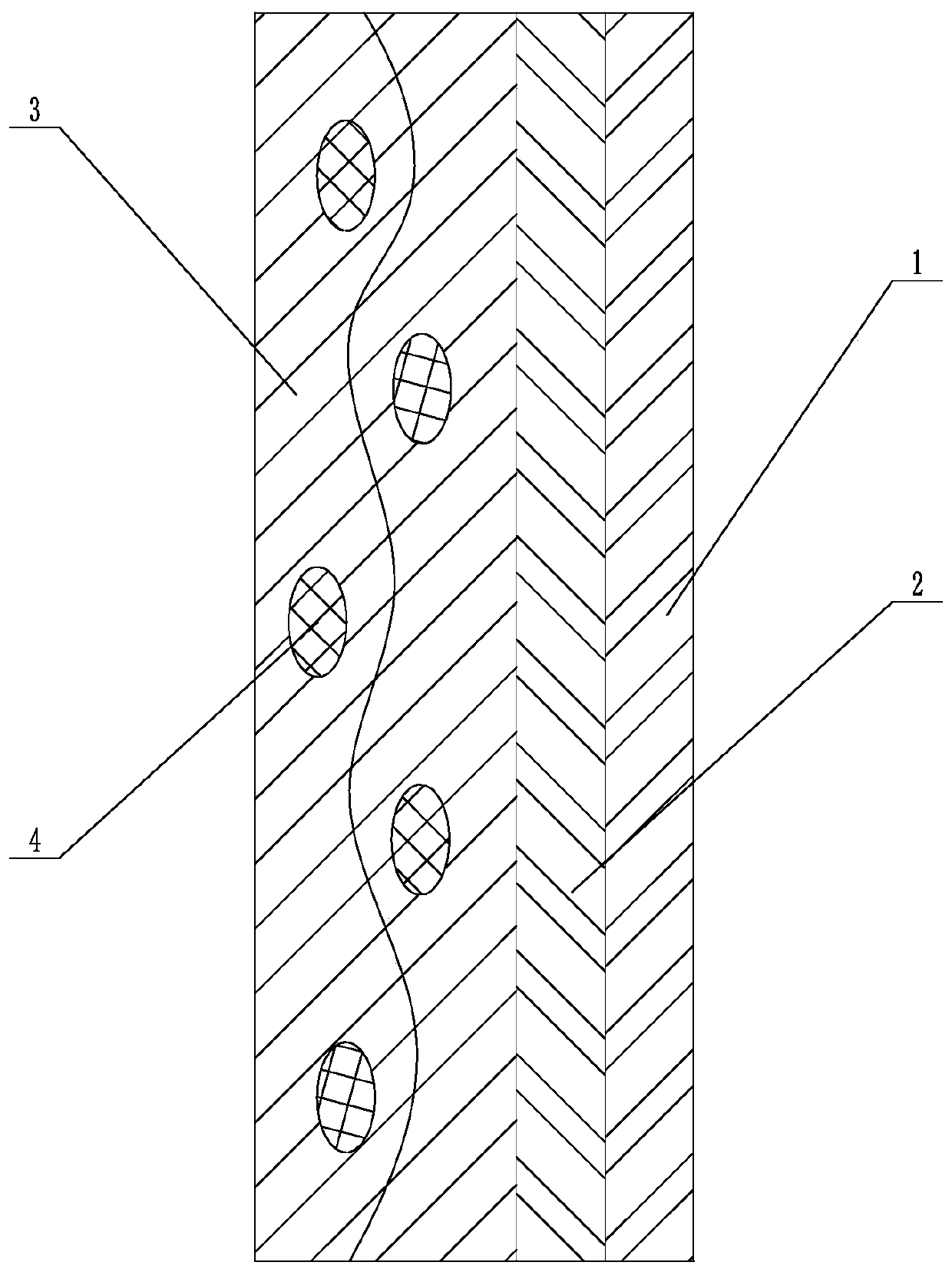
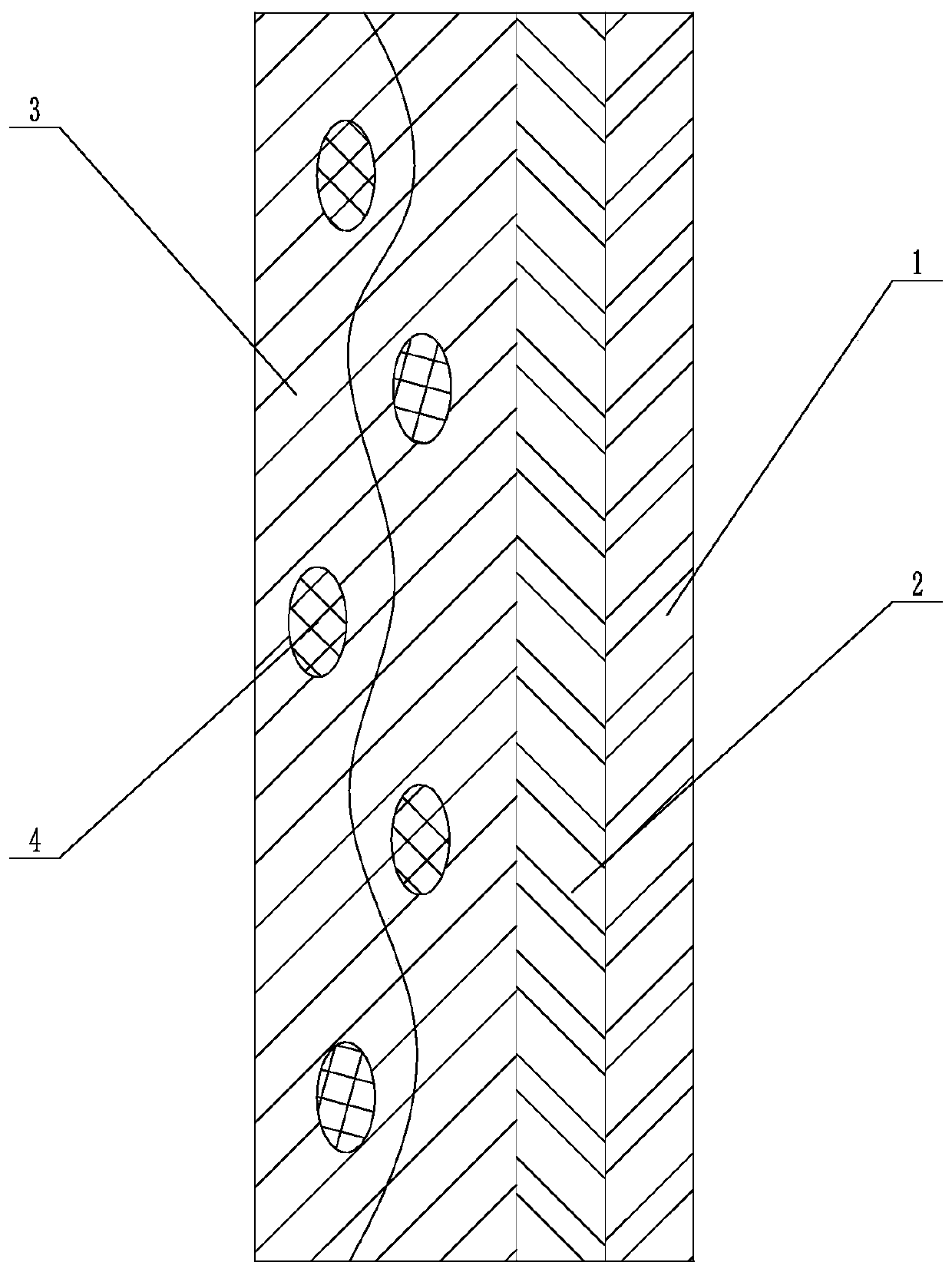
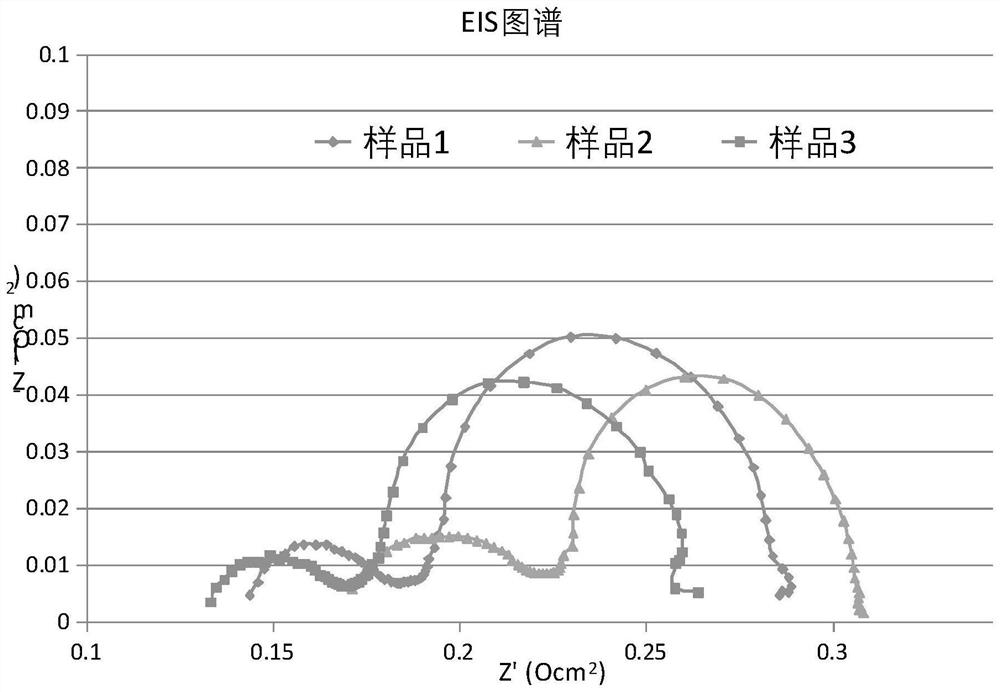
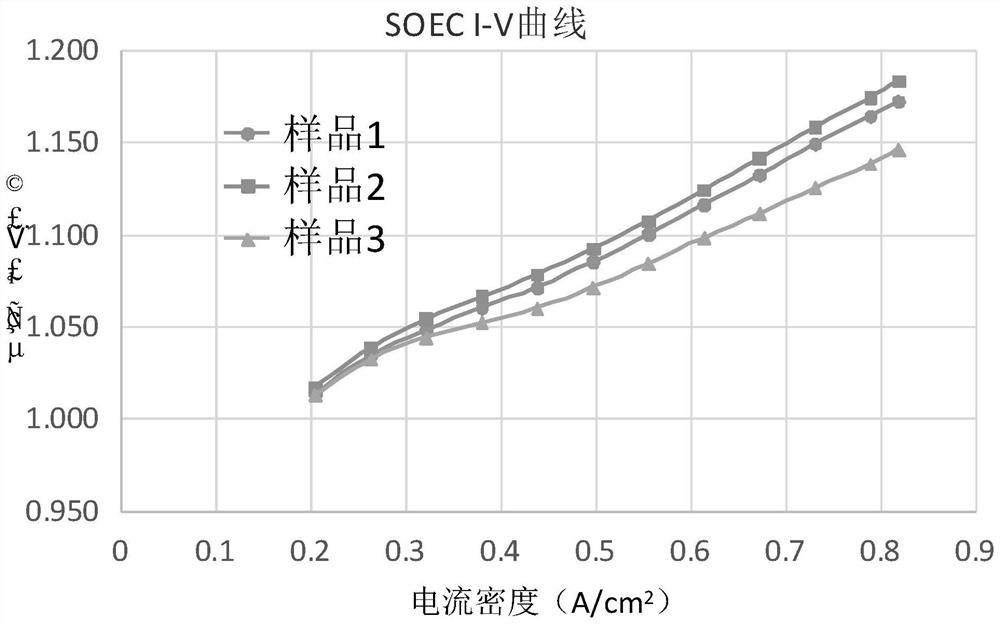
Patents
Literature
77results about How to "Reduce the electrolysis voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
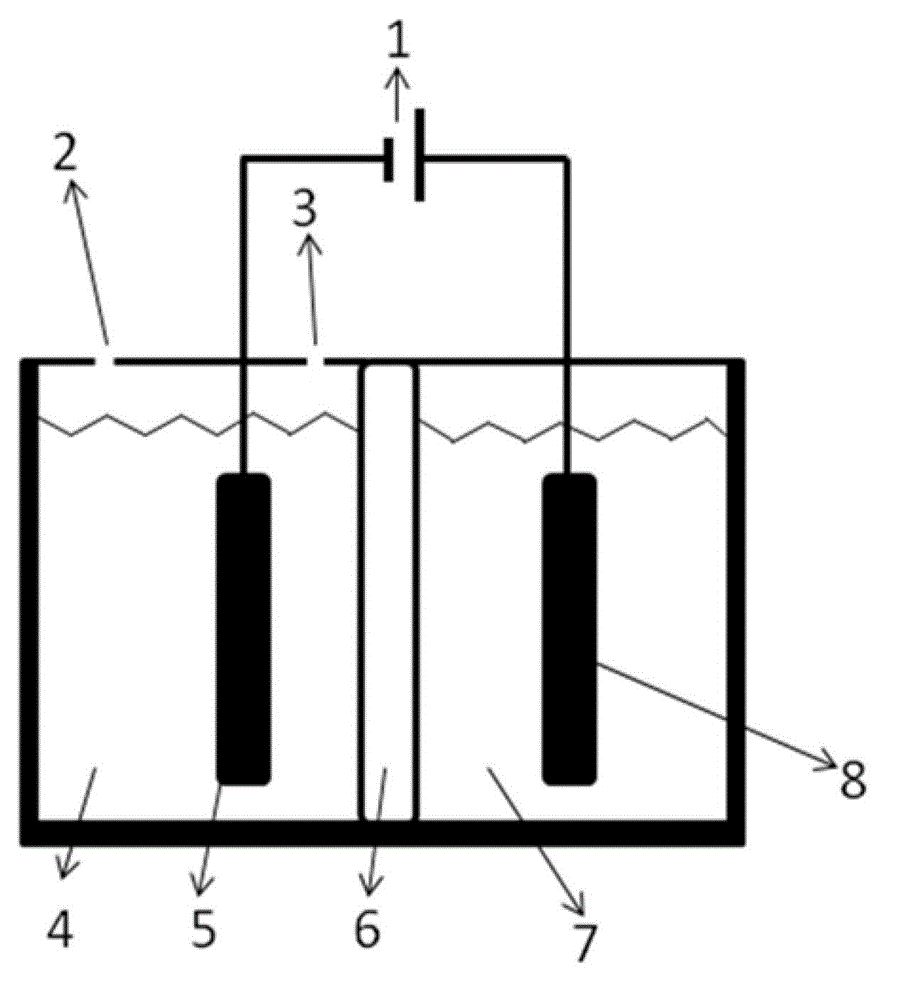
Electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank using bipolar membrane as diaphragm and application of electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank
InactiveCN102912374AReduce the electrolysis voltageAchieving electrochemical reductionOrganic diaphragmsElectrolytic organic productionCarbon dioxideIndium
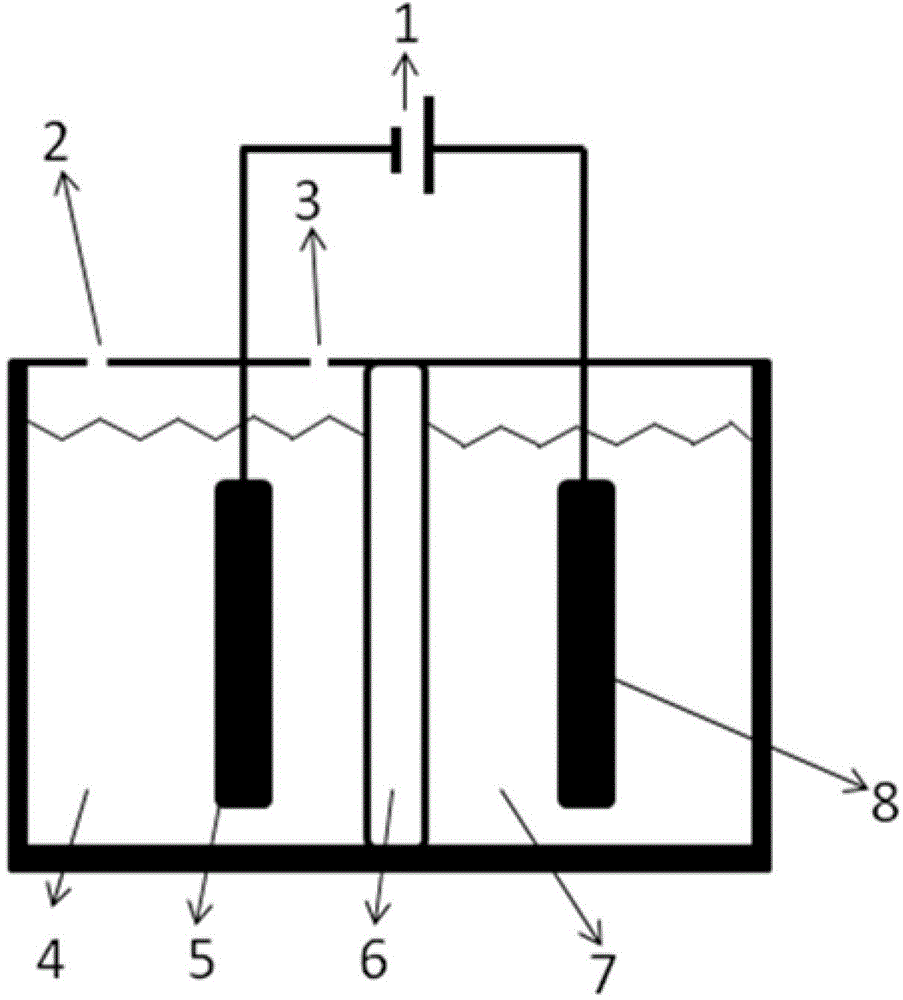
The invention relates to an electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank using a bipolar membrane as a diaphragm and an application of the electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank. The electrolytic tank comprises a cathode electrolysis compartment, cathode liquor, an anode electrolysis compartment, anolyte and the bipolar membrane for dividing the cathode electrolysis compartment and the anode electrolysis compartment. The electrode materials of the cathode electrolysis compartment include Pb (Plumbum), In (Indium) and Cu (Copper) etc, and the cathode liquor is an alkaline aqueous solution; and the electrode materials of the anode electrolysis compartment include Pt (Platioum) and Pd (Palladium) etc, and the anolyte is an acidic aqueous solution containing iodate. The hydroxy radicals in the cathode electrolysis compartment and the protons in the anodic electrolysis compartment are diffused to the bipolar membrane to generate water so as to form a voltage drop, so that the working voltage in the electrolytic tank is reduced. Compared with an anodic reaction that water and the electricity are oxidized to generate oxygen, the iodide ions are oxidized to generate an iodine elementary substance with low potential, small overpotential and quick dynamic process, so that the working voltage in the electrolytic tank is further reduced. CO2 is electrically reduced in a cathode compartment so as to generate small molecular fuels, such as formate, methanel, and methane; and the iodide ions are electrically oxidized to generate the elementary substance iodine in an anode compartment.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Membrane electrode for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis battery and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101388463AReduce loadReduce contact resistanceCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsNano catalystElectrolysis
The invention discloses a proton exchange membrane water electrolyte battery membrane electrode and a process for preparation thereof, which belongs to the technical field of preparing hydrogen gas through electrolyzing water, wherein the proton exchange membrane water electrolyte battery membrane electrode comprises a polymer electrolyte membrane, an anode catalyst layer, a cathode catalyst layer, an anode diffusion layer, a cathode diffusion layer, a support layer and a flow field plate, wherein hydrophilic thin layer structures which are formed by catalyst are respectively brushed on both surfaces of the polymer electrolyte membrane. Anode catalyst is noble metal or metallic material, and the diffusion layer is carbon material or metallic material. A catalyst layer and the relative diffusion layer and the support layer are compacted in a titanium plate to prepare membrane electrode through utilizing external force under normal temperature. The invention lowers the load of catalyst, improves the operating factor of catalyst, avoids the deformation of membranes in the process of heat pressing, and is drawn supported from the catalytic and corrosion resistance property of an anti-corrosion diffusion layer with catalytic property, and the electrolytic property and the stability of a battery are improved. The invention has the advantages of simple technique, convenient operation and excellent repeatability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Catalyst for water electrolysis and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101733095AMicrocrystalline particle size reductionLarge specific surface areaCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
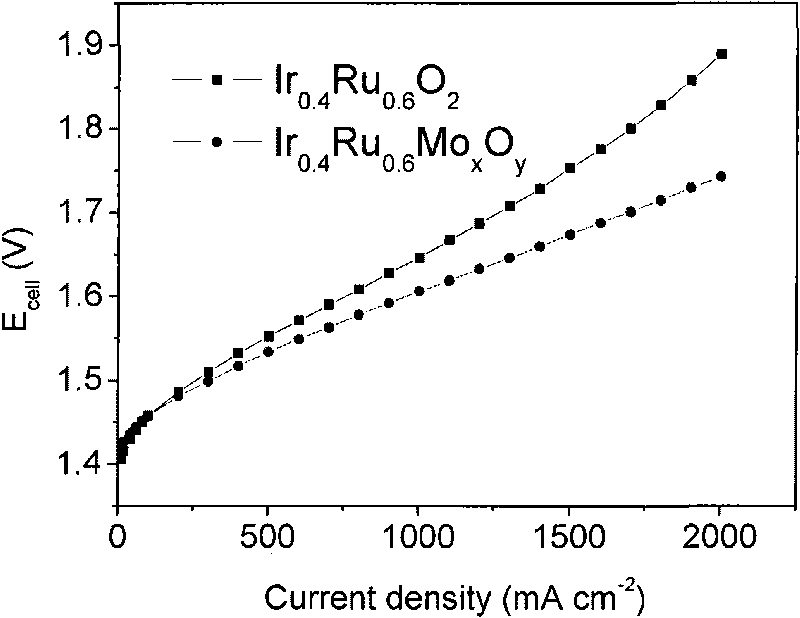
The invention relates to an anode catalyst used for a water electrolysis device of solid polymer electrolyte. The molecular formula of the catalyst is IrxRu1-xMyOz, wherein x is more than 0 and not more than 1, y is more than 0 and not more than 0.3, z is more than 1.5 and not more than 2.9, and M is one or more of such transition metals as Mo, W and Cr. In terms of the gross weight of the catalyst, the weight ratio of M in the catalyst is less than 10wt%. The required catalyst is characterized in that addition of the third component (or the fourth component) reduces the microcrystal grains of the catalyst, enlarges the specific surface area of the catalyst and improves the catalytic activity of the catalyst. The catalyst has lower overpotential and long life when serving as the anode catalyst in an SPE water electrolysis cell. The catalyst is used for the electrodes for oxygen evolution of the SPE water electrolysis cell, catalyst-membrane assemblies (CCM), membrane-electrode assemblies (MEA), regenerative fuel cells (RFC) and sensors.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
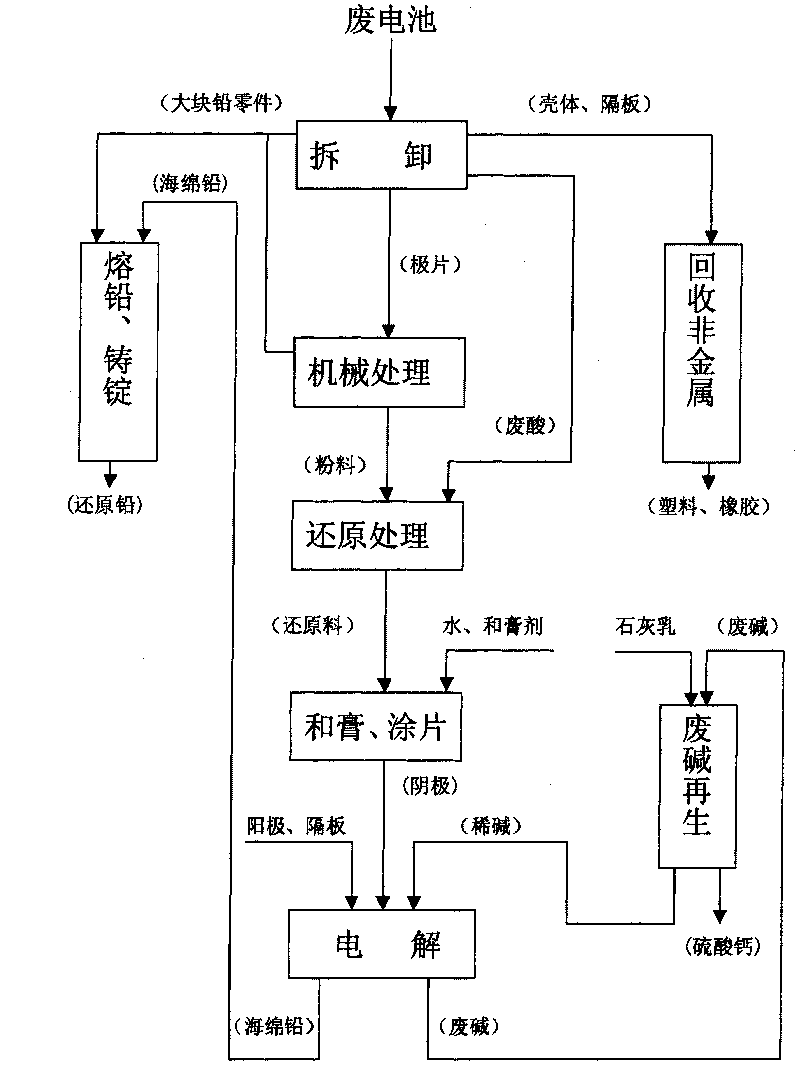
Method for recovering lead from waste lead acid batteries
InactiveCN101748277AResidue reductionIncrease productivityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisMaterials science
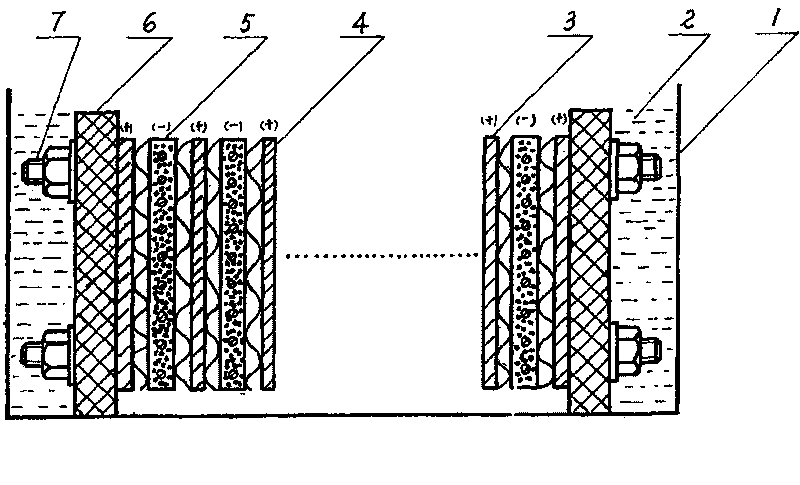
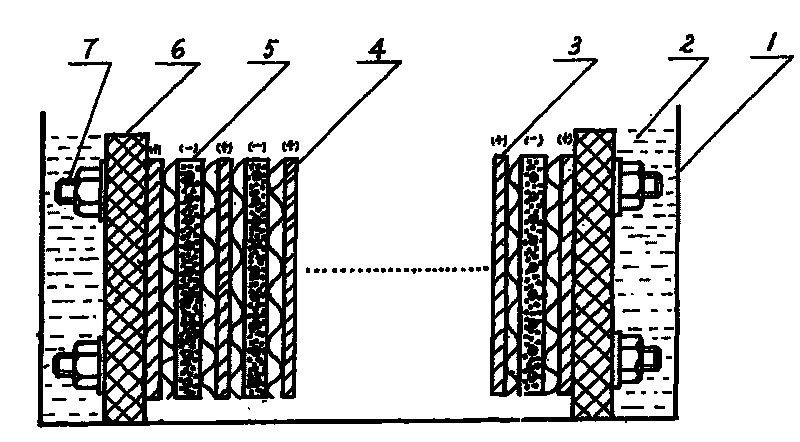
The present invention relates to a method for recovering lead from waste lead acid batteries. The electrolytic device adopted comprises an electrolytic bath, dilute alkali electrolyte, an anode, a baffle and a pasted cathode. The anode, the baffle and the pasted cathode are arranged in a tight assembly structure. The pasted cathode is prepared from waste lead powder processed by reduction, water and paste. Lead is reduced from the pasted cathode with a solid phase reduction electrolytic method. Besides the advantage of no pollution, the present invention also has the advantages of short electrolysis time, low energy consumption and low production cost due to the characteristics of low electrolysis voltage, large current density and high current efficiency.
Owner:江苏航虹电源有限公司
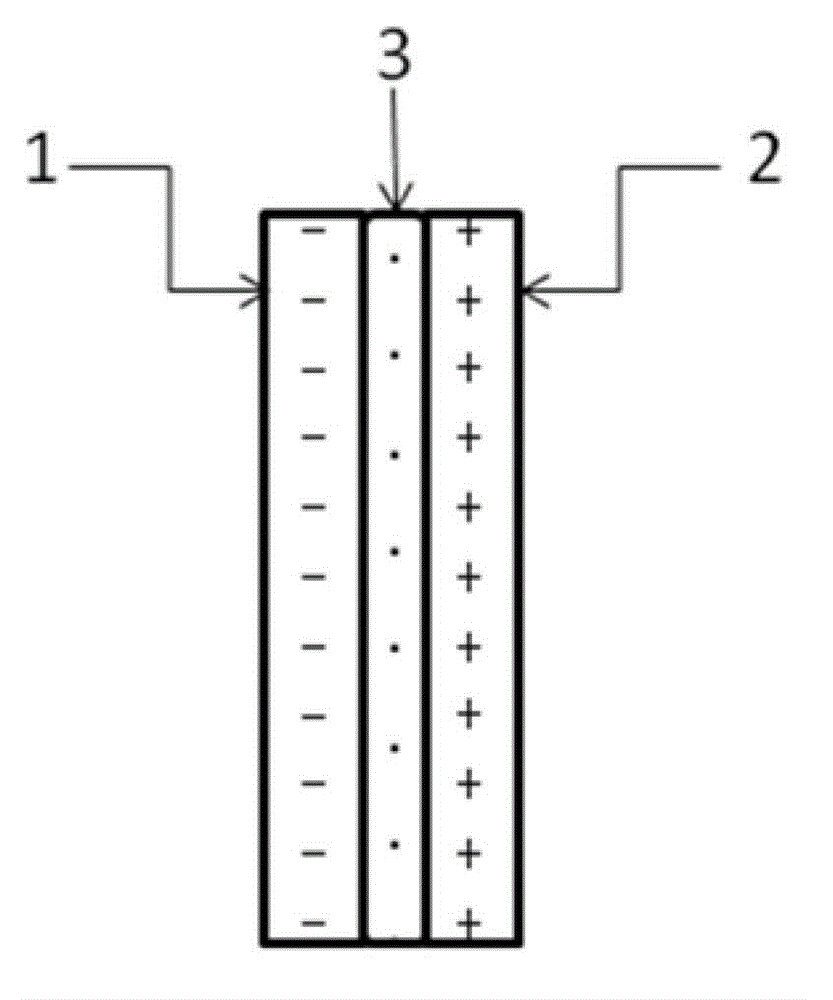
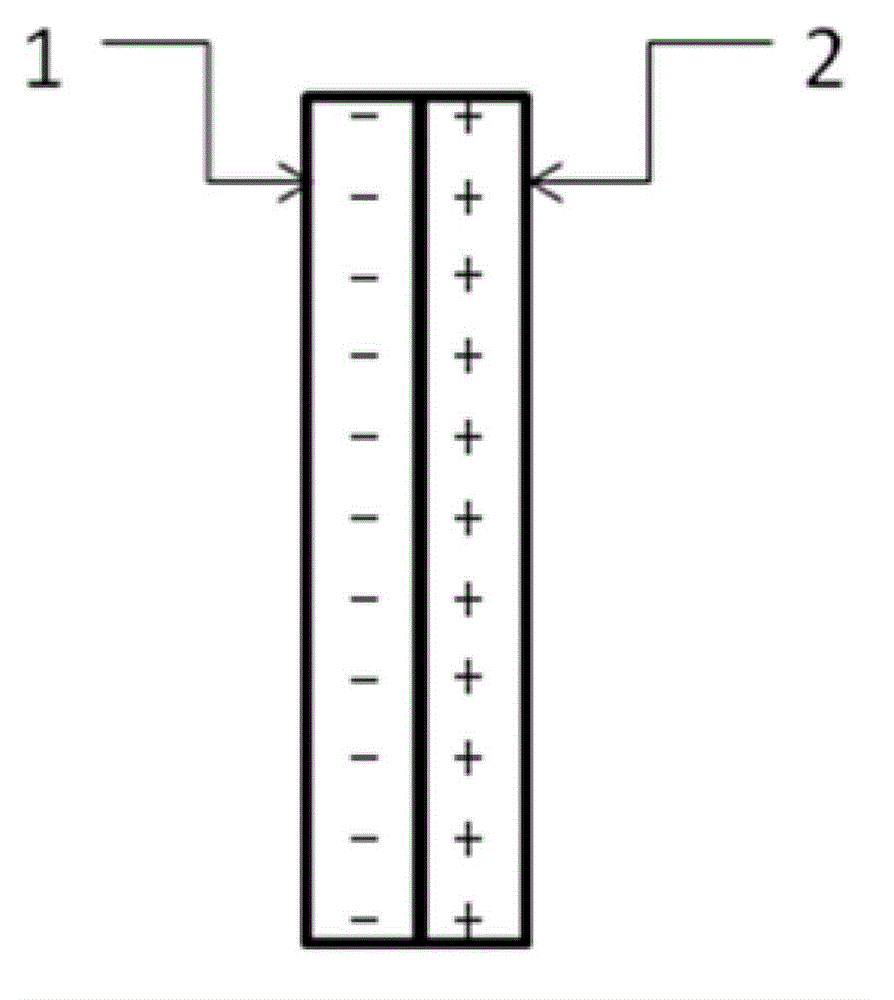
Auxiliary purification device for water purifier
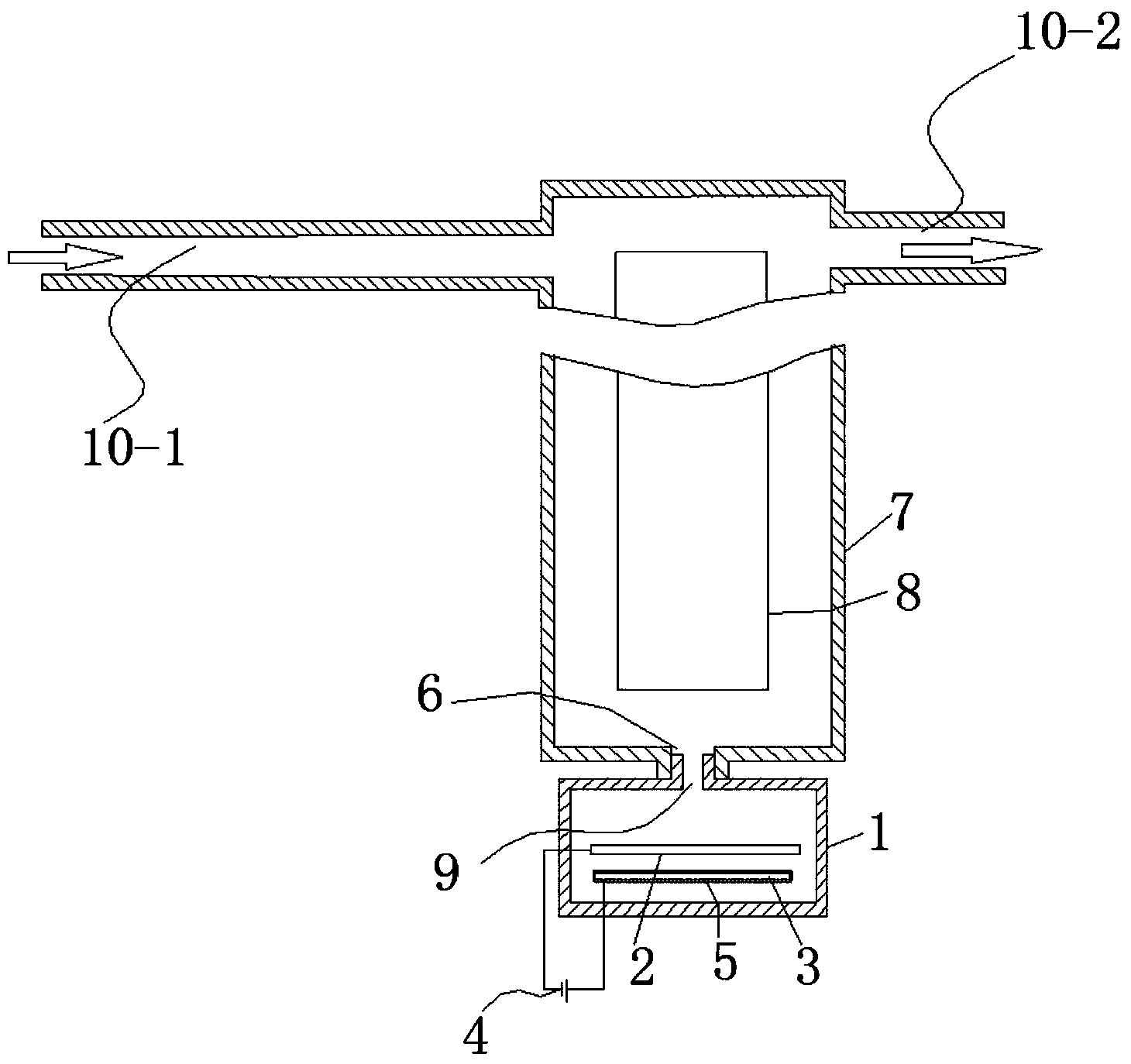
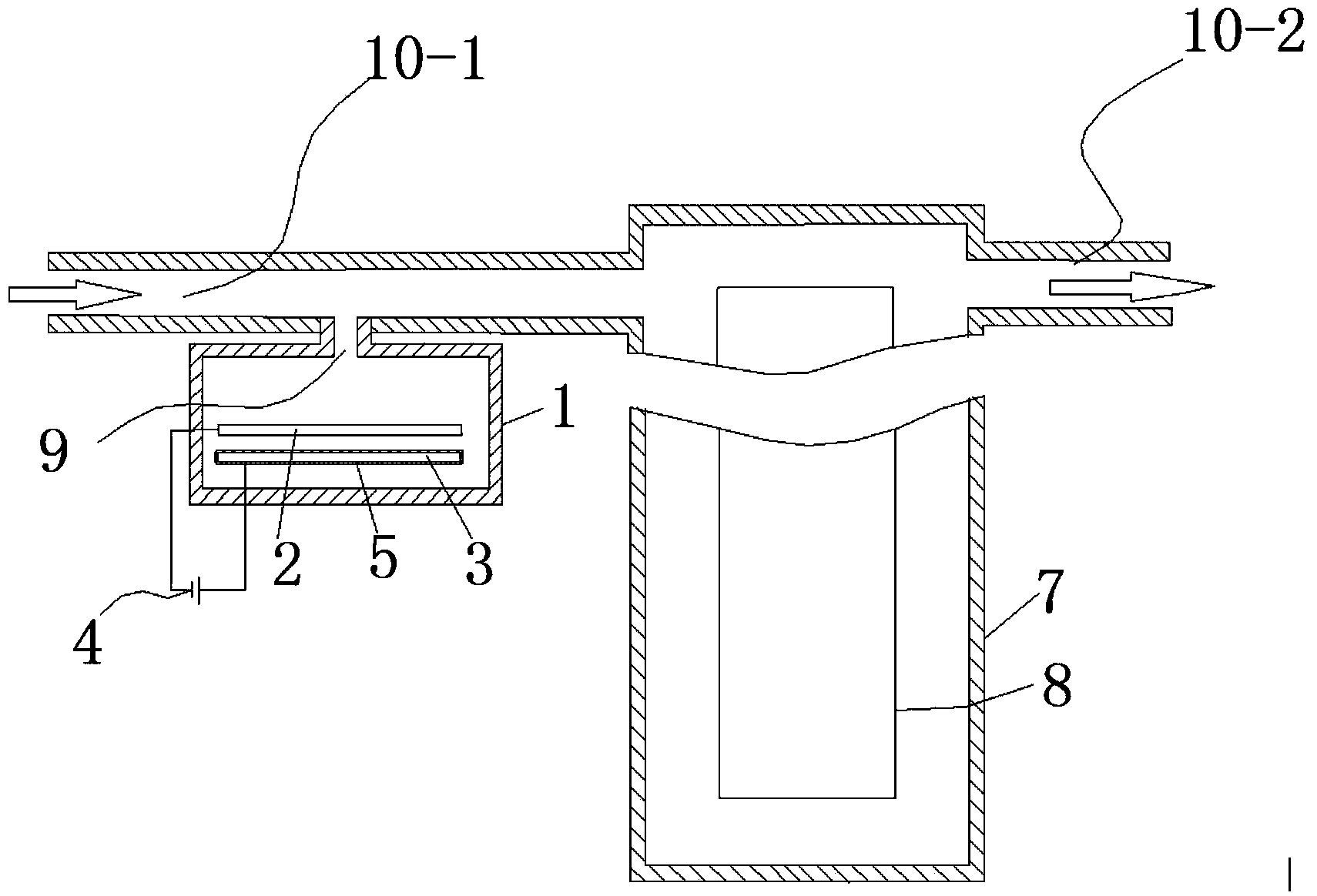
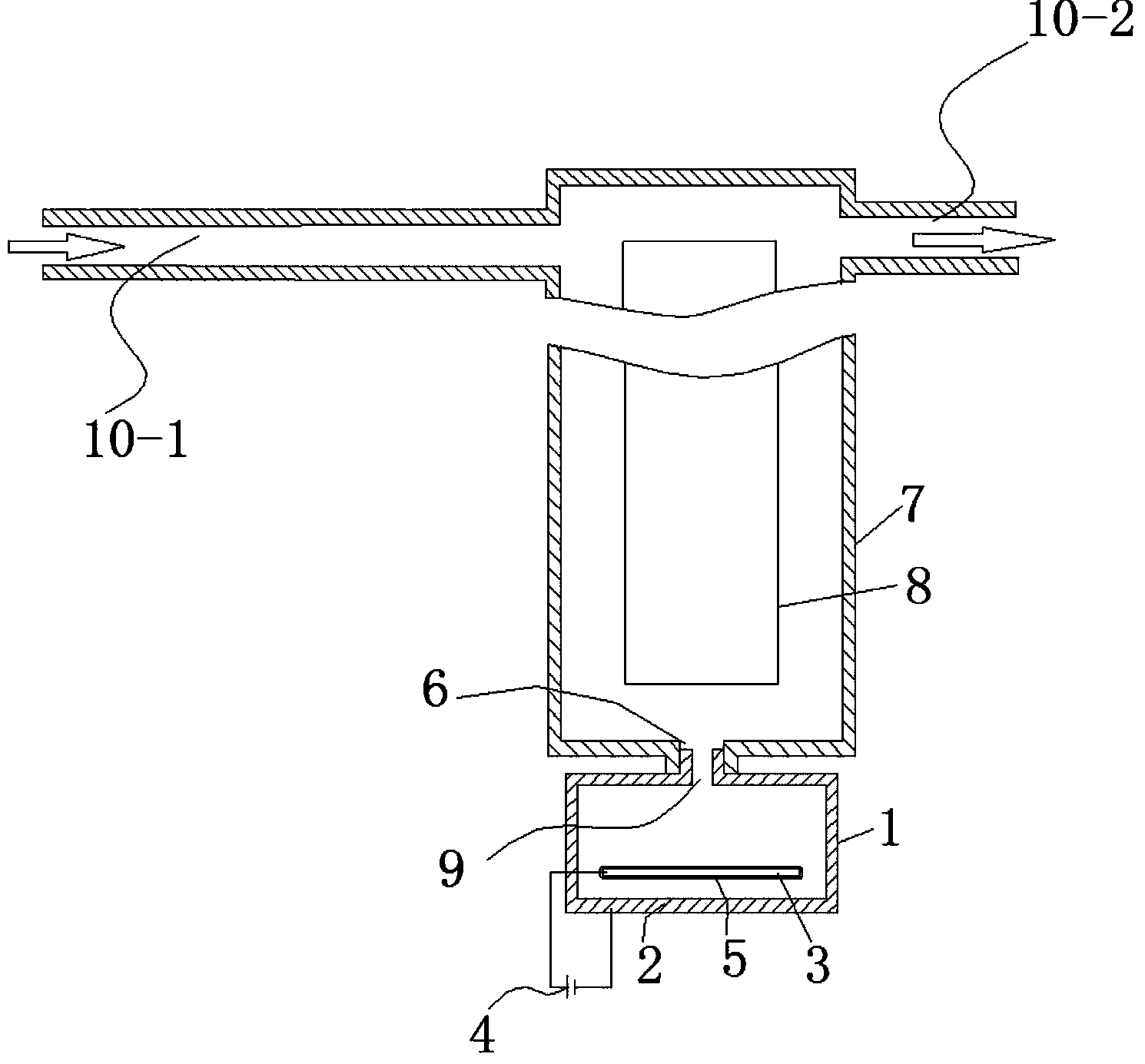
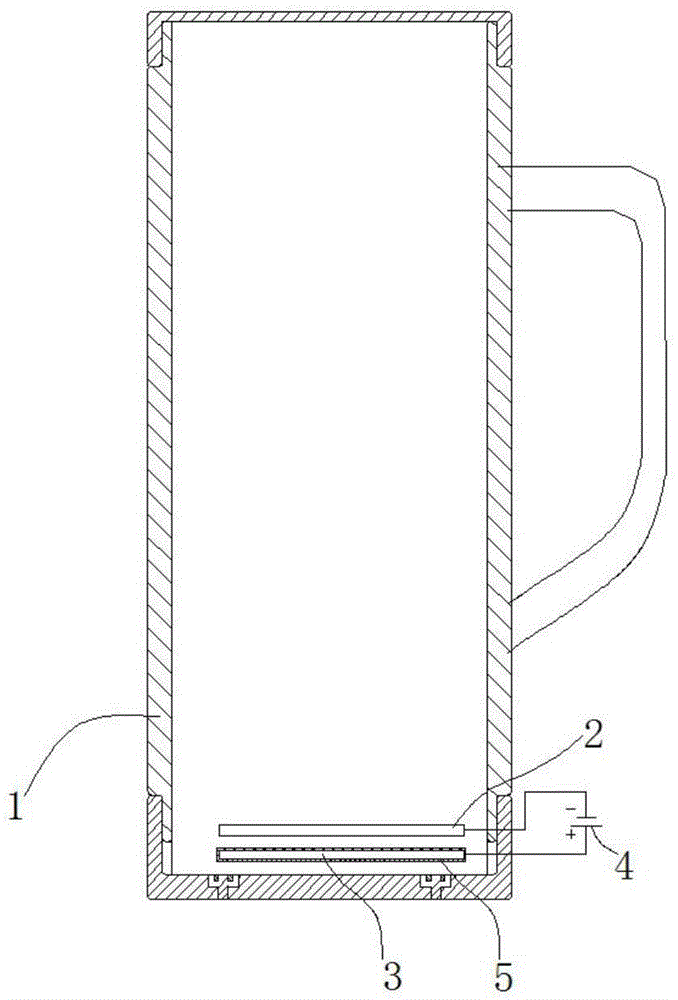
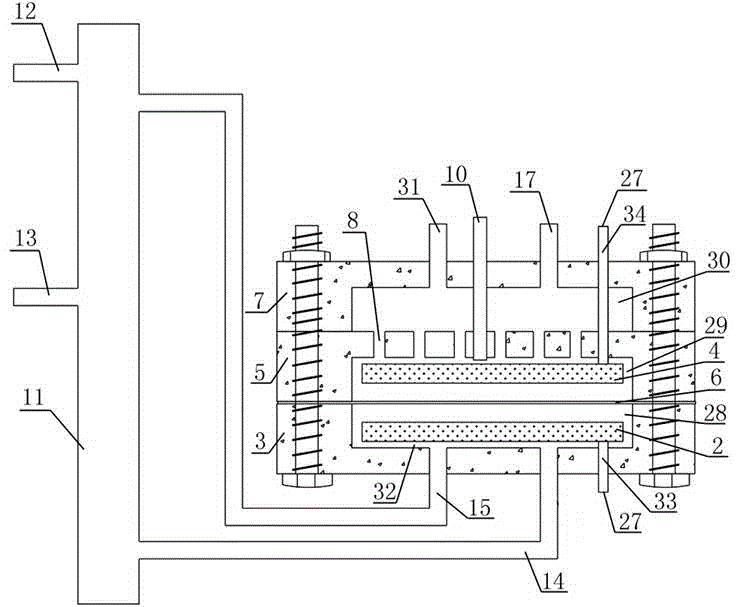
ActiveCN103936111AHigh unit voltage strengthImprove the sterilization and purification effectWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processElectricityElectrolysis
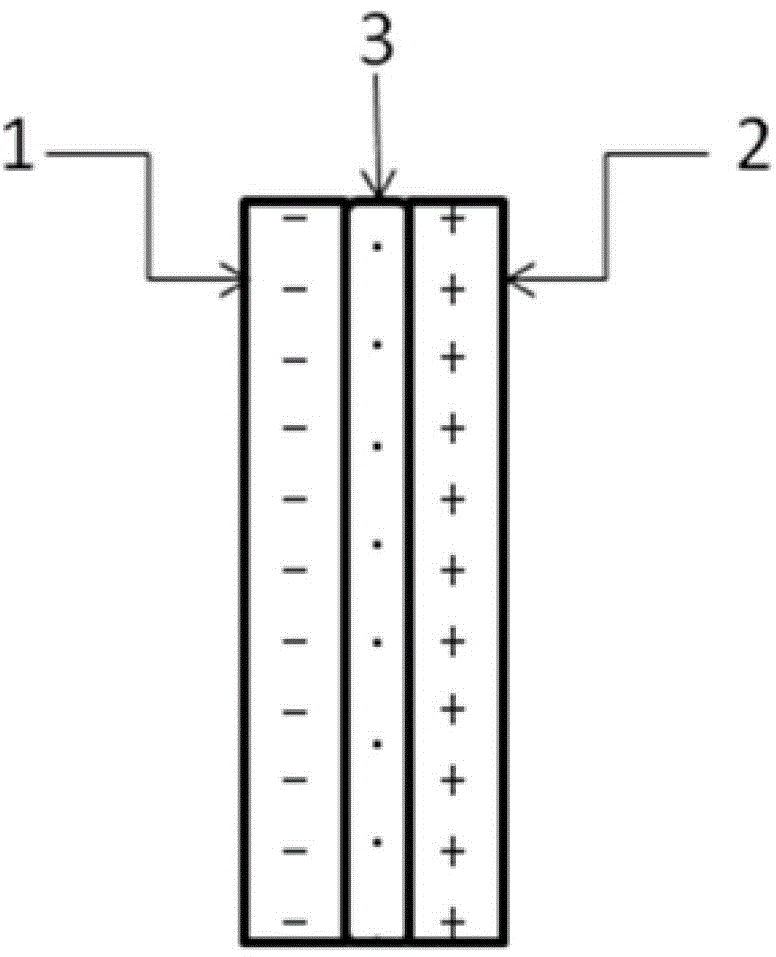
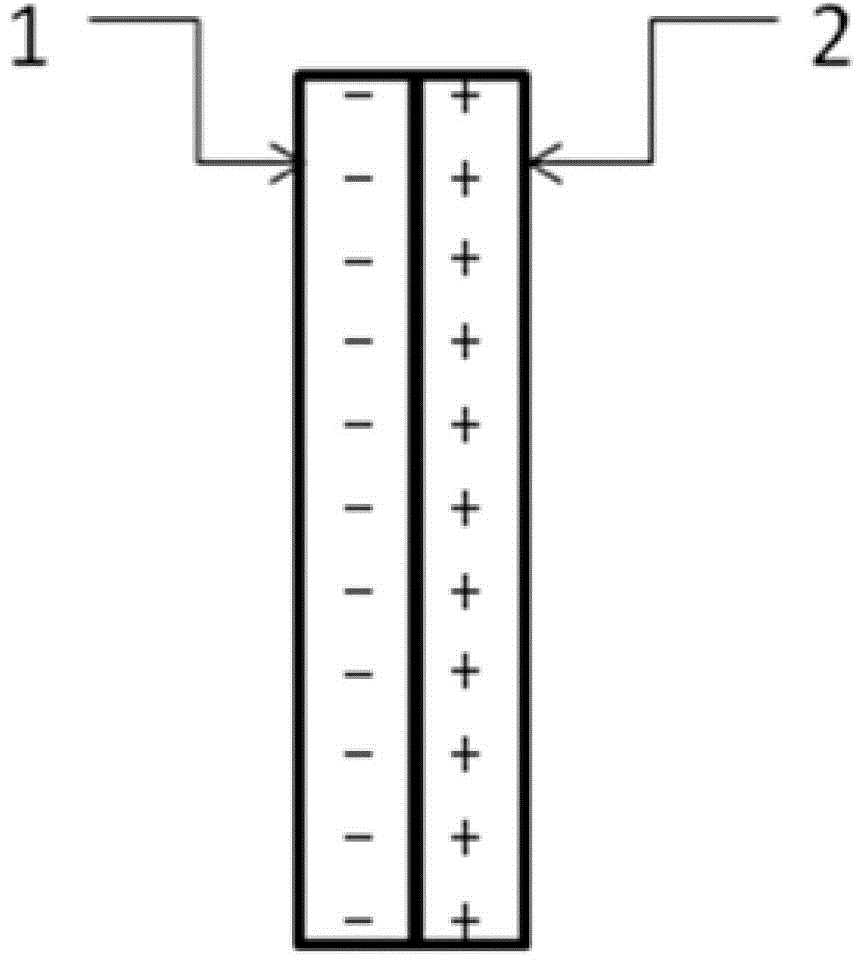
The invention relates to an auxiliary purification device for a water purifier, and belongs to the technical field of electrolysis equipment. The device comprises a water container with a water inlet and an electrolysis power supply used for supplying electricity to a negative electrode and a positive electrode, wherein the water inlet is communicated with the water purifier; the negative electrode and the positive electrode are arranged in the shell of the water container; a water-permeable diaphragm is arranged between the mated negative and positive electrodes; the positive electrode is coated with the water-permeable diaphragm, and the interval theta between the water-permeable diaphragm and the negative electrode is in a range of more than or equal to 0mm and less than or equal to 10mm. The device can be used for generating massive hydrogen-oriented super-micro bubbles and strong oxidation factors and purifying and sterilizing source water, can be combined with a conventional water purifier to produce drinking water with high safety.
Owner:DALIAN SHUANGDI INNOVATIVE TECH RES INST
Water electrolysis cup
InactiveCN103951015ALower redox potentialImproved sterilization and purification abilityWater/sewage treatmentOxidation reductionEngineering
The invention relates to a water electrolysis cup, and belongs to the technical field of electrolysis equipment. The water electrolysis cup comprises an electrolysis power supply, and an inner tank provided with a negative electrode and a positive electrode; the positive electrode and the negative electrode are connected with the cathode and the anode of the electrolysis power supply respectively; an pervious diaphragm is arranged between the negative electrode and the positive electrode; the positive electrode is coated with the pervious diaphragm; and the distance (delta) between the pervious diaphragm and the negative electrode is equal to or larger than 0 and is equal to or less than 10mm. The water electrolysis cup can be used for preparing water which is rich in active hydrogen, is low in oxidation reduction potential, and is suitable for drinking.
Owner:DALIAN SHUANGDI TECH
Iron-carbon pipe component capable of purifying waste water, integrated magnetoelectric oxidation biological filter chamber and application system
ActiveCN101264946AConductive strongImprove adsorption capacityWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesFiltrationSludge
An iron / carbon nanotube component capable of treating wastewater comprises a central tube with a plurality of pores on the tube wall, wherein the central tube arranged into the inner cavity of an outer sleeve is coated with an electrode material layer on the outer wall thereof, having the inner cavity thereof communicated with a water inlet port, and provided at the central position thereof with an anode tube connected with an external power supply; and the upper and the lower ends of the outer sleeve are sealed and respectively provided thereon with a water outer port and a wastewater drainage port. The invention also provides a magnetoelectric oxidation biological filter tank containing the above iron / carbon nanotube component and integrating catalytic oxidation / reduction reaction and precipitation, biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal, filtration and sludge discharging, comprising a tank body and a total water inlet tube and a total water outlet tube arranged on the tank body, wherein a tank body bracket and an iron / carbon nanotube supporting frame are arranged inside the inner cavity of the tank body, iron / carbon nanotube components arranged in rows are arranged on the tank body bracket, and a water distribution tube communicating with the total water input tube is arranged on the iron / carbon nanotube supporting frame; and an aeration plate and a filtering filler are arranged among iron / carbon nanotube components. The inventive iron / carbon nanotube component can be used for treating electroplating wastewater, concentrated fluid generated from nanofiltration membrane or RO membrane, dyeing wastewater, pharmaceutical wastewater and other wastewater that is difficultly treated by using biological method, and the operating cost and floor space are half of those in conventional process, so that the inventive iron / carbon nanotube component has wide application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN ENVIRONMENT ENG SCI TECH CENT +1
Chlorine dioxide generator adopting high-efficiency electrolytic method
The invention relates to a chlorine dioxide generator adopting a high-efficiency electrolytic method. The chlorine dioxide generator mainly comprises a chlorine dioxide electrolytic module, a soluble salt system, an electrolytic salt quantitative adding system, an alkaline liquid circulating discharge system and a programmable logic controller (PLC) control system. The chlorine dioxide generator has the characteristics of compact and reasonable structure, high electrolytic efficiency, simple production, mounting and maintenance of equipment, intelligent control, flexibility, convenience, high safety performance and the like.
Owner:江西富诚生态环境科技集团有限公司
Business water machine
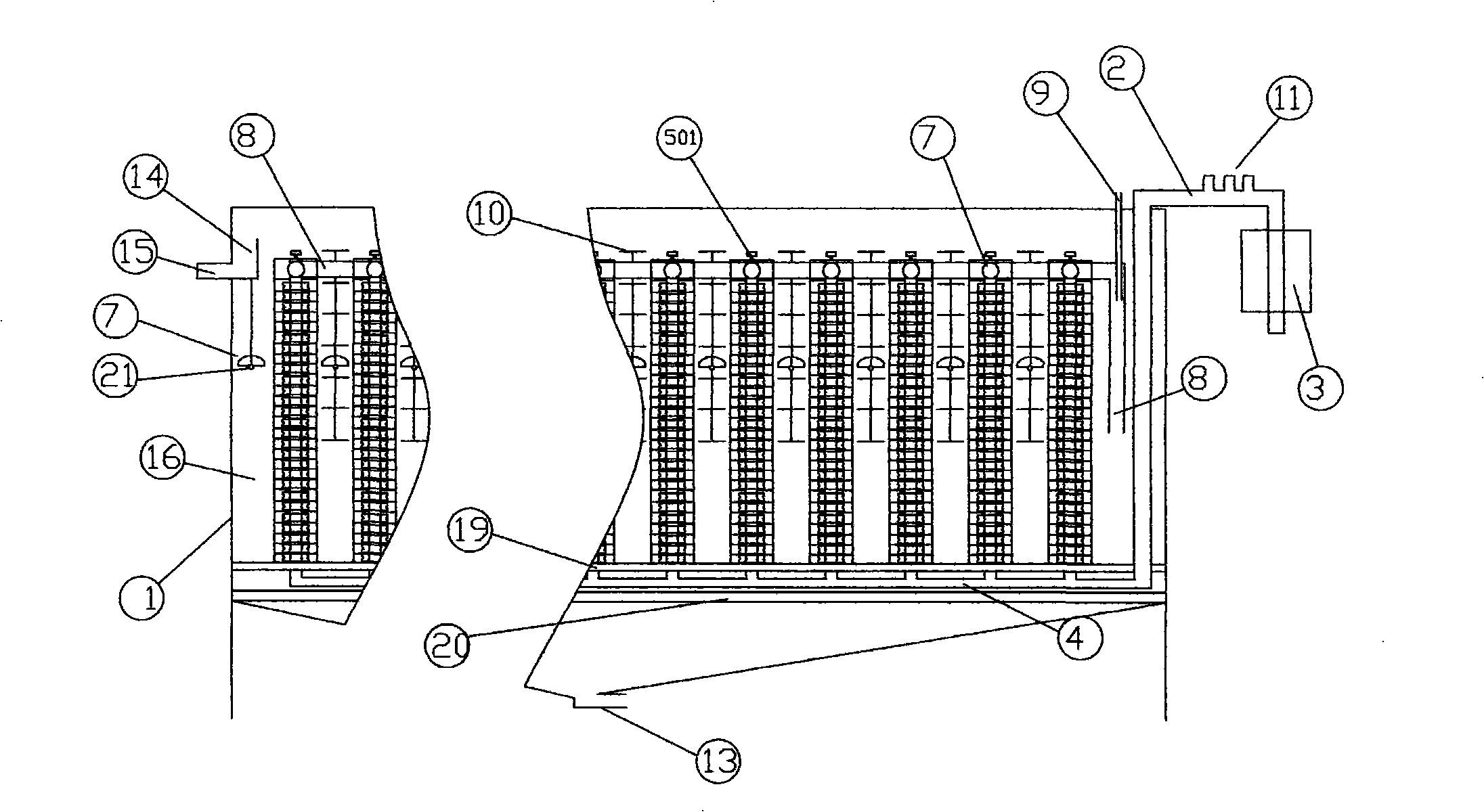
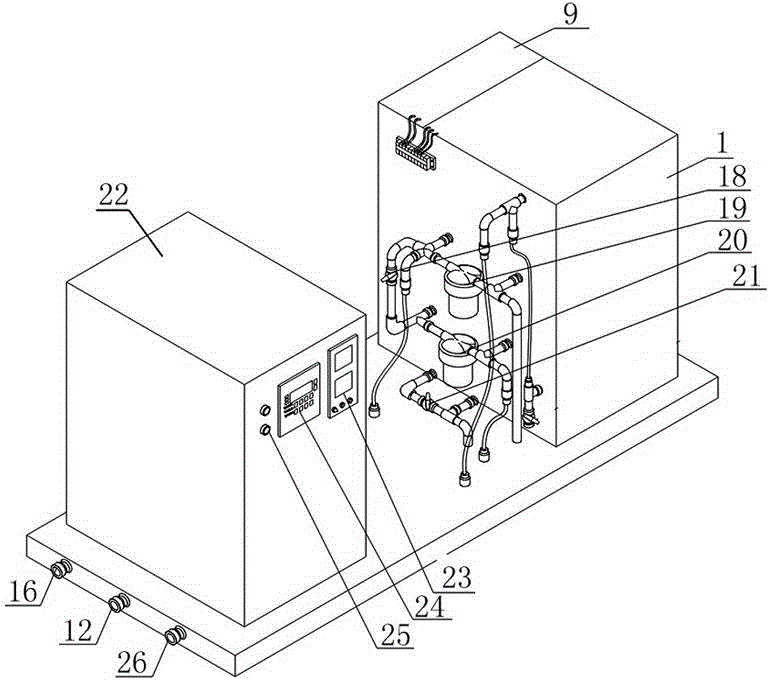
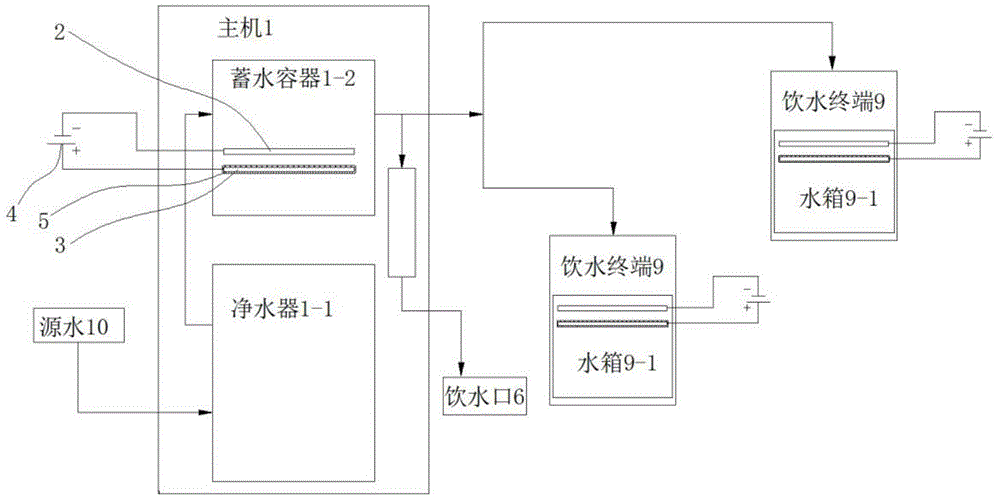
ActiveCN103951118AImprove the sterilization and purification effectReduce the electrolysis voltageMultistage water/sewage treatmentHydrogenElectrolysis
The invention relates to a business water machine which comprises a host and a drinking water terminal, wherein the host comprises a water purifier and a water storage container communicated with the water purifier; the drinking water terminal is provided with a water tank; the water tank is communicated with the water storage container; a first sterilization device is arranged in the water storage container; a second sterilization device is arranged in the water tank; each of the first sterilization device and the second sterilization device comprises at least one pair of negative and positive electrodes and an electrolysis power supply for supplying power to the negative and positive electrodes; a water-permeable membrane is arranged between the negative and positive electrodes in pairs and covers the positive electrode; the distance delta between the water-permeable membrane and the negative electrode is not less than 0mm and not more than 10mm. The water machine is capable of preparing active hydrogen-rich drinking water with low redox potential.
Owner:DALIAN SHUANGDI TECH
Method and device for preparing rare-earth metal through lower cathode electrolysis and in-situ ingot casting synchronization
The invention relates to a method and a device for preparing rare-earth metal through lower cathode electrolysis and in-situ ingot casting synchronization. The device comprises an electrolysis furnace and an ingot casting furnace which are arranged on a machine frame, wherein a carbon anode is hung at a hearth opening of the electrolysis furnace through an anode conducting rod and is communicated with a positive electrode of a power supply; the anode conducting rod is fixedly arranged on an automatic ascending and descending feeding device arranged on the machine frame; the lower part of a hearth of the electrolysis furnace is provided with a funnel-shaped insulation inner liner; an upper cooling water jacket is arranged outside the furnace wall of the electrolysis furnace; the lower part of the outer side of the upper cooling water jacket is provided with an electromagnetic stirring device; an ingot casting cavity is arranged on the ingot casting furnace; the ingot casting cavity is centered with an outlet of the funnel-shaped insulation inner liner; the lower part of the ingot casting cavity is provided with a sliding ingot guide rod in a matched way; the bottom of the ingot guide rod is connected with an ingot drawing rod and is communicated with the cathode of the power supply through a conducting wire; a lower cooling water jacket is arranged outside the furnace wall of the ingot casting furnace. Constant-voltage or constant-current electrolysis is carried out under the conditions that the temperature is 900 to 1200 DEG C, the voltage is 5 to 30V, and the current is 1000 to 10000A. The rare-earth metal can be continuously and automatically prepared.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst Coating and Process for Production Thereof
InactiveUS20140224667A1Reduce overpotentialReduce the electrolysis voltageMachining electrodesElectrode thermal treatmentElectrolysisSolvent
A process for wet-chemical production of a catalyst coating on an electrically conductive support for electrodes for chloralkali or hydrochloric acid electrolysis with electrocatalytically active components based on noble metal oxides, in which the catalyst coating is produced by; producing a coating solution or dispersion comprising a precursor compound of a noble metal and / or a metal oxide of a noble metal, and a solvent or dispersant, with addition of one or more acids to the coating solution or dispersion, where the molar ratio of the total of the amounts of acid (in mol) present in the coating solution or dispersion to the sum of the amounts of the metals from the metal-containing components present in the coating solution or dispersion is at least 2:1; applying the coating solution or dispersion to the support; substantially freeing the layer applied of solvent or dispersant by drying; and subjecting the dried layer obtained to a thermal treatment to form the catalyst coating.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG +1
Anode for electrowinning and electrowinning method using same
ActiveCN103476970ALower potentialReduce the electrolysis voltageElectrodesTitanium electrodeElectrolysis
Provided is an anode for electrowinning such that, in electrowinning using a sulfuric acid-based electrolyte solution, the electric potential for oxygen generation is lower than for a lead electrode, lead alloy electrode, and coated titanium electrode, the electrolysis voltage for electrowinning can be reduced, and the basic units for electric energy can be reduced for a desired metal. This anode can be used as the anode for electrowinning of various types of metal and has superior mass productability. The anode for electrowinning is used in the electrowinning that uses a sulfuric acid-based electrolyte solution, and a catalyst layer that includes noncrystalline ruthenium oxide and noncrystalline tantalum oxide is formed on a conductive base substance.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
Anode for electrowinning and method for electrowinning using same
InactiveUS20140054180A1ElectrolyticReduce the electrolysis voltageMachining electrodesPhotography auxillary processesLead alloyLead electrode
Provided is an anode for electrowinning in a sulfuric acid based electrolytic solution. The anode produces oxygen at a lower potential than a lead electrode, lead alloy electrode, and coated titanium electrode, thereby enabling electrowinning to be performed at a reduced electrolytic voltage and the electric power consumption rate of a desired metal to be reduced. The anode is also available as an anode for electrowinning various types of metals in volume with efficiency. The anode is employed for electrowinning in a sulfuric acid based electrolytic solution and adopted such that a catalyst layer containing amorphous ruthenium oxide and amorphous tantalum oxide is formed on a conductive substrate.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
Preparation and application of molybdenum-doped cobalt selenide foamed nickel composite electrode for electrolyzing water
InactiveCN111101151ALow hydrogen evolution overpotentialOxygen evolution overpotential is lowElectrode shape/formsComposite electrodeElectrolysed water
The invention discloses preparation and application of a molybdenum-doped cobalt selenide foamed nickel composite electrode for electrolyzing water. The composite electrode is formed by depositing a molybdenum-doped cobalt selenide compound on a foamed nickel electrode, and the composite electrode is marked as Mo-CoSe2NS-NF. The electrode is applied to water electrolysis and has good electro-catalytic performance and stability on hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution at the same time, the catalytic hydrogen evolution [eta]10 is 89mV, and the Tafel slope is 69mV dec-1; the catalytic oxygen evolution [eta]10 is 234 mV, the Tafel slope is 58 mV dec-1, the Tafel serves as a cathode and an anode to form an electrolytic cell, and the electrolytic voltage is only 1.56 V when the current densityin an alkaline medium reaches 10 mA cm <-2>. The catalytic active substance of the composite electrode is directly deposited on the foamed nickel electrode, the synthesis method is simple, green andenvironment-friendly, and the composite electrode has an efficient bifunctional catalytic effect, so that the designed water electrolysis tank is simple in structure and suitable for industrial large-scale application of water electrolysis.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Fluorine-containing ion exchange membrane for alkali chloride electrolysis
ActiveCN110699706AImprove interface compatibilityImprove interlayer adhesionOrganic diaphragmsPhysical chemistryCarboxylic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of ion exchange membranes, and relates to a fluorine-containing ion exchange membrane for alkali chloride electrolysis. The fluorine-containing ion exchange membrane comprises a fluorine-containing polymer layer with carboxylic acid type functional groups, a fluorine-containing polymer layer with sulfonic acid type and carboxylic acid type functional groups, and a fluorine-containing polymer layer with sulfonic acid type functional groups; wherein a reinforcing material is embedded in the fluorine-containing polymer layer with the sulfonic acid typefunctional group, and the reinforcing material is parallel to the fluorine-containing polymer layer with the carboxylic acid type functional group and the fluorine-containing polymer layer with the sulfonic acid type functional group and the carboxylic acid type functional group; the surface of the fluorine-containing ion exchange membrane is provided with a surface modification coating formed byion exchange resin and inorganic ions. According to the invention, the electrolytic voltage during alkali chloride electrolysis can be reduced, the defect of interlayer stripping of the multi-layer composite membrane in the application process is inhibited, and the product is suitable for running in a zero-polar-distance electrolytic cell under novel high-current density conditions.
Owner:SHANDONG DONGYUE POLYMER MATERIAL
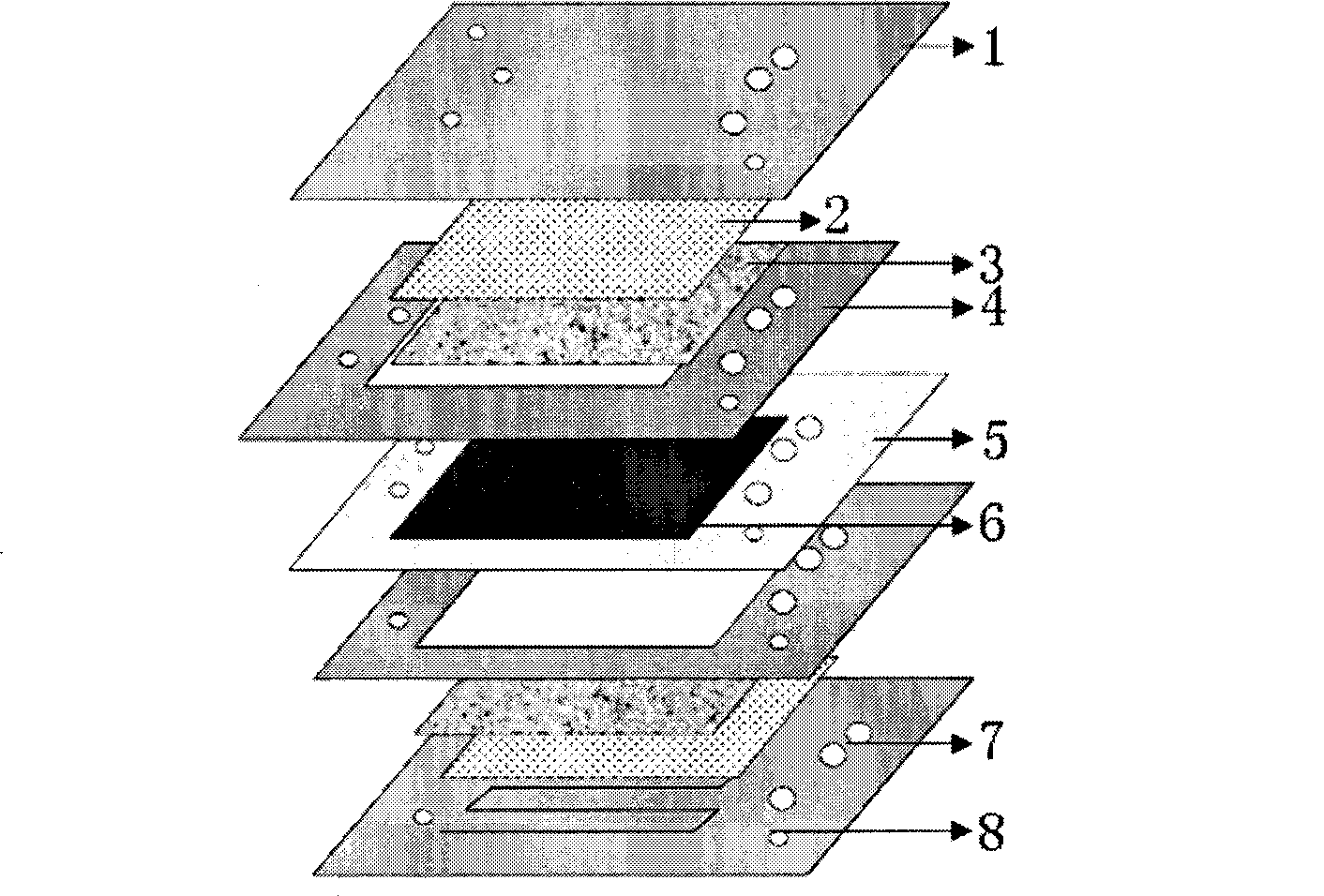
Oxygen electrode slurry of solid oxide electrolytic cell, preparation method of oxygen electrode slurry and solid oxide electrolytic cell
ActiveCN111962098ALower impedanceLower overpotentialCellsElectrode shape/formsMetal oxide nanoparticlesElectrolytic cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of solid oxide electrolytic cells, and particularly relates to oxygen electrode slurry of a solid oxide electrolytic cell, a preparation method of the oxygen electrode slurry and the solid oxide electrolytic cell. The invention provides a preparation method of oxygen electrode slurry of the solid oxide electrolytic cell, which comprises the following steps: step 1, loading metal oxide nanoparticles in an oxygen electrode powder material to prepare oxygen electrode powder; and 2, mixing the oxygen electrode powder, a second pore-forming agent and a binder to prepare the oxygen electrode slurry of the solid oxide electrolytic cell. The invention provides oxygen electrode slurry of the solid oxide electrolytic cell, a preparation method of the oxygen electrode slurry and the solid oxide electrolytic cell, and can effectively overcome the technical defects that the initial internal resistance of the existing SOEC is large and the impedance of anoxygen electrode is increased quickly.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
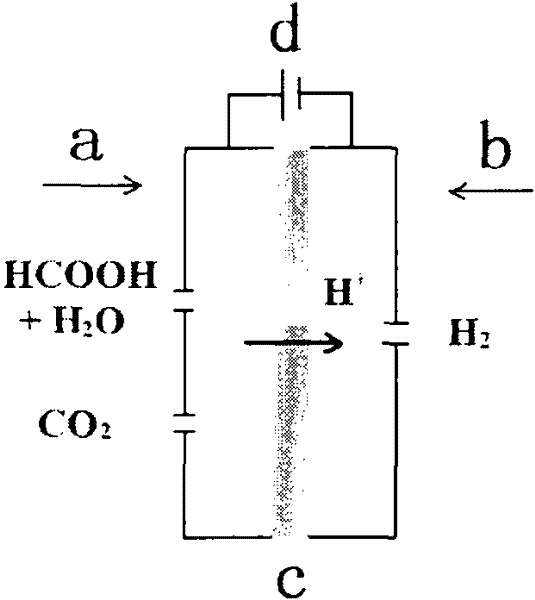
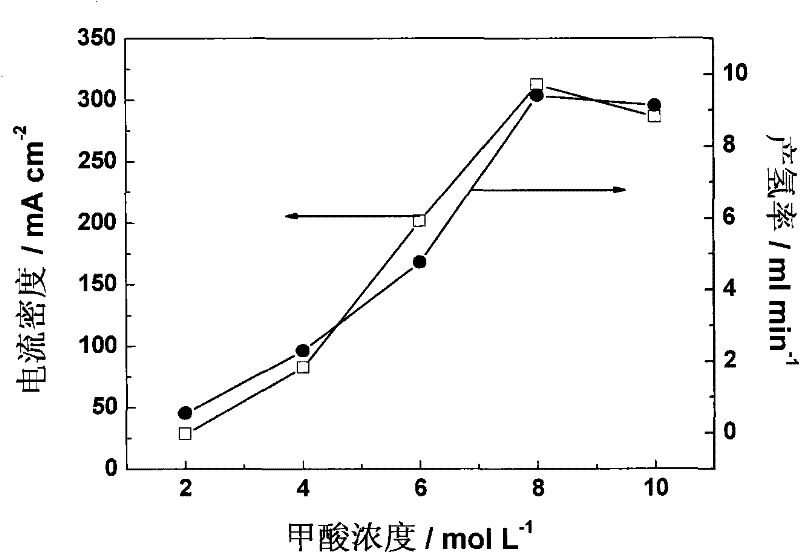
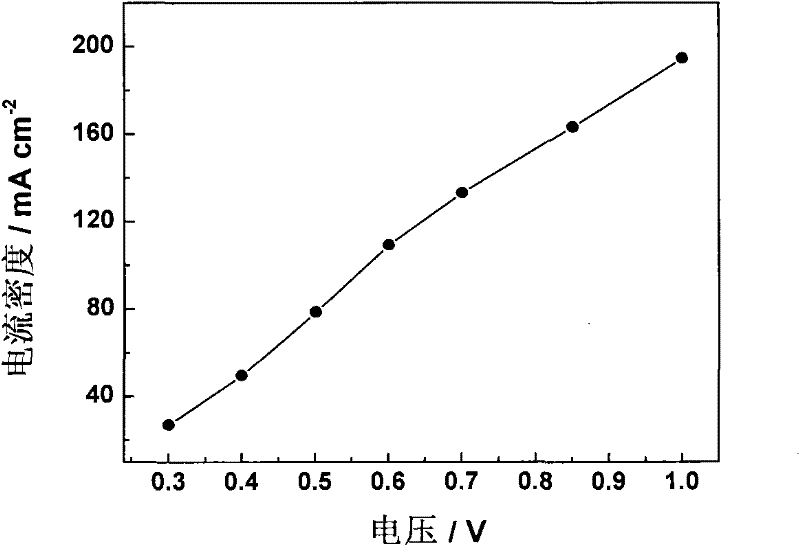
Method for electrolytically preparing hydrogen from formic acid
InactiveCN102456903AThe hydrogen production method is simpleConvenient hydrogen production methodOrganic diaphragmsFuel cellsPolymer electrolytesElectrolysis
The invention provides a method for electrolytically preparing hydrogen from a formic acid. The hydrogen is electrolytically prepared from a fuel which is an aqueous solution of formic acid by a polymer electrolyte film electrolyzer. An anode, an electrolyte film and a cathode are sequentially stacked and hot-pressed to form an electrolysis electrode, and the electrolysis electrode is clamped between two polar plates to form the polymer electrolyte film electrolyzer. The aqueous solution of formic acid is introduced in the anode side of the electrolyzer, a voltage is applied between the cathode and the anode so that the formic acid undergoes electro-catalytic oxidation reaction at the anode, and the hydrogen is generated on a cathode side. The method is a small-scale in-situ hydrogen preparation method which is convenient, quick and flexible, and has the advantages of low electrolysis voltage, low energy consumption, high hydrogen preparation efficiency and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for fluorinated carbon material
InactiveCN105002518AEliminate resistanceEliminate pollutionElectrolysis componentsSupporting electrolyteAlloy
The invention discloses a preparation method for a fluorinated carbon material, relates to an electrochemical preparation method for the fluorinated carbon material, and aims to solve the problems that the conventional preparation method for the fluorinated carbon material is severe in reaction condition as well as difficult and very dangerous in fluorine gas storage and conveying. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) in a single-chamber electrolytic cell, carrying out electrolysis for a certain period till the reaction is finished, wherein Ni, Fe, or a Ni-Ti alloy is adopted as a cathode, Ni or a Ni alloy is adopted as an anode, a metal fluoride is adopted as a supporting electrolyte, a carbon material is adopted as a raw material, and hydrogen fluoride is adopted as an electrolyte solution; (2) after the electrofluorination reaction is finished, cooling the electrolytic cell, leading the electrolyte solution, the metal fluoride and the carbon material subjected to the electrofluorination reaction into a plastic bottle, heating, cooling to recover hydrogen fluoride, carrying out washing to remove residual HF and metal fluoride, and carrying out vacuum drying to obtain the fluorinated carbon material. The preparation method has the advantage that fluorine gas is indirectly utilized, so that the extremely severe reaction conditions required by the utilization of fluorine gas are not needed, and the potential safety hazards during fluorine gas storage and conveying can be avoided.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chlorine evolution anode
InactiveUS20140231249A1Reduce the electrolysis voltageLow evolutionMachining electrodesSeawater treatmentElectrolysisAqueous solution
Provided is a chlorine evolution anode in which a main reaction of the anode is chlorine evolution, and the chlorine evolution anode which is low in potential of the anode for chlorine evolution, thereby being able to decrease an electrolytic voltage and lower an electric energy consumption rate. The chlorine evolution anode of the present invention is a chlorine evolution anode in which chlorine evolution from an aqueous solution is a main reaction of the anode and also in which a catalytic layer containing amorphous ruthenium oxide and amorphous tantalum oxide is formed on a conductive substrate.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
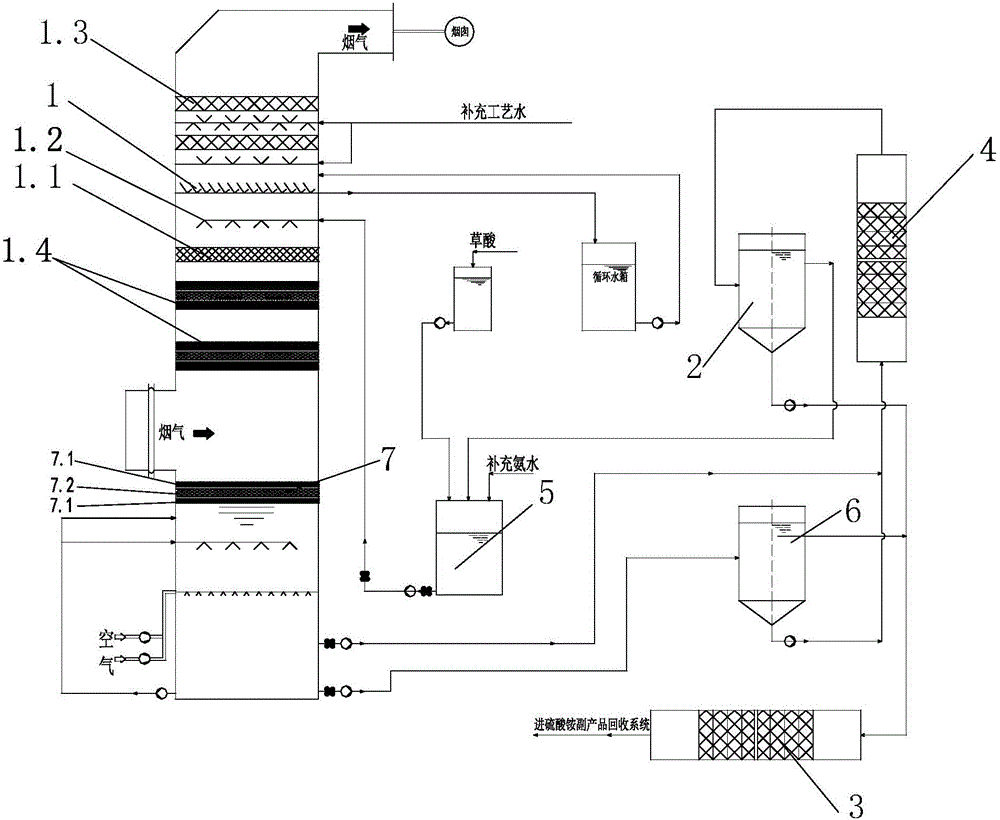
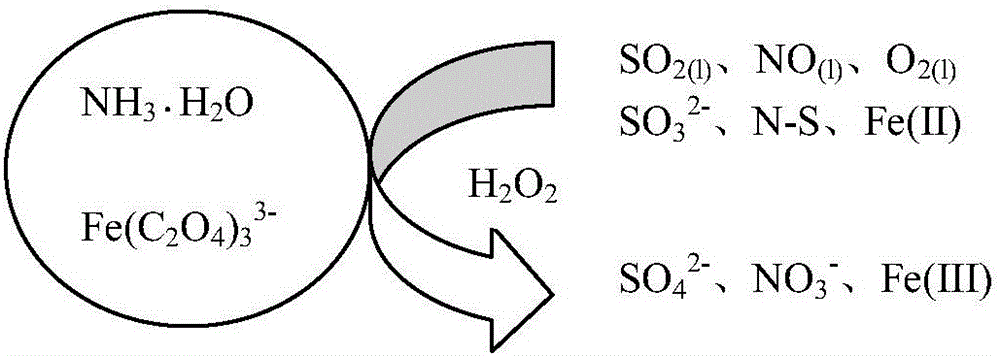
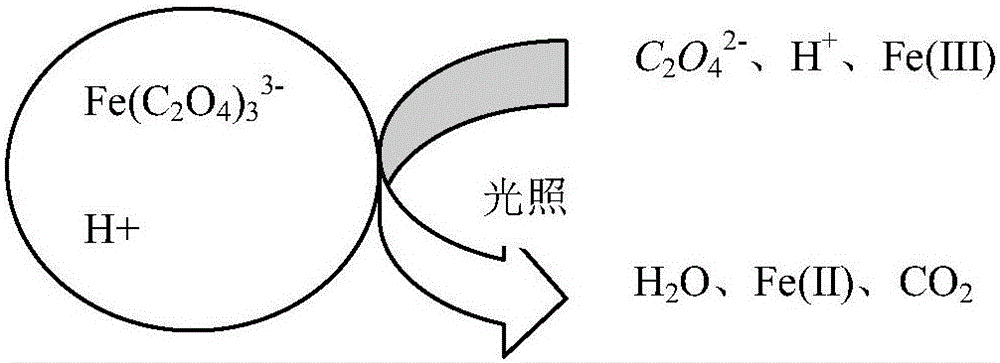
Sintering flue gas synchronous desulfurization and denitration process based on optical-electric type fenton coupling regeneration
InactiveCN105833724AEfficient regenerationReduce the burden onGas treatmentDispersed particle separationOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEReaction layer
The invention relates to a sintering flue gas synchronous desulfurization and denitration process based on optical-electric type fenton coupling regeneration. The sintering flue gas synchronous desulfurization and denitration process comprises the following steps: flue gas is fed into an absorption tower to have a reverse contact reaction with a circulating absorption solution sprayed out by a spraying layer, and then is discharged out from the top of the absorption tower, specifically, the flue gas enters the absorption tower from a flue gas inlet in the middle of the absorption tower, sequentially passes through at least one photochemical reaction layer, a packing layer and the spraying layer, which are arranged at the upper part of the tower, to have the reverse contact reaction with the circulating absorption solution, and then is discharged out from a flue gas outlet at the top of the absorption tower; after the circulating absorption solution sprayed out by the spraying layer at the upper part of the absorption tower sequentially passes through the packing layer and the at least one photochemical reaction layer to have the reverse contact reaction with the flue gas, the circulating absorption solution is electrolyzed to be regenerated through an electrolysis regeneration layer at the lower part of the absorption tower, and then is conveyed to a photocatalysis regeneration reaction system from the bottom of the absorption tower to be regenerated; and ammonia water and oxalic acid are supplemented into a regenerated slurry groove and then are conveyed back into the spraying layer at the upper part of the absorption tower to be sprayed into the tower. The sintering flue gas synchronous desulfurization and denitration process is simple, and is low in operation cost, good in denitration effect and good in byproduct quality.
Owner:JIANGSU DISA MACHINERY +1
Device and method for purifying rare earth halide
ActiveCN103409769ASimple purification processImprove stabilityChemical industryElectrode shape/formsElectrolysisShielding gas
The invention discloses a device and a method for purifying rare earth halide. The device comprises a crucible used for electrolytic purification, a positive pole, a negative pole and a ventilation pipeline system used for supplying shielded gas into an electrolytic system, wherein the positive pole and the negative pole are arranged in the crucible; a solid oxygen permeation membrane is arranged on the surface of the positive pole; the melting point of the solid oxygen permeation membrane is larger than that of to-be-purified rare earth halide. The method comprises the step of electrolytically purifying rare earth halide by adopting the device provided by the application. The electrolytic device is simple, purification technology is simple, the stability is high, the electrolysis voltage is low, the electrolysis time is short, and energy conservation, environmental protection and large scale industrial production are facilitated. Rare earth halide obtained by using the device and the purifying method provided by the invention is high in purity, and the oxygen content is less than 50 ppm.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank using bipolar membrane as diaphragm and application of electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank
InactiveCN102912374BAchieving electrochemical reductionReduce the electrolysis voltageOrganic diaphragmsElectrolytic organic productionElectrolytic agentFormate
The invention relates to an electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank using a bipolar membrane as a diaphragm and an application of the electrochemical reduction CO2 electrolytic tank. The electrolytic tank comprises a cathode electrolysis compartment, cathode liquor, an anode electrolysis compartment, anolyte and the bipolar membrane for dividing the cathode electrolysis compartment and the anode electrolysis compartment. The electrode materials of the cathode electrolysis compartment include Pb (Plumbum), In (Indium) and Cu (Copper) etc, and the cathode liquor is an alkaline aqueous solution; and the electrode materials of the anode electrolysis compartment include Pt (Platioum) and Pd (Palladium) etc, and the anolyte is an acidic aqueous solution containing iodate. The hydroxy radicals in the cathode electrolysis compartment and the protons in the anodic electrolysis compartment are diffused to the bipolar membrane to generate water so as to form a voltage drop, so that the working voltage in the electrolytic tank is reduced. Compared with an anodic reaction that water and the electricity are oxidized to generate oxygen, the iodide ions are oxidized to generate an iodine elementary substance with low potential, small overpotential and quick dynamic process, so that the working voltage in the electrolytic tank is further reduced. CO2 is electrically reduced in a cathode compartment so as to generate small molecular fuels, such as formate, methanel, and methane; and the iodide ions are electrically oxidized to generate the elementary substance iodine in an anode compartment.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ion-exchange membrane for alkali chloride electrolysis, manufacturing method, and alkali chloride electrolysis device
ActiveCN107109673AReduce the electrolysis voltageHigh strengthIon-exchange process apparatusCellsMetal chlorideElectrical resistance and conductance
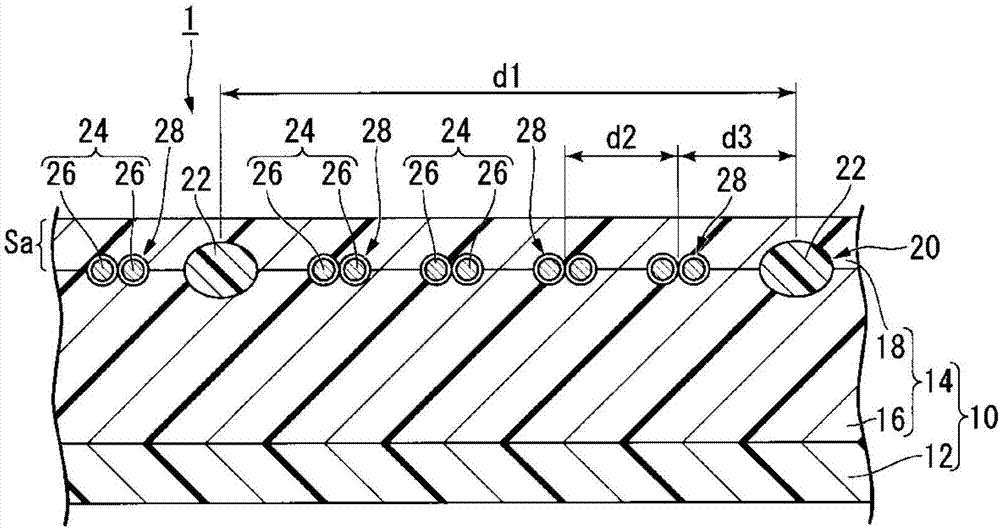
Provided is an ion-exchange membrane for alkali chloride electrolysis which has increased membrane strength and reduced membrane resistance, thereby reducing the electrolysis voltage for alkali chloride electrolysis. In this ion-exchange membrane (1) for alkali chloride electrolysis, a reinforcing material (20) formed by weaving reinforcing threads (22) and sacrificial threads (24) is disposed in a layer (S) (14), and layer (S) (14) comprises elution parts (28) which are formed by elution of at least portions of the sacrificial threads (24). In a cross section perpendicular to the warp threads of the reinforcing threads, the average distance (d1) from the center of a reinforcing thread (22) to the center of an adjacent reinforcing thread (22), the total area (P) obtained by adding the cross-sectional areas of the elution parts (28) and the cross-sectional areas of the remaining sacrificial threads (24) in the elution parts (28), the number (n) of elution parts between adjacent reinforcing threads (22), and the ion exchange capacity of a layer (Sa) in layer (S) (14) closest to the positive electrode side upon alkali chloride electrolysis are controlled within specific ranges.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Anode for electroplating and method for electroplating using anode
ActiveUS20150027899A1Anode potential may be decreasedReduce energy consumptionAnodisationMachining electrodesAqueous solutionElectroplating
Provided is an anode for electroplating which uses an aqueous solution as an electrolytic solution, and the anode which is low in potential when compared with a conventional anode, able to decrease an electrolytic voltage and an electric energy consumption rate and may also be used as an anode for electroplating various types of metals, and which is low in cost. Also provided is a method for electroplating which uses an aqueous solution as an electrolytic solution, in which the anode is low in potential and electrolytic voltage, thereby making it possible to decrease the electric energy consumption rate. The anode for electroplating of the present invention is an anode for electroplating which uses an aqueous solution as an electrolytic solution, in which a catalytic layer containing amorphous ruthenium oxide and amorphous tantalum oxide is formed on a conductive substrate.
Owner:DOSHISHA CO LTD
Method for simultaneously obtaining hydrogen and biomass fuel rod by using biomass raw material
The invention relates to a method for united circulation of biomass hydrothermal carbonization and electrolytic hydrogen production, and particularly relates to the method for simultaneously obtaininghydrogen and a biomass fuel rod by using a biomass raw material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the biomass raw material, an oxidant and water, heating at a constant speed, andperforming hydrothermal reaction; (2) performing solid and liquid separation on products generated after the hydrothermal reaction; (3) performing electrochemical reaction by taking the liquid obtained after the hydrothermal reaction in the step (2) as an anode, collecting hydrogen and obtaining anode electrolyte after electrolysis is completed; (4) mixing the anode electrolyte obtained after electrolysis in the step (3) with a solid substance obtained after the hydrothermal reaction in the step (2), and performing hydrothermal reaction again; (5) repeating the steps (2) to (4) until no hydrogen is collected in the step (3); and (6) washing and drying the solid products generated in the hydrothermal reaction in the step (4) and pressing to form the fuel rod. By directly utilizing the biomass raw material, the method disclosed by the invention creatively opens up a way and a method for clean utilization of biomass energy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM (transmission electron microscopy) sample
InactiveCN109406556AImprove production efficiencySafe preparationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectrolysisAlcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of alloy material detection and analysis, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM (transmission electron microscopy) sample. The method aims at solving the technical problems that the existing method for preparing the GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM sample is low in efficiency, and that the quality is poor. The method aims to provide the economical, efficient, convenient and fast method for preparing the GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM sample. The method for preparing the GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM sample is characterized by comprising the following steps that after the thickness of a GH4169 high-temperature alloy sample is reduced to 70 to 80 mu m, an electrolysis double-spray method isused for thinning; used electrolyte is a mixed solution of 10-percent perchloric acid and 90-percent absolute ethyl alcohol. The TEM sample prepared by the method has high surface quality and large thin regions; the method is very applicable to the large-batch preparation of high-quality GH4169 high-temperature alloy TEM samples.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Device and method for producing hydrogen through step-by-step water electrolysis based on all-vanadium liquid flow redox medium
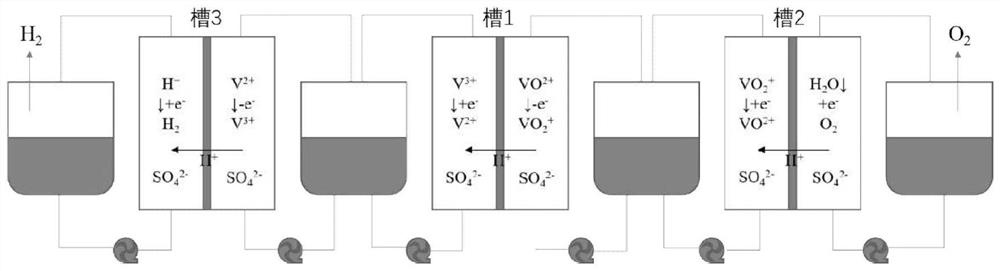
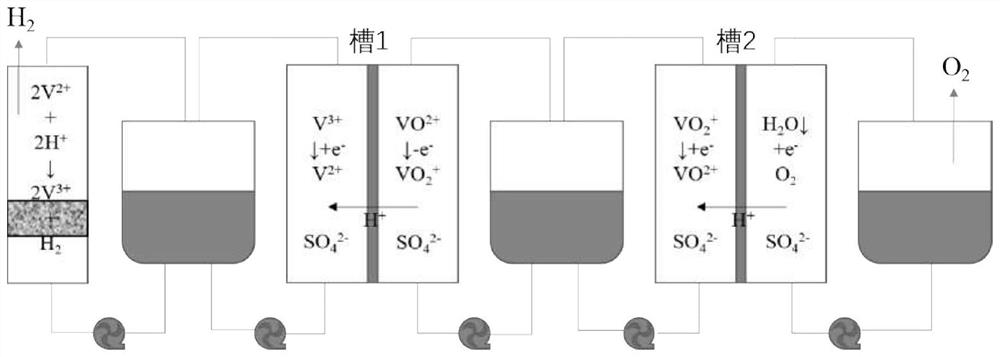
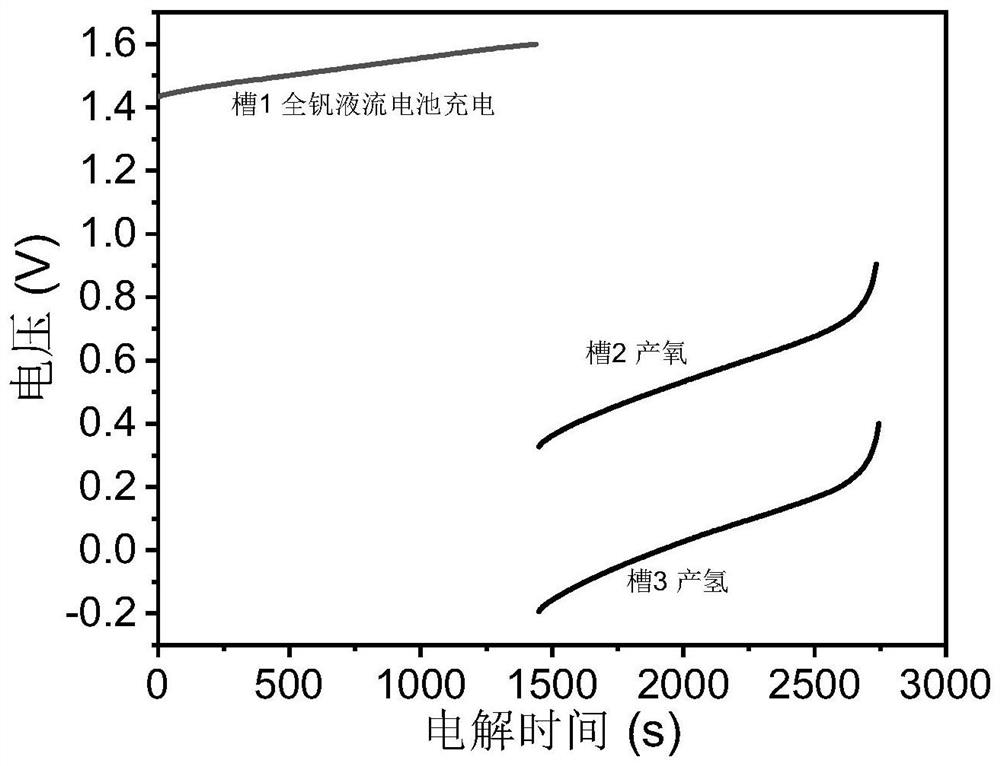
InactiveCN113416972AReduce the electrolysis voltageRegulating hydrogen productionCellsRegenerative fuel cellsPhysicsElectrical battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of water electrolysis, and relates to a device and method for producing hydrogen through step-by-step water electrolysis based on an all-vanadium liquid flow redox medium The device comprises two diaphragm electrolytic cells (a cell 1 and a cell 2), a hydrogen evolution unit and an acidic all-vanadium electrolyte. According to the method, the water electrolysis is divided into two steps, charging an all-vanadium redox flow battery and producing hydrogen and oxygen. According to the first step, VO < 2 + > in an anode chamber in a tank 1 is oxidized into VO < 2 + >, and the VO 2 <+> is introduced into a tank 2; and V < 3 + > in a cathode chamber in the tank 1 is reduced into V < 2 + >, and meanwhile, the V < 2 + > is introduced into the hydrogen evolution unit. According to the second 2, in a tank 2, VO 2 <+> in the cathode chamber is reduced into VO < 2 + > and the VO < 2 + > is circulated back to the tank 1, and meanwhile, the anode generates oxygen; and V < 2 + > is oxidized into V < 3 + > in the hydrogen evolution unit and the V < 3 + > is circulated back to the tank 1, and hydrogen is generated at the same time. According to the method of the invention, hydrogen and oxygen can be separated out in different spaces and time, so that high-purity hydrogen is prepared; meanwhile, the electrolysis voltage is reduced, and the hydrogen production volume can be adjusted by controlling the amount of the electrolyte.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Catalyst coating and process for production thereof
InactiveUS20170067172A1Reduce overpotentialReduce the electrolysis voltageElectrode thermal treatmentMultiple component coatingsElectrolysisActive component
A process for wet-chemical production of a catalyst coating on an electrically conductive support for electrodes for chloralkali or hydrochloric acid electrolysis with electro catalytically active components based on noble metal oxides, in which the catalyst coating is produced by; producing a coating solution or dispersion comprising a precursor compound of a noble metal and / or a metal oxide of a noble metal, and a solvent or dispersant, with addition of one or more acids to the coating solution or dispersion, where the molar ratio of the total of the amounts of acid (in mol) present in the coating solution or dispersion to the sum of the amounts of the metals from the metal-containing components present in the coating solution or dispersion is at least 2:1; applying the coating solution or dispersion to the support; substantially freeing the layer applied of solvent or dispersant by drying; and subjecting the dried layer obtained to a thermal treatment to form the catalyst coating.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG +1
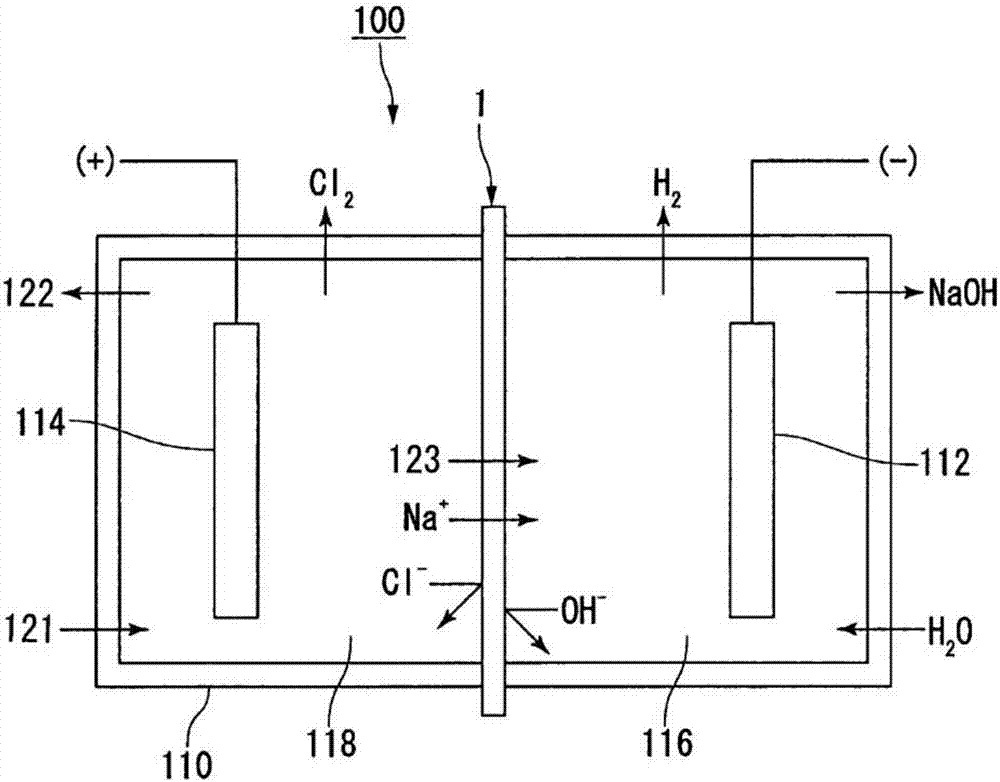
Chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell and method for producing Cl2 and NaOH by using the same
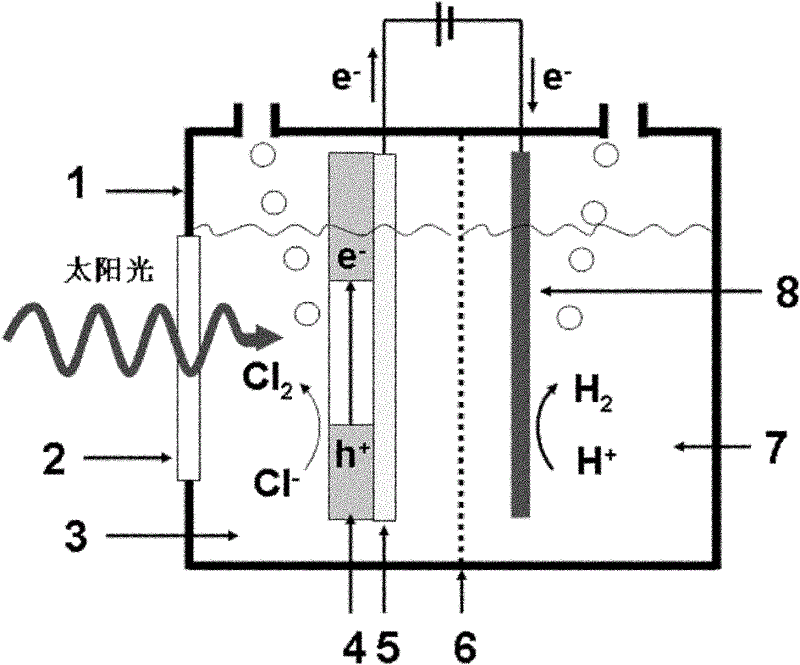
InactiveCN102618880ALow costReduce the electrolysis voltageCellsElectrodesElectrolytic agentBattery cell
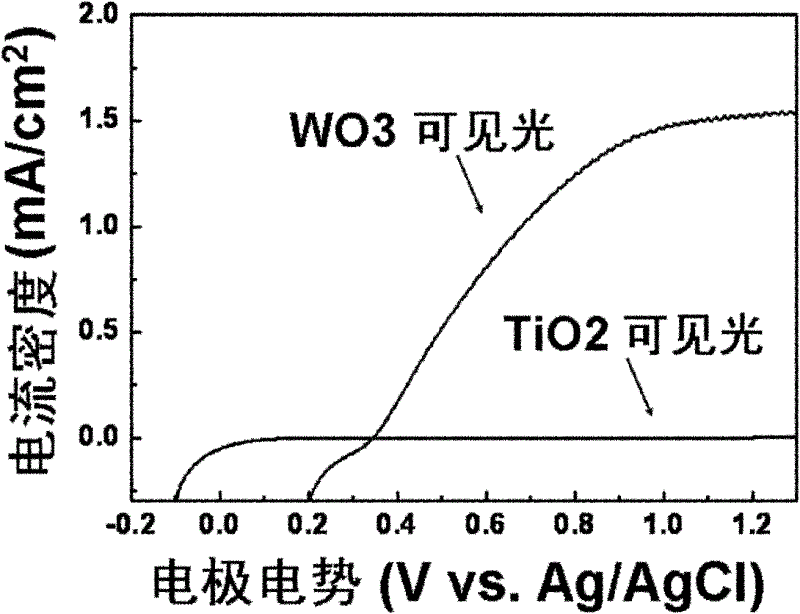
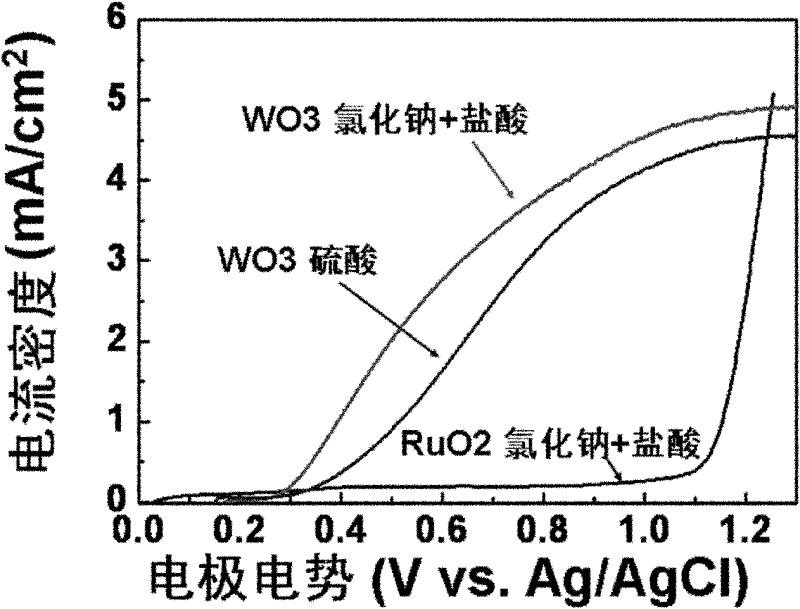
The invention relates to a chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell which is cheap and can effectively reduce electrolytic voltage. The invention further provides a method for producing Cl2 and NaOH by using the chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell. The chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell comprises an electrolytic bath formed by an anodic pool and a cathodic pool, wherein the anode in the anodic pool is made from a photoanode material WO3, the anodic pool is provided with a light-transparent window in order to let sunlight irradiate on the anode, and the anode electrolyte is an acidic saturated saline solution. The chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell can be used in chlor-alkali industry for producing Cl2 and NaOH by electrolysis. WO3 is used in the invention as the photoanode material. The anode material is a film with the optimal thickness of 1000-5000 nm. The optimal anode material is a porous structure with the pore structure size of 50-200 nm. The chlor-alkail photoelectrolytic cell has low cost, and can effectively reduce the electrolytic voltage when being used in chlor-alkali industry for producing Cl2 and NaOH by electrolysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Water electrolysis catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106732609AMicrocrystalline particle size reductionLarge specific surface areaMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesPower flowOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses a water electrolysis catalyst. The catalyst is characterized by being represented by a molecule NixMy, wherein x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 1, y is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.4, and M is one or more than one of Mo, Cr and Co. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the water electrolysis catalyst. The catalyst disclosed by the invention is a compound (a homogeneous phase), and the content of doping components is low; and a lot of catalysts in other related inventions are mixtures, and the doping components independently form phases so that the catalytic activity is influenced. When the catalyst disclosed by the invention is used for a cathode of an alkaline water electrolysis device under the same current density, the utilization effect is better than that of the catalyst which is not doped with the element.
Owner:刘贝涛
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com