Anode for electrowinning and method for electrowinning using same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0054]A commercially available titanium plate (5 cm in length, 1 cm in width, 1 mm in thickness) was immersed and etched in a 10% oxalic acid solution at 90° C. for 60 minutes and then washed and dried. Next, prepared was an application liquid which was obtained by adding ruthenium trichloride trihydrate (RuCl3.3H2O) and tantalum pentachloride (TaCl5) to a butanol (n-C4H9OH) solution containing 6 vol % concentrated hydrochloric acid so that the molar ratio between ruthenium and tantalum is 30:70 and the total of ruthenium and tantalum is 50 g / L in terms of metal. This application liquid was applied to the titanium plate dried as mentioned above, dried at 120° C. for 10 minutes, and then thermally decomposed for 20 minutes in an electric furnace that was held at 260° C. This series of application, drying, and thermal decomposition was repeated five times in total in order to prepare an anode for electrowinning according to Example 1, the anode having a catalytic layer formed on the t...
example 2
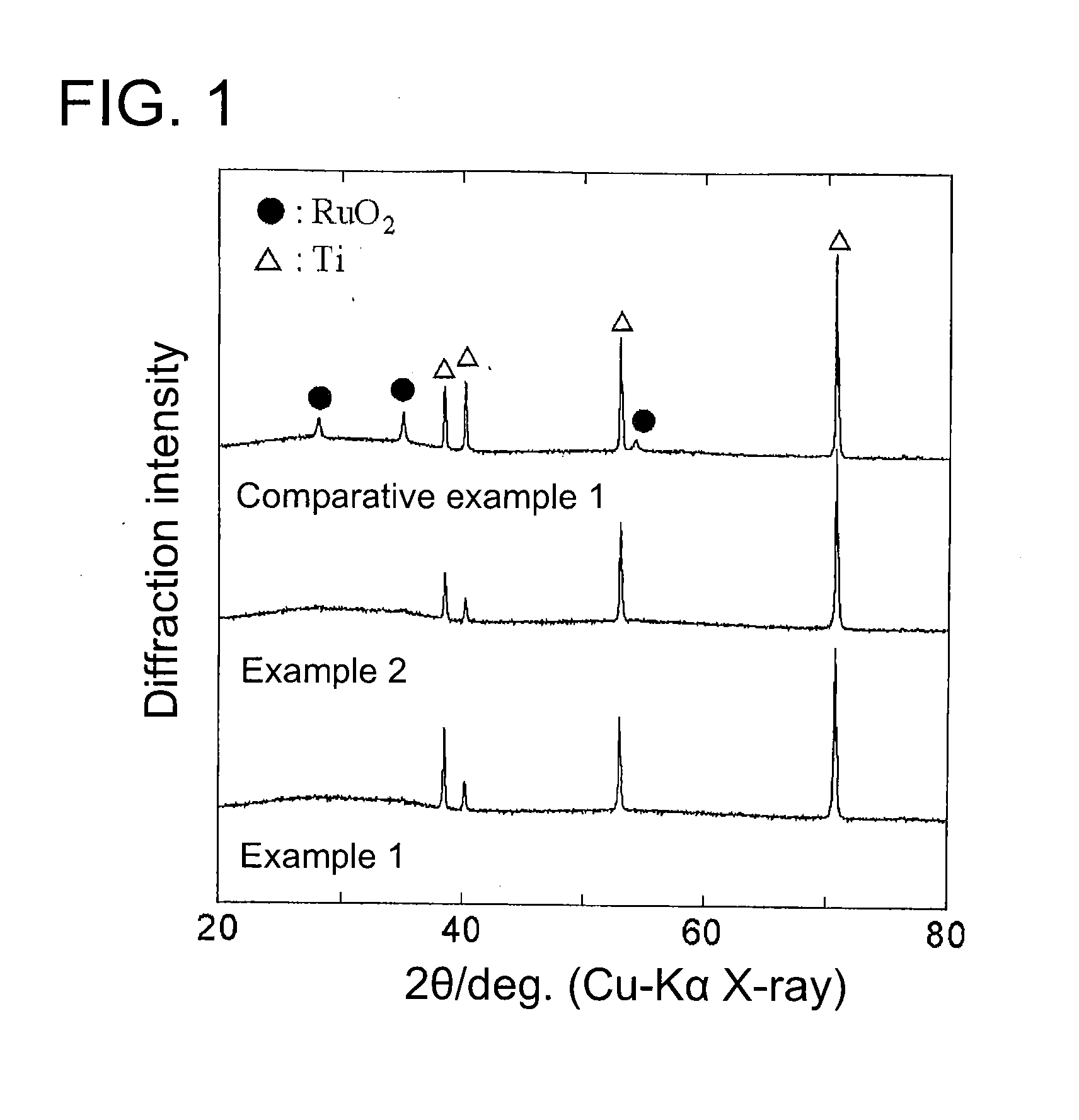
[0057]An anode for electrowinning according to Example 2 was manufactured by the same method as that of Example 1 except that the catalytic layer was formed at a thermal decomposition temperature of not 260° C. but 280° C. An X-ray diffraction analysis of the structure of the anode for electrowinning according to Example 2 shows that as shown in FIG. 1, the diffraction peak equivalent to RuO2 was not observed, and the diffraction peak equivalent to Ta2O5 was not observed, either. Note that the diffraction peak of Ti was observed; however, this was caused by the titanium plate. That is, the anode for electrowinning according to Example 2 had the catalytic layer of amorphous ruthenium oxide and amorphous tantalum oxide formed on the titanium plate.
[0058]Prepared was an electrolytic solution of a 0.80 mol / L of ZnSO4 and 2.0 mol / L of sulfuric acid, and a zinc plate (2 cm×2 cm) was immersed as the cathode in this electrolytic solution. Furthermore, the anode for electrowinning according ...
example 3
[0068]The electrolytic solution of Example 1 was replaced with an electrolytic solution of 0.60 mol / L of CuSO4 and 0.90 mol / L of sulfuric acid, and with other conditions kept the same as those of Example 1, the inter-terminal voltage (electrolytic voltage) was measured between the anode for electrowinning and the cathode while performing electrowinning of copper.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric potential / voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electric potential / voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com