Attenuation reduction grounding pattern structure for connection pads of flexible circuit board
a flexible circuit board and grounding pattern technology, applied in the direction of printed circuits, printed circuit details, high frequency circuit adaptations, etc., can solve the problems of electromagnetic signal scattering, signal transmission and receipt loss, signal waveform distortion, etc., to reduce the probability of error, reduce reflection loss, excellent effect of impedance match
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0038]Referring to FIG. 7, which is schematic view illustrating an application in which the flexible circuit board 100 according to the present invention is insertable into a female socket connector 7, the female socket connector 7 is provided on a flexible circuit board 71. When the flexible circuit board 100 of the present invention is inserted into an insertion slot 72 of the female socket connector 7, the high frequency connection pads 2a, 2b of the flexible circuit board 100 are positioned to respectively engage conductive terminals 73 mounted in the female socket connector 7.
[0039]Referring to FIGS. 8 and 9, which are respectively an exploded view and a cross-sectional view of a second embodiment of the present invention, the instant embodiment provides a flexible circuit board 200 having a structure that is substantially similar to that of the first embodiment with a difference therebetween residing in that the first end 11 of the component surface 14 of the substrate 1 is pr...
third embodiment
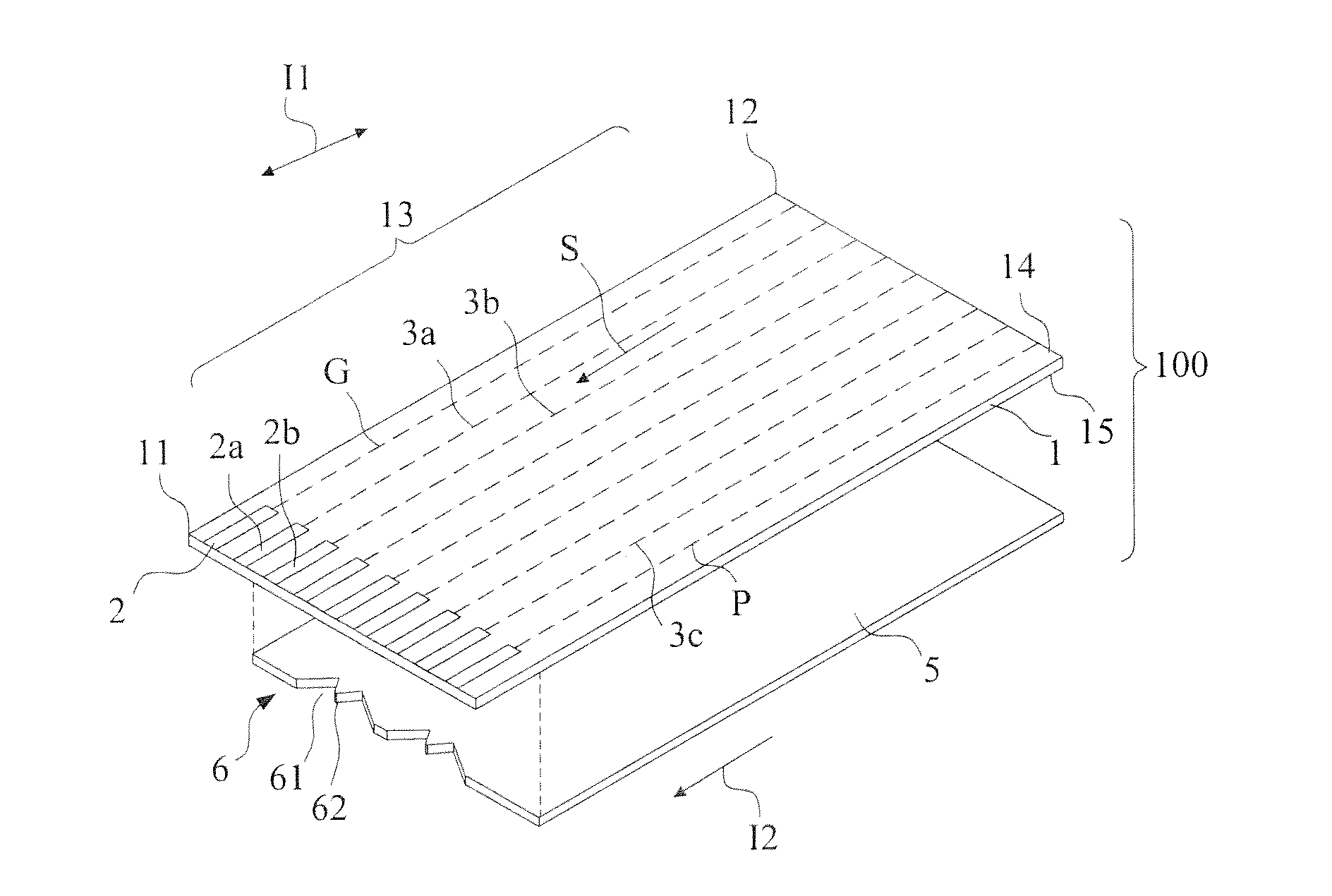
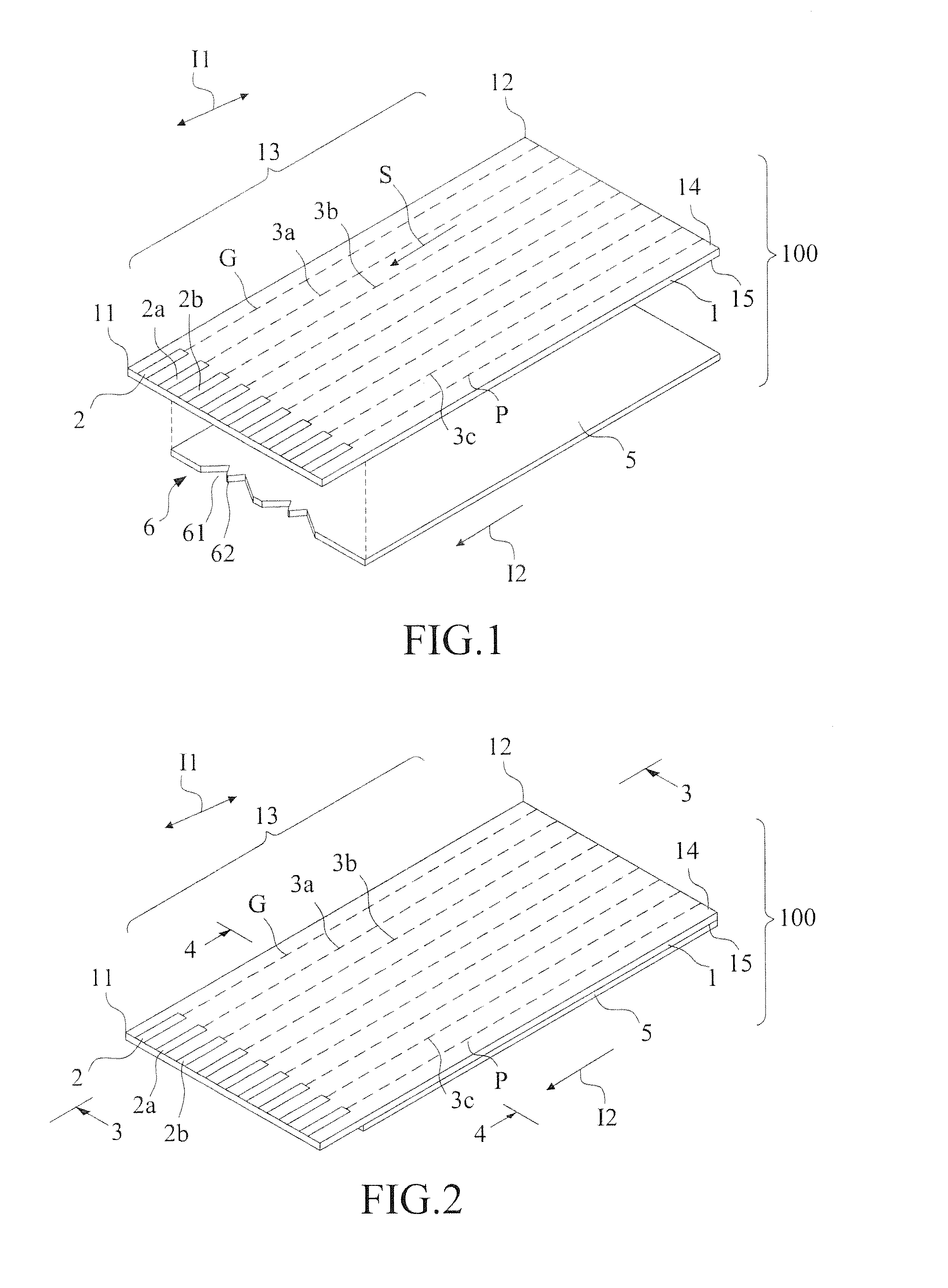
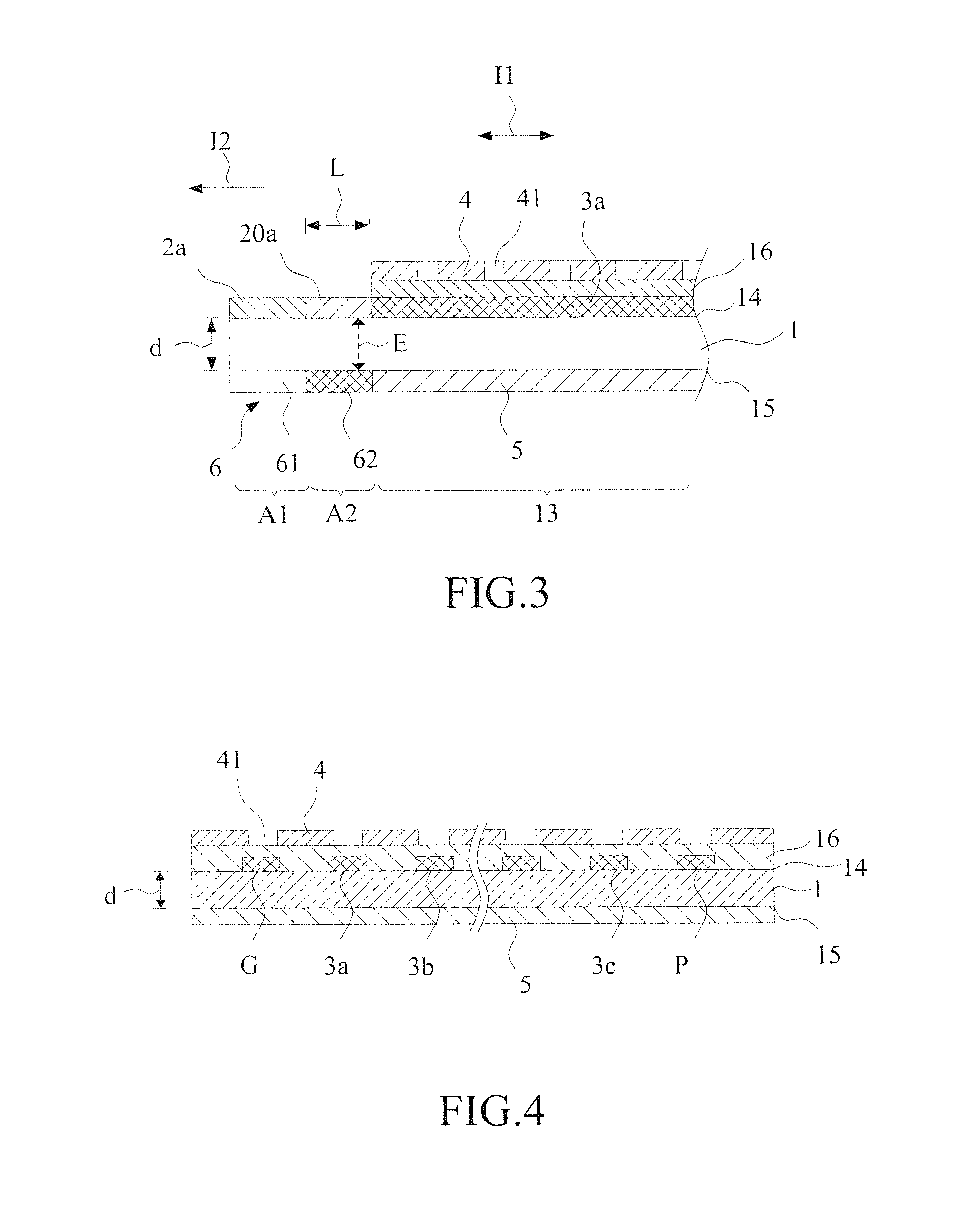
[0044]In the third embodiment, a grounding layer 5 is formed on the grounding surface 15a of the substrate 1. The grounding layer 5 is connected to the grounding line G. Connection of the differential mode signal lines 3a, 3b through the conductive vias 22a, 22b to the high frequency connection pads 2a, 2b is defined as a transition zone A2′.
[0045]The grounding layer 5 comprises a hollowed area 61 and the protruded portion 62 formed in the transition zone A2′ corresponding to the connection pad laying zone A1 and the conductive via arrangement extension sections 21a, 21b to constitute an attenuation reduction grounding pattern structure 6b. The attenuation reduction grounding pattern structure 6b similarly helps the protruded portion 62 and the high frequency connection pads 2a, 2b to form a polarization-direction-varying electrical field in the transition zone A2′ to reduce reflection loss occurring in the transmission of a high frequency signal, achieve an excellent effect of impe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com