High optical efficiency CMOS image sensor
a high optical efficiency, image sensor technology, applied in the direction of basic electric elements, electrical equipment, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of achieve high optical inter-pixel optical isolation, and high fill factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
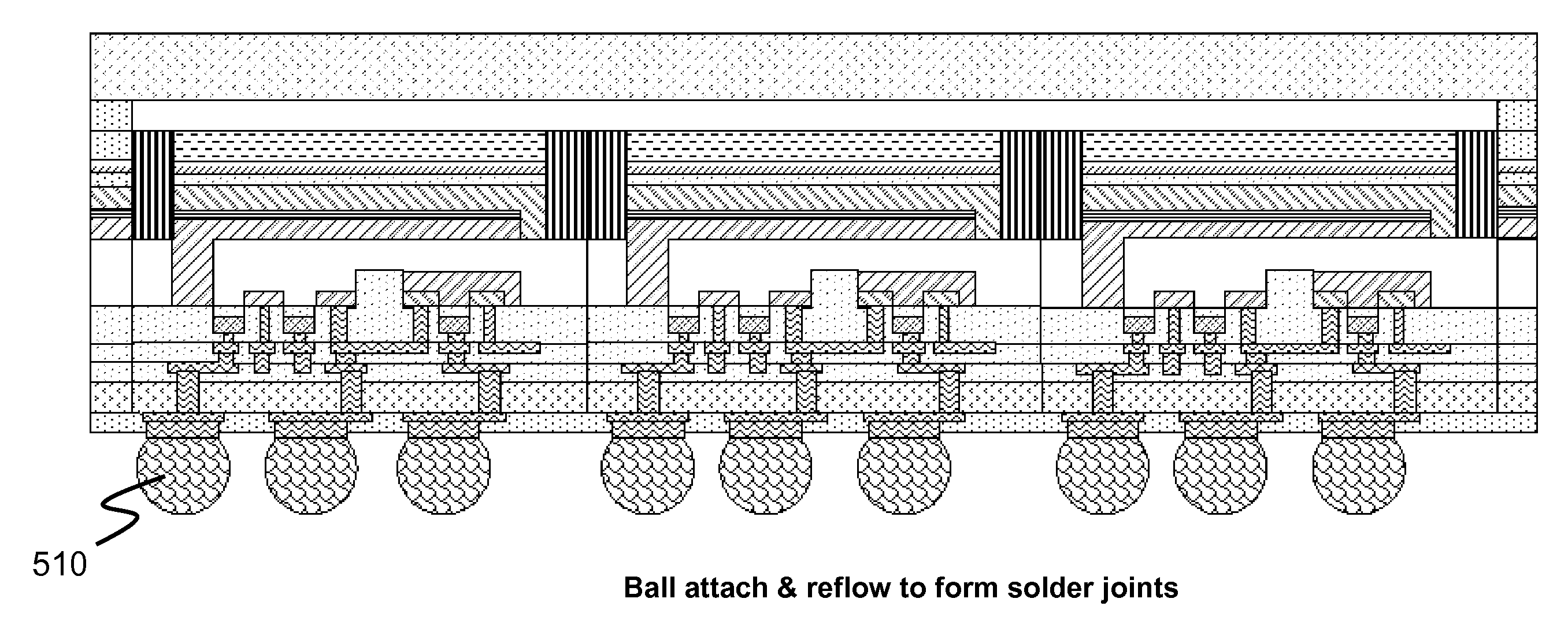
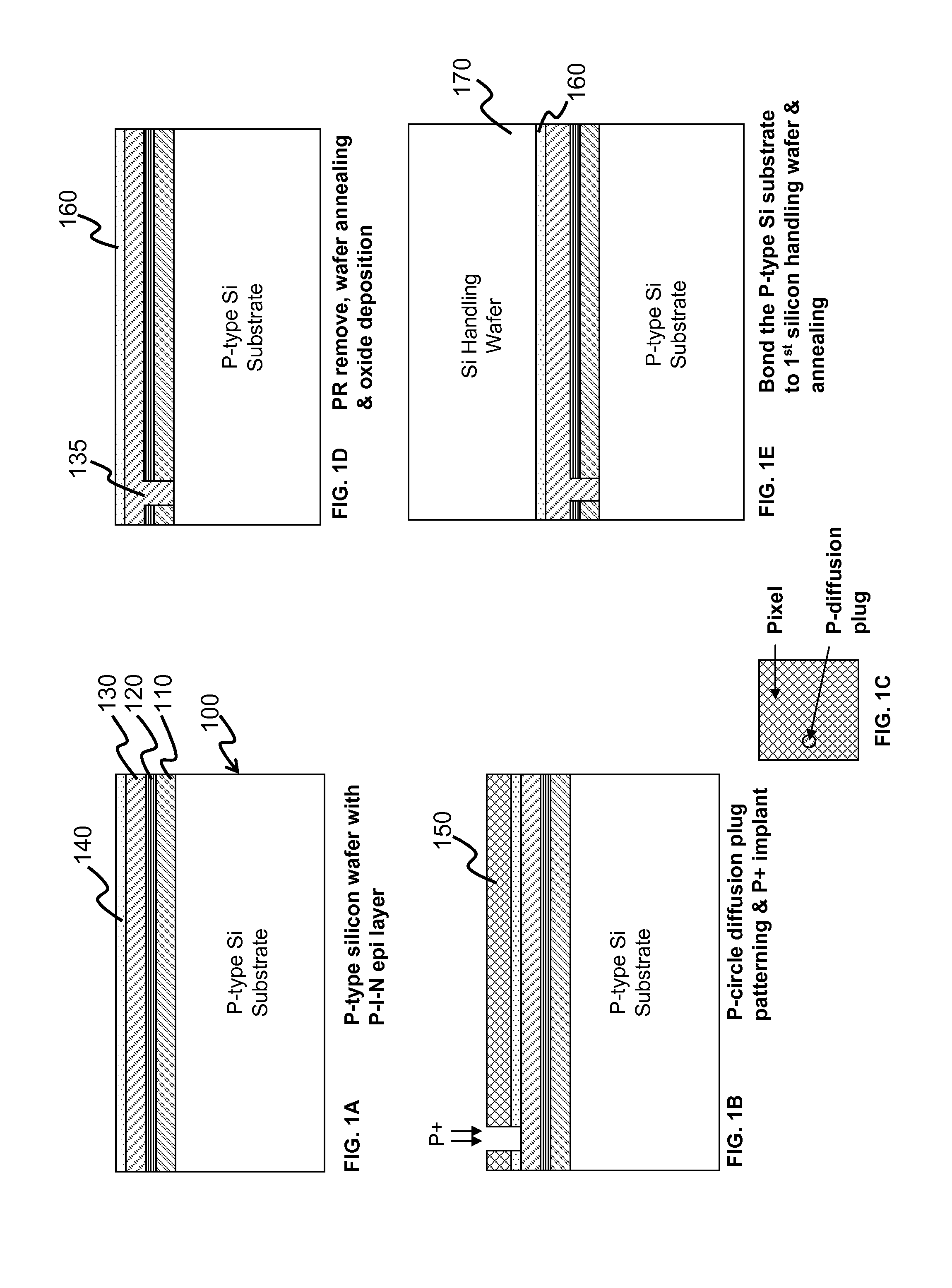
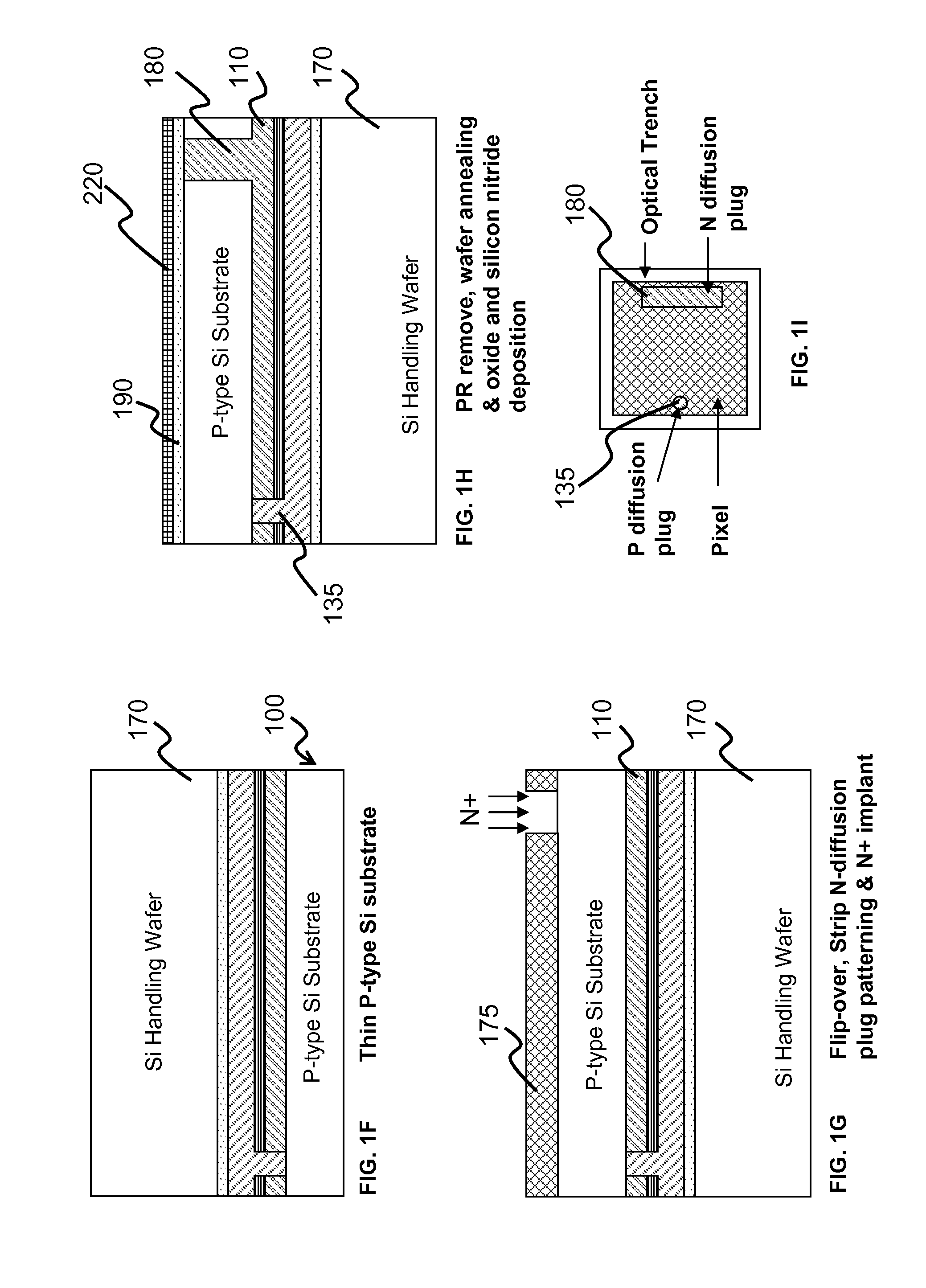
[0013]The fabrication of a CMOS image sensor having isolation grids is depicted with respect to the drawings in which FIG. 1A depicts a cross-sectional view of a p-doped silicon wafer 100 having a photodiode structure formed thereon. In this exemplary embodiment, the photodiode structure is an epitaxial p-i-n layer structure formed on the substrate; however, any photodiode structure can be used in the image sensor of the present invention. The n-layer (n-doped silicon) is designated as 110, the i-layer (intrinsic or non-doped silicon) as 120 and the p-layer (p-doped silicon) as 130. It is noted that all of the processes of the present invention rely on well-established CMOS fabrication techniques; therefore, detailed description of the process conditions is well-known to those of ordinary skill in the art. Any CMOS processing technique can be used to form the various layers and structures of the present invention.
[0014]A glass / SiO2 layer 140 is formed over the p-i-n structure. A pat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com