Titanium incorporation into absorber layer for solar cell
a solar cell and absorber layer technology, applied in the direction of sustainable manufacturing/processing, climate sustainability, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of large vsub>oc/sub>deficit of czts devices, difficult to achieve an efficiency above 11%, and relatively low performance of czts solar cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
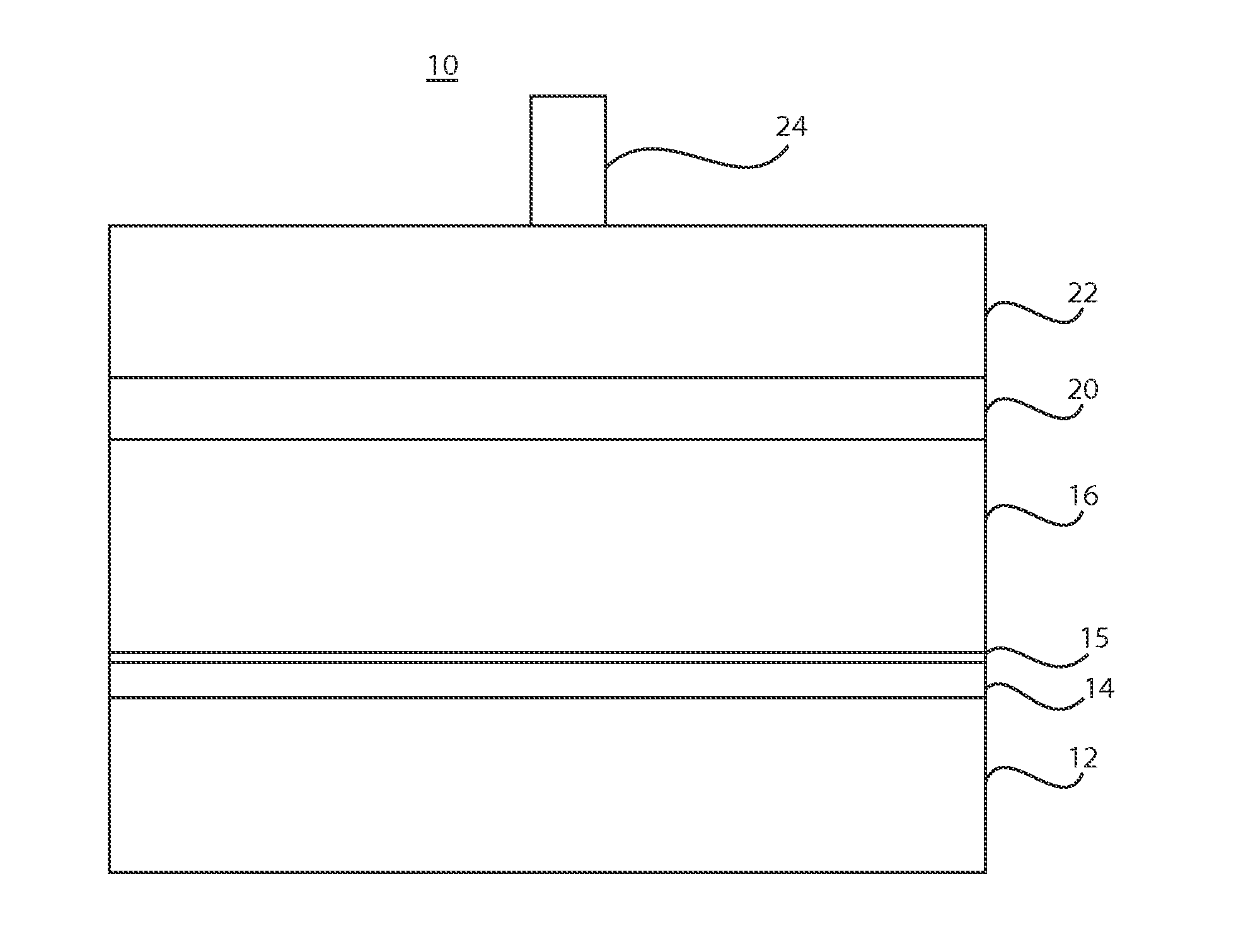
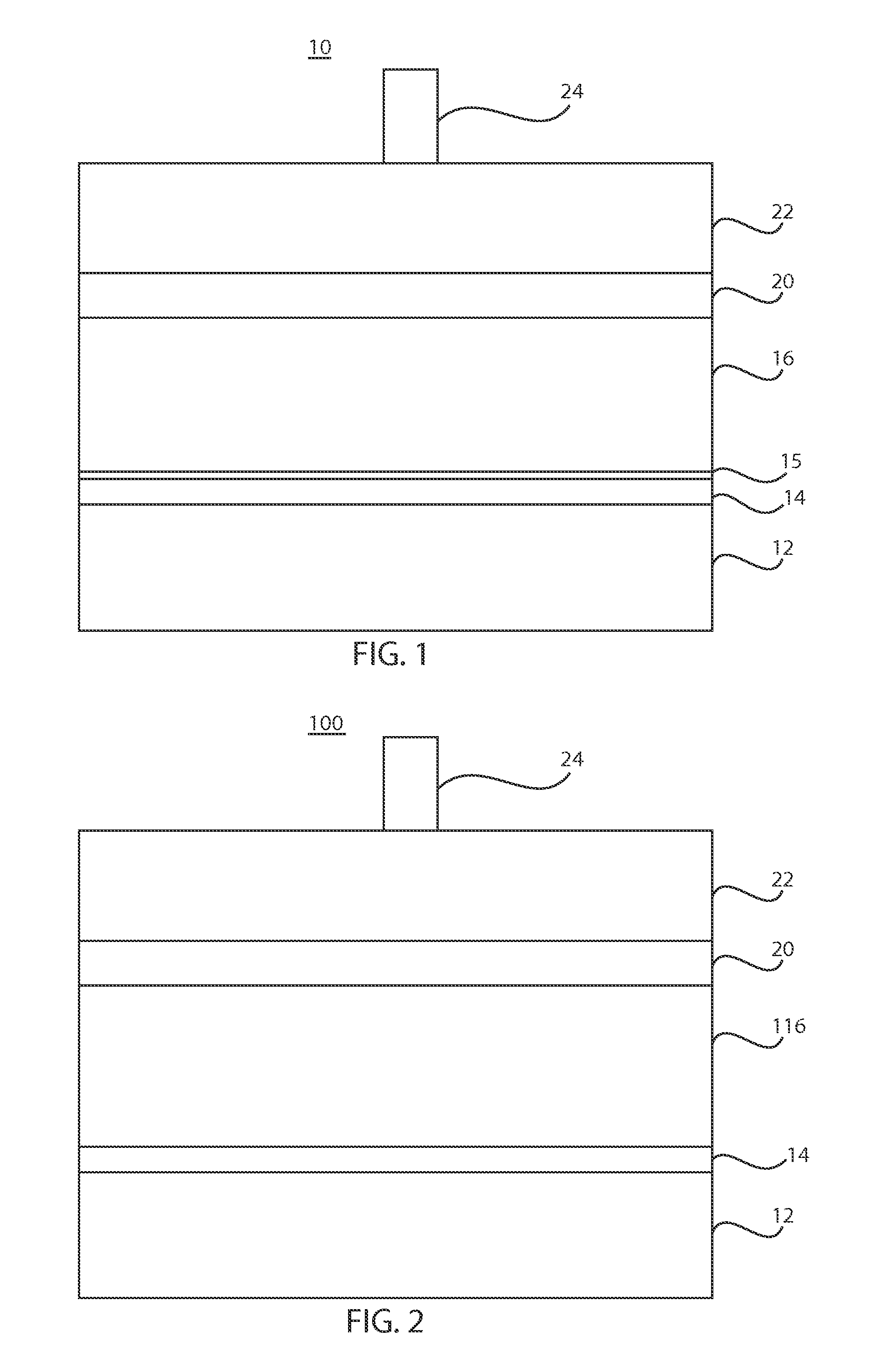
[0057]For making Ti-free devices, solution A (3.3M Cu2S) was made by dissolving Cu and S in hydrazine. Similarly, Sn and Se were stirred in hydrazine to form slurry B (1.5 M SnSes); Solution A and slurry B were mixed together and transferred to a vial containing zinc formate, yielding solution C with final composition Cu / (Zn+Sn)=0.8, Zn / Sn=1.22 and nominal kesterite CZTSSe concentration of approximately 0.4 M. The thin film CZTS absorber layer with final thickness of 2-2.5 microns was prepared by spin coating this mixture over six consecutive layers at 600 rpm and then subsequently subjecting it to a short anneal on a ceramic hot plate with a set point of 630 degrees C.
[0058]The CdS buffer, ZnO window, and indium doped tin oxide (ITO) layers were subsequently deposited by chemical bath deposition and RF magnetron sputtering, respectively, giving a CZTSSe device structure with a device area of approximately 0.45 cm2, as defined by mechanical scribing. A Ni / Al collection grid and 110-...
example 2
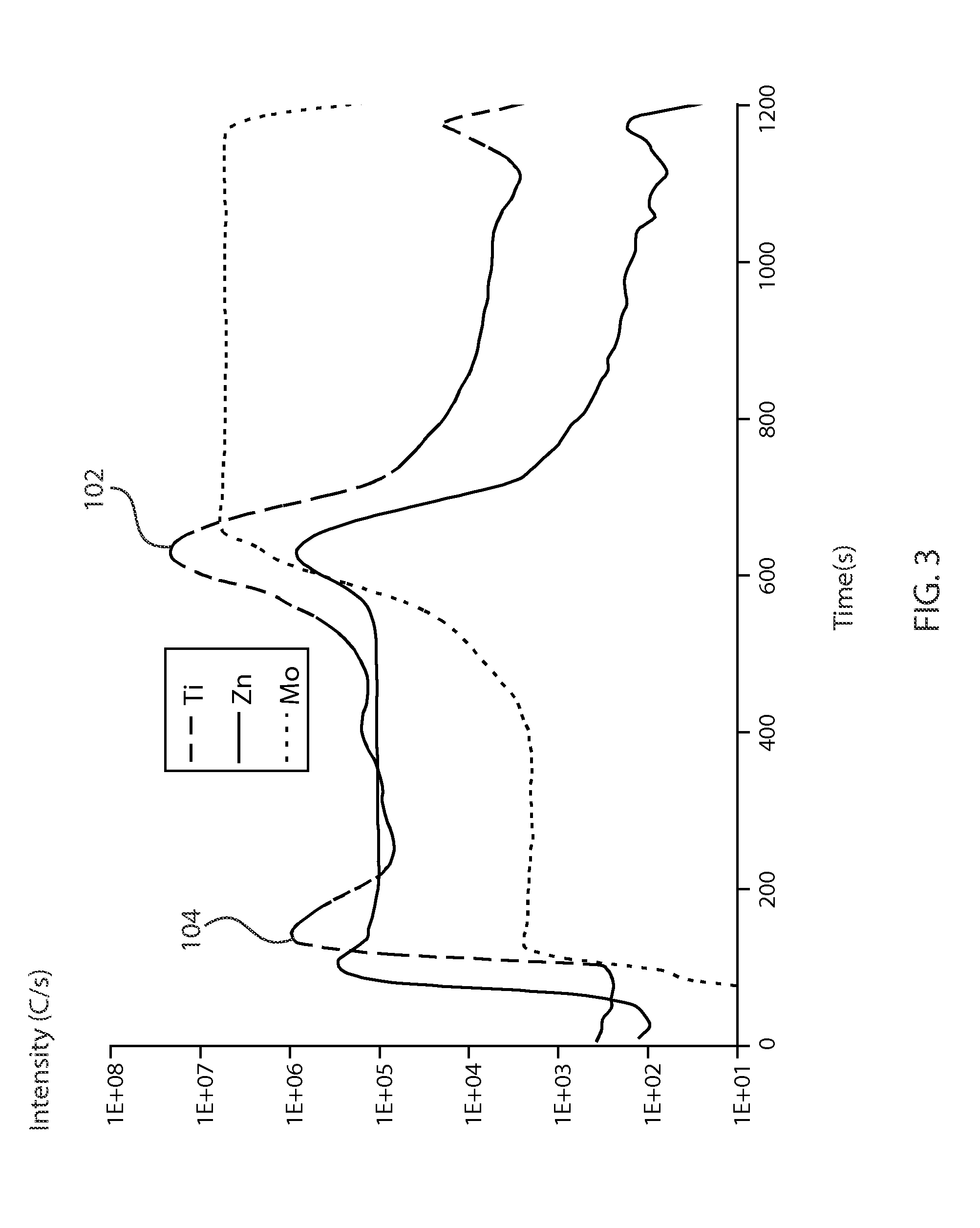
[0059]For making Ti-incorporating devices, a solution A (3.3M Cu2S) was made by dissolving Cu and S in hydrazine. Similarly, Sn and Se were stirred in hydrazine to form slurry B (1.5 M SnSes); Solution A and slurry B were mixed together and transferred to a vial containing zinc formate, yielding solution C with final composition Cu / (Zn+Sn)=0.8, Zn / Sn=1.22 and nominal kesterite CZTSSe concentration of approximately 0.4 M. A 20 nm titanium thin film was deposited on molybdenum-coated glass by electron-beam evaporation. The Ti- and Mo-coated glass was used as a substrate for CZTS deposition.
[0060]The thin film CZTS absorber layer with final thickness of 2-2.5 microns was prepared by spin coating this mixture over six consecutive layers at 600 rpm and then subsequently subjecting it to a short anneal on a ceramic hot plate with a set point of 630 degrees C. The CdS buffer, ZnO window, and indium doped tin oxide (ITO) layers were subsequently deposited by chemical bath deposition and RF ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| open circuit voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com