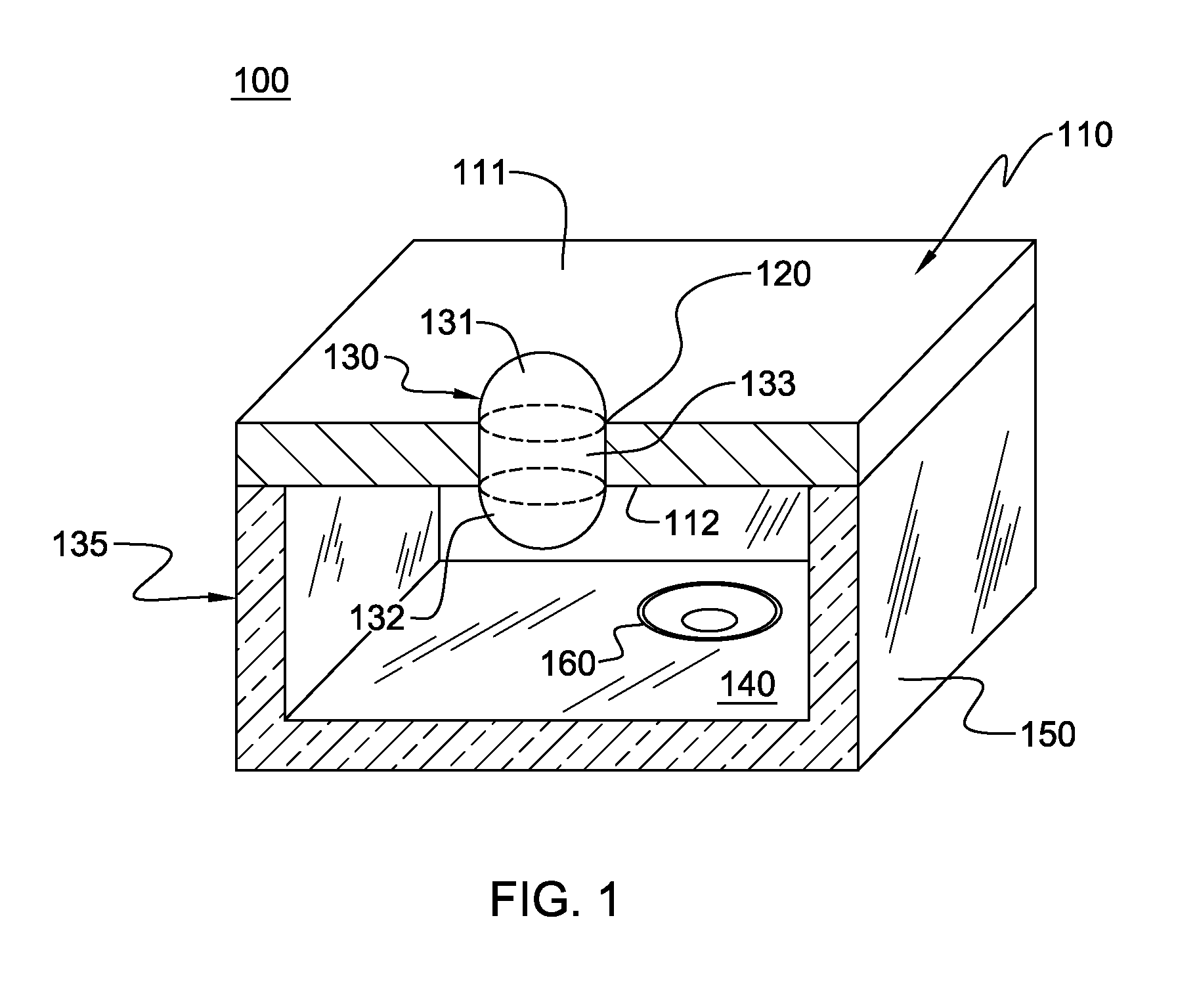
Pinned-contact oscillating liquid lens and imaging system
ActiveUS20090316003A1Television system detailsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsImage systemLiquid drop
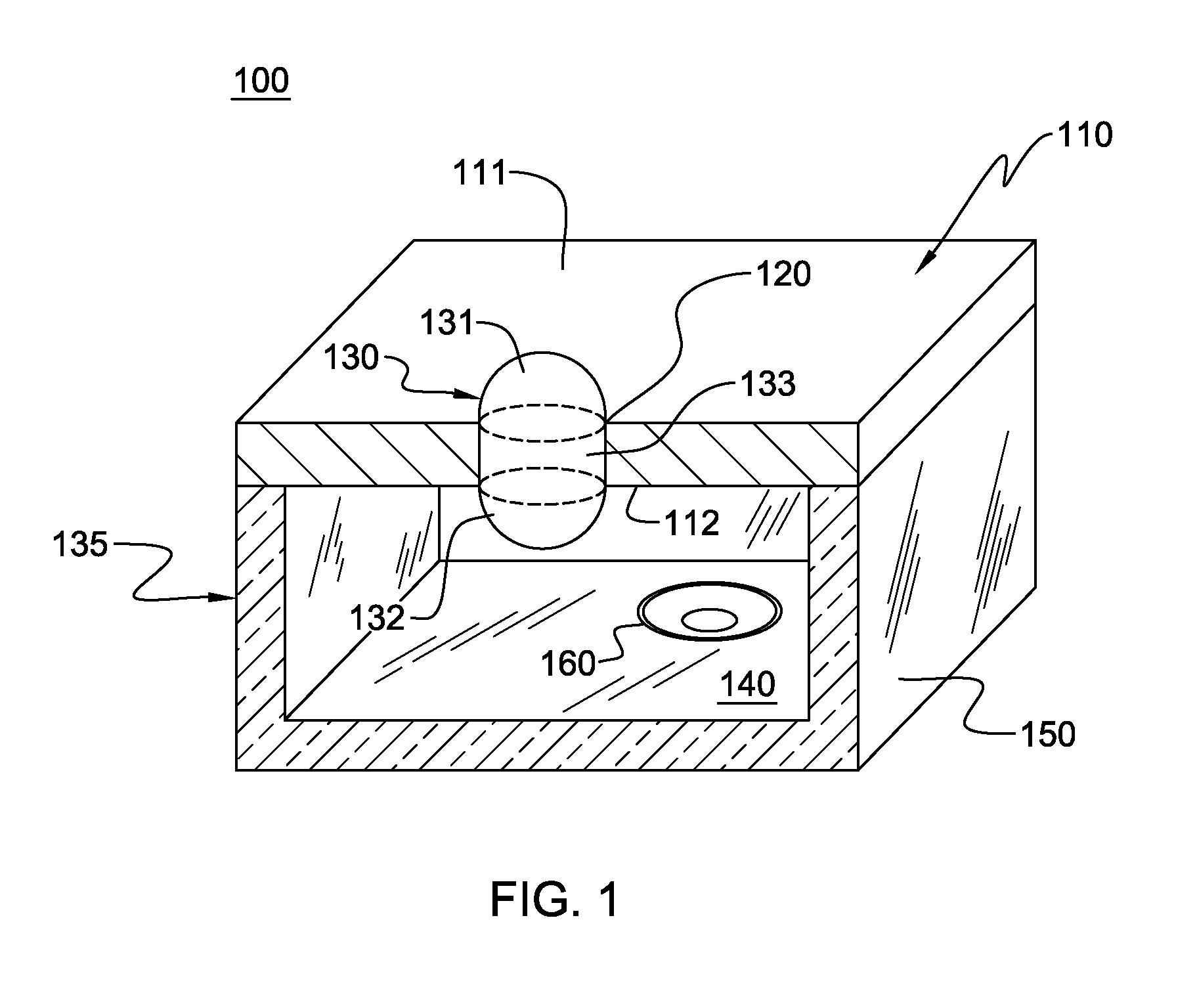
An oscillating liquid lens and imaging system and method employing the lens are provided. The liquid lens includes a substrate with a channel opening extending therethrough between a first and second surface. A liquid drop is disposed within the channel and is sized with a first droplet portion, including a first capillary surface, protruding away from the first surface, and a second droplet portion, including a second capillary surface, protruding away from the second surface. The liquid lens further includes an oscillator operatively coupled to either the first droplet portion or the second droplet portion for oscillating the liquid drop within the channel. The imaging system, in addition to the oscillating liquid lens, also includes an image sensor coupled to an image path which passes through the first and second droplet portions for capturing one or more images through the oscillating liquid drop.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Process and system for separating finely aerosolized elemental mercury from gaseous streams
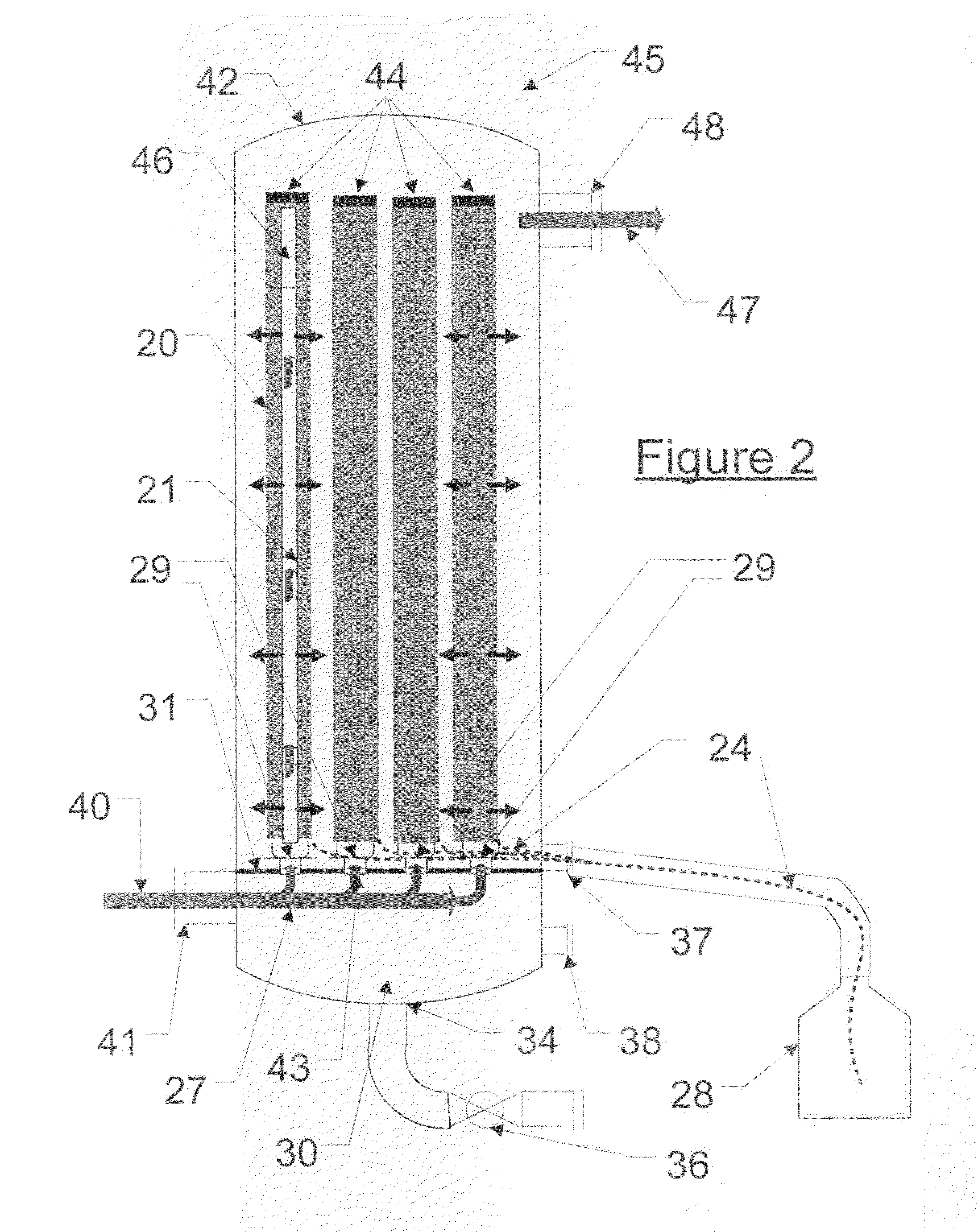
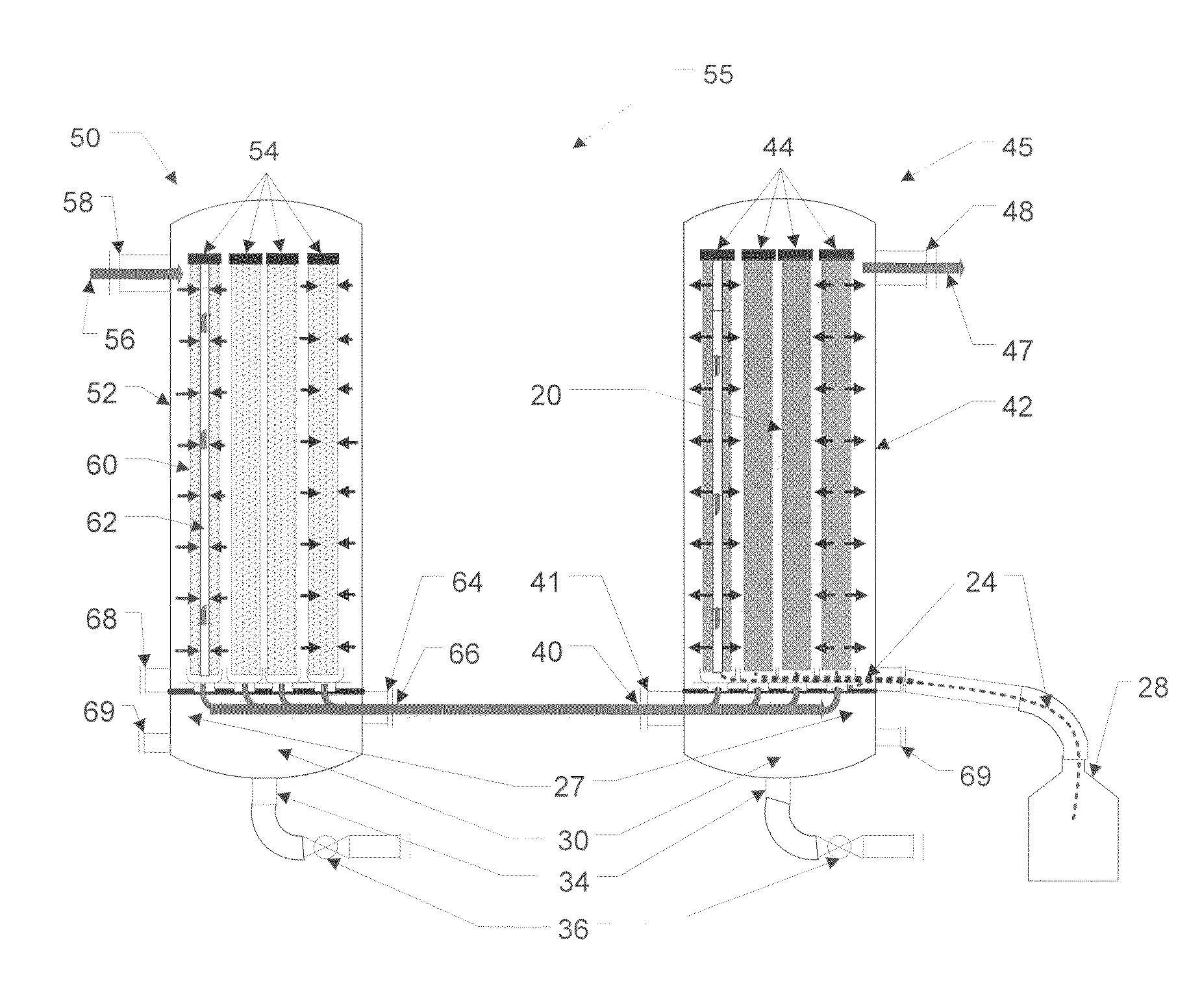
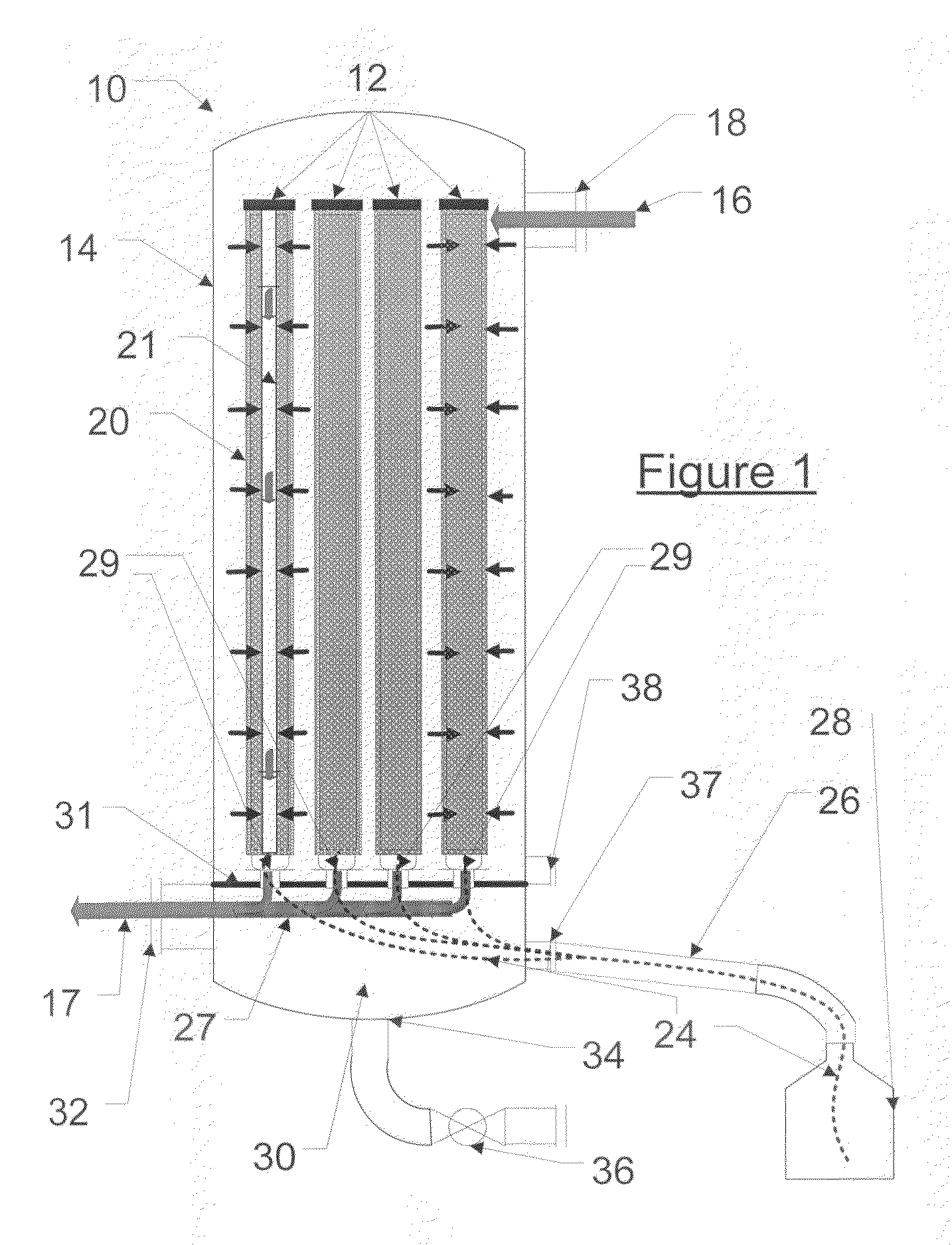
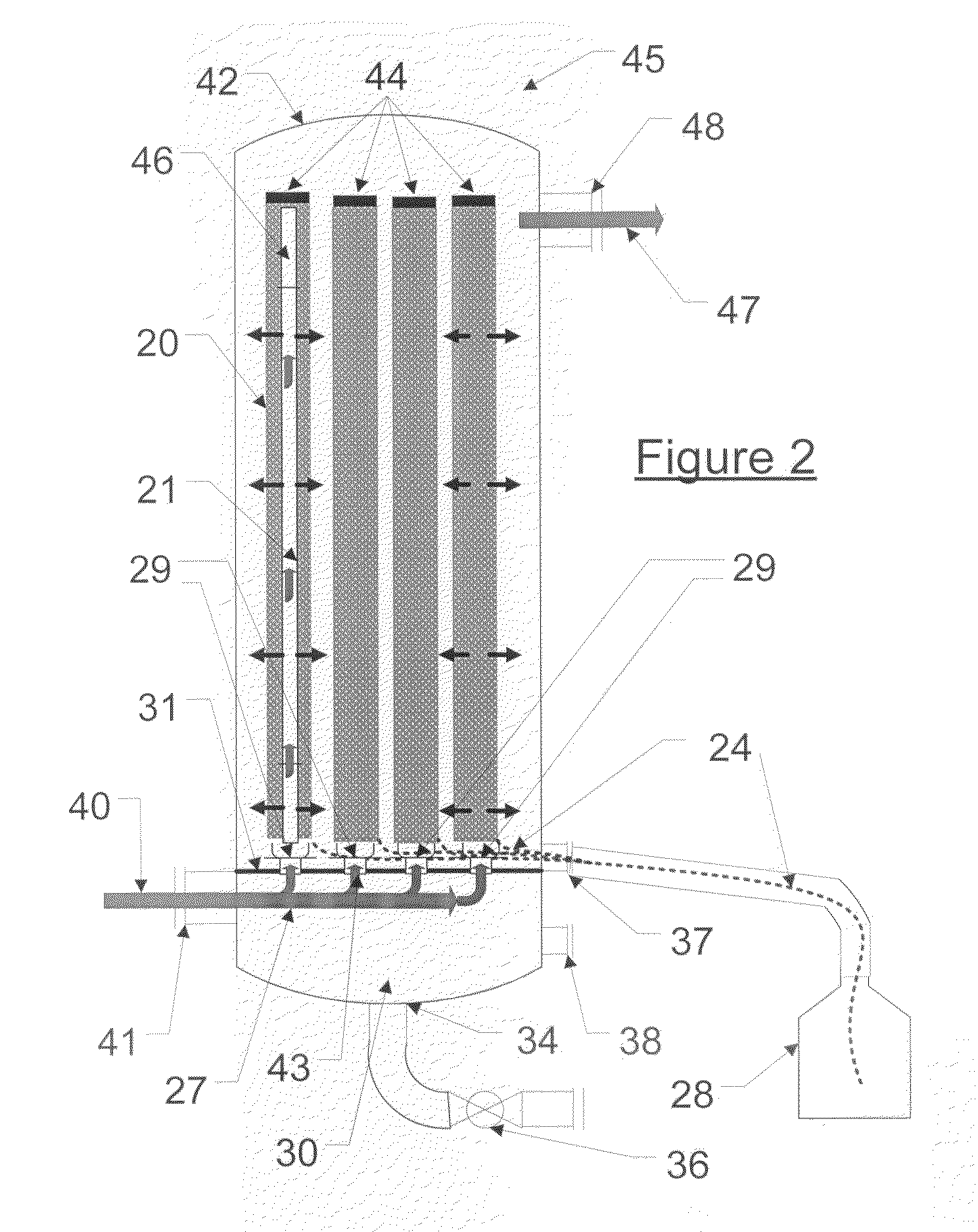
ActiveUS20100000409A1Large dropImprove removal efficiencyCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentGravitational forceElemental mercury
A method and apparatus for practicing the method are provided for separating droplets of finely aerosolized elemental mercury from a gaseous stream in which the droplets are dispersed. In the method a gold plated metallic capillary surface is contacted with the gaseous stream, causing the aerosolized droplets to deposit on the capillary surface and by capillary action to coalesce with other of such droplets to form increasingly large drops of mercury. The surface is oriented to allow the mercury to flow by gravitational forces and capillary action to the lowermost portions of the surface, at which it accumulates, and is then collected at a suitable vessel.
Owner:MYCELX TECH CORP
Process and system for separating finely aerosolized elemental mercury from gaseous streams
ActiveUS8105423B2Improve removal efficiencyDegree of filtration efficiencyCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentGravitational forceElemental mercury
Owner:MYCELX TECH CORP
Capillary seal with fill pool
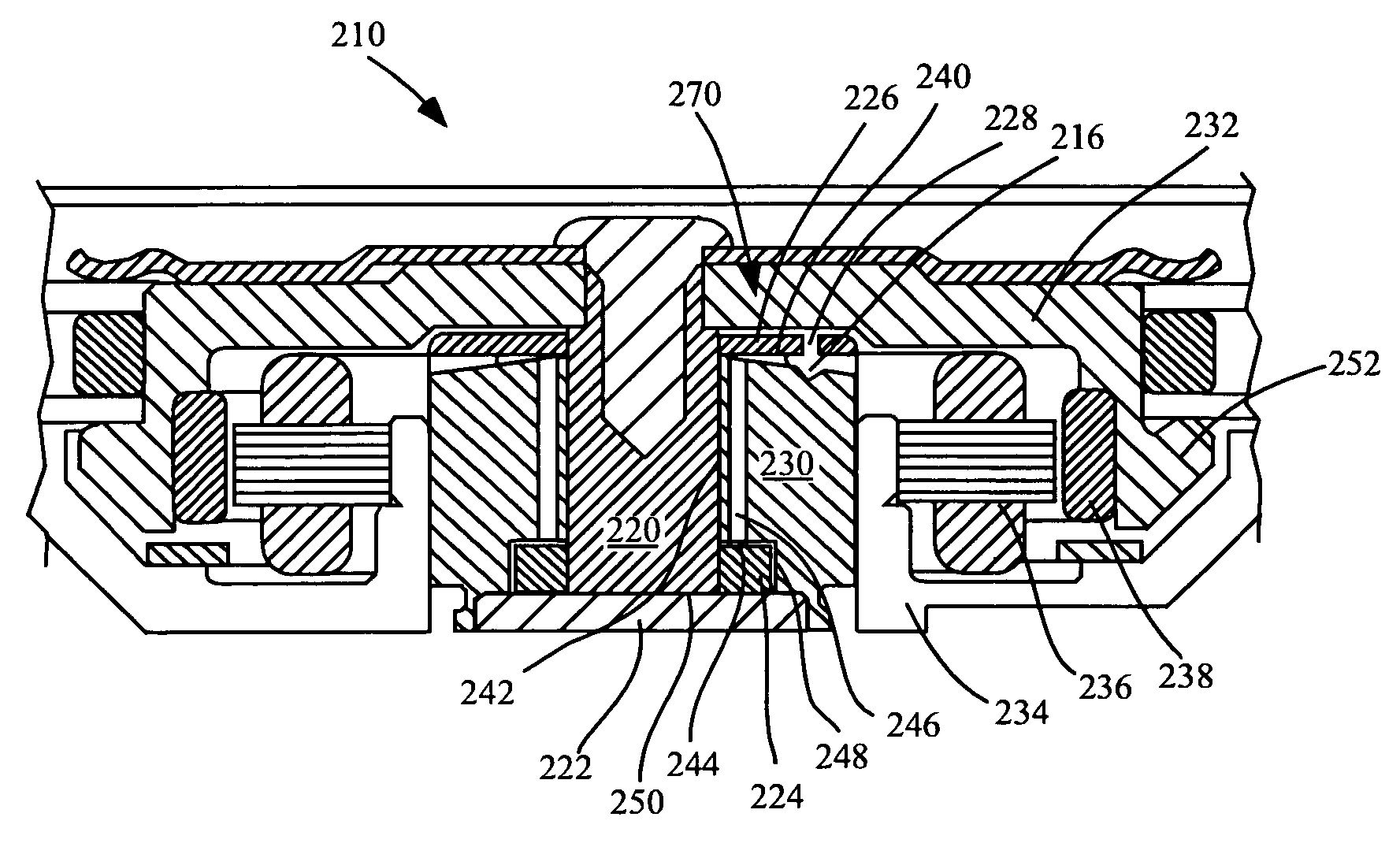
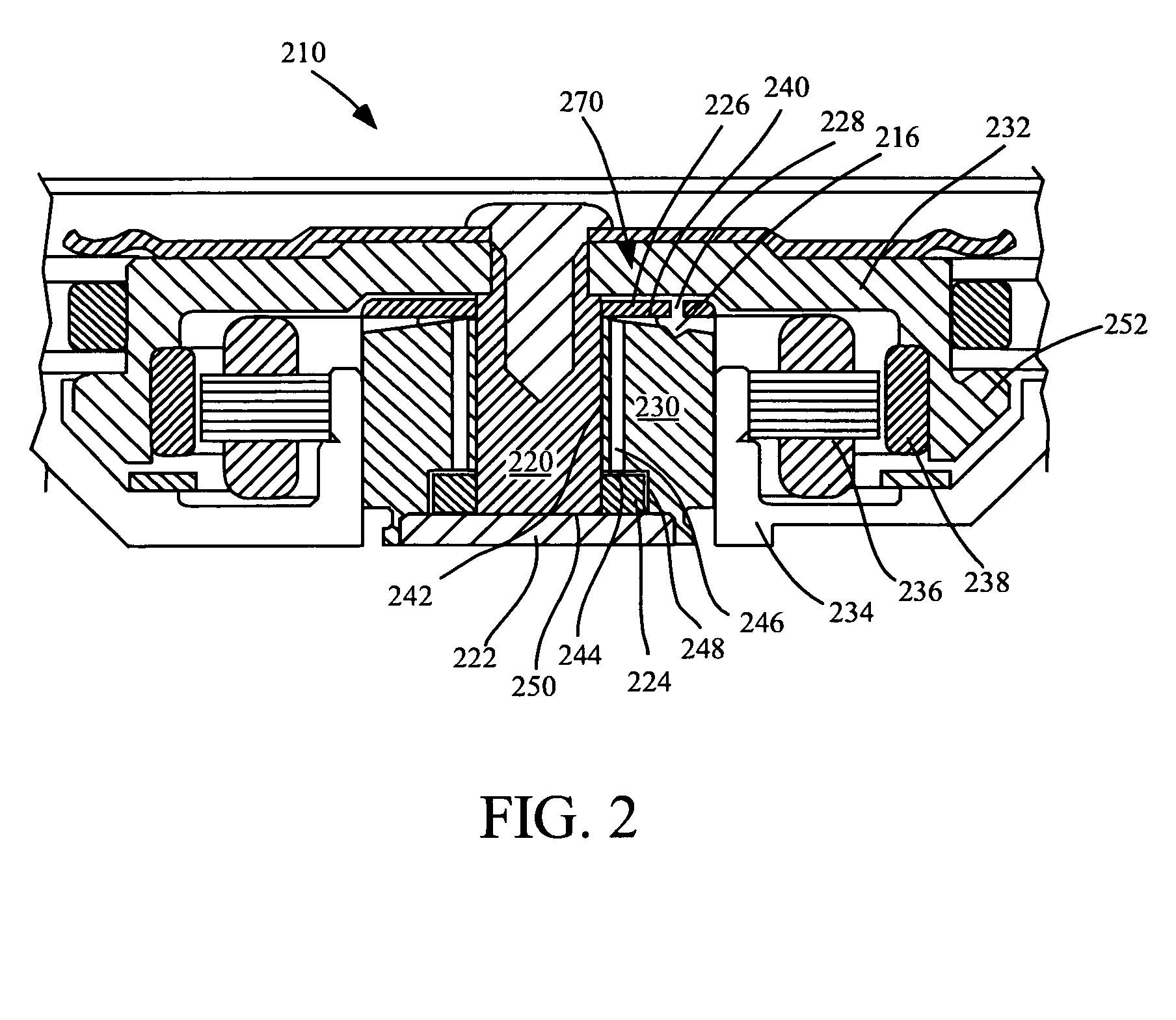
InactiveUS7056026B2Optimizing bearing stiffnessImprove performanceEngine sealsLeakage preventionCapillaria obsignataEvaporation
Improved capillary sealing is provided for withstanding shock events, vibration and evaporation, for use with fluid dynamic bearings. In an aspect, minimal axial space is occupied by a fluid reservoir and the sealing system and method withstands at least 1000 G shock events. A fluid reservoir having a capillary surface is formed between diverging walls. A fluid fill pool, separate from the fluid reservoir and having a steeper angle than the fluid reservoir, is positioned adjacent to a fluid fill hole. The fill pool, having a greater diverging angle than the fluid reservoir provides an unstable region for fluid to remain and any fluid is pulled by capillary force gradient to the fluid reservoir.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Reconfigurable, non-oscillating liquid lens and imaging systems
ActiveUS20120026599A1Facilitates adjusting configurationOvercomes shortcomingOptical articlesLensActuatorSubstrate surface
A non-oscillating liquid lens and imaging system and method employing the lens are provided. The liquid lens includes a substrate with a channel opening extending through the substrate. A liquid lens drop is held within the channel and is sized with a first droplet portion, including a first capillary surface, protruding away from a first substrate surface, and a second droplet portion, including a second capillary surface, protruding away from a second substrate surface. The liquid lens further includes an enclosure at least partially surrounding the substrate, and which includes a chamber. The liquid lens drop resides within the chamber, and the liquid lens includes a second liquid disposed within the chamber in direct or indirect contact with the liquid lens drop, and an actuator which facilitates adjusting configuration of the liquid lens drop within the channel, and thus, a focal distance of the liquid lens.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Microstructured multicore optical fibre (mmof), a device and the fabrication method of a device for independent addressing of the cores of microstructured multicore optical fibre
InactiveCN106255906ANo freedom of movementMovement restrictionsLaser detailsMulticore optical fibreEtchingRefractive index
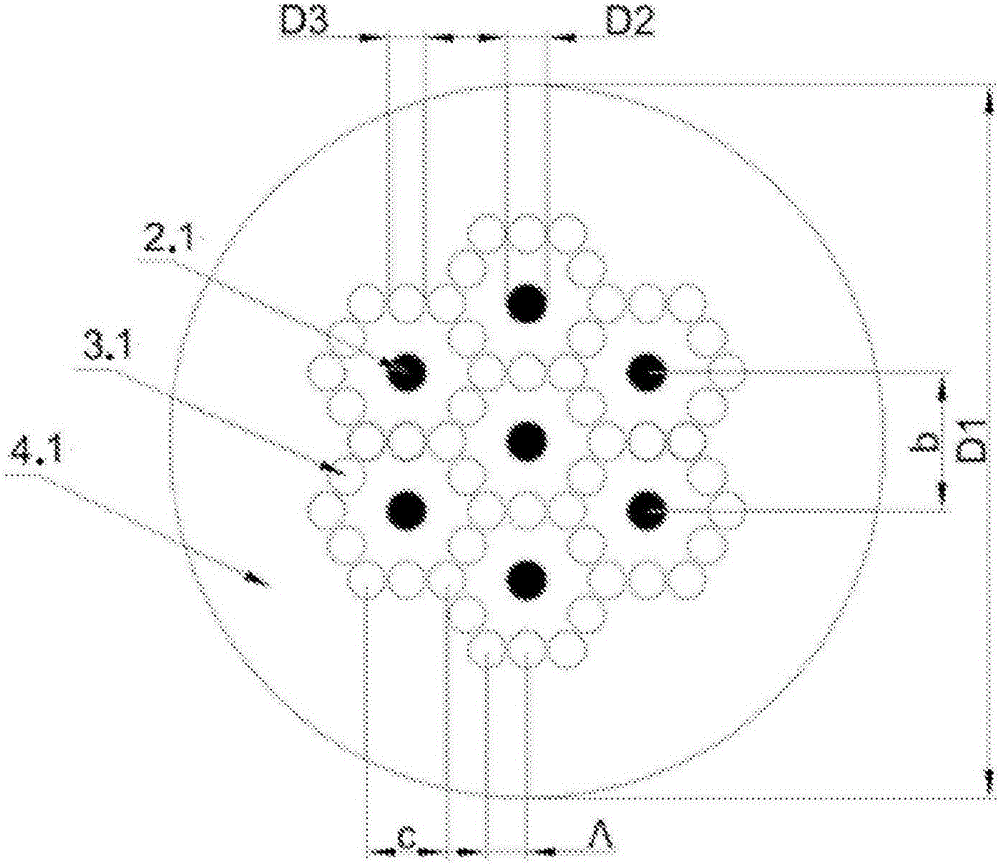
Microstructured multicore optical fibre with a microstructure area, in which, at least two basic cells are embedded, where each of them contains a core, preferably made of glass, specifically including doped silica glass or polymer, together with the surrounding it longitudinal areas with lower refraction index vs. that of the cladding, which areas may adopt the shape of holes, filled with gas, in particular with the air or a fluid or a polymer or spaces of another glass with doping allowing to reduce refractive index(further referred to as holes), embedded in a matrix of glass, in particular of silica glass or polymer. The refraction index of the holes is decreased vs. that of the matrix of glass, in particular of silica glass or polymer. The basic cell is characterised by the diameter of D2 core, the diameter of D3 core and the distance between adjacent holes, corresponding to lattice constant. The centres of the holes are localised on the vertices and the middle points of the sides of the hexagon, the centre of which is designated by the core; the length of side c of the hexagon, created by the centres of holes, is equal to the preferably doubled lattice constant. The juxtaposed, at least, two basic cells are surrounded by the cladding, preferably made of glass, in particular of silica glass or polymer. Device for addressing cores of the multicore optical fibre, characteristic in that it contains single-core, single-mode optical fibres, with parallel layout in the capillary, (further referred to as single-mode optical fibres), in the number, corresponding to the number of the cores of the multicore optical fibre, while the capillary with single-mode optical fibres is connected with the multicore optical fibre, e.g., the microstructured optical fibre, according to this invention, while the cross-sections of the optical fibres in the capillary and the cross- section of the multicore optical fibre are parallel in their configuration. The fabrication method of the device for addressing cores consists in: 1. an analysis of the structure of multicore optical fibre and determination of the number of cores of the multicore optical fibre, the diameter of cores and the distances among them, 2. measurement of the diameters of the cores and of the claddings of single-mode optical fibres, with which the multicore optical fibre is connected, and the scale of tapering of the single-mode optical fibres is deteremined, 3. removal of the cladding of single-mode optical fibres and cleaning their surface, 4. etching, preferably with hydrofluoric acid, the exposed and cleaned fragments of the single-mode optical fibres, so that after their possible tapering and mutual reassembly, the alignment of the cores of the multicore optical fibre was possible with the cores of the single-mode optical fibre, 5. tapering of single-mode optical fibres, according to the calculated scale of tapering, allowing to achieve the diameters of their cores equal to the dimensions of the diameters of the cores of the multicore optical fibre (provided its preferable), 6. preparation of a capillary by its tapering to the size, allowing for insertion of single- mode optical fibres and glass rods, so that the inserted element shad no freedom of movement or that their movement was limited, 7. laying of single-mode optical fibres and glass rods in the capillary, 8. tapering and clamping of the laid and spliced structure in the capillary by its heating and tensing, while, if it is necessary, the multicore optical fibre is also tapered, 9. cleaving the capillary with the laid and spliced structure under right angle to the axis of the longitudinal capillary, preferably with a cleaver for optical fibres with various outer diameters and internal structures, with a possibility of controlled stretching of the fibre, preferably the capillary surface is polished, together with structure, laid in the capillary, 10. cleaving the multicore optical fibre and preferably polishing its surface, 11. orientation of the capillary vs. the multicore optical fibre, together with the structure, laid and welded in its inside, 12. connection of the multicore optical fibre with the capillary and the structure in its inside by means of any disclosed technology, preferably by splicing.
Owner:信息技术有限公司
Pinned-contact, oscillating liquid-liquid lens and imaging systems
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
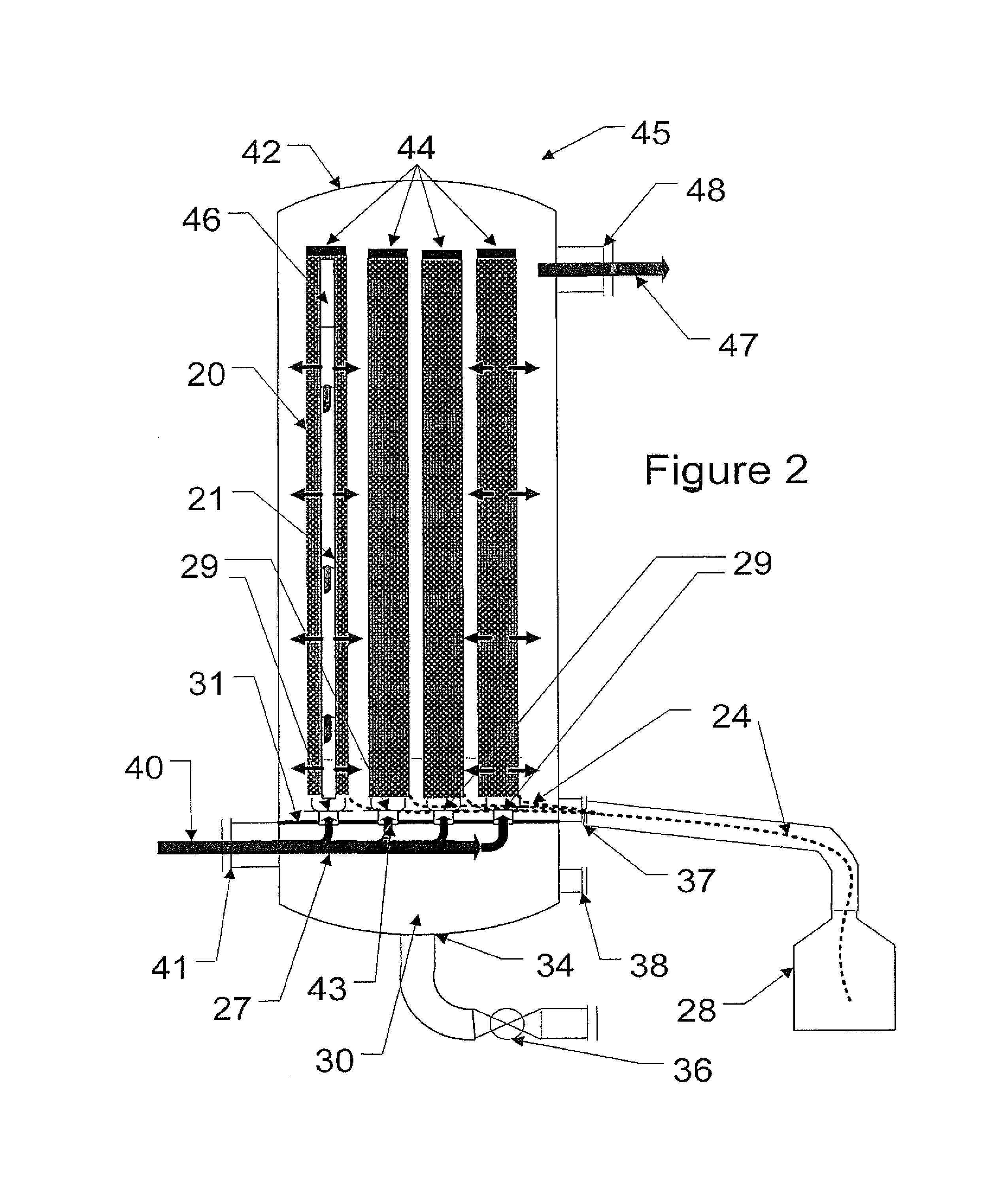
Groove slit water channel
ActiveUS8199491B2Digital data processing detailsLoose filtering material filtersWater channelEngineering
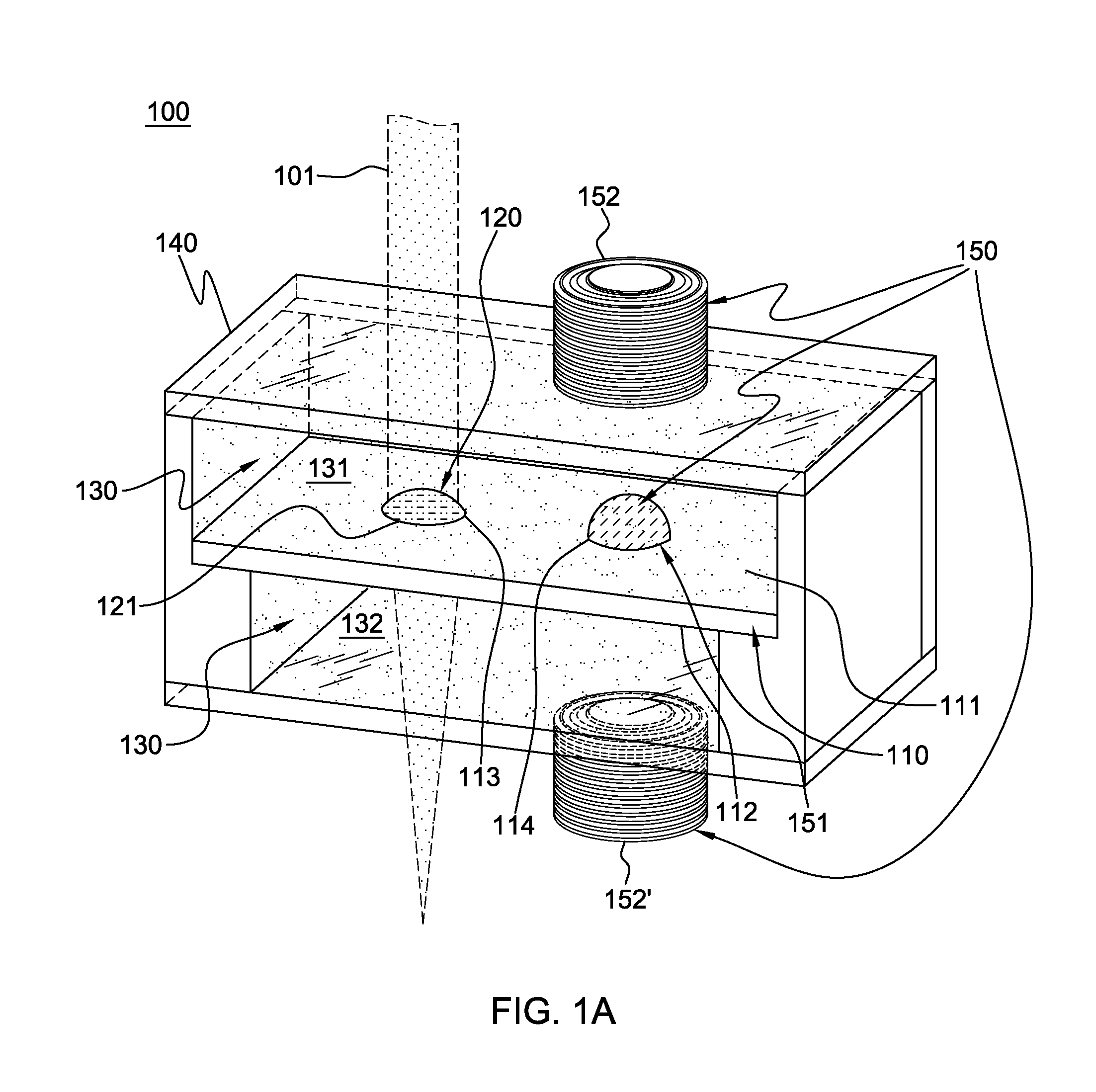
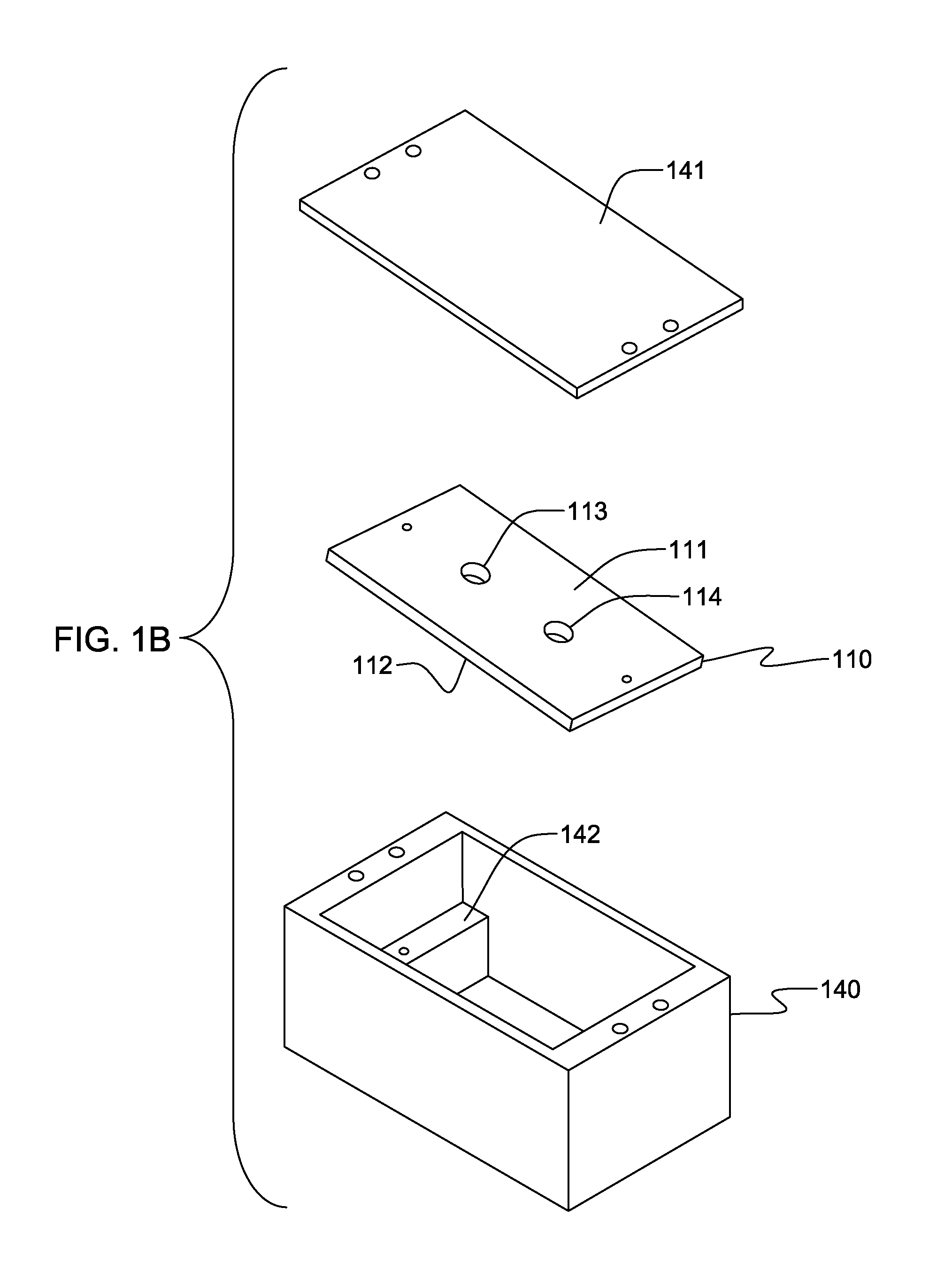
A drainage system is provided for draining liquid accidentally spilled on a casing having a plurality of pushbuttons on a surface of the casing. An electronic apparatus may comprise a casing and a drainage system. The drainage system may be connected with the casing. The drainage system may include a liquid collecting basin, a drainage exit, and a liquid passageway. The liquid passageway may have a capillary surface and may lead the liquid from the liquid collecting basin to the drainage exit.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Reconfigurable, non-oscillating liquid lens and imaging systems
ActiveUS8564884B2Facilitates adjusting configurationOvercomes shortcomingOptical articlesLensCamera lensActuator
A non-oscillating liquid lens and imaging system and method employing the lens are provided. The liquid lens includes a substrate with a channel opening extending through the substrate. A liquid lens drop is held within the channel and is sized with a first droplet portion, including a first capillary surface, protruding away from a first substrate surface, and a second droplet portion, including a second capillary surface, protruding away from a second substrate surface. The liquid lens further includes an enclosure at least partially surrounding the substrate, and which includes a chamber. The liquid lens drop resides within the chamber, and the liquid lens includes a second liquid disposed within the chamber in direct or indirect contact with the liquid lens drop, and an actuator which facilitates adjusting configuration of the liquid lens drop within the channel, and thus, a focal distance of the liquid lens.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Preparation method of silicate glass hollow fiber membrane
ActiveCN102688702AEvenly distributedMeet the use requirementsSemi-permeable membranesParaffin waxEtching
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silicate glass hollow fiber membrane, which comprises the following steps: mixing and melting liquid paraffin and solid paraffin, and putting a silicate glass capillary into the melt to coat a paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface; attaching sodium chloride particles with a certain particle size range onto the paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface, and immersing the glass capillary into water until the sodium chloride particles are completely dissolved, thereby forming a porous structure on the paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface; immersing the glass capillary with a porous paraffin layer on the surface into a 5-30 wt% HF water solution to perform etching, thereby obtaining pores with pore sizes of 5-100 mu m on the silicate glass capillary surface; and calcining the glass capillary at 300-600 DEG C to lose the paraffin layer on the surface by burning, thereby finally obtaining the silicate glass hollow fiber membrane. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, has the advantage of low technical cost, and can obtain the silicate glass hollow fiber membrane with the surface pore sizes of 5-100 mu m.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
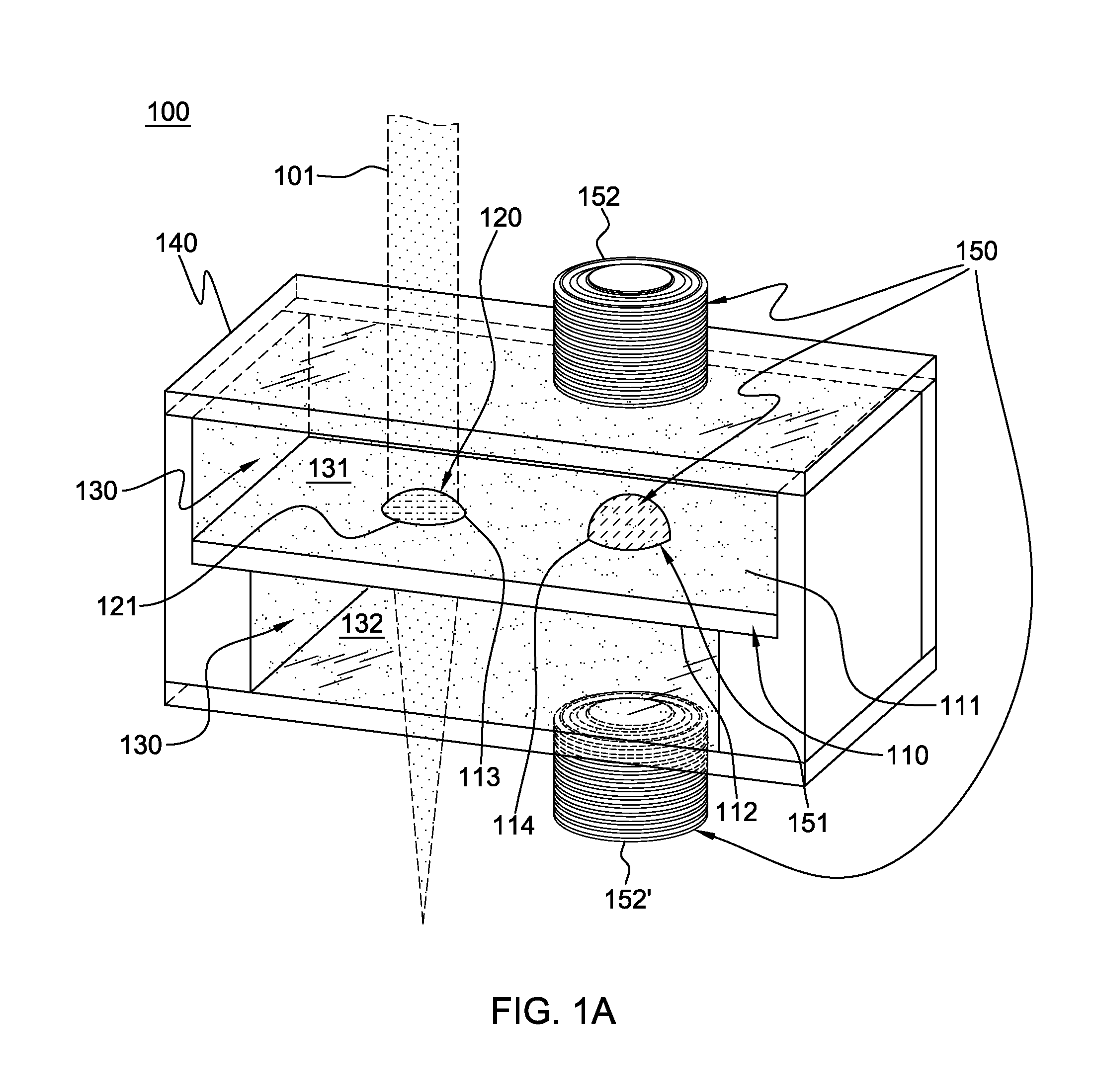
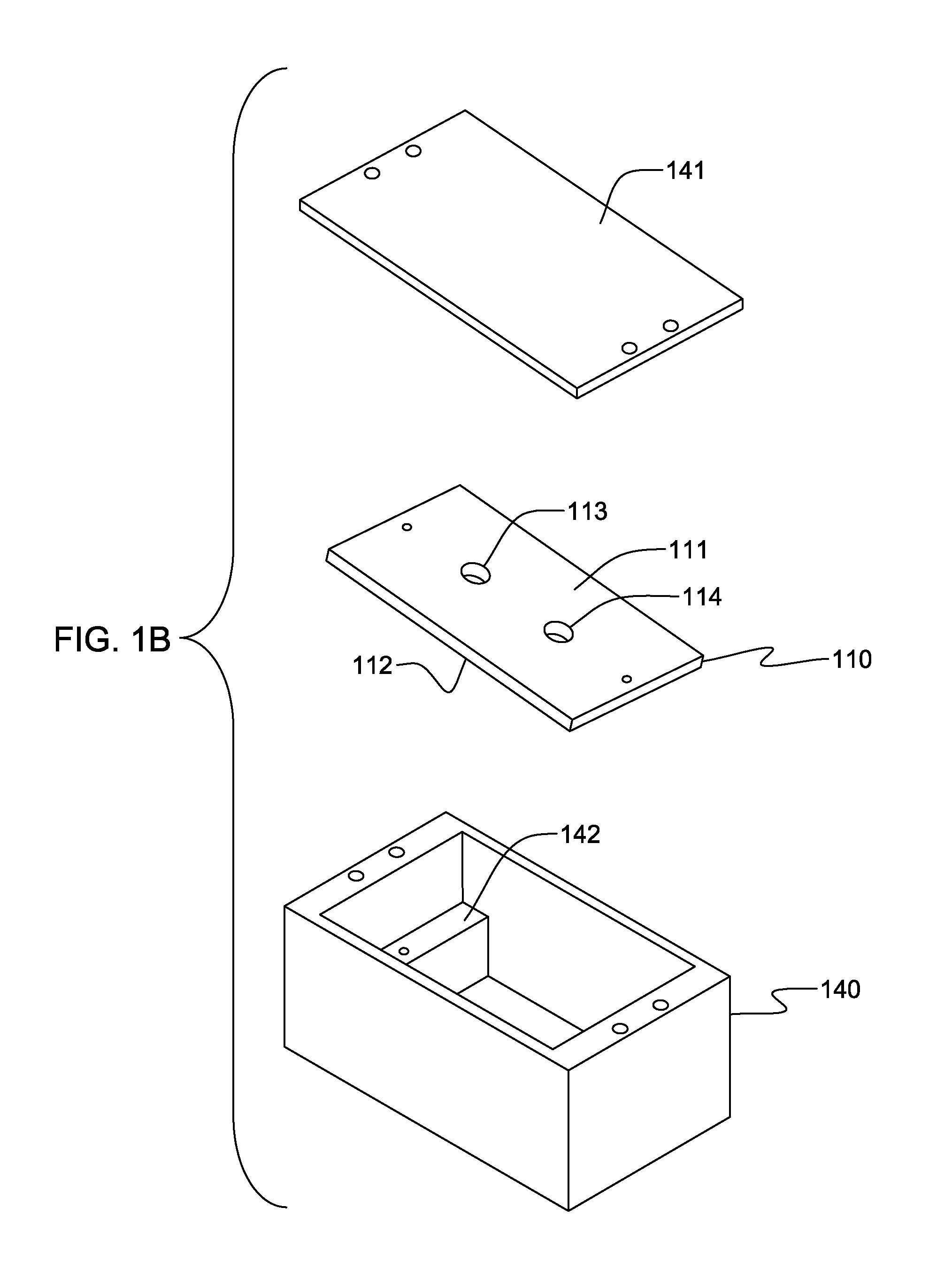
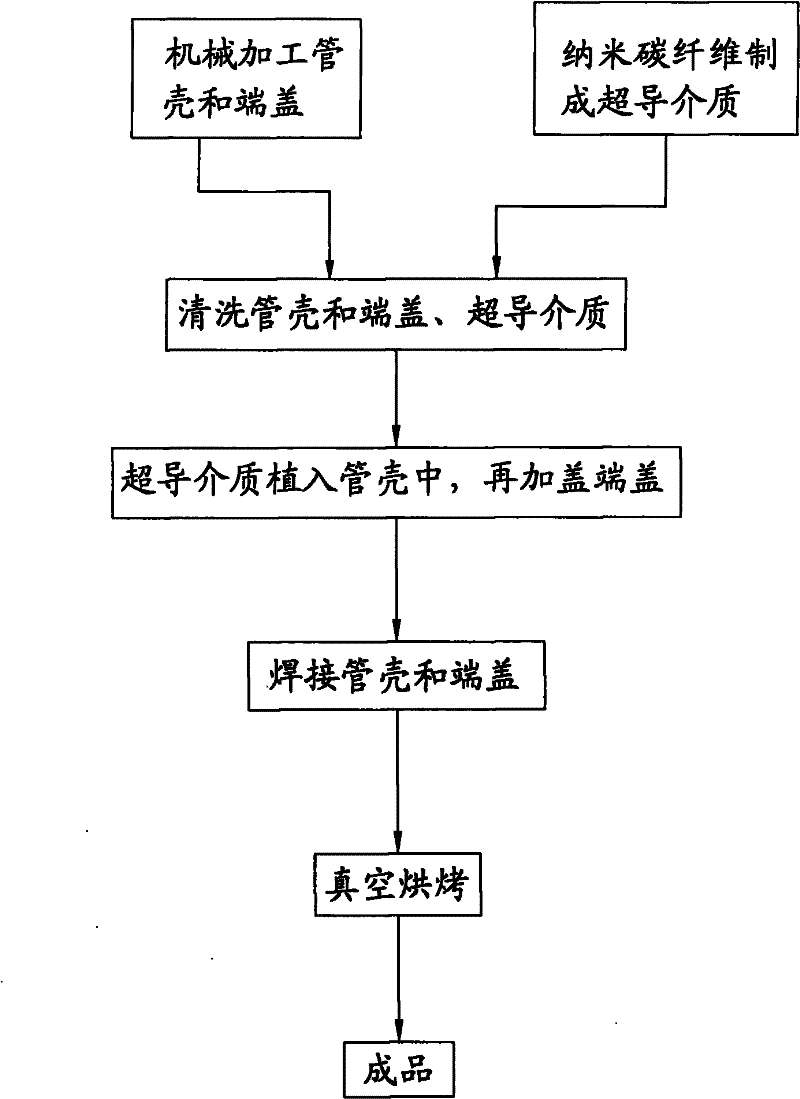
Nanometer carbon fiber vacuum superconducting heat pipe and manufacturing method thereof
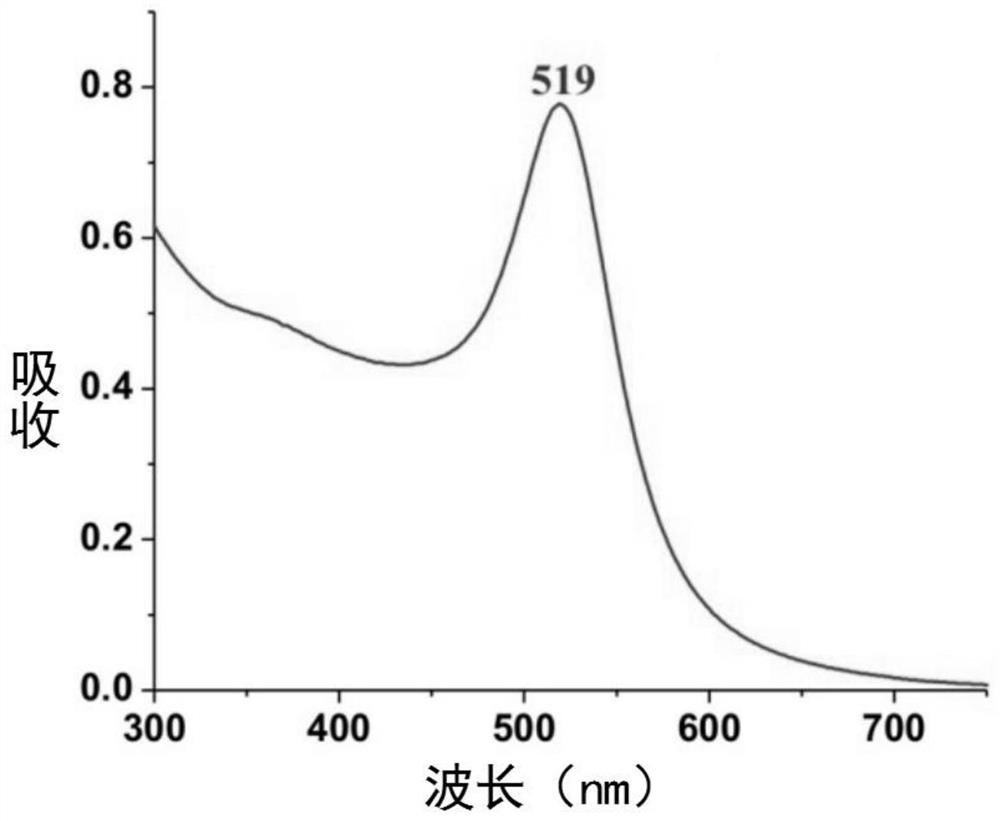
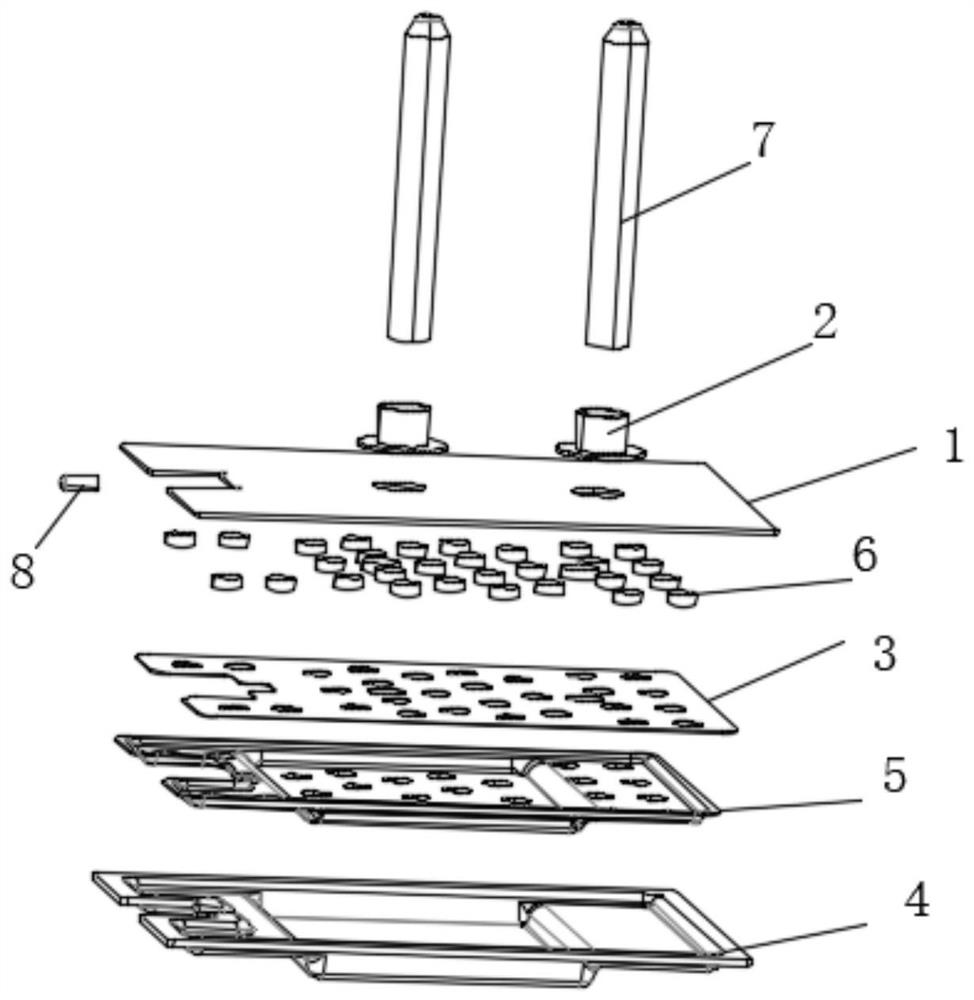
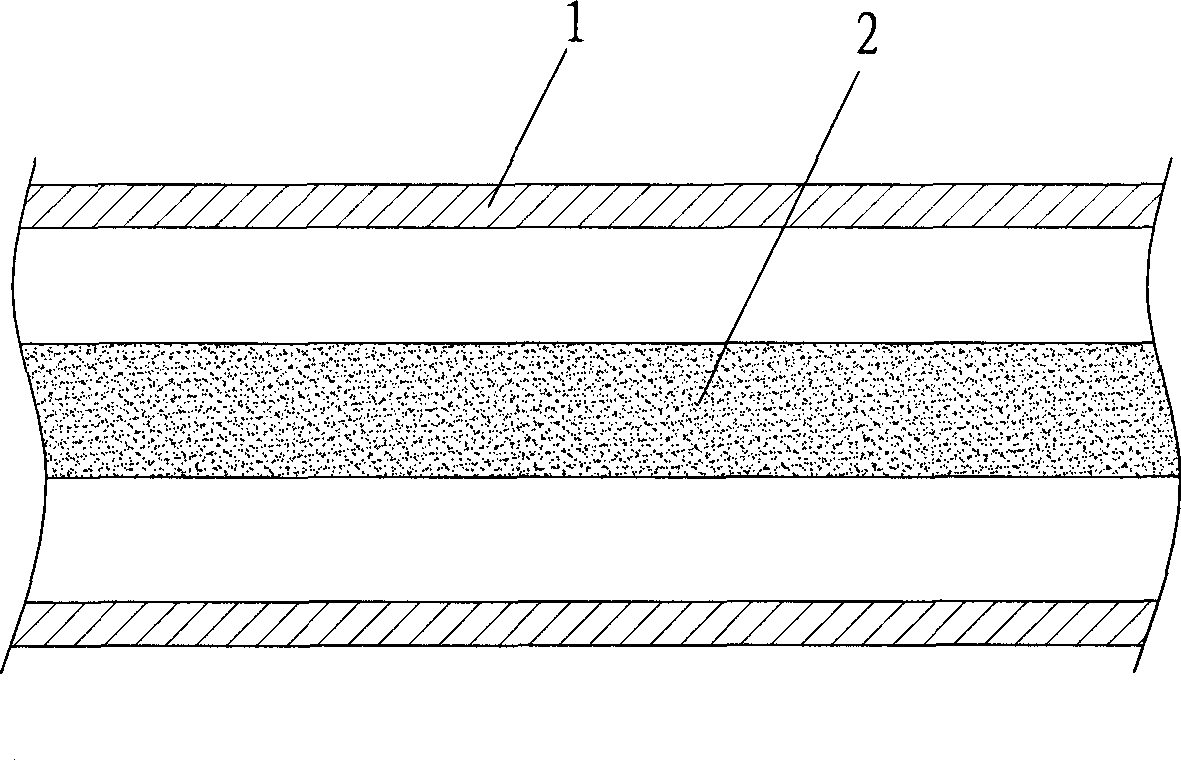
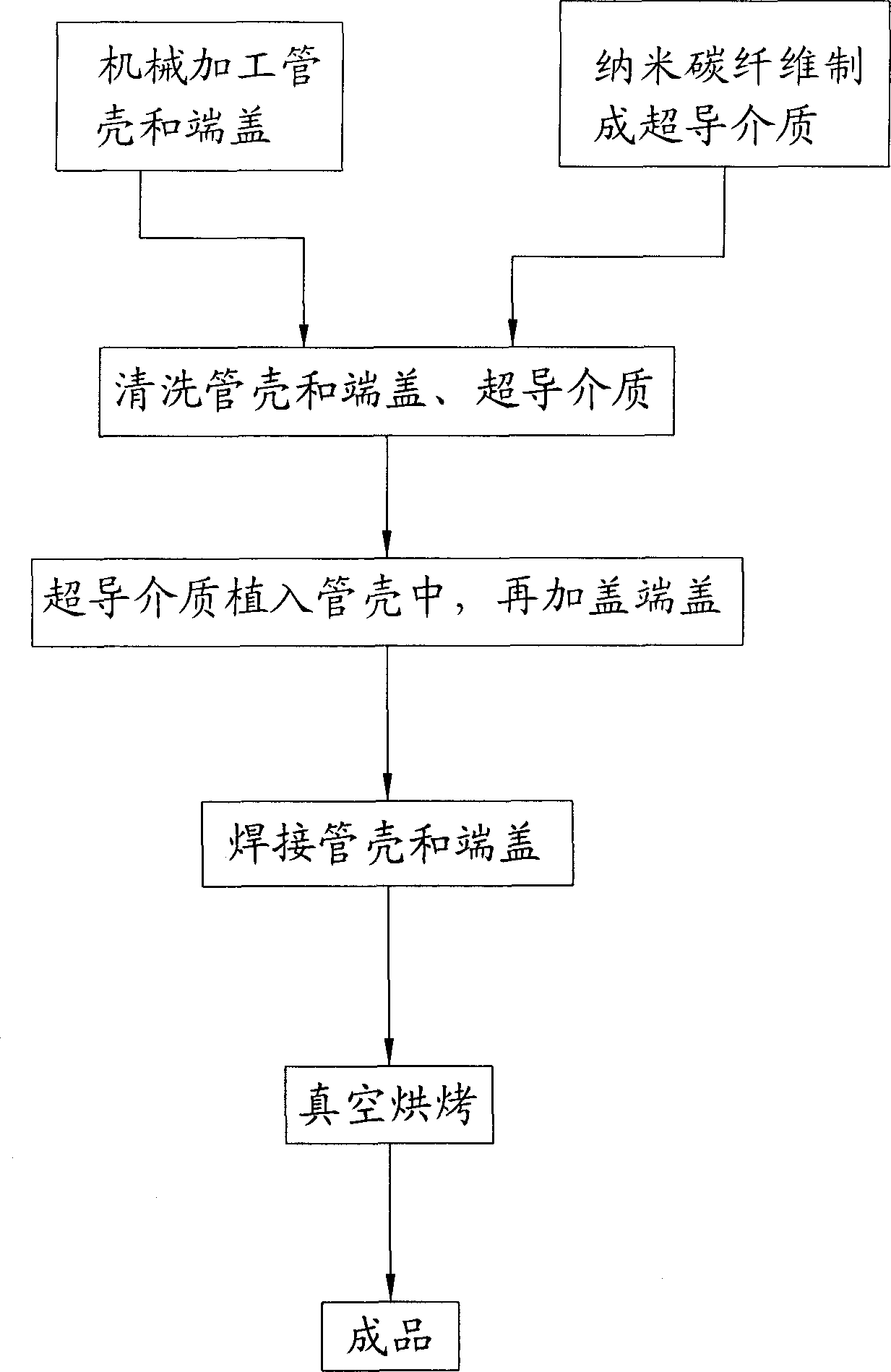
The invention discloses a nanometer carbon fiber vacuum superconducting heat pipe which comprises a superconducting medium prepared from a vacuum pipe and nanometer carbon fibers, wherein the vacuum pipe is formed by sealing a pipe shell and an end cover; and the superconducting medium is implanted in the sealed vacuum pipe. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly machining the pipe shell and end cover of the vacuum pipe, and manufacturing the superconducting medium by adopting the nanometer carbon fibers; then cleaning, scrubbing and dedusting the pipe shell, the end cover and the superconducting medium; then implanting the superconducting medium into the pipe shell, and capping the end cover; then welding the pipe shell and the end cover, checking whether the vacuum pipe leaks air, removing the air in the vacuum pipe, and sealing the vacuum pipe; and finally carrying out vacuum roasting, and carrying out dehydration and deoxidation treatment on the capillary surface for a heat pipe assembly at the high temperature of 200+ / -10 DEG C under the vacuum environment, thus the finished product is obtained. According to the invention, because the heat transfer medium is composed of the nanometer carbon fibers, under the stimulation of the external temperature difference, heat is transferred by virtue of the high-frequency vibration of macroparticles, and the heat pipe has the advantages of no phase change, extremely small heat resistance and long service life.
Owner:XIAMEN GREENER OPTOELECTRONICS
Heat conductor with ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure
InactiveCN104422324ANot easy to dent contactIncrease the areaIndirect heat exchangersEvaporationEngineering
The invention provides a heat conductor with an ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure. The heat conductor comprises a flat plate type hollow shell and the capillary structure, wherein the capillary structure is arranged in the shell and is in contact with the inner wall of the shell, the capillary structure is a thin plate type body and is provided with a flat surface and an extrusion surface which is opposite to the flat surface, the flat surface is attached to the inner wall of the shell, the extrusion surface is provided with a plurality of long narrow concave surfaces which are arranged at intervals, a steam flow passage is respectively formed in the shell by each concave surface, and a long narrow capillary organization communication area is formed between all concave surfaces and the flat surface of the capillary structure. According to the heat conductor with the ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure, provided by the invention, the thinned capillary structure can be formed on the inner wall of the heat conductor, thus enough space is enabled to be maintained by an air flow passage in an ultra-thin heat conductor for carrying out heat exchange of evaporation and condensation after the heat conductor is pressed into the ultra-thin heat conductor, due to an inner supporting structure which is maximum in capillary surface area and truncation transmission surface and is better in strength, a heat tube does not easily concave, the contact heat resistance is smaller, and the purpose of enabling the heat conductor to be ultra-thin can be achieved.
Owner:白豪
Capillary surface plasmon resonance sensor
InactiveCN102608075AStructure miniaturizationLow costScattering properties measurementsPrismSurface plasmon resonance imaging
The invention discloses a capillary surface plasmon resonance sensor, which comprises an LED (light emitting diode) light source, a collimating lens, a telescopic system, a polarizing film, a capillary to double as a flow cell, and a CCD (charge coupled device) detector; an anti-reflection film is plated at the outer surface of the capillary, and a metal thin film is plated at the inner surface; and the polarized light obtained by the polarizing film is refracted into the capillary by the anti-reflection film arranged at the outer surface of the capillary, and then reflected into the CCD detector by the metal thin film arranged at the inner surface of the capillary. According to the capillary surface plasmon resonance sensor provided by the invention, the conversion of beam pattern and the excitation of SPR (surface plasma resonance) are achieved by the capillary plated with the metal thin film at the inner surface thereof, the traditional prism coupling mode is replaced, the capillary is synchronously to double as the flow cell, and namely the sensor is integrated with the flow cell; and in this way, the structure of the sensor system is smaller, the cost is lower, and the use is more convenient and more reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Heat tube with ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure
InactiveCN104422323AAchieve ultra-thin effectNot easy to dentIndirect heat exchangersEvaporationEngineering
The invention discloses a heat tube with an ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure. The heat tube comprises a shell and the capillary structure, wherein the capillary structure is arranged in the shell and comprises heat exchange areas and a liquid transmission passage which is connected between the heat exchange areas, and each heat exchange area is divided into an evaporation part and a condensation part; each heat exchange area is respectively provided with a flat surface and an extrusion surface which is opposite to the flat surface, a plurality of long narrow concave surfaces which are arranged at intervals are formed on the extrusion surfaces, steam flow passages are formed in the shell by the concave surfaces, long narrow capillary organization communication areas are formed by the concave surfaces and the flat surfaces, and hollow areas which are located at two sides of the liquid transmission passage are formed in the shell between the heat exchange areas. According to the heat tube with the ultra-thin flat plate type capillary structure, disclosed by the invention, enough space is provided for carrying out heat exchange of evaporation and condensation, due to an inner supporting structure which is maximum in capillary surface area and truncation transmission surface and is better in strength, the heat tube does not easily concave, the contact heat resistance is smaller, and the effect of enabling a heat conductor to be ultra-thin can be achieved.
Owner:白豪
Polymers for separation of biomolecules by capillary electrophoresis
InactiveUS7045048B2High precisionConstant of suppressionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementSolubilityPolynucleotide
The invention provides uncharged water-soluble silica-adsorbing polymers for suppressing electroendoosmotic flow and to reduce analyte-wall interactions in capillary electrophoresis. In one aspect of the invention, one or more of such polymers are employed as components of a separation medium for the separation of biomolecules, such as polynucleotides, polysaccharides, proteins, and the like, by capillary electrophoresis. Generally, such polymers are characterized by (i) water solubility over the temperature range between about 20° C. to about 50° C., (ii) concentration in a separation medium in the range between about 0.001% to about 10% (weight / volume), (iii) molecular weight in the range of about 5×103 to about 1×106 daltons, and (iv) absence of charged groups in an aqueous medium having pH in the range of about 6 to about 9. In one embodiment, polymers of the invention are selected from the group consisting of polylactams, such as polyvinylpyrrolidone; N,N-disubstituted polyacrylamides; and N-substituted polyacrylamides. In accordance with the method of the invention, a sufficient amount of polymer adsorbs to the capillary surface to establish a zone of high viscosity that shields the analyte from the wall and impedes the movement of an electrical double layer under an electric field.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods and compositions for performing molecular separations
The present invention provides methods of electrophoretically separating macromolecular species, as well as compositions and systems useful in carrying out such methods. Specifically, the methods of the present invention comprise providing a substrate that has at least a first capillary channel disposed therein. The surface of the channel has a first surface charge associated therewith, and is filled with a water soluble surface adsorbing polymer solution that bears a net charge that is the same as the charge on the capillary surface.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Polymers for separation of biomolecules by capillary electrophoresis
InactiveUS20060137982A1High precisionConstant of suppressionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementSolubilitySilicon dioxide
The invention provides uncharged water-soluble silica-adsorbing polymers for suppressing electroendoosmotic flow and to reduce analyte-wall interactions in capillary electrophoresis. In one aspect of the invention, one or more of such polymers are employed as components of a separation medium for the separation of biomolecules, such as polynucleotides, polysaccharides, proteins, and the like, by capillary electrophoresis. Generally, such polymers are characterized by (i) water solubility over the temperature range between about 20° C. to about 50° C., (ii) concentration in a separation medium in the range between about 0.001% to about 10% (weight / volume), (iii) molecular weight in the range of about 5×103 to about 1×106 daltons, and (iv) absence of charged groups in an aqueous medium having pH in the range of about 6 to about 9. In one embodiment, polymers of the invention are selected from the group consisting of polylactams, such as polyvinylpyrrolidone; N,N-disubstituted polyacrylamides; and N-substituted polyacrylamides. In accordance with the method of the invention, a sufficient amount of polymer adsorbs to the capillary surface to establish a zone of high viscosity that shields the analyte from the wall and impedes the movement of an electrical double layer under an electric field.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Groove slit water channel
A drainage system is provided for draining liquid accidentally spilled on a casing having a plurality of pushbuttons on a surface of the casing. An electronic apparatus may comprise a casing and a drainage system. The drainage system may be connected with the casing. The drainage system may include a liquid collecting basin, a drainage exit, and a liquid passageway. The liquid passageway may have a capillary surface and may lead the liquid from the liquid collecting basin to the drainage exit.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrate based on unilateral multi-window capillary tube as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111678903AReduce lossGuaranteed sensitivityRaman scatteringSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyPesticide residue
The invention provides a single-side multi-window capillary surface enhanced Raman spectrum substrate which comprises a capillary, windows are formed in the side wall of the capillary, and the inner side wall of the capillary is modified with a noble metal nanoparticle layer. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the surface enhanced Raman spectrum substrate, and detection of drug poisons, pesticide residues, pigments, environmental pollutants, illegal additives and the like can be achieved. According to the surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrateof the unilateral multi-window capillary tube, light loss is greatly reduced, and a local electric field generated by incident light on the surface is enhanced to the maximum extent under the actionof planarization of the single-layer noble metal nanoparticles and coverage of signals of the capillary tube, so that efficient Raman signals can be obtained. Therefore, the sensitivity and the stability of SERS detection are ensured.
Owner:陈简一
Integrated 3D uniform temperature plate and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN111811307AImprove heat transfer efficiencyImprove yieldIndirect heat exchangersHeat exchange apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of uniform temperature plates, in particular to an integrated 3D uniform temperature plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The integrated 3D uniform temperature plate comprises a second plate body, the second plate body is in a groove shape, an opening in the upper end of the second plate body is covered with a first plate body and is welded and sealed, a first capillary plate and a second capillary plate are arranged in a groove-shaped inner cavity of the second plate body in a stacked mode, a plurality of inserting holes are formed in the outer wall of the first capillary plate and the outer wall of the second capillary plate, supporting columns are connected into the inserting holes in an inserted mode, a pair of heat pipe inserting holesis formed in the upper end face of the first plate body, flange rings are welded to the heat pipe inserting holes, and heat pipes are connected into the flange rings in an inserted mode. According tothe integrated 3D uniform temperature plate and the manufacturing method thereof, the problems that capillary surface cutoff occurs when the uniform temperature plate and a heat pipe are combined andlong and short pipes (different insertion depths) appear in the combination process of the heat pipe and an uniform temperature plate body in production engineering are solved, the heat conduction efficiency after the uniform temperature plate and the heat pipe are combined into a whole can be greatly improved, and the product yield and the heat dissipation effect of a product are improved.
Owner:陈豪
Nanometer carbon fiber vacuum superconducting heat pipe and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a nanometer carbon fiber vacuum superconducting heat pipe which comprises a superconducting medium prepared from a vacuum pipe and nanometer carbon fibers, wherein the vacuum pipe is formed by sealing a pipe shell and an end cover; and the superconducting medium is implanted in the sealed vacuum pipe. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly machining the pipe shell and end cover of the vacuum pipe, and manufacturing the superconducting medium by adopting the nanometer carbon fibers; then cleaning, scrubbing and dedusting the pipe shell, the end cover and the superconducting medium; then implanting the superconducting medium into the pipe shell, and capping the end cover; then welding the pipe shell and the end cover, checking whether the vacuum pipe leaks air, removing the air in the vacuum pipe, and sealing the vacuum pipe; and finally carrying out vacuum roasting, and carrying out dehydration and deoxidation treatment on the capillary surface for a heat pipe assembly at the high temperature of 200+ / -10 DEG C under the vacuum environment, thus the finished product is obtained. According to the invention, because the heat transfer medium is composed of the nanometer carbon fibers, under the stimulation of the external temperature difference, heat is transferred by virtue of the high-frequency vibration of macroparticles, and the heat pipe has the advantages of no phase change, extremely small heat resistance and long service life.
Owner:XIAMEN GREENER OPTOELECTRONICS
Pinned-contact oscillating liquid lens and imaging system
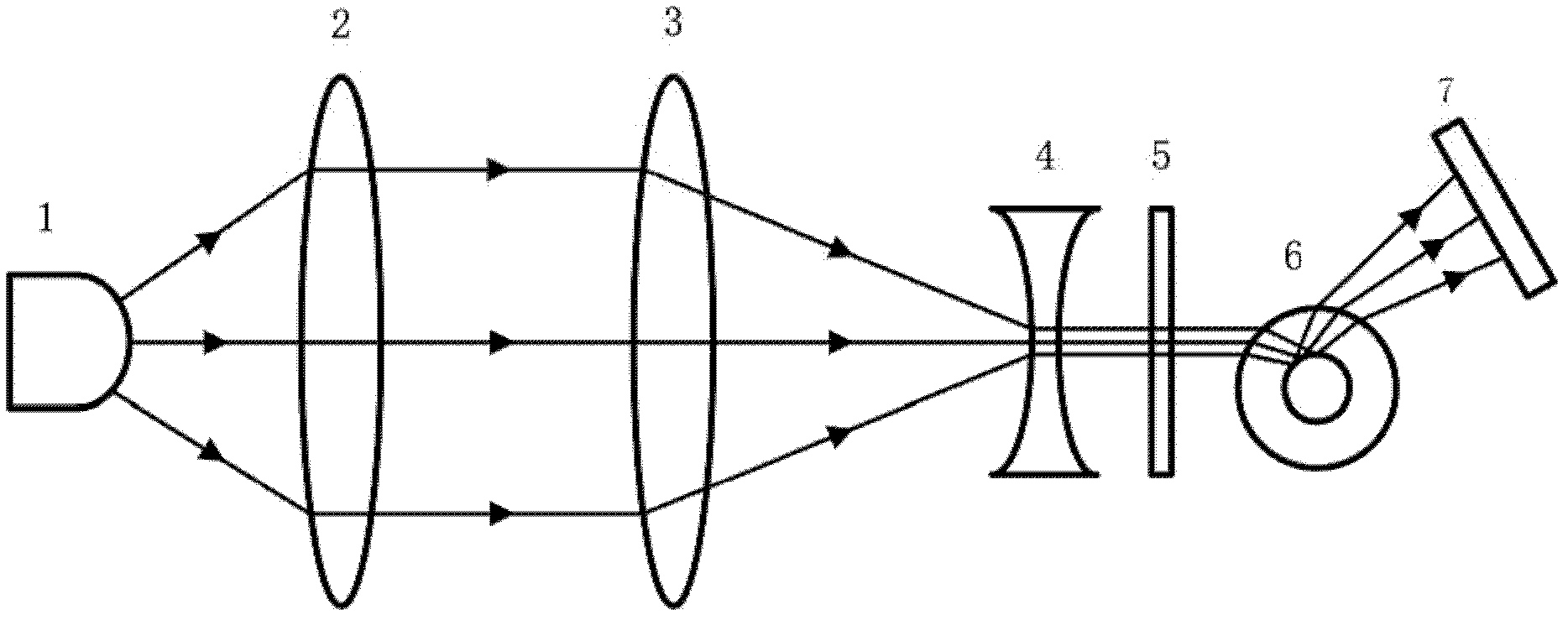
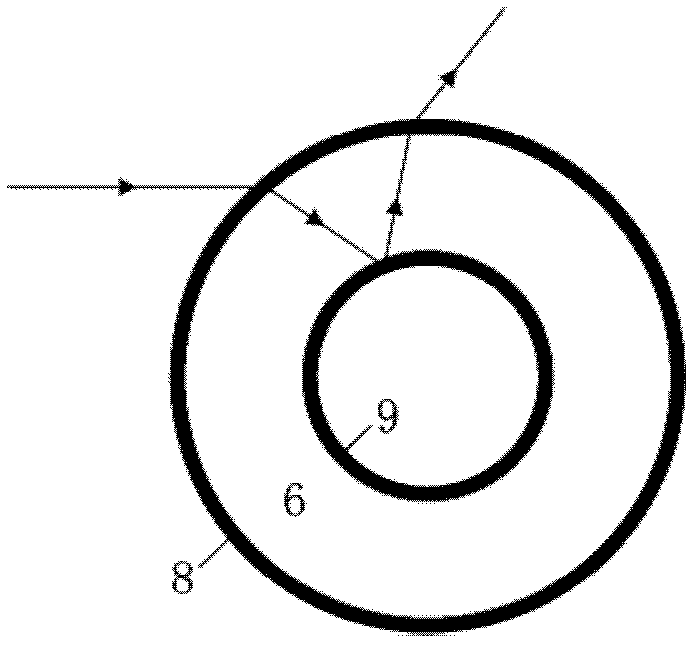
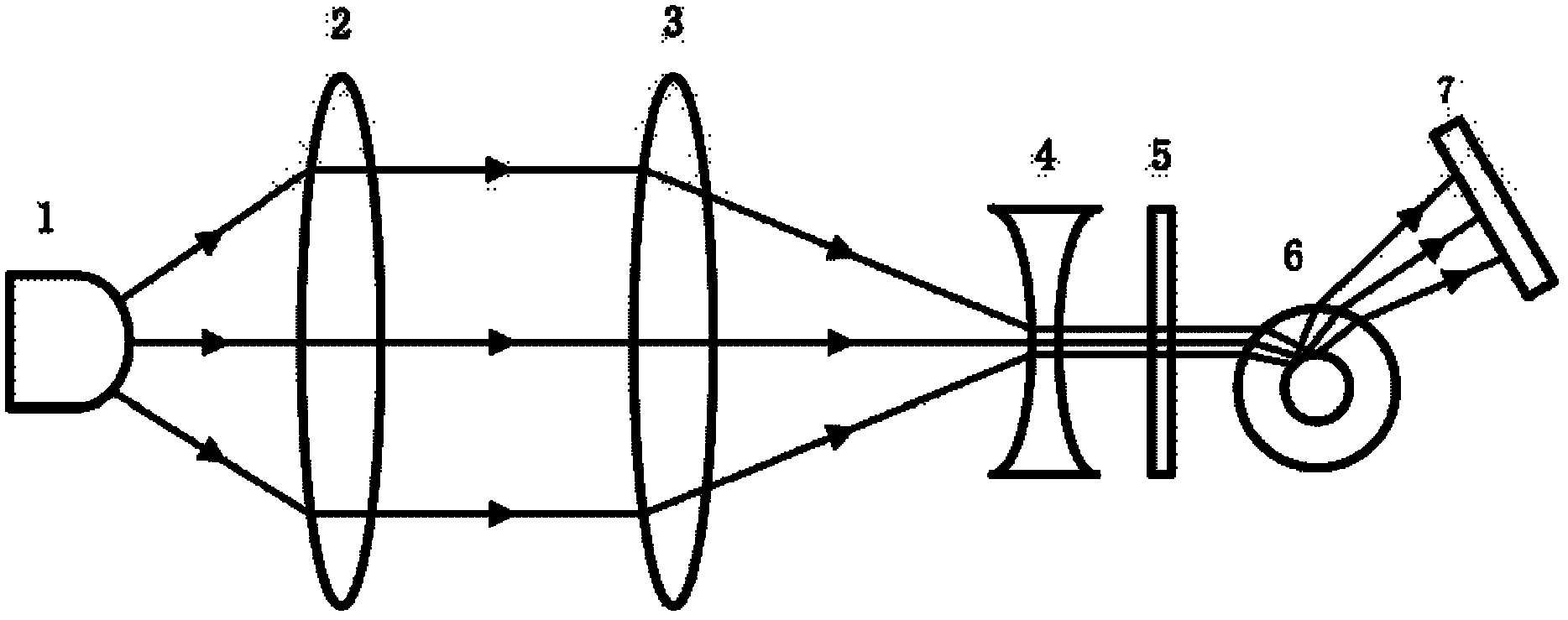
ActiveUS8148706B2Television system detailsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsCapillary surfaceLiquid lens
An oscillating liquid lens and imaging system and method employing the lens are provided. The liquid lens includes a substrate with a channel opening extending therethrough between a first and second surface. A liquid drop is disposed within the channel and is sized with a first droplet portion, including a first capillary surface, protruding away from the first surface, and a second droplet portion, including a second capillary surface, protruding away from the second surface. The liquid lens further includes an oscillator operatively coupled to either the first droplet portion or the second droplet portion for oscillating the liquid drop within the channel. The imaging system, in addition to the oscillating liquid lens, also includes an image sensor coupled to an image path which passes through the first and second droplet portions for capturing one or more images through the oscillating liquid drop.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
A kind of preparation method of silicate glass hollow fiber membrane
ActiveCN102688702BEvenly distributedMeet the use requirementsSemi-permeable membranesParaffin waxEtching
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silicate glass hollow fiber membrane, which comprises the following steps: mixing and melting liquid paraffin and solid paraffin, and putting a silicate glass capillary into the melt to coat a paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface; attaching sodium chloride particles with a certain particle size range onto the paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface, and immersing the glass capillary into water until the sodium chloride particles are completely dissolved, thereby forming a porous structure on the paraffin layer on the glass capillary surface; immersing the glass capillary with a porous paraffin layer on the surface into a 5-30 wt% HF water solution to perform etching, thereby obtaining pores with pore sizes of 5-100 mu m on the silicate glass capillary surface; and calcining the glass capillary at 300-600 DEG C to lose the paraffin layer on the surface by burning, thereby finally obtaining the silicate glass hollow fiber membrane. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, has the advantage of low technical cost, and can obtain the silicate glass hollow fiber membrane with the surface pore sizes of 5-100 mu m.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Process and system for separating finely aerosolized elemental mercury from gaseous streams
ActiveUS9504946B2Improve removal efficiencyDegree of filtration efficiencyCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationPlatinumGravitational force
A method and apparatus are provided for separating droplets of finely aerosolized elemental mercury from a fluid stream in which the droplets are dispersed, particularly a gaseous stream. In the method, a precious metal wire capillary surface or precious metal-coated wire capillary surface is contacted with the gaseous stream, causing the aerosolized droplets to deposit on the capillary surface and by capillary action to coalesce with other of such droplets. The surface is oriented to allow the mercury to flow by gravitational forces and capillary action to the lowermost portions of the surface, where it accumulates and can be collected. Metallic capillary surfaces comprised of finely braided strands of silver, gold, palladium, platinum, or rhodium wire, or wire coated with one or more of these metals, are particularly preferred.
Owner:MYCELX TECH CORP
Sol-gel chitosan grafting cyclodextrin capillary electrochromatography open tubular column
InactiveCN103055542BGood adsorption and separation performanceExcellent chromatographic performanceOther chemical processesComponent separationCyclodextrinCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a sol-gel chitosan grafting cyclodextrin capillary electrochromatography open tubular column as well as a preparation method and application thereof, which belongs to the field of a chromatographic technology. The preparation method of the sol-gel chitosan grafting cyclodextrin capillary electrochromatography open tubular column comprises the following steps: (1) capillary pretreatment; (2) capillary surface silanization; (3) sol-gel preparation; and (4) inner capillary wall decoration. A stationary phase of the capillary open tubular column is chitosan grafting cyclodextrin sol-gel. The sol-gel chitosan grafting cyclodextrin capillary electrochromatography open tubular column provided by the invention combines the identification property of cyclodextrin and the adsorption property of chitosan. An obtained coating has the characteristics of firmness in bonding, stable property and good repeatability, and can be used within a wider pH (Potential of Hydrogen) range; the direction and the size of electroosmotic flow of the coating can be controlled by adjusting a pH value of a mobile phase; and the obtained coating has a good separation effect on Xanthopterin isomers and phenoxy carboxylic acid herbicides.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
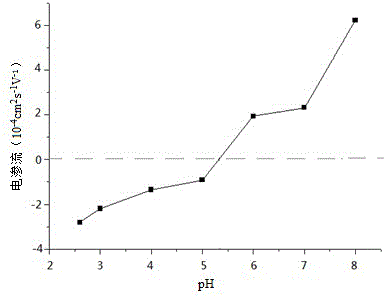
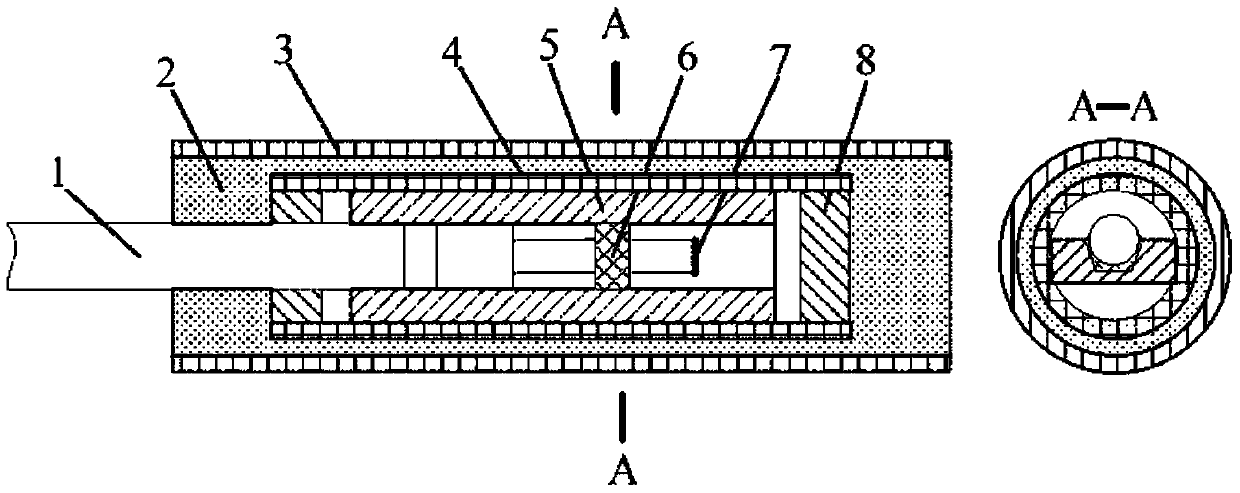
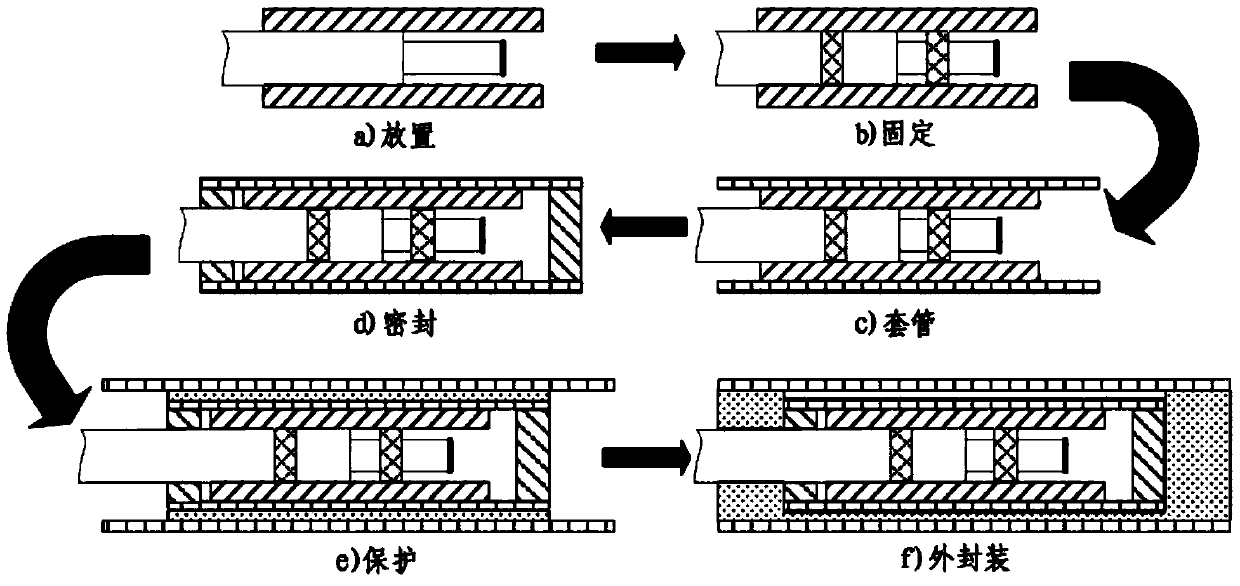
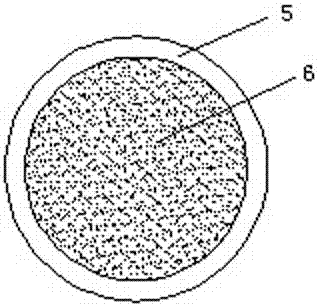
A kind of optical fiber end face reflector packaging method
ActiveCN104950395BSimple structureImprove reliabilityCoupling light guidesEngineeringInstrument transformer
The present invention specifically relates to a packaging method for an optical fiber end face reflector of a reflective optical fiber current transformer, comprising the following steps: (1.1) placement: the optical fiber end face reflector is horizontally placed in a quartz plate groove; (1.2) fixing: in Apply the first optical fiber fixing adhesive to the left side of the anti-reflection film and the right side of the left port of the quartz plate, and let it stand after heating and curing; (1.3) Sleeve and sealing: put the quartz plate into the quartz capillary, and coat the ports on both sides. The second type of optical fiber fixing adhesive is heated and cured and then left to stand; (1.4) Drying: put the quartz capillary in a high-temperature drying oven to dry and then leave to stand; (1.5) Protection and outer packaging: evenly coat the surface of the capillary with packaging glue , externally covered with a toughened glass tube; (1.6) temperature cycle; (1.7) use after standing. The structure obtained by the optical fiber end mirror packaging method has the outstanding advantages of simple structure, small volume, good sealing performance, high reliability and long-term use stability.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
A capillary tube, an irrigation system using the capillary tube for water delivery, and a warehouse dehumidification device using the capillary tube
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Glass capillary surface antibody fixing method
PendingCN110938147AIncrease surface areaIncrease capacityCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesMaterial analysisAntiendomysial antibodiesCapillary Tubing
The invention discloses a glass capillary surface antibody fixing method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, carrying out modifying processing; to be specific, modifying the surface of a glass capillary; S2, coating an antibody; to be specific, fixing a diluted coating antibody solution to the modified glass capillary tube; and S3, carrying out sealing; to be specific, sealing the glass capillary tube coated with the antibody in the S2. According to the invention, amination modification treatment is carried out on the solid-phase glass capillary and the unique structure of dendritic macromolecules is introduced into capillary inner wall modification, so that the surface of the glass capillary becomes uneven and the superficial area and capacity of the capillary are greatly increased to realize the good capacity of adsorbing protein. Therefore, a novel thought is provided for glass capillary surface antibody coating.
Owner:CHENGDU POLYTECH BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Coated Capillary Electrophoresis Tubes and System
InactiveUS20110064869A1Improve scalabilityHigh positive charge densityCoatingsSpecial surfacesAnalyteCapillary electrophoresis
The invention is directed to a capillary tube for electrophoresis that has a positively charged coating on the capillary inner surface that prevents positively charged analytes from adsorbing to the inner capillary surface. The capillary tube has an inner surface that is coated with a first polymer layer having a plurality of polymer groups comprising polyethylene imine, designated herein as (CH2CH2NH)X. The inner surface of the capillary typically has a second polymer layer covalently bonded to the first polymer layer. The invention includes a capillary tube where two or more than two polymer groups are covalently bonded to each other by a cross-linker. Also provided are an electrophoresis system the uses the coated capillary tubes, a method of performing electrophoresis that utilizes the coated capillary tubes, and a process for preparing the coated capillary tubes.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com