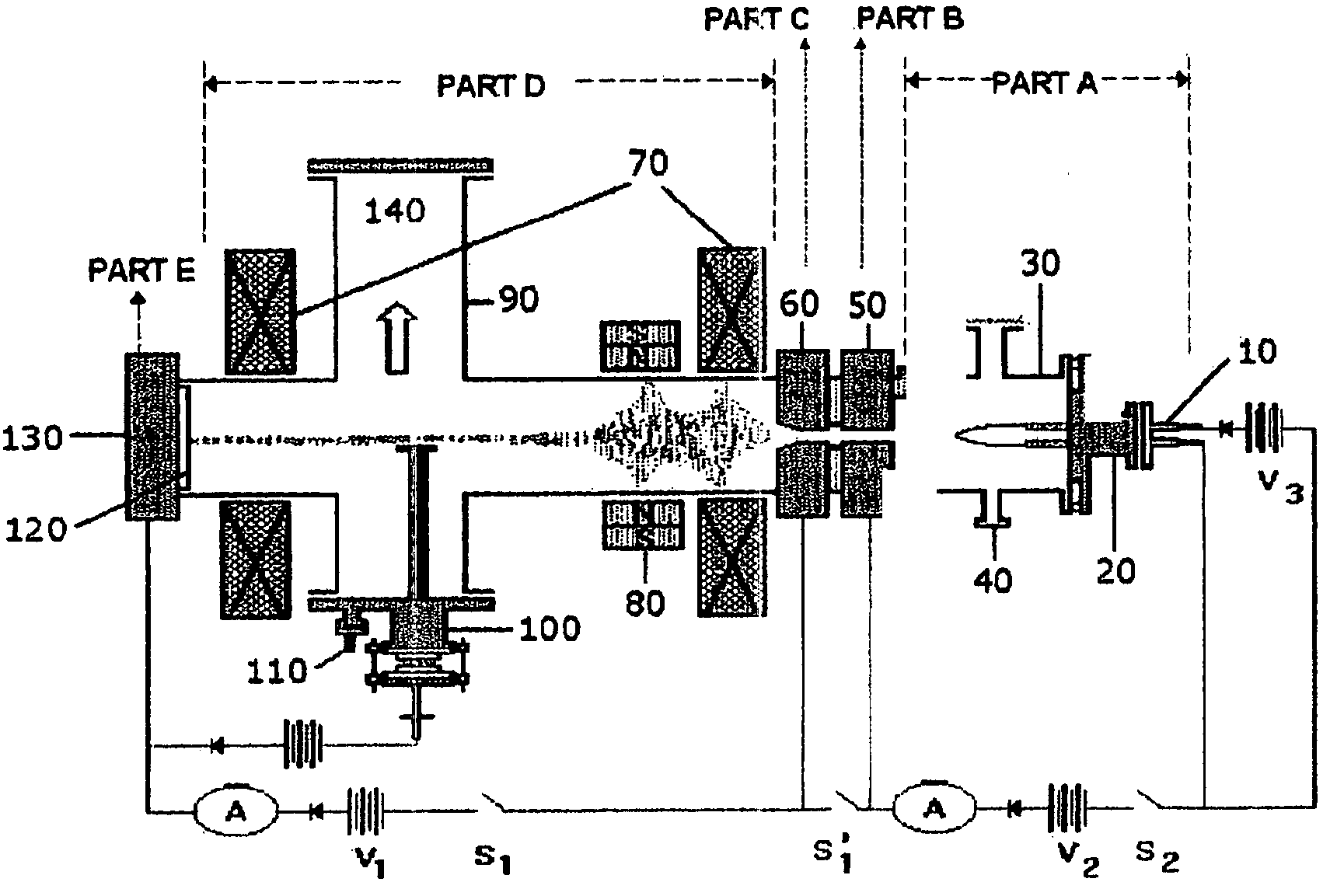
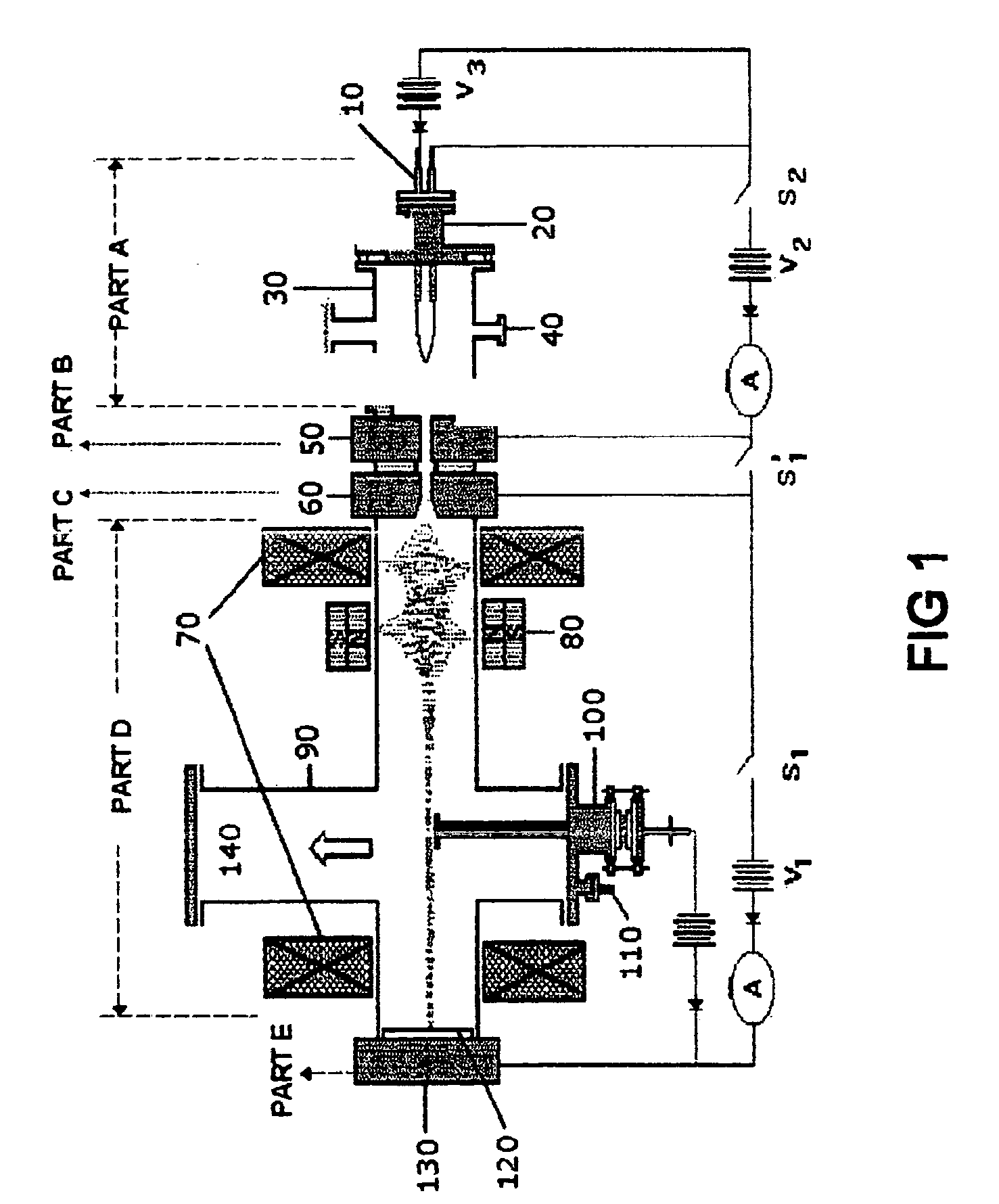
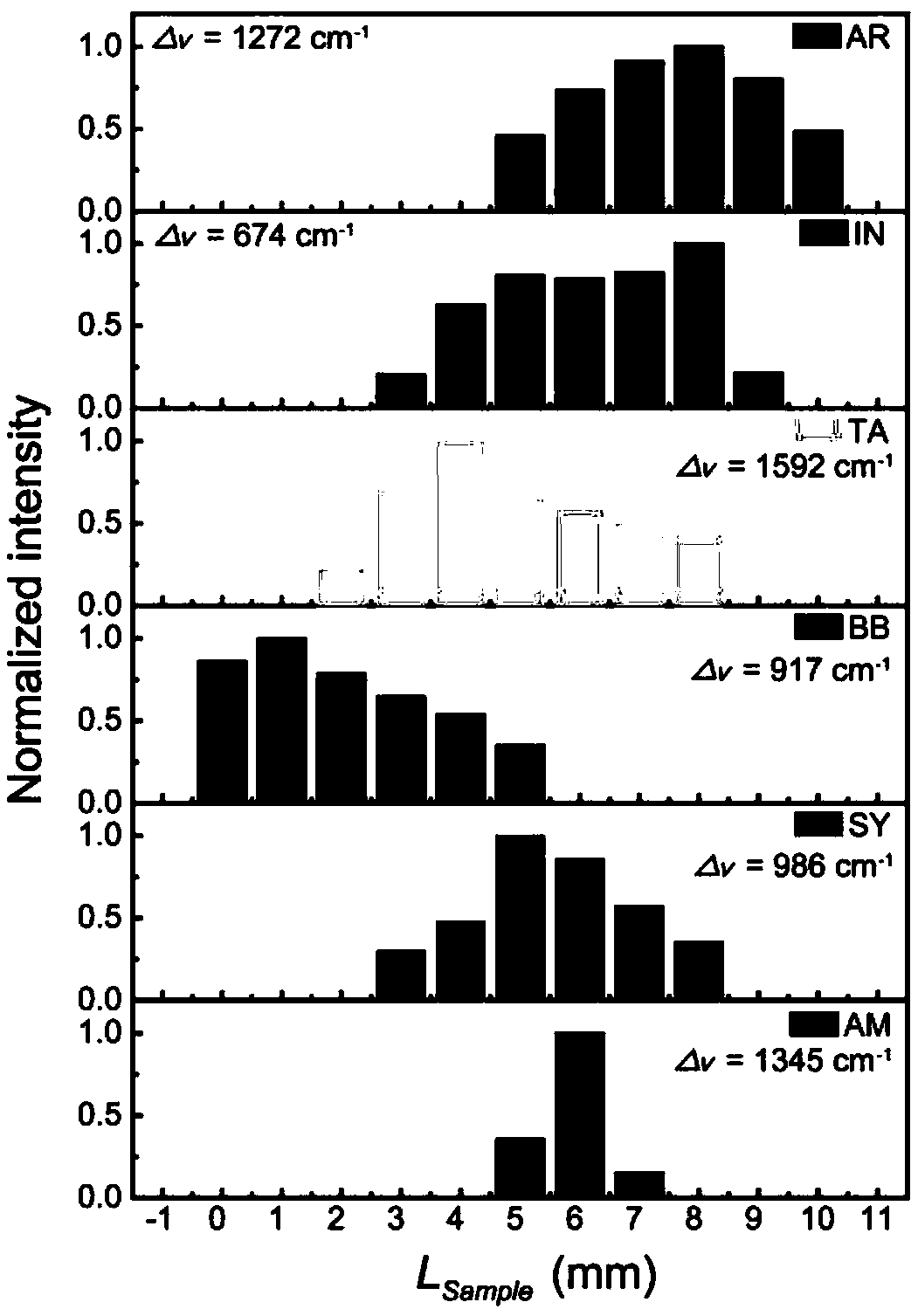
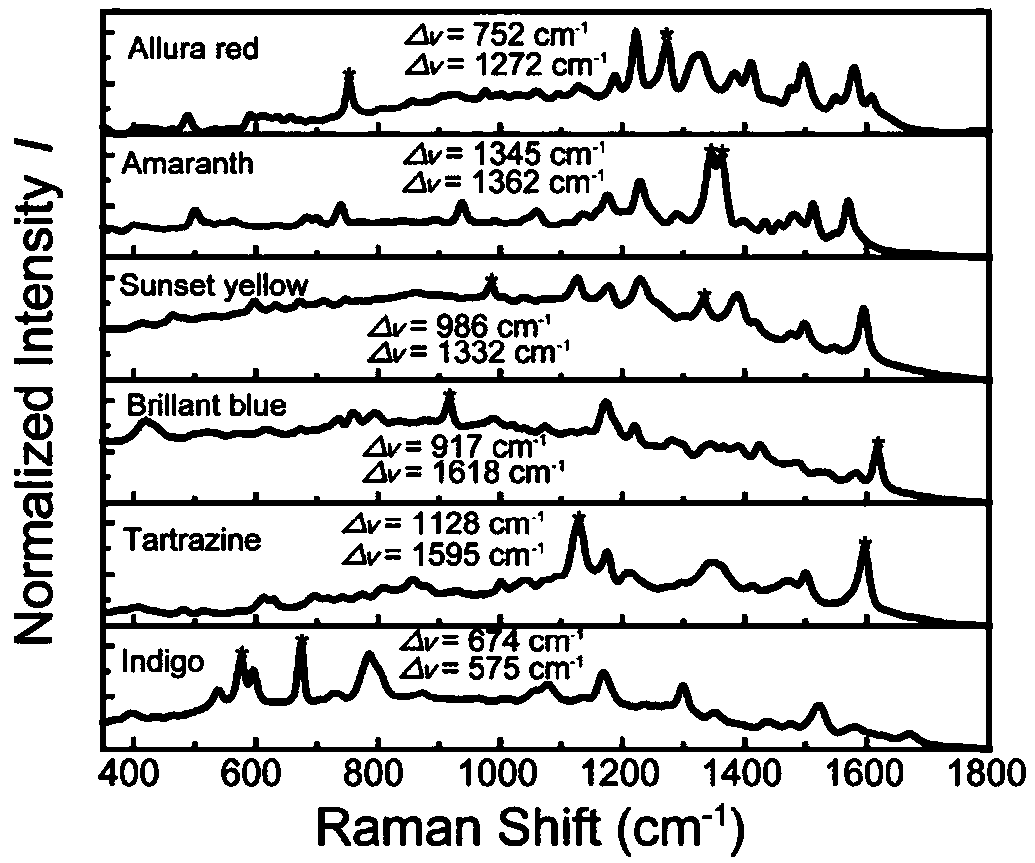
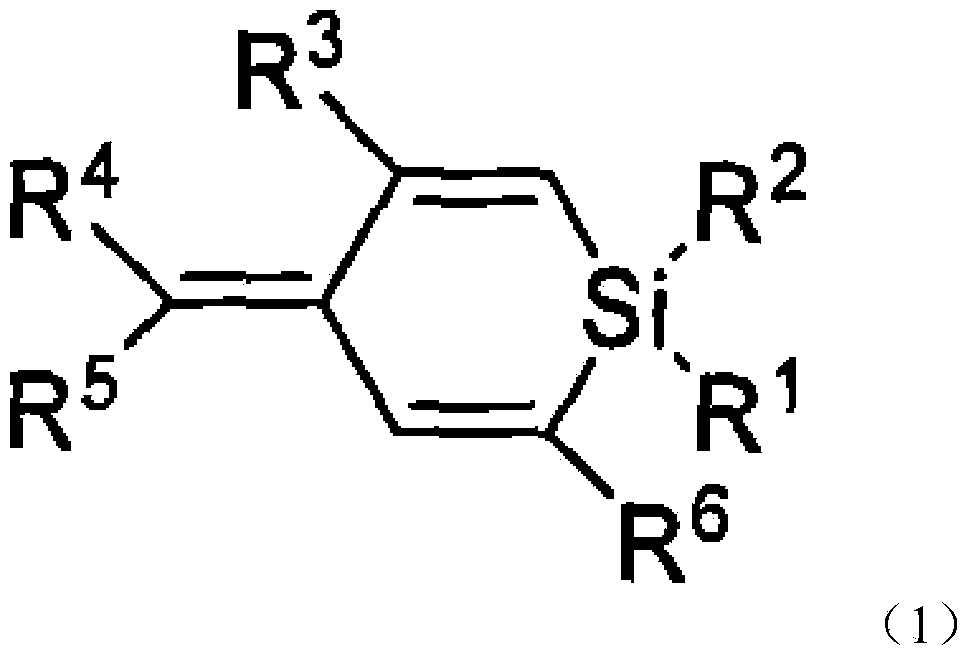
Patents
Literature
89 results about "Titanium thin film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxygen depleted etching process
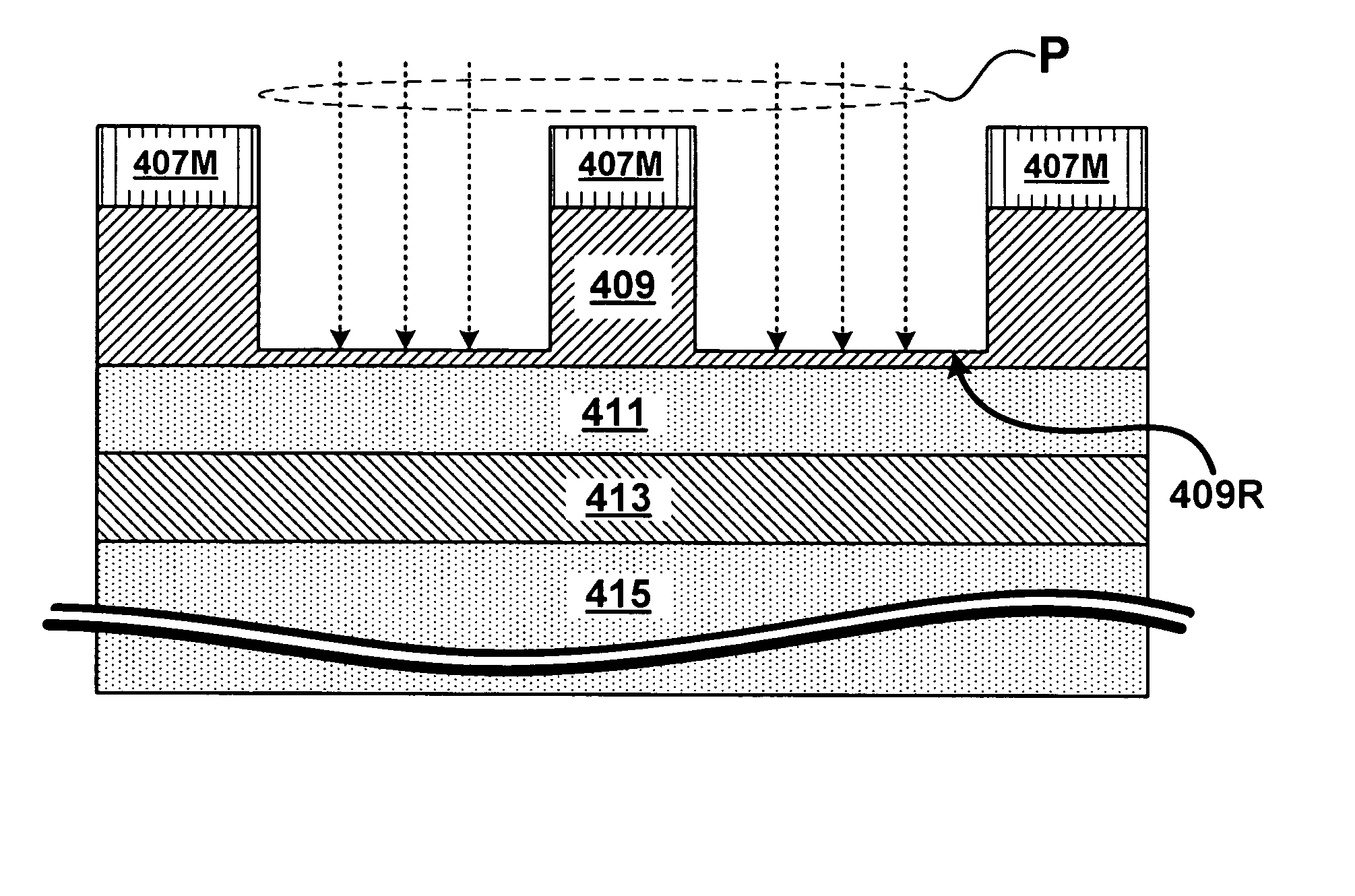
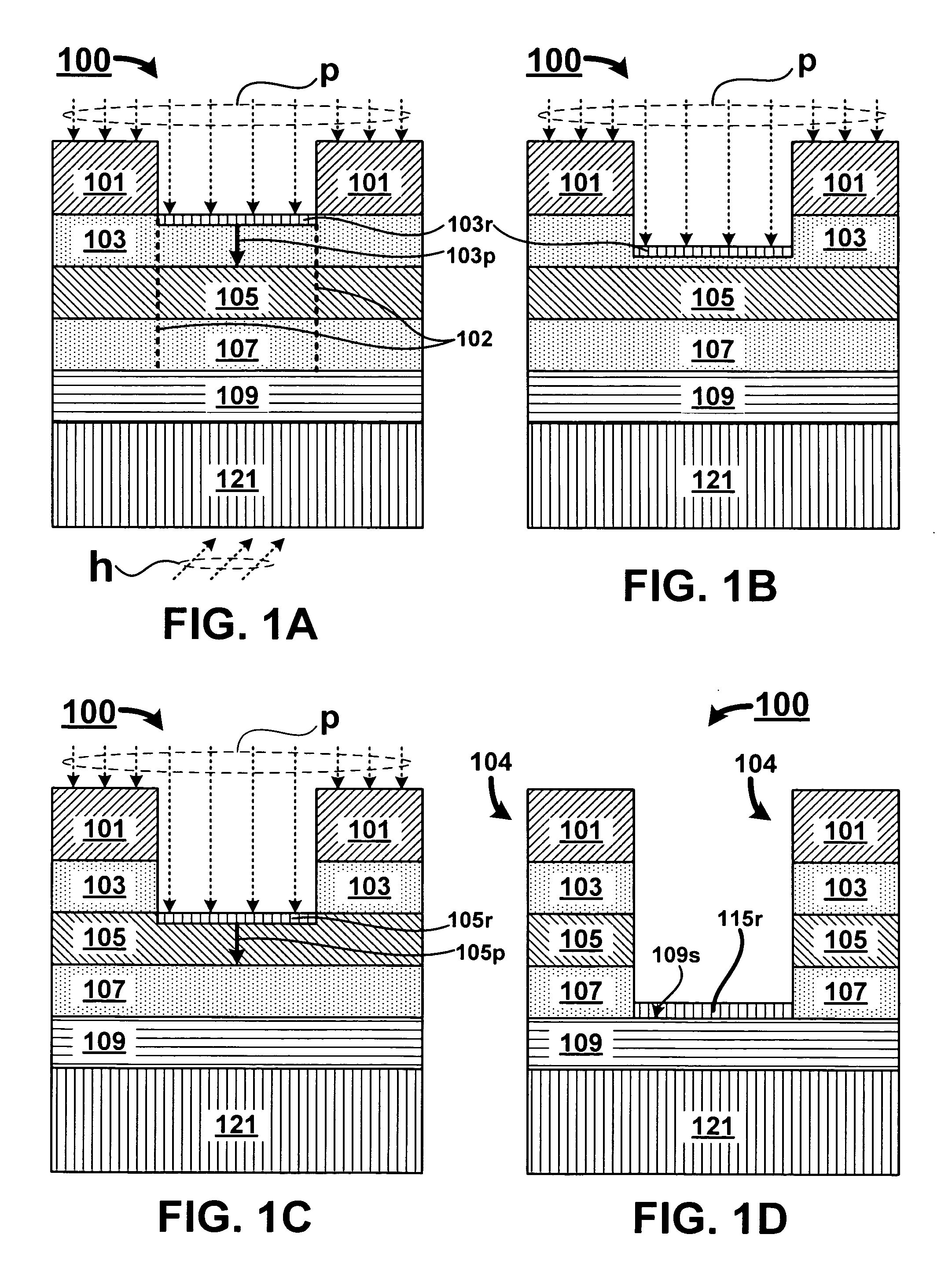
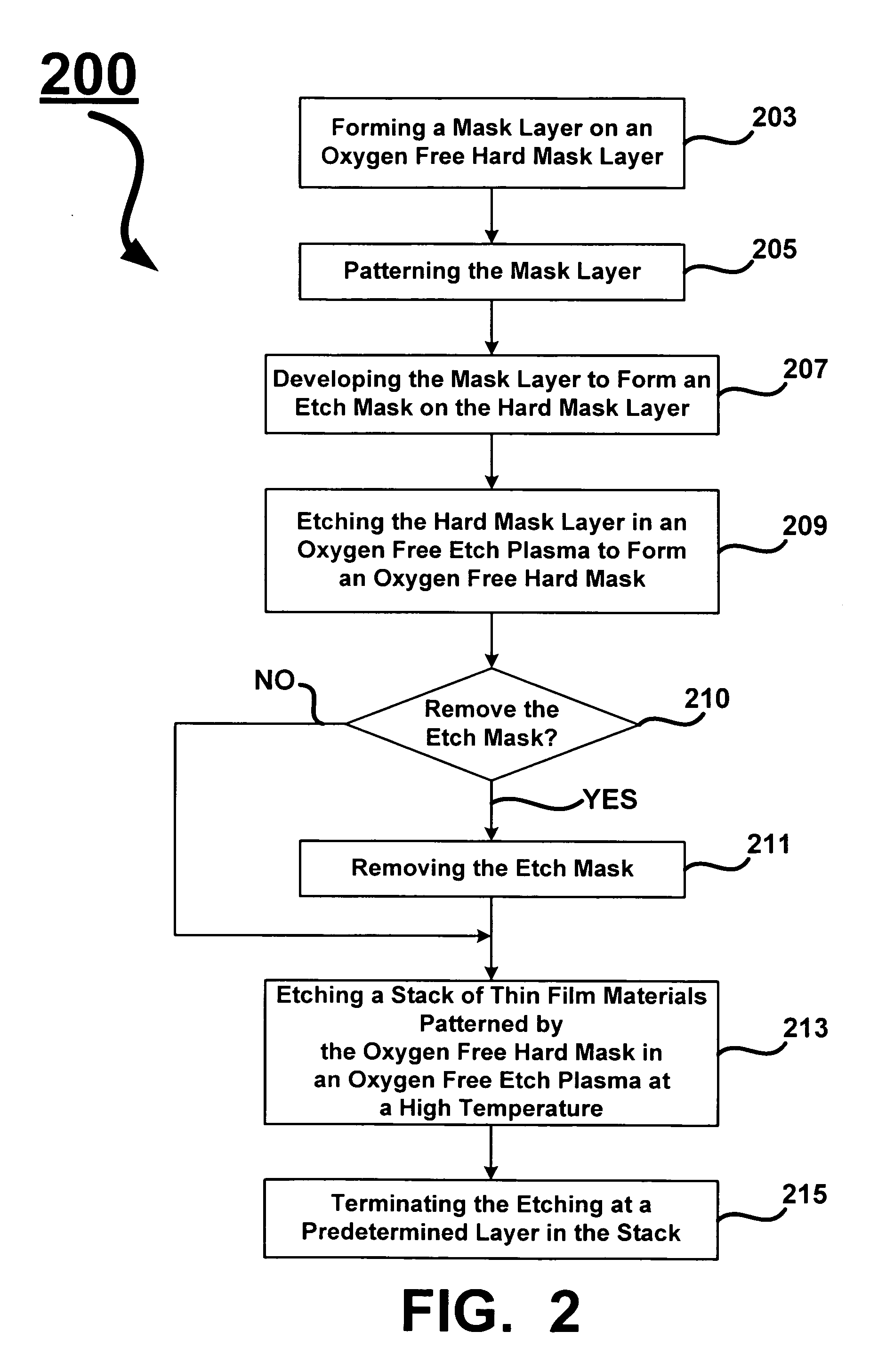
A method for oxygen depleted plasma etching and mixed mode plasma etching are disclosed. The method includes using an oxygen free etch plasma or a substantially oxygen free etch plasma at a high temperature to etch a stack including a plurality of layers of thin film materials. The oxygen depleted etching prevents or substantially reduces by-product re-deposition of titanium oxides generated by etching of titanium thin films in the stack. The titanium oxides can serve as a secondary mask layer that can cause defects in devices formed from the stack. Mixed mode plasma etching can include etching the stack with an oxygen free plasma, a substantially oxygen free plasma, and an oxygen containing plasma at different stages of a process.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Room-temperature magnetoelectric multiferroic thin films and applications thereof
ActiveUS8803264B1Well behaved and saturated C(V) hysteresisReduce leakageTransistorDevice material selectionDielectric lossRoom temperature
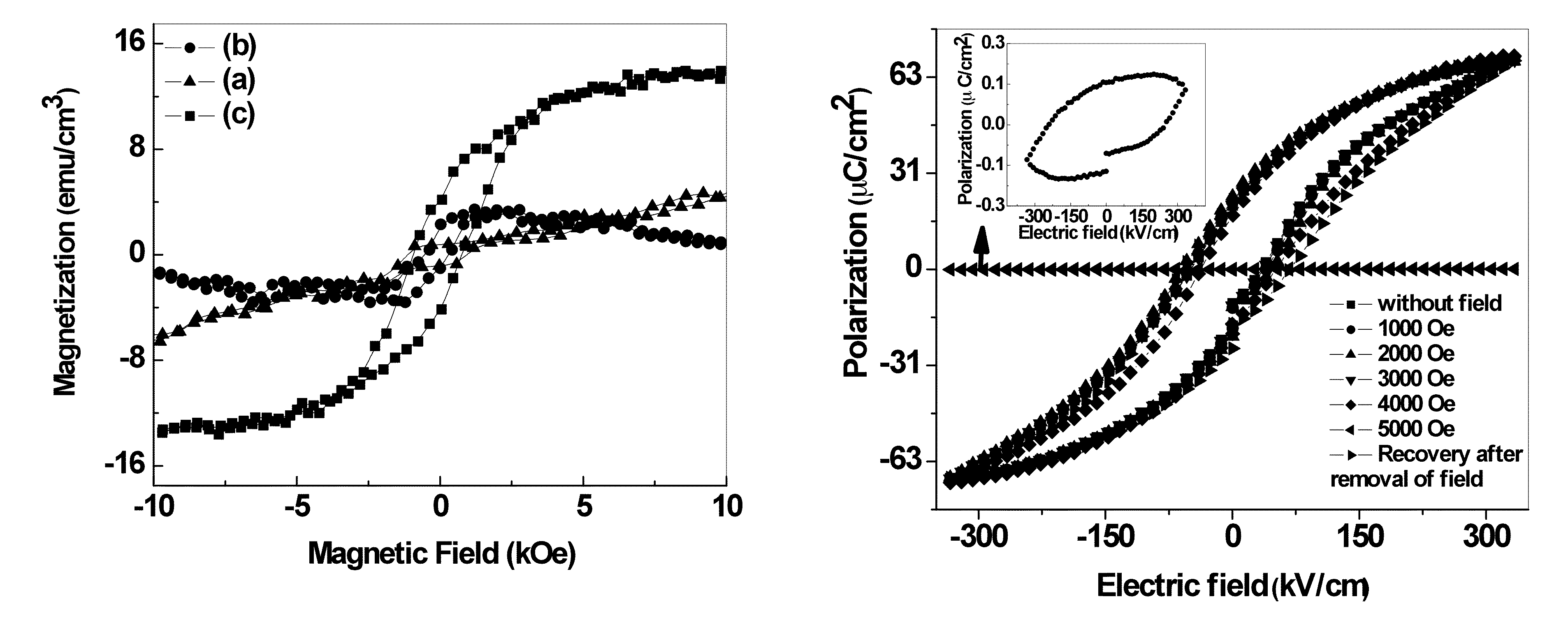
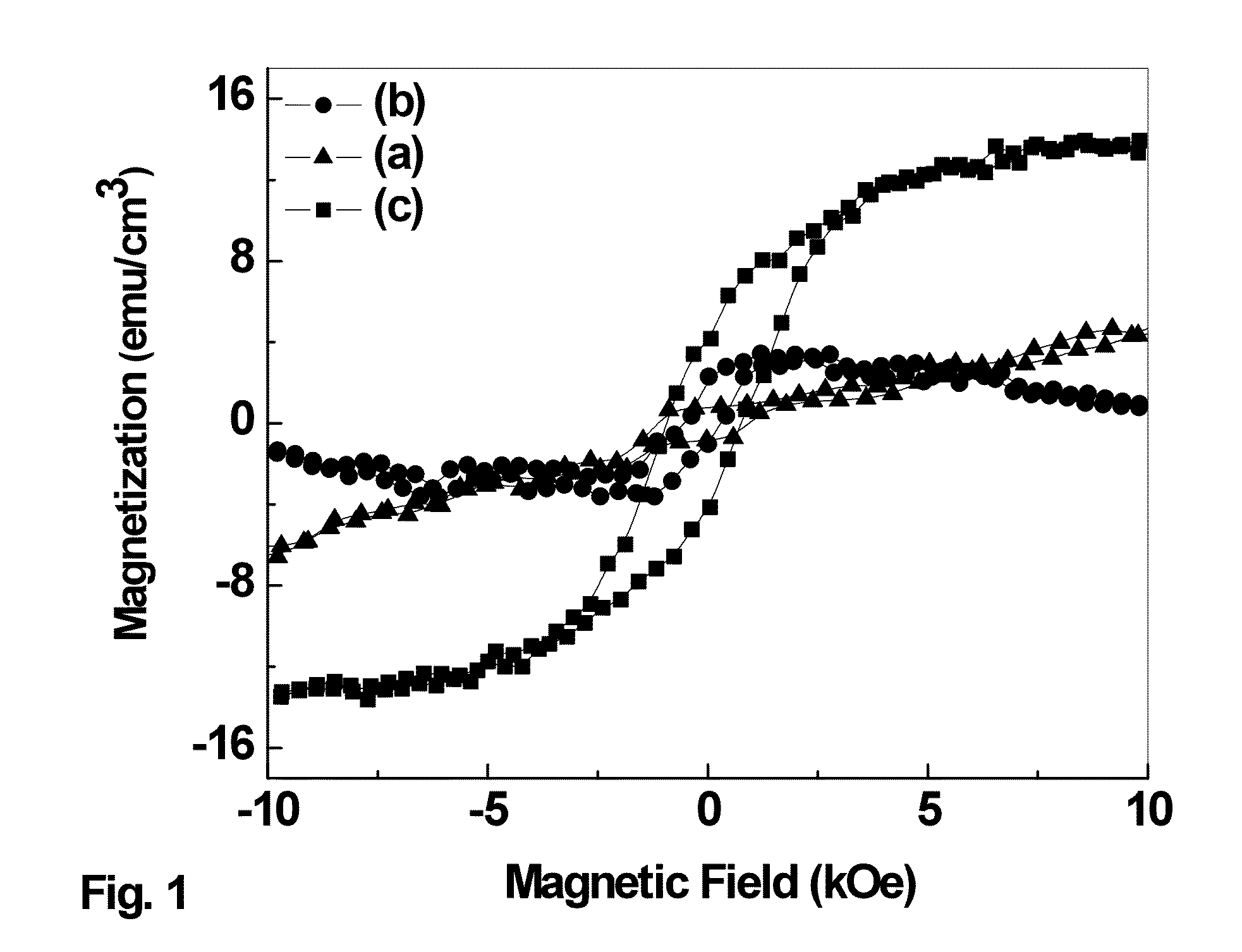
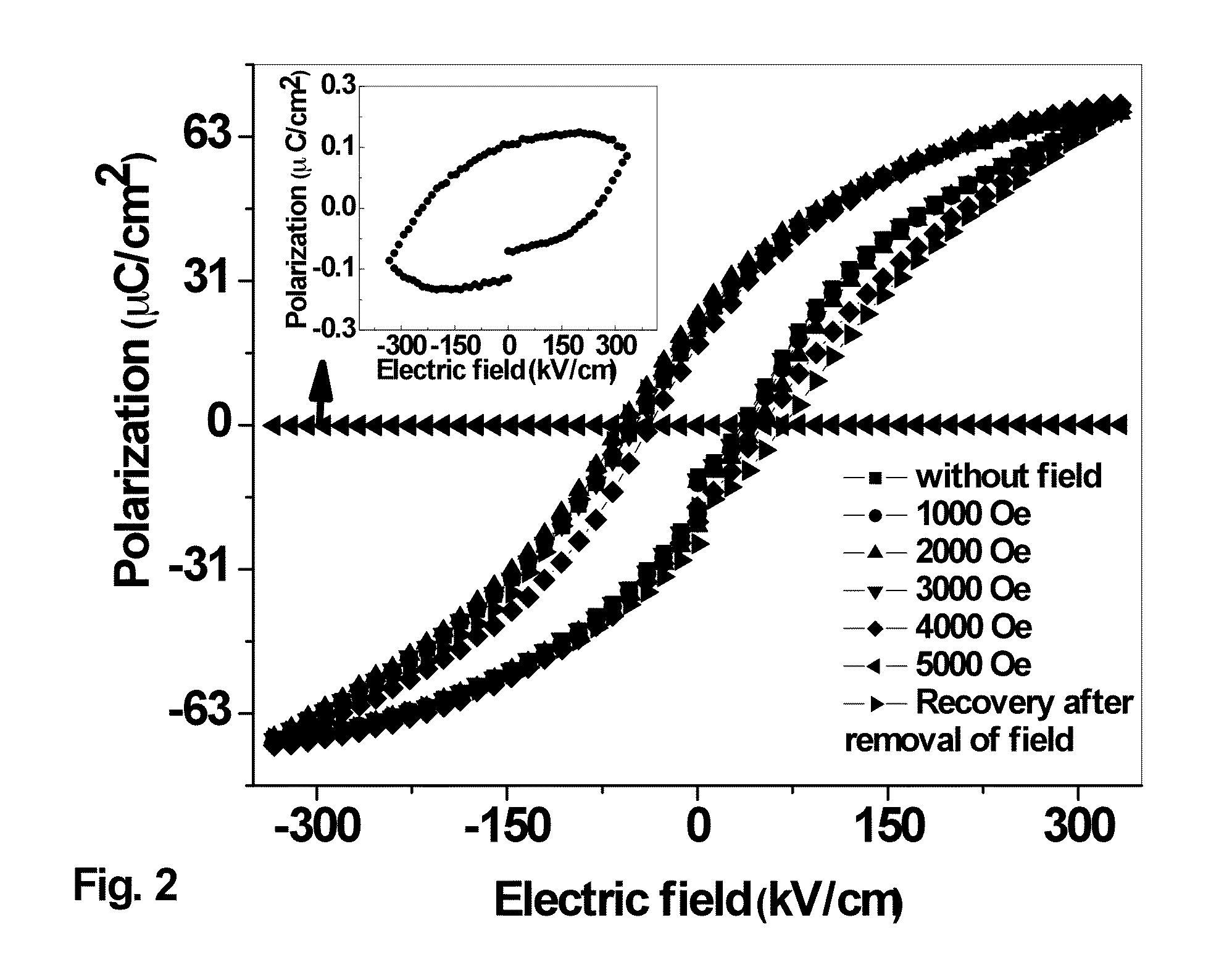
The invention provides a novel class of room-temperature, single-phase, magnetoelectric multiferroic (PbFe0.67W0.33O3)x (PbZr0.53Ti0.47O3)1-x (0.2≦x≦0.8) (PFWx−PZT1-x) thin films that exhibit high dielectric constants, high polarization, weak saturation magnetization, broad dielectric temperature peak, high-frequency dispersion, low dielectric loss and low leakage current. These properties render them to be suitable candidates for room-temperature multiferroic devices. Methods of preparation are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO
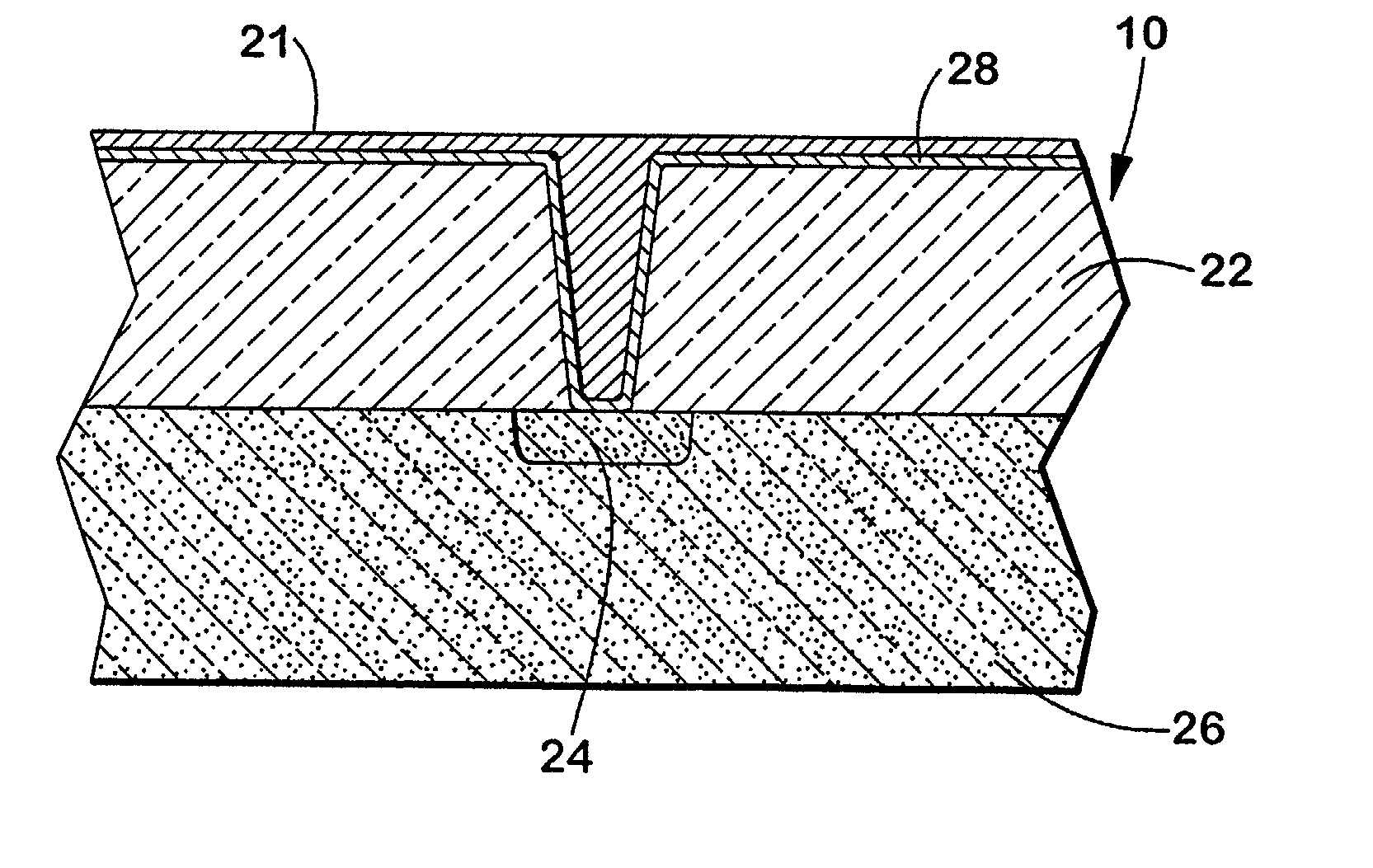
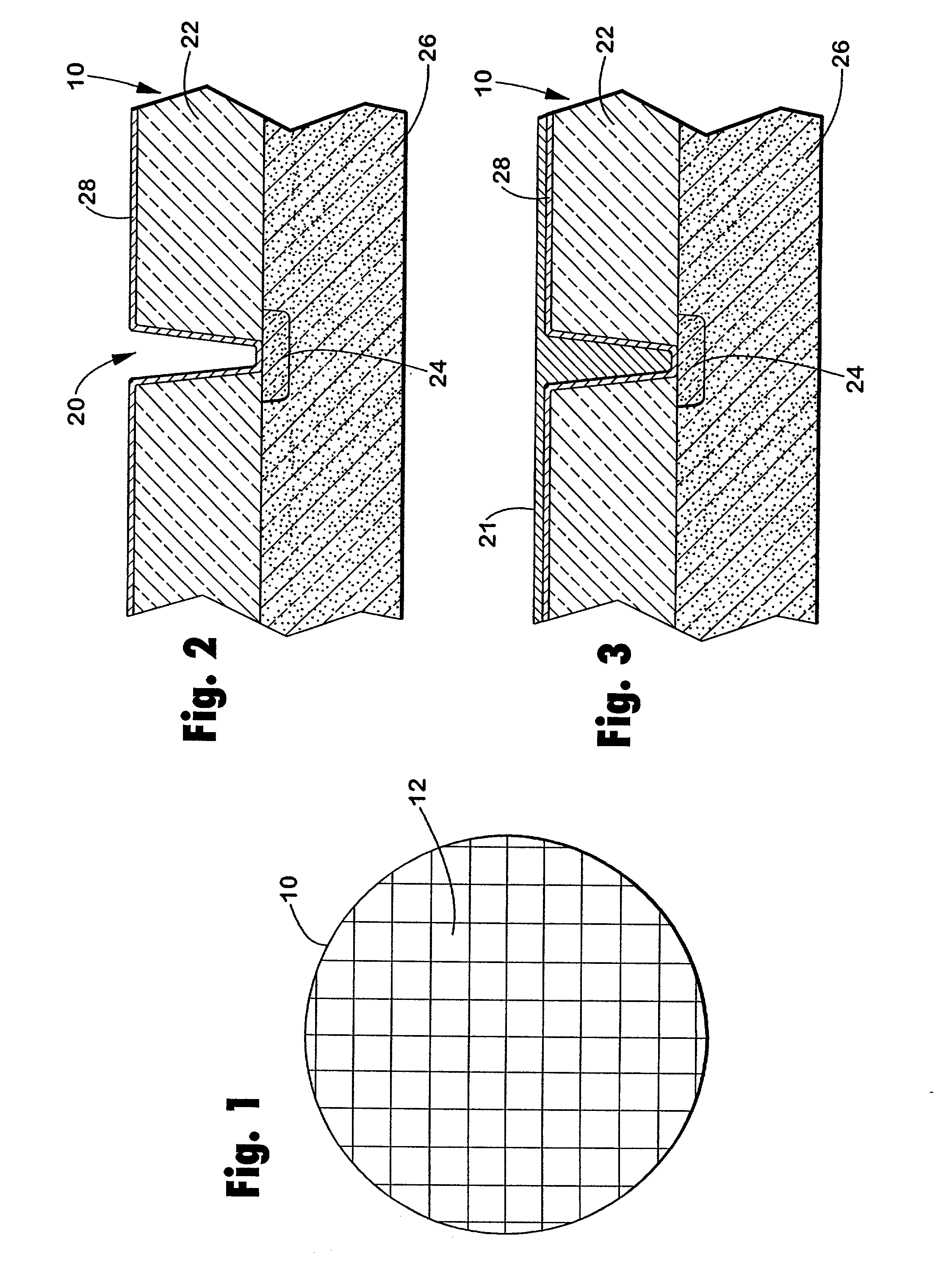
Graphite surface titanium metallization method and product manufactured with the same
InactiveCN104694897ASolve the technical difficulties of low bonding strengthGood for diffusion reactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMetallic materialsGraphite substrate
The invention discloses a graphite surface titanium metallization method and a product manufactured with the same to solve the problem that when graphite is connected with Cu or Cu alloy, it is difficult to wet graphite with liquid metal, the difference between graphite and Cu or Cu alloy is large in terms of expansion factor and elasticity modulus, and connection is hard. According to the method, a titanium film is deposited on the surface of a graphite substrate with the magnetron sputtering method, and then hot isostatic pressing is conducted on the deposited titanium film, so that a titanium thin film is formed on the surface of the graphite substrate. The problem that coating-substrate combination strength of a surface titanium metallization layer is low during diffusion bonding of the non-metal material graphite can be effectively solved, and the metal titanium thin film high in coating-substrate combination strength can be prepared on the graphite substrate. According to the titanium thin film, the concentration of titanium becomes larger gradually from the graphite substrate to the outside in a gradient mode, and the strength of combination between a titanium coating and the substrate is high. The method can meet the requirement for research of fusion reactor plasma facing materials and has great significance for development of fusion reactor elements.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Titanium dioxide/cadmium sulfide/titanium dioxide composite film and application thereof
ActiveCN103736500AImprove catalytic performanceSimple methodPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationComposite filmWastewater
The invention discloses a titanium dioxide / cadmium sulfide / titanium dioxide composite film and an application thereof in the technical field of wastewater treatment. A preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps: depositing titanium on a substrate by adopting a tilting growth method, thereby obtaining a nano bar array film with favorable discreteness; annealing the titanium film at the air condition of 450 DEG C for 2 hours, thereby obtaining a titanium dioxide nano bar array film; depositing cadmium sulfide nano particles on a titanium dioxide nano bar array by a continuous ion layer adsorption reaction method, thereby obtaining a titanium dioxide / cadmium sulfide composite film, wherein the film has a favorable organic wastewater processing effect under visible light; and depositing a layer of titanium dioxide on the film again on the titanium dioxide / cadmium sulfide composite film by an atomic layer deposition method. The visible light organic wastewater degrading efficiency of the titanium dioxide / cadmium sulfide / titanium dioxide structure is improved obviously compared with that of the titanium dioxide / cadmium sulfide. The processing method is simple, the visible catalytic performance of the composite film is obviously improved, and the composite film has a wide application prospect in wastewater treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film for photocatalysis
The invention provides a preparation method of a zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film for photocatalysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: heating to 100-200 DEG C in the rough vacuum of below 20PMa, and cleaning a reaction cavity; cleaning a substrate, drying the substrate, introducing a precursor tetrakis (dimethylamino)titanium to the reaction cavity to pulse for 3 seconds, and cleaning; pulsing steam, and cleaning the steam to finish one cycle of titanium oxide deposition; introducing a precursor diethyl zinc to pulse for 2 seconds, and cleaning; introducing the steam to pulse for 4 seconds, and cleaning to finish one cycle of zinc oxide deposition; and forming a large cycle by a plurality of cycles of the titanium oxide deposition and one cycle of the zinc oxide deposition, and annealing at the temperature of 450 DEG C for 2 hours after a plurality of large cycles are finished, i.e., the zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film deposition process is finished. The film is precise and adjustable in thickness and component and excellent in optical transmittance and photocatalysis efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Method for preparing carbon-doped titanium oxide thin film with photocatalytic activity
InactiveCN102489286ASolve the immobilization problemProcess stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsSputter cleaningTitanium thin film
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
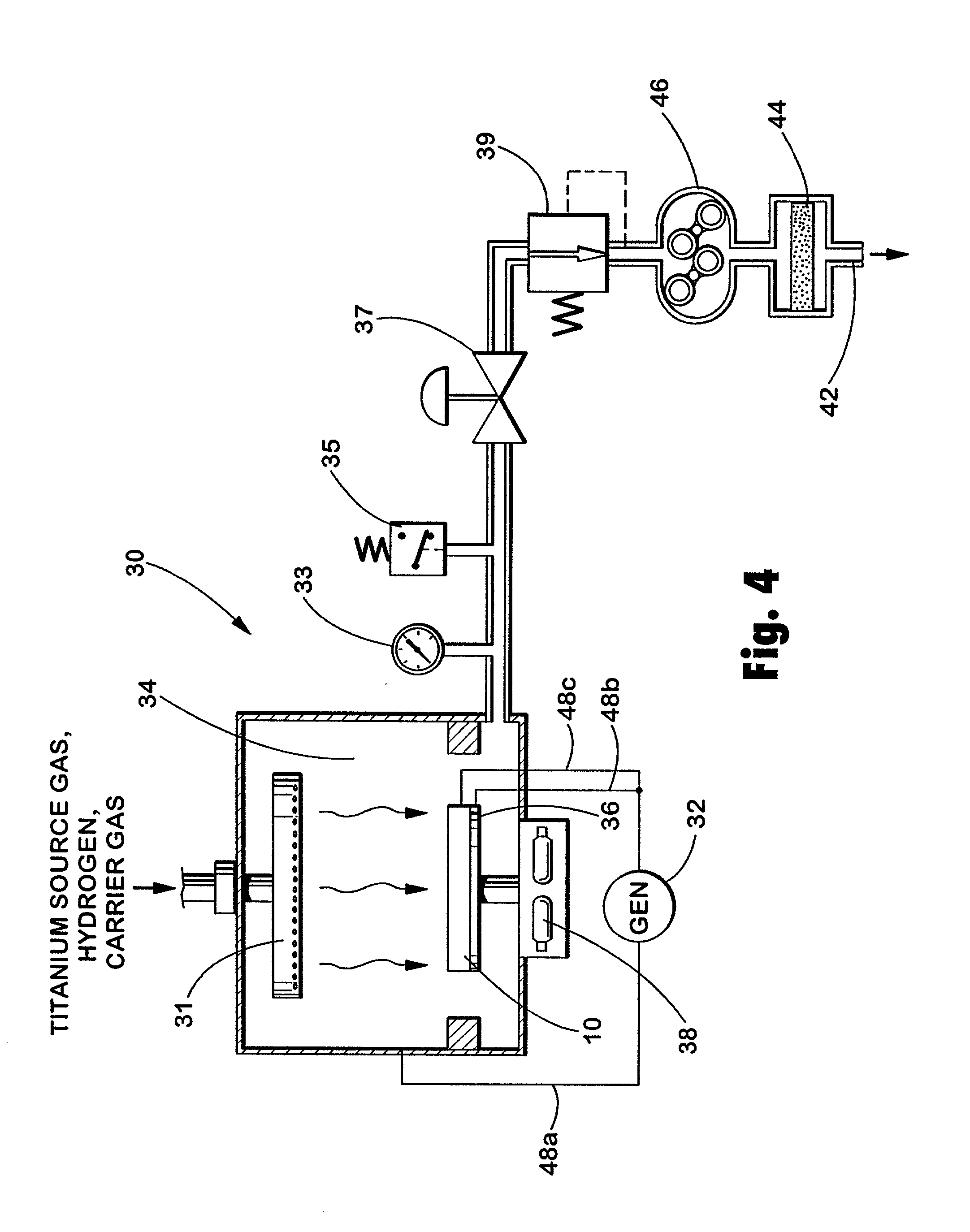
Chemistry for chemical vapor deposition of titanium containing films
InactiveUS20020013050A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium nitrideChemical vapor deposition
Titanium-containing films exhibiting excellent uniformity and step coverage are deposited on semiconductor wafers in a cold wall reactor which has been modified to discharge plasma into the reaction chamber. Titanium tetrabromide, titanium tetraiodide, or titanium tetrachloride, along with hydrogen, enter the reaction chamber and come in contact with a heated semiconductor wafer, thereby depositing a thin titanium-containing film on the wafer's surface. Step coverage and deposition rate are enhanced by the presence of the plasma. The use of titanium tetrabromide or titanium tetraiodide instead of titanium tetrachloride also increases the deposition rate and allows for a lower reaction temperature. Titanium silicide and titanium nitride can also be deposited by this method by varying the gas incorporated with the titanium precursors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Thin film-laminated film
ActiveUS20170153200A1Good chemical stabilityLow costSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingOptoelectronicsTitanium
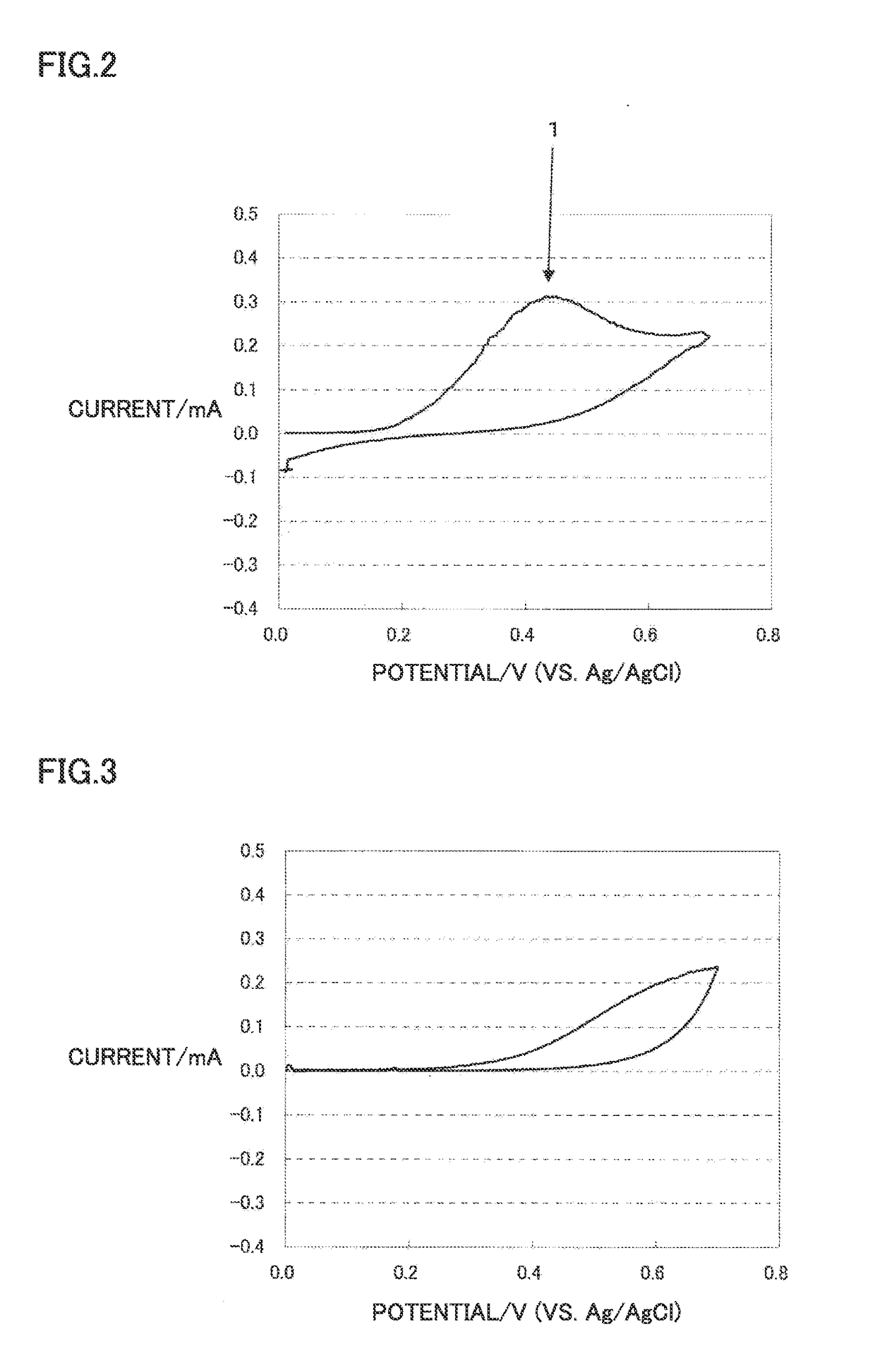
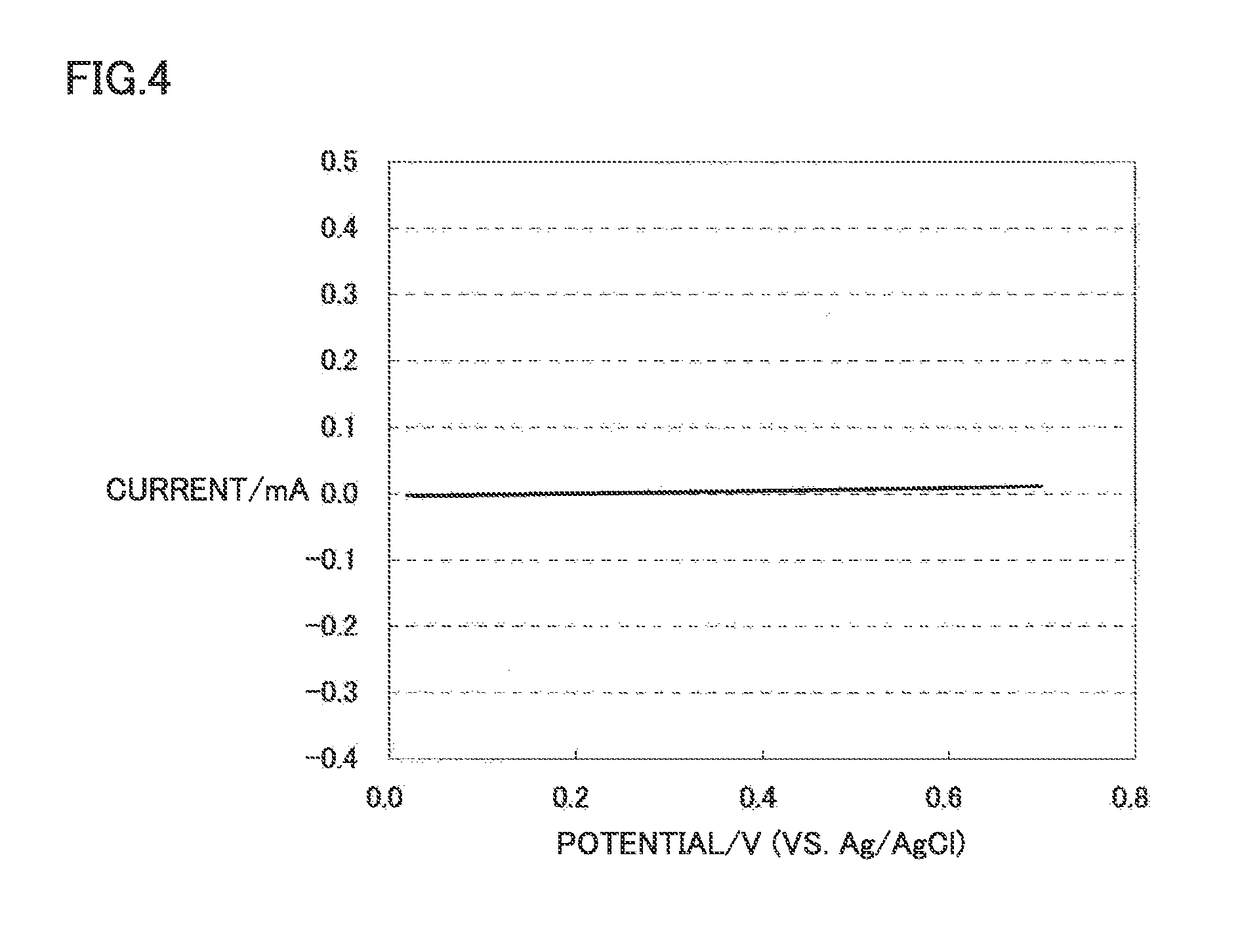
The present invention provides the following thin film-laminated film that has high chemical stability even at low costs and that can preferably be used as an electrode film of a strip for a blood sugar level sensor. The thin film-laminated film including a film substrate, and a titanium thin film and a carbon thin film laminated in this order on at least one surface of the film substrate. Preferably, the above-described thin film-laminated film, in which the titanium thin film has a film thickness of from 10 to 400 nm, and the carbon thin film has a film thickness of from 0.2 to 50 nm. In addition, a strip for a blood sugar level sensor, including the above-described thin film-laminated film. Further, a blood sugar level sensor device including the above-described strip for a blood sugar level sensor.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Method for photocatalysis of water by adopting nanometer porous titanium oxide film
InactiveCN102603051AImprove photocatalytic oxidation rateLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationTitanium oxideMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for photocatalysis of water by adopting a nanometer porous titanium oxide film. According to the method, clear water flows through a valve, a front filter, a flowmeter and an O-type split-flow ring to lead into a glass pipe cavity and then lead out of the O-type split-flow ring, and then the clear water flows through a rear filter and a mineral substance injector; and the inner wall of a glass pipe is provided with bamboo-shaped stabs which are criss-cross, a nanometer porous titanium oxide film is coated on the surfaces of the bamboo-shaped stabs, and an ultraviolet ray lamp tube is arranged in the middle of the stabs. The method for photocatalysis of water by adopting the nanometer porous titanium oxide film is utilized to prepare clean and oxygen-rich neutral activated water which has the advantages of strong seepage force, dissolving power and metabolism capability; and the method relates to self-cleaning of the glass pipe, and the glass pipe is semipermanent, the filter can be disassembled and washed, the filter can repeatedly be used, the mineral substance injector can supply and economy is excellent good.
Owner:唐世茂
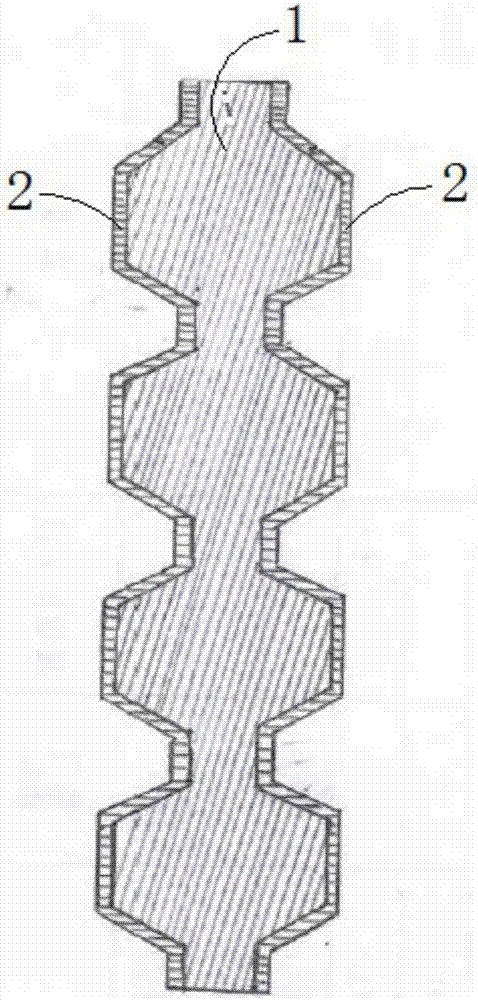
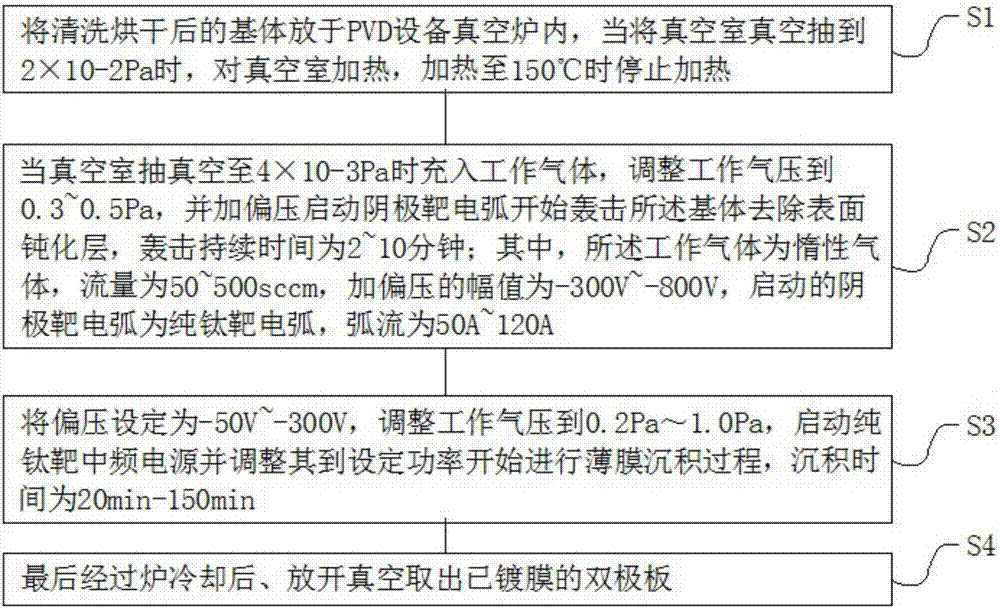
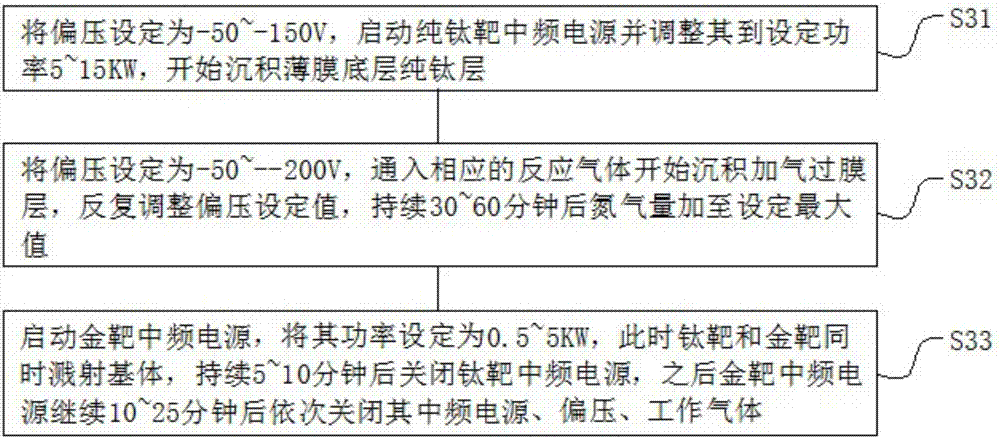
Fuel cell bipolar plate and preparation method of titanium thin films on surfaces thereof
PendingCN107195909AReduce contact resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceCell electrodesComposite filmTitanium thin film
The invention discloses a fuel cell bipolar plate and a preparation method of titanium thin films on surfaces thereof, and belongs to the field of a fuel cell. The bipolar plate comprises a substrate and titanium nanometer composite thin film layers, wherein the titanium nanometer composite thin film layers are arranged at two side surfaces of the substrate and are deposited and formed on the surfaces of the substrate by employing an arc ion plating technology, and the bipolar plate plated with the titanium thin films is obtained by controlling a film coating parameter during the deposition process of the titanium thin films. By the bipolar plate, the corrosion resistance is improved by three orders of magnitude under a voltage of 0.6V in a fuel cell simulation environment and is improved by two orders of magnitude under 1.36V, the contact resistance is reduced to 0.5 milliohm.cm<2> or below (pressure of 0.2MPa), the bipolar plate has favorable corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity after test on corrosion resistance of the cell simulation environment for a long time, and the long-term running requirement of a regenerative fuel cell sectem and a proton exchange membrane cell are met.
Owner:苏州邦华真空镀膜科技有限公司
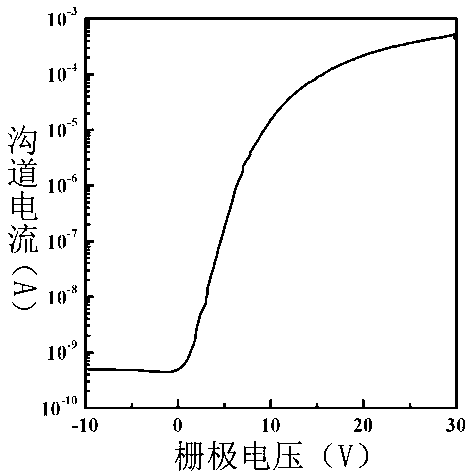
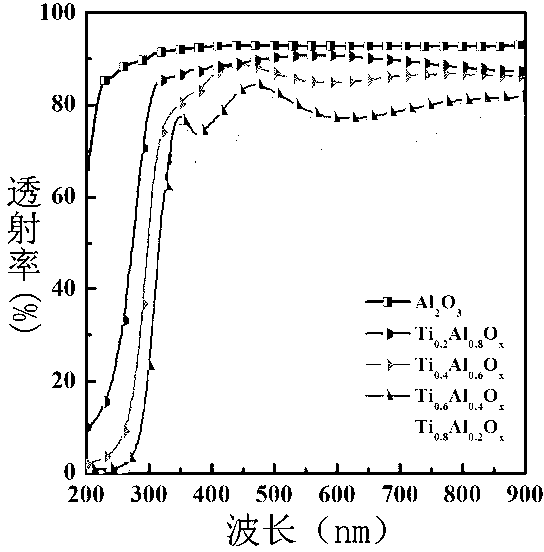
Titanium aluminum oxide thin film and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103274435AImprove performanceAvoid hydrolysisAluminium oxides/hydroxidesGate dielectricSwitched current
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of transistors, and in particular relates to a titanium aluminum oxide thin film and a preparation method and application thereof. The aluminum oxide titanium thin film is prepared by a sol-gel method. The method comprises the following steps of: with ethylene glycol monomethyl ether as a solvent and concentrated hydrochloric acid as an additive, dissolving Al(C4H9O)3 and Ti(C4H9O)4 in the solvent to form a clear and stable precursor solution; and spirally coating the precursor solution on a glass substrate, and obtaining the aluminum oxide titanium thin film after thermal pretreatment and subsequent high-temperature heat treatment. The invention further relates to a preparation method of a thin film transistor by using titanium aluminum oxide as a gate dielectric layer. According to the IZO thin film transistor with the titanium aluminum oxide as the gate dielectric layer, the switching current ratio is greater than 1*10<6>, the saturation migration rate is greater than 1.1cm<2> / Vs, and the subthreshold amplitude is less than 1.5V / dec.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
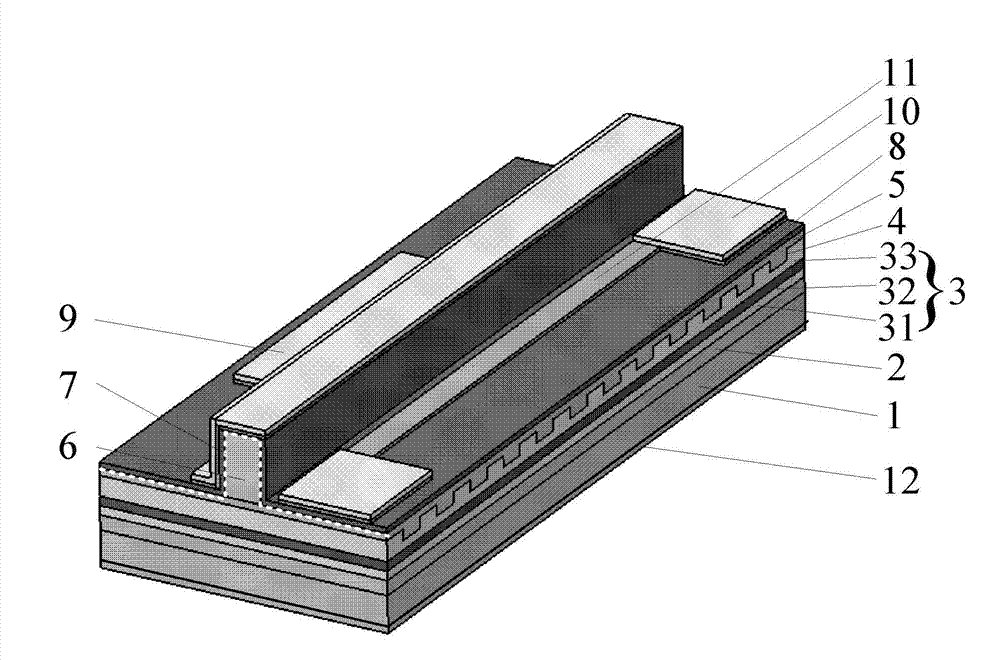
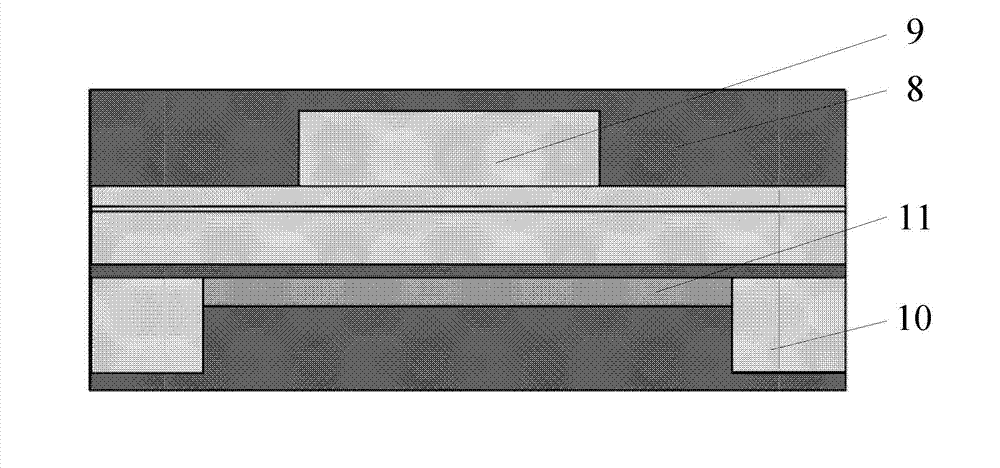
Manufacture method for monolithic integration titanium film thermal resistor tunable distributed feed back (DFB) laser
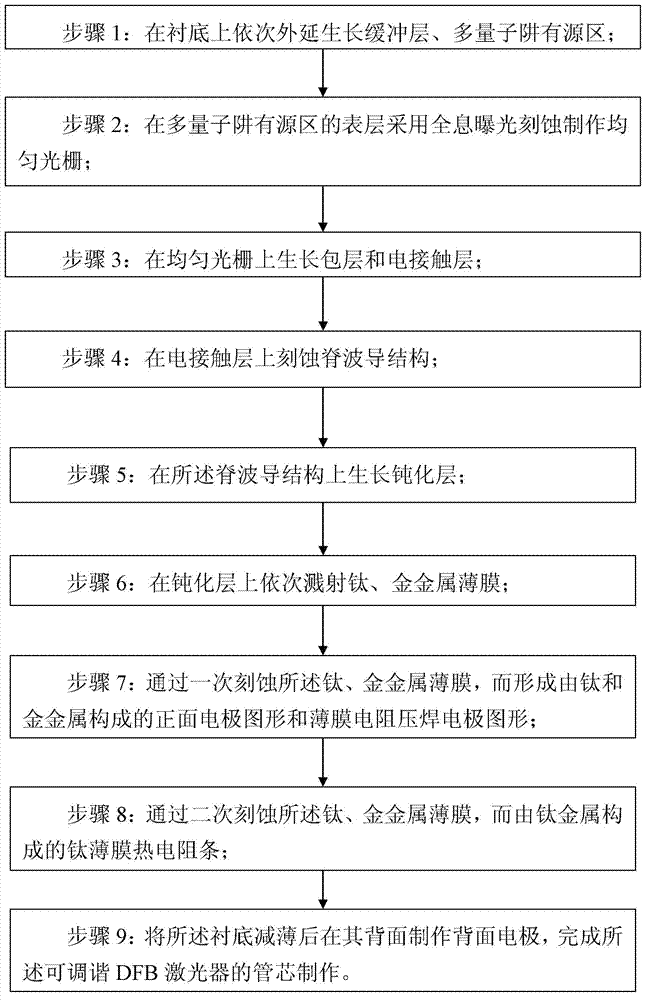
ActiveCN103094832AHigh resistivityHigh current tuning efficiencyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingWaveguide
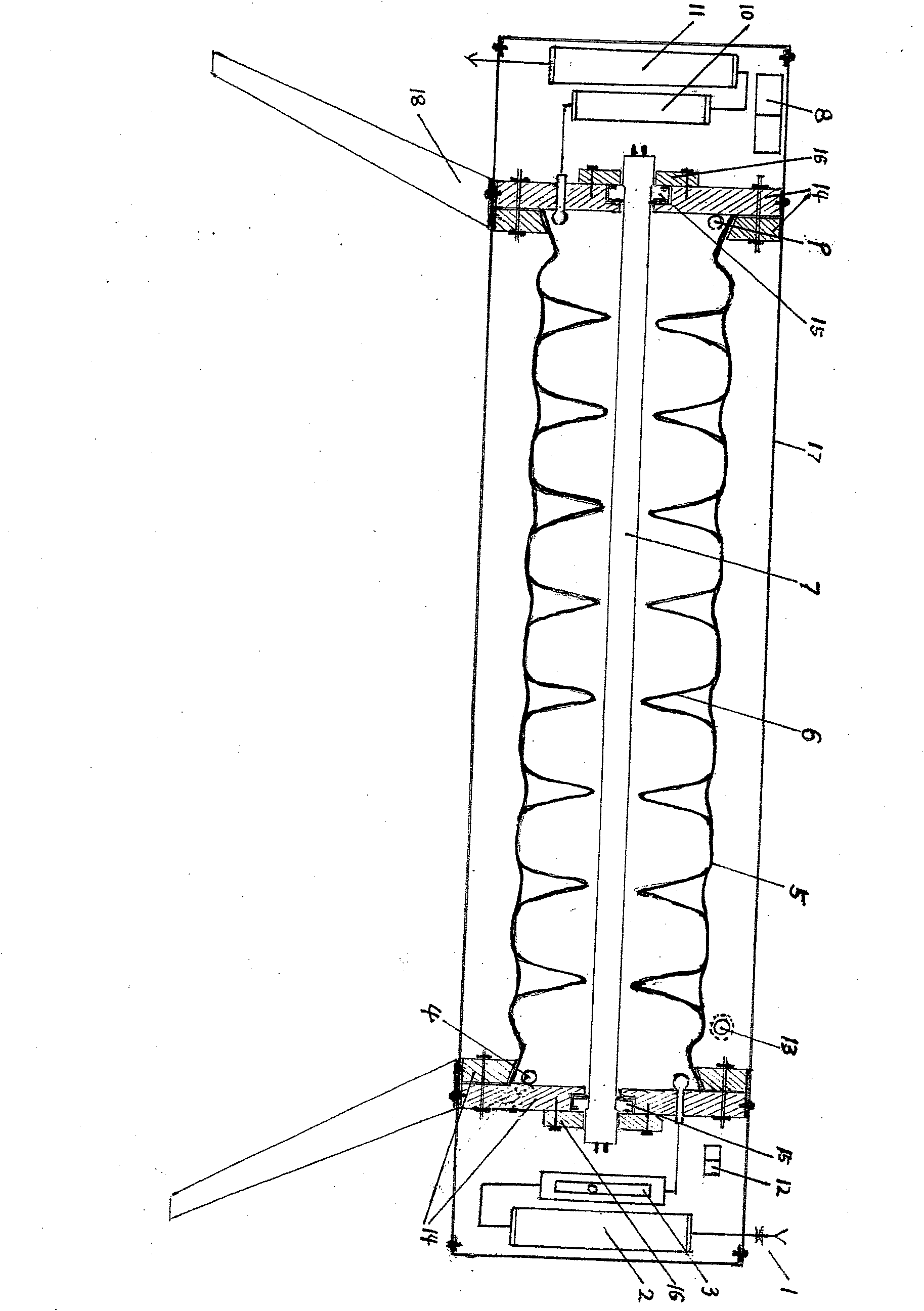
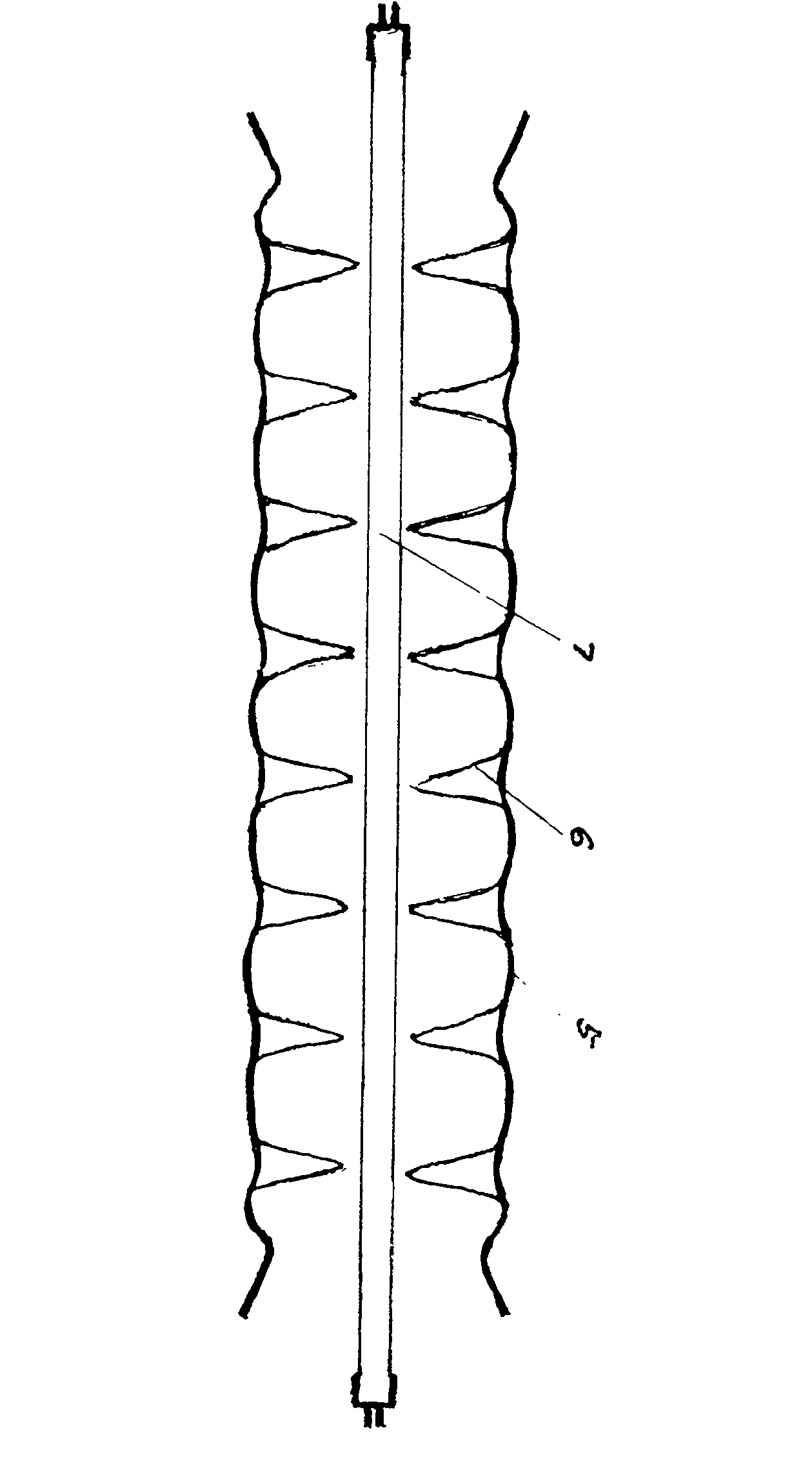
The invention discloses a manufacture method for a monolithic integration titanium film thermal resistor tunable distributed feed back (DFB) laser. The manufacture method comprises the steps of selecting an indium phosphide substrate 1, sequentially and epitaxially growing a buffer layer 2 and a multiple quantum wells active area 3 on the substrate 1, manufacturing even gratings 4 on the surface layer of the multiple quantum wells active area 3 by adopting holographic exposure etching, growing a cladding 5 and an electric contact layer 6 on the even gratings 4, adopting a regular photoetching and etching process, manufacturing a ridge waveguide structure 7 on the electric contact layer 6, growing a passivation layer 8 on the manufactured ridge waveguide structure 7, sputtering titanium and gold metal film on the passivation layer 8 after a front face electrode window is opened by adopting regular photoetching, coating photoresist on the metal film, photoetching a front face electrode pattern 9, a film resistor pressure welding electrode pattern 10 and a film resistor area 11 for once, photoetching and selectively etching for twice to form a titanium film thermal resistor strip 11, manufacturing a back face electrode 12 on the back face of the substrate 1 after the indium phosphide substrate 1 is thinned, and achieving manufacturing of a tube core.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing resistive random access memory device capable of multilevel memory
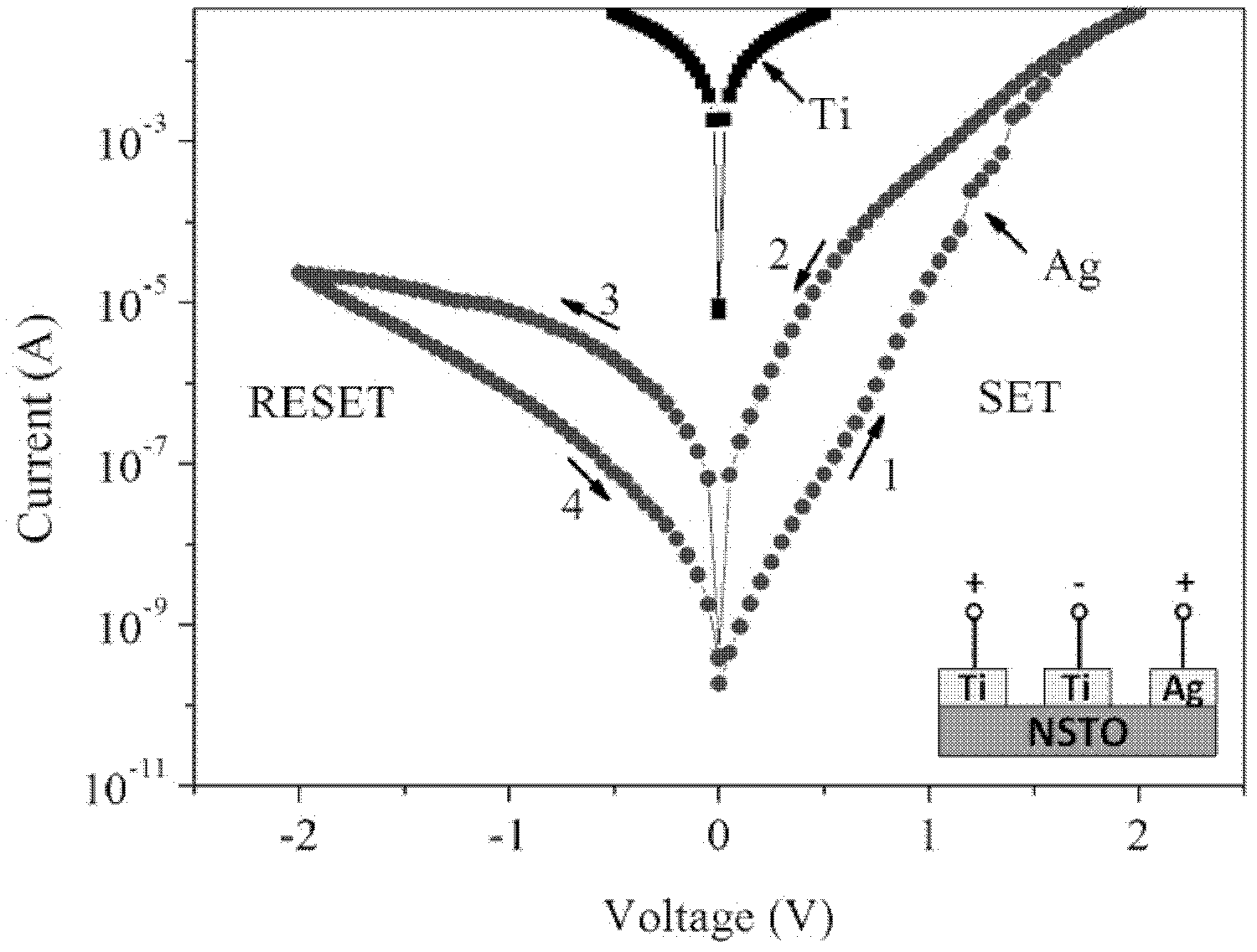
InactiveCN102593354AStructural continuityStrong process controllabilityElectrical apparatusComputer hardwareMultilevel memory
The invention discloses a resistive random access memory device based on interface oxygen vacancy to achieve the performance of multilevel memory. Specifically, the memory structure utilizes argentums (Ag) and titanium (Ti) as an upper electrode and a lower electrode respectively, utilizes Nb: SrTiO3 as a resistive layer to achieve the performance of multilevel memory. By aid of a magnetron sputtering method, the method for producing resistive random access memory device capable of multilevel memory includes sputtering titanium thin films on Nb: SrTiO3 substrates, coating argentums ( Ag adhesive), obtaining the memory device with an Ag / Nb: SrTiO3 / Ti structure and achieving the performance of multilevel memory. The method for producing resistive random access memory device capable of multilevel memory has the advantages of achieving the excellent performance of multilevel memory by regulating the height of potential barriers through the oxygen vacancy at different positive and negative bias voltages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
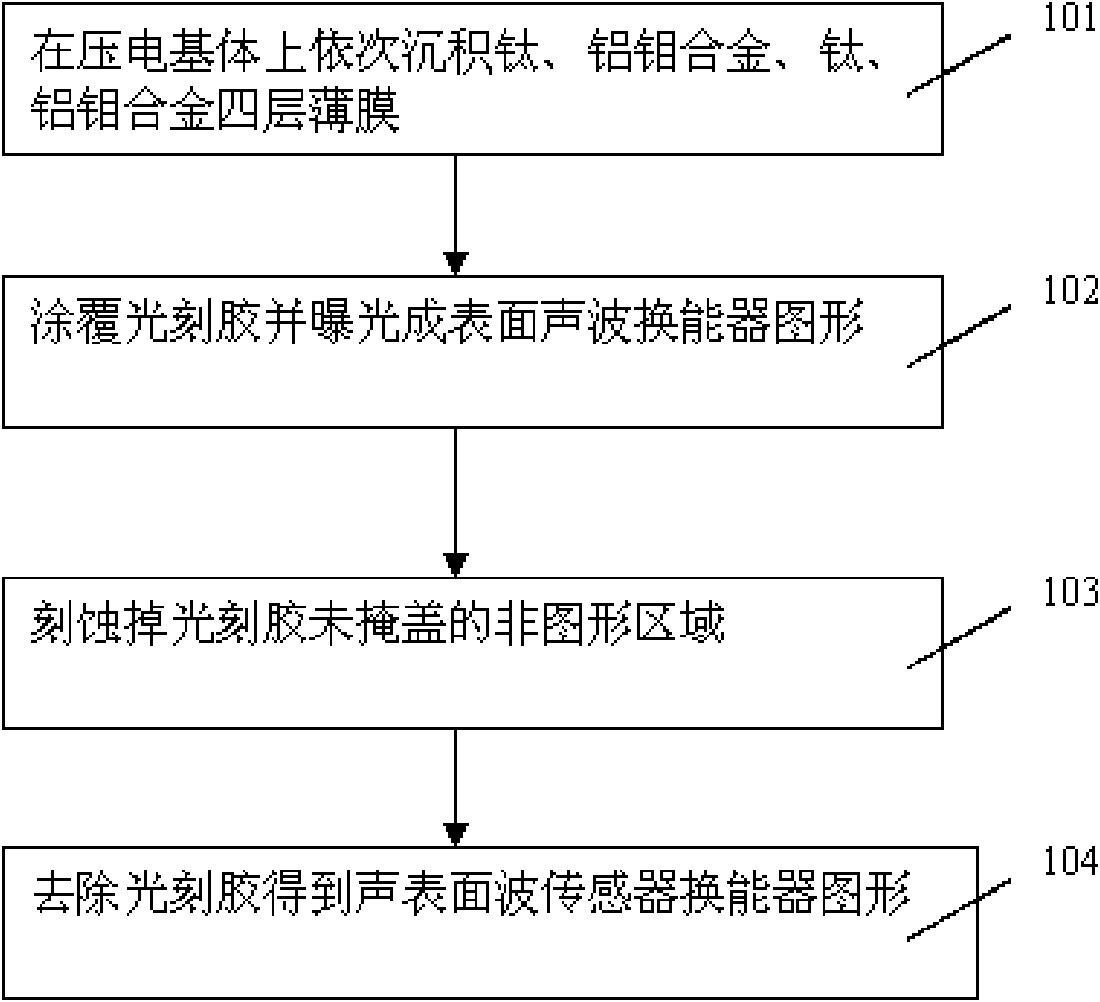
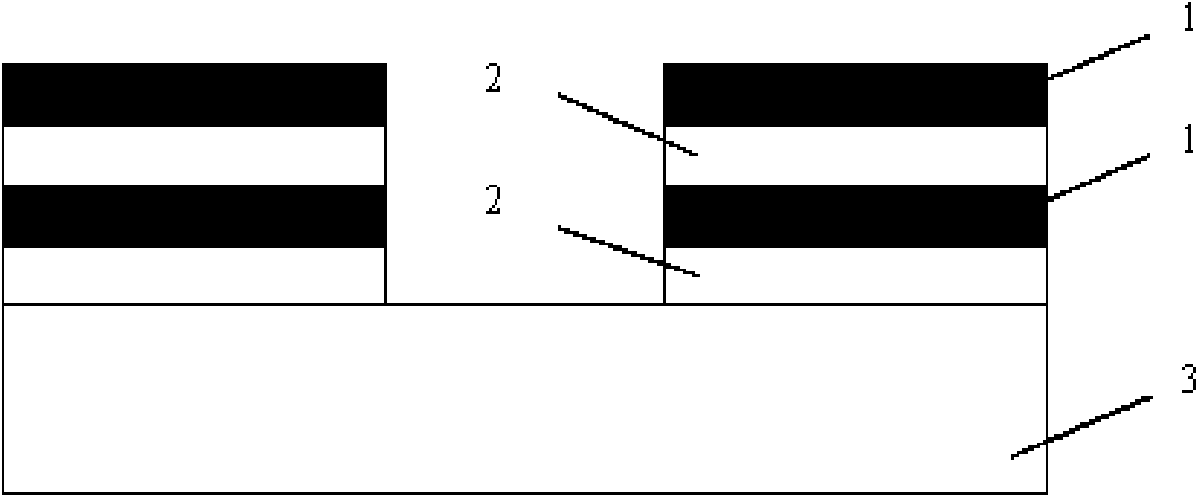
Manufacturing method for surface acoustic wave transducer
InactiveCN101599749AImprove adhesionImprove the forceImpedence networksBoron trichlorideReactive-ion etching
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a surface acoustic wave transducer, which belongs to the field of sensor production. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that: firstly, a titanium thin film, an aluminum and molybdenum alloy thin film, a titanium thin film, an aluminum and molybdenum alloy thin film are deposited on a piezoelectric substrate sequentially; secondly, photoresist is coated on the films and exposed to form graphics of the surface acoustic wave transducer, and a mixed gas of chlorine and boron trichloride etches away non-graphical areas that the photoresist does not cover; and finally, the photoresist is removed to obtain the graphics of the surface acoustic wave transducer. The four layers of films of the manufacturing method can inhibit the movement of aluminum atoms and improve the adhesive attraction of the films and the power-carrying capacity. The manufacturing method improves the performance of the aluminum film as well as the accuracy of the etching graphics of reactive ions, thereby improving the performance of the transducer and prolonging the service life of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
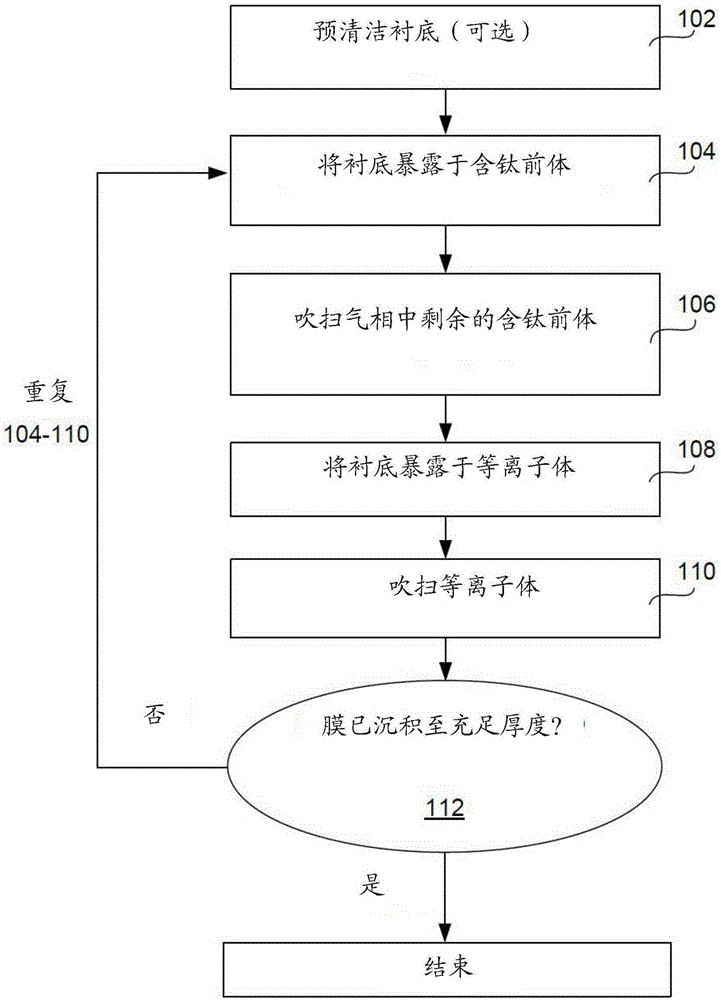
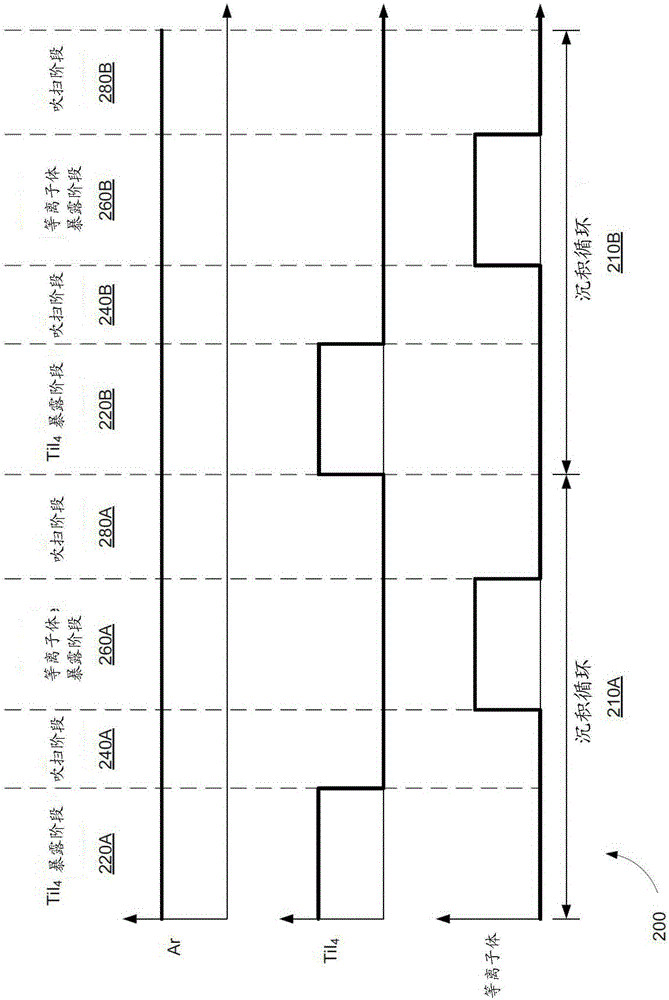
Method and apparatus to deposit pure titanium thin film at low temperature using titanium tetraiodide precursor
ActiveCN105390370AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow temperature depositionThin membrane
Provided are a method and apparatus to deposit a pure titanium thin film at low temperature using a titanium tetraiodide precursor. Methods of depositing highly conformal and pure titanium films at low temperatures are provided. Methods involve exposing a substrate to titanium tetraiodide, purging the chamber, exposing the substrate to a plasma, purging the chamber, and repeating these operations. Titanium films are deposited at low temperatures less than about 450 DEG C.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Embedded grating structure-based narrow-band near-infrared thermo-electronic photoelectric detector
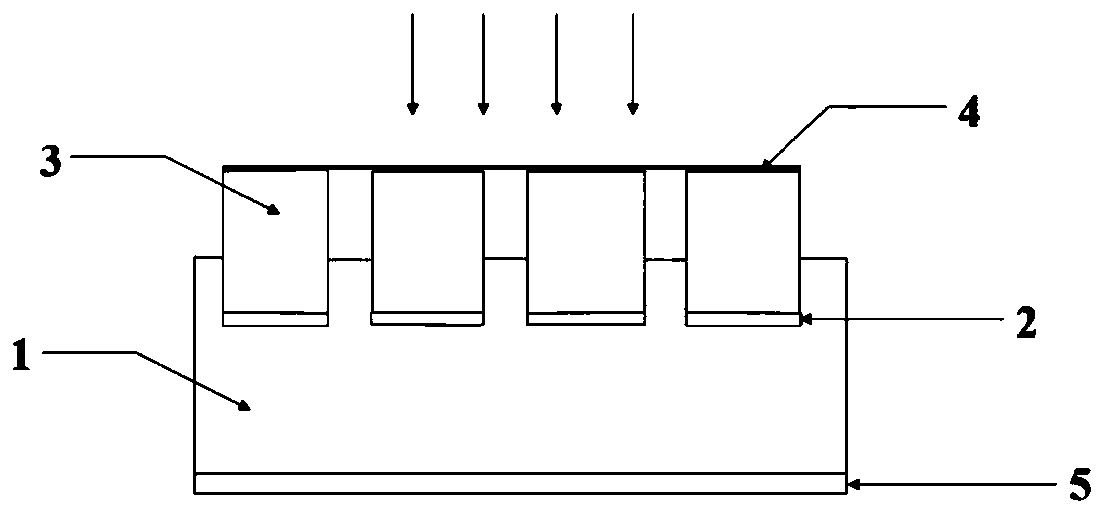
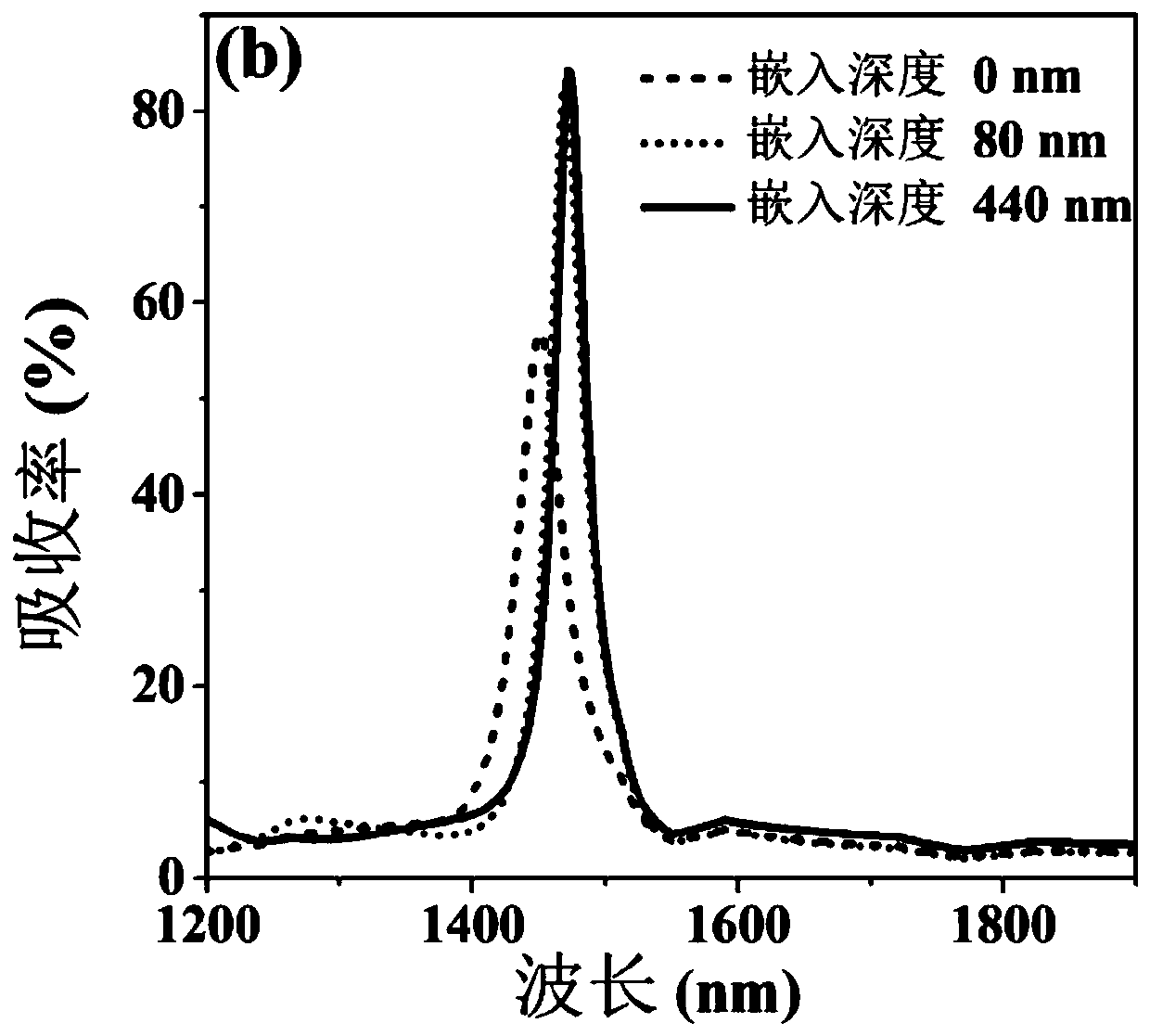
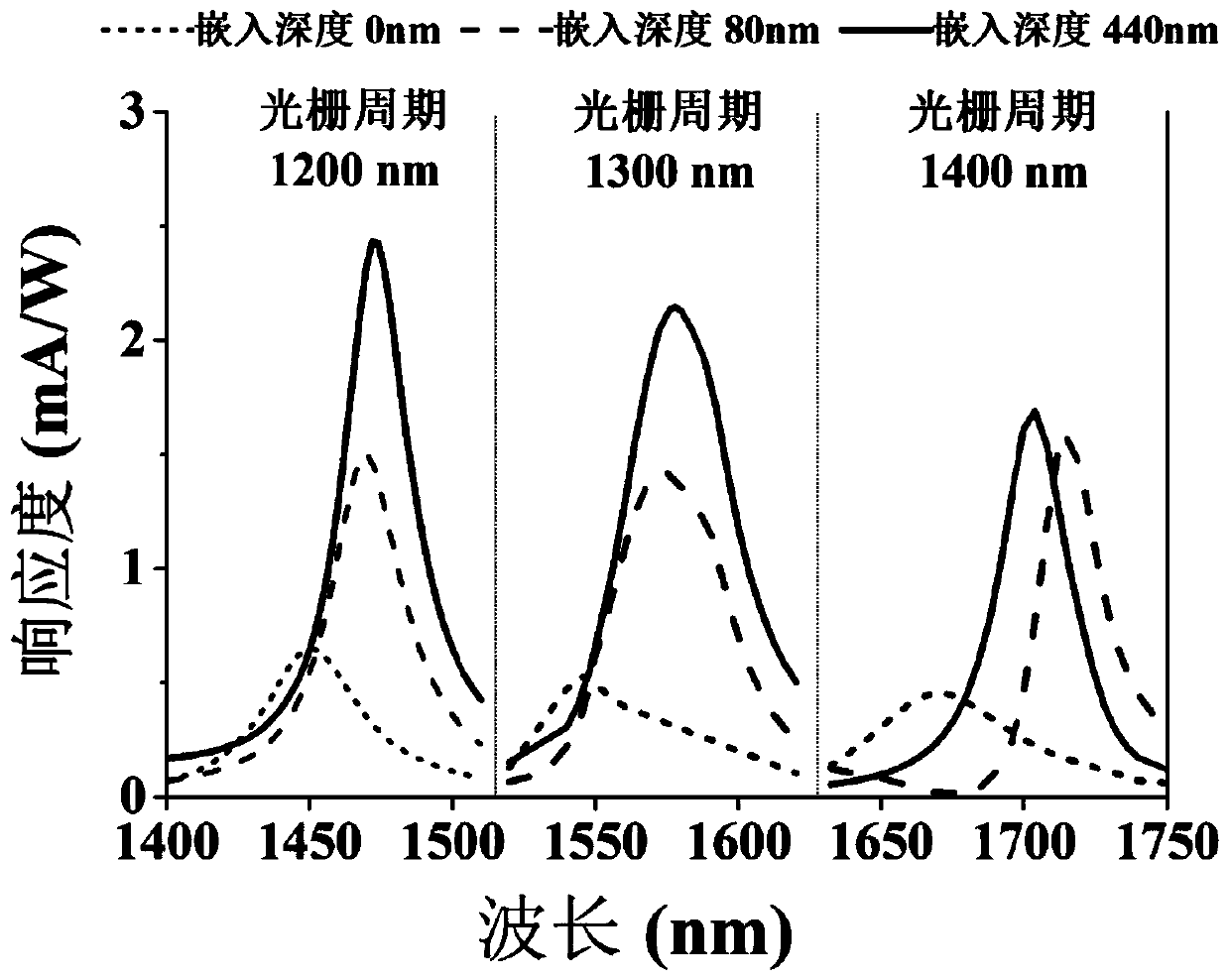
ActiveCN110729372ARealize photodetectionIncrease incidenceSemiconductor devicesGeneration rateMetallic grating
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric sensing and provides an embedded grating structure-based narrow-band near-infrared thermo-electronic photoelectric detector. The inventionaims to solve the problem of the low responsivity of a photoelectric detector in the prior art. The embedded grating structure-based narrow-band near-infrared thermo-electronic photoelectric detectorcomprises a silicon substrate and a metal grating, a titanium film is arranged between the metal grating and the silicon substrate so as to serve as an adhesive layer; the metal grating is connectedto a top conductive electrode; and a bottom conductive electrode is arranged on a silicon back surface. The metal grating is embedded into the silicon substrate, so that the light absorption efficiency of metal and the generation rate of hot electrons are improved, and the thermalization loss of the hot electrons is reduced; a Schottky interface on the side surface of the grating is additionally adopted, so that the collection efficiency of the hot electrons transferred into silicon is improved, and therefore, the responsivity of the photoelectric detector is improved; and the response wavelength of the detector can be changed by adjusting the period of the metal grating, so that the wavelength-adjustable near-infrared photoelectric detector is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for formation of titanium nitride films
InactiveUS20050126903A1Without quality of filmSynthesis is relatively shortElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingPlasma currentGas phase
A procedure for the synthesis of titanium nitride (TiN) thin films on metal substrate by vapor deposition using a magnetized sheet plasma source is disclosed. TiN films on metal substrate exhibiting the stoichiometric TiN and Ti2N were synthesized in a mixed N2 / Ar plasma with initial gas filing ratio of preferably 1:3 under the following conditions: total initial gas filing pressure of at least about 40 mTorr, plasma current in the range of about 2A to 3A and plasma discharge potential in the range of about 125V to about 150V.
Owner:UNIV OF THE PHILLIPPINES DILLMAN
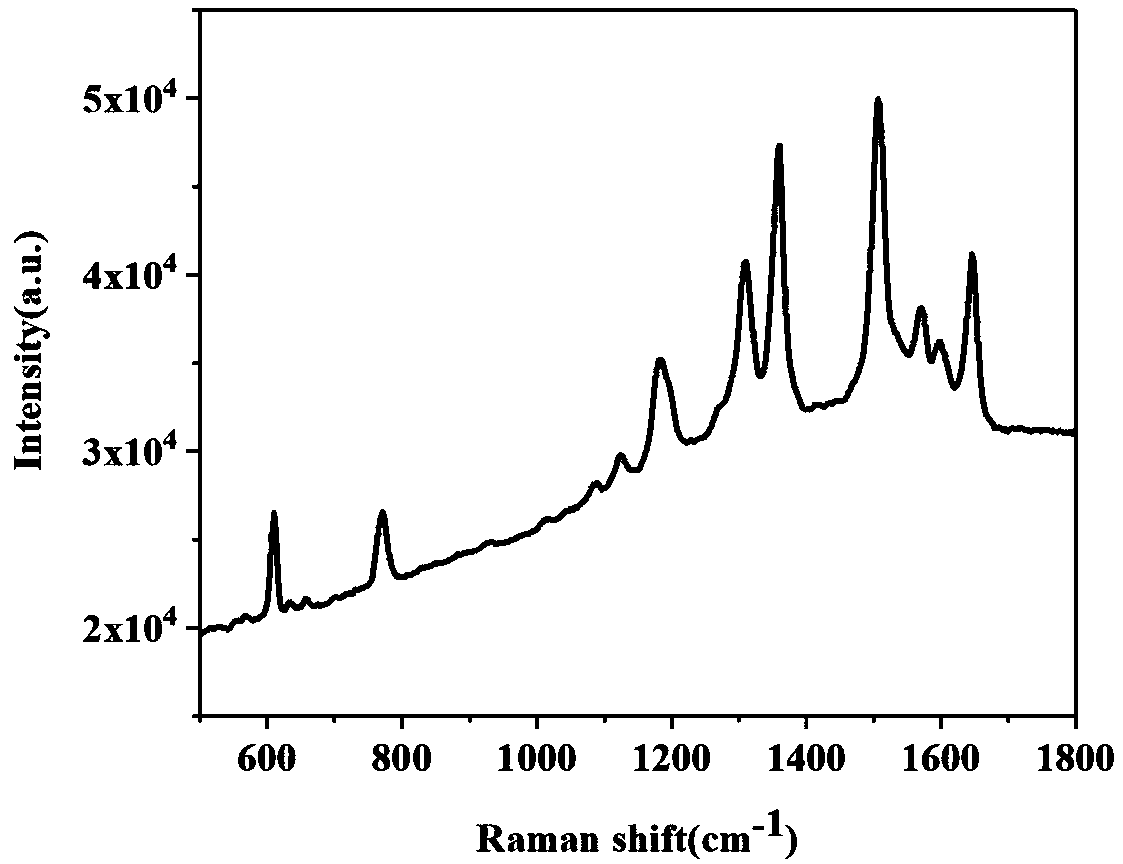
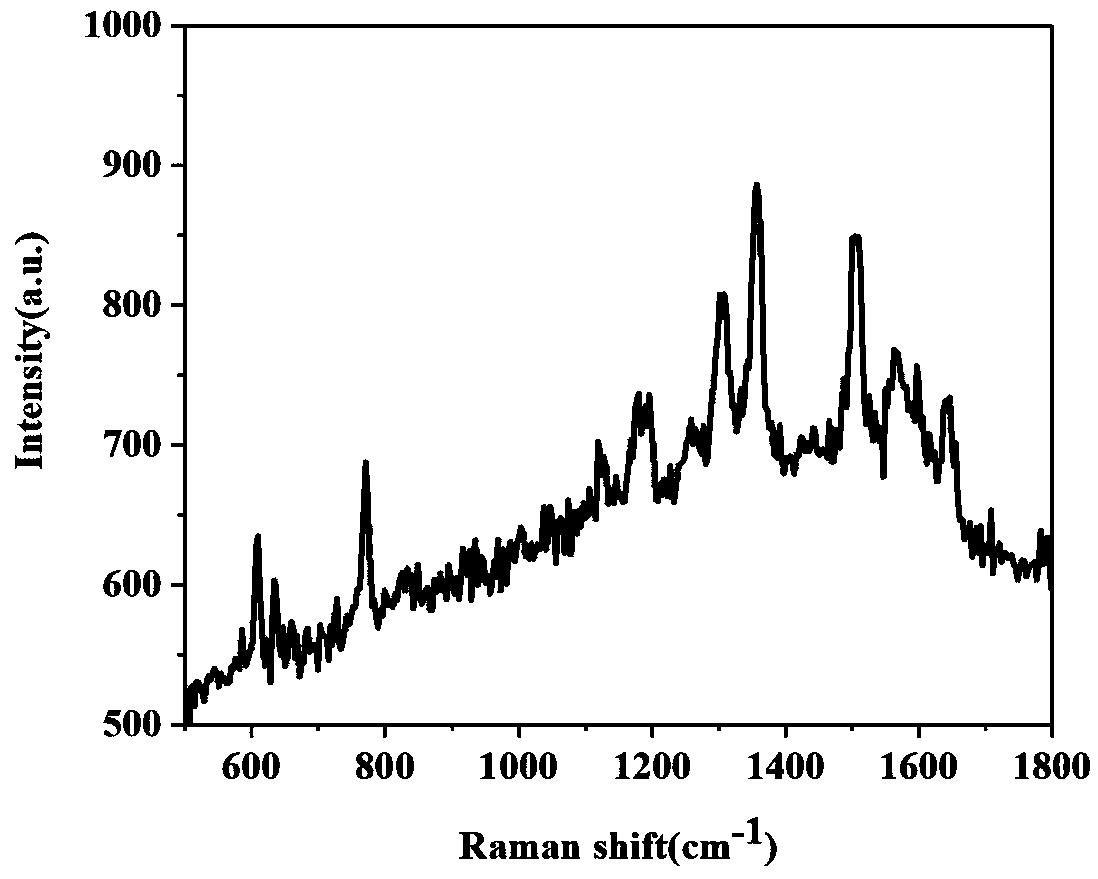
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate for detecting artificially synthesized pigments and preparation method and application of substrate
The invention discloses a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate for detecting artificially synthesized pigments and a preparation method and application of the substrate. The substrate comprises a substrate body, a titanium thin film layer covering the surface of the substrate body, a silver thin film layer covering the surface of the titanium thin film layer, and a silver nanorod array layer covering the surface of the silver thin film layer, wherein the included angle between each silver nanorod and the surface of a glass sheet is 86 degrees. The substrate is prepared in the steps of cleaning the substrate body, preparing the titanium thin film layer, preparing the silver thin film layer, preparing the silver nanorod array layer and the like, is used for detecting the artificially synthesized pigments, and is especially suitable for on-site rapid detection of food safety problems.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Magnesium oxide titanium high dielectric constant thin film and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103489766AHigh dielectric constantAvoid hydrolysisTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricTitanium thin film
The invention belongs to the technical field of oxide dielectric layer thin films, and particularly provides a magnesium oxide titanium high dielectric constant thin film and a preparation method and application of the magnesium oxide titanium high dielectric constant thin film. According to the magnesium oxide titanium high dielectric constant thin film, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether is used as a solvent, concentrated hydrochloric acid is used as a stabilizer, and Mg (OC2H5) 2 and Ti (C4H9O) 4 are dissolved in the solvent to form a clear and stable precursor solution; a glass substrate is coated by the precursor solution in a spinning mode and subjected to preheating and follow-up high-temperature heat treatment to obtain a magnesium oxide titanium thin film. The invention further relates to a thin film transistor which adopts the magnesium oxide titanium thin film as a gate dielectric layer. According to an IZO thin film transistor which adopts the magnesium oxide titanium thin film as a gate dielectric layer material, the switching current ratio is 6*106, the saturation migration rate is 3.4cm2 / Vs, and the sub-threshold swing is 0.32V / dec.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Infrared detector with a titanium oxide thermosensitive layer prepared by oxidation method and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107068780AImprove stabilityFast recovery of resistanceFinal product manufacturePyrometry using electric radation detectorsLeg regionTitanium
The present invention relates to an infrared detector with a titanium oxide thermosensitive layer prepared by an oxidation method. A bridge floor region of a support layer is provided with a titanium oxide film, the titanium oxide film is a semiconductor, and a bridge leg region connecting a metal and the support layer is provided with a titanium film in the same layer as the titanium oxide film, the titanium film is provided with a first protective layer, and the titanium oxide film and the first protective layer are provided with a second protective layer. The present invention also relates to a preparing method for the detector, and the method includes the steps of sequentially depositing a titanium film and a first protective layer on a support layer; removing a film of the first protective layer on a bridge floor; and oxidizing the titanium film exposed on the bridge floor to form a titanium oxide film as a thermosensitive film. The titanium film is directly deposited on the support layer, and the titanium film in the bridge floor region is oxidized and converted into the titanium oxide film as the thermosensitive film, so that the process of depositing a specific metal electrode layer is not required, the process steps can be greatly simplified, and the production capacity is improved.
Owner:YANTAI RAYTRON TECH
Low concentration detection SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) substrate of PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure
The invention discloses a low concentration detection SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) substrate of a PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure, which sequentially comprisesa glass substrate, a titanium film, a gold film, a PMMA film, gold nanocubes and a to-be-detected object adsorbed on the surfaces of the PMMA film and the gold nanocubes. When TM polarized light is normally incident on the surface of the PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure, local surface plasmas and propagation surface plasma are excited, strong resonance coupling occurs between the two kinds of surface plasmas to result in very strong electric field enhancement, and thus a strong surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectrum is generated for low-concentration SERSdetection. The low concentration detection SERS substrate has the advantages of easy operation, low cost and high sensitivity, and can be widely applied to low concentration detection.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
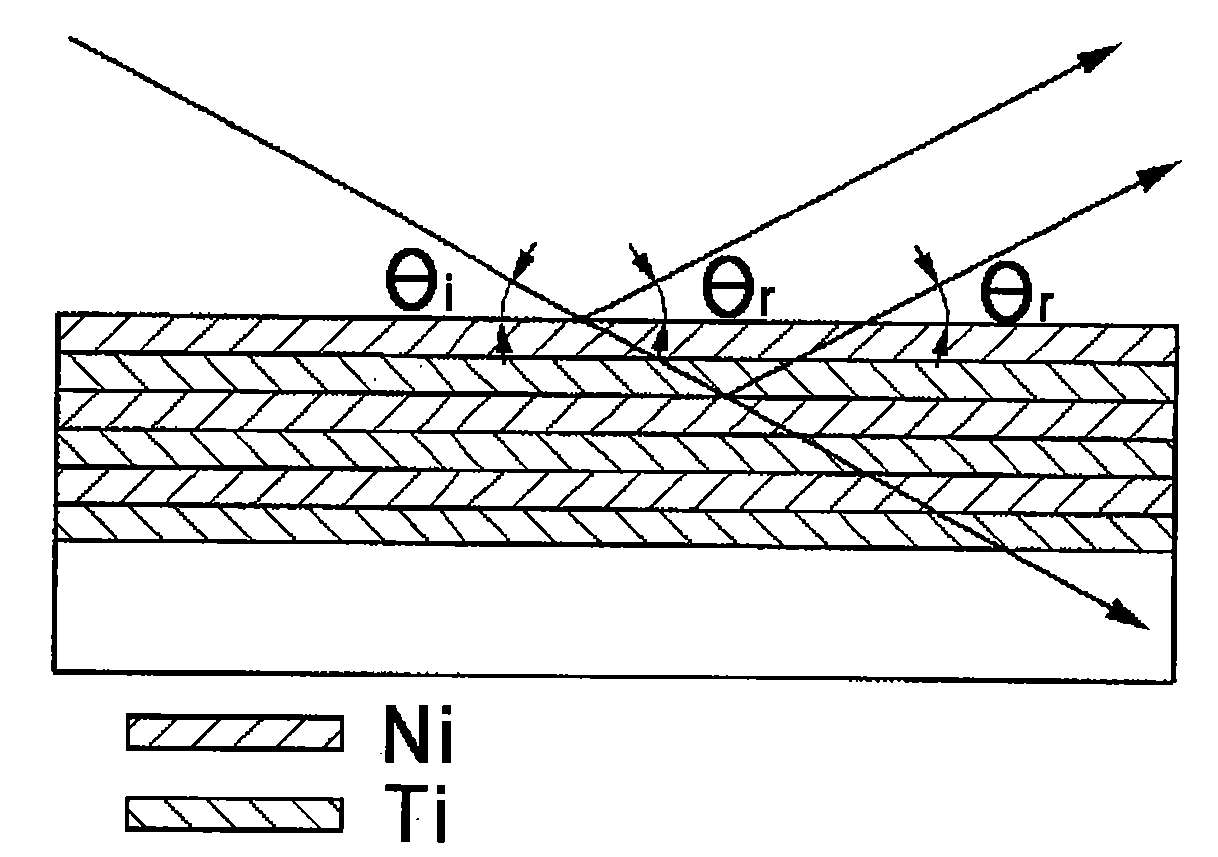
Method for fabricating neutron supermirror using neutron monochromator structures
InactiveUS20080115338A1Improve reflectivityEasy extractionMirrorsNanoinformaticsMonochromatorMonochromatic color
A method for fabricating a supermirror for forming a neutron guide. In the method, a neutron supermirror, which is widely used in the formation of thin films in cold neutron guides and the spectrometer field, is fabricated with nickel thin films and titanium thin films, having varying thickness, using a combination of monochromator structures in which nickel thin films and titanium thin films, having the same thickness, are stacked in the form of periodic structures. According to the method, a combination of monochromator structures having a variety of different thicknesses is formed, such that the amount of the overlap of peaks due to the monochromator structures can be adjusted to increase reflectivity, and some of the monochromator structures can be removed during the fabrication of the supermirror to make it easy to extract monochromatic beams, such that it is easy to fabricate a transmission monochromator, rather than a reflection monochromator.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
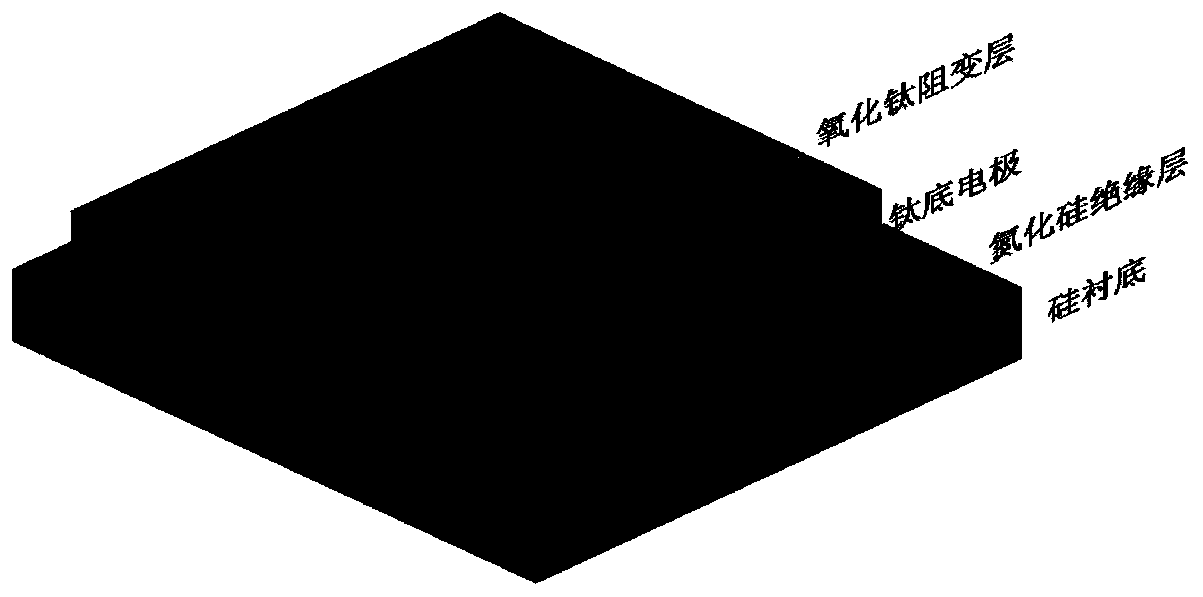
Preparation method of titanium oxide film memristor
The invention relates to a preparation method of a titanium oxide film memristor, and belongs to the field of non-volatile memories. The memristor is characterized by sequentially comprising a siliconsubstrate, an insulating layer, a bottom electrode, a resistive layer and a top electrode from bottom to top. The resistive layer is made of a titanium oxide film, the bottom electrode is made of titanium, and the top electrode is made of platinum. The prepared titanium oxide film can make the switching of the device higher, the high and low resistance states more stable, and the stress between the films is reduced. The method can be practically applied to a future novel non-volatile memory device.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for preparing anti-corrosion pure Ti film through DC magnetron sputtering
InactiveCN110952067AImprove corrosion resistanceNo pollution in the processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringThin membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing an anti-corrosion pure Ti film through DC magnetron sputtering. The method comprises the steps such as substrate surface processing, placement of a coating chamber on a substrate, substrate surface cleaning with reverse sedimentation, sputtering coating and production of a finished product after removal of a coated substrate. The method has the beneficial effects that rational technologies of surface processing, tooling fixation and sputtering coating can be adopted aiming at products such as valves and reaction kettles; the pure Ti film can be loaded on surfaces of the products, so the products can satisfy requirements for quality and corrosion prevention; technological processes are simple and efficient; courses are controllable; no environmental pollution is generated; and industrial production can be realized easily.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
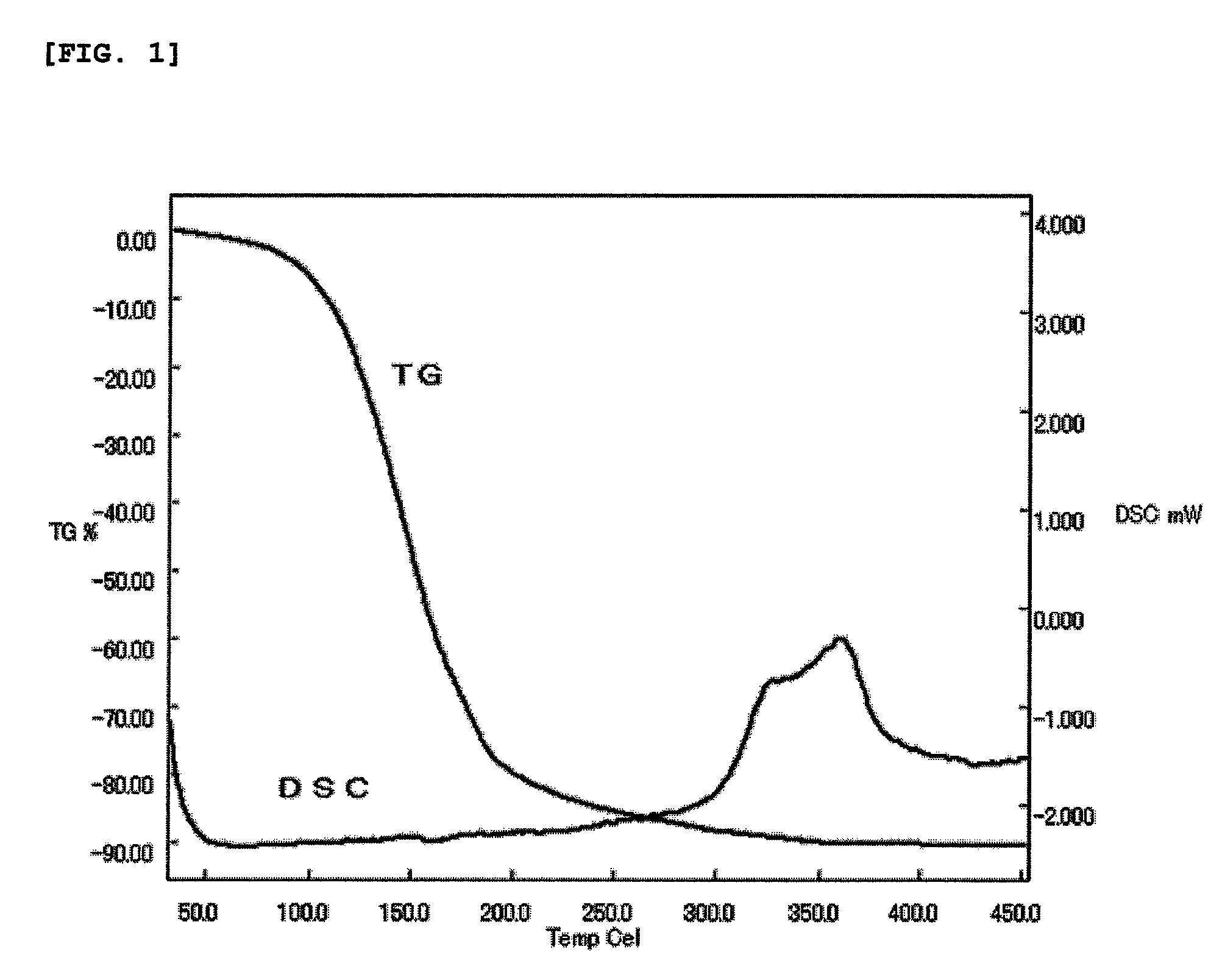
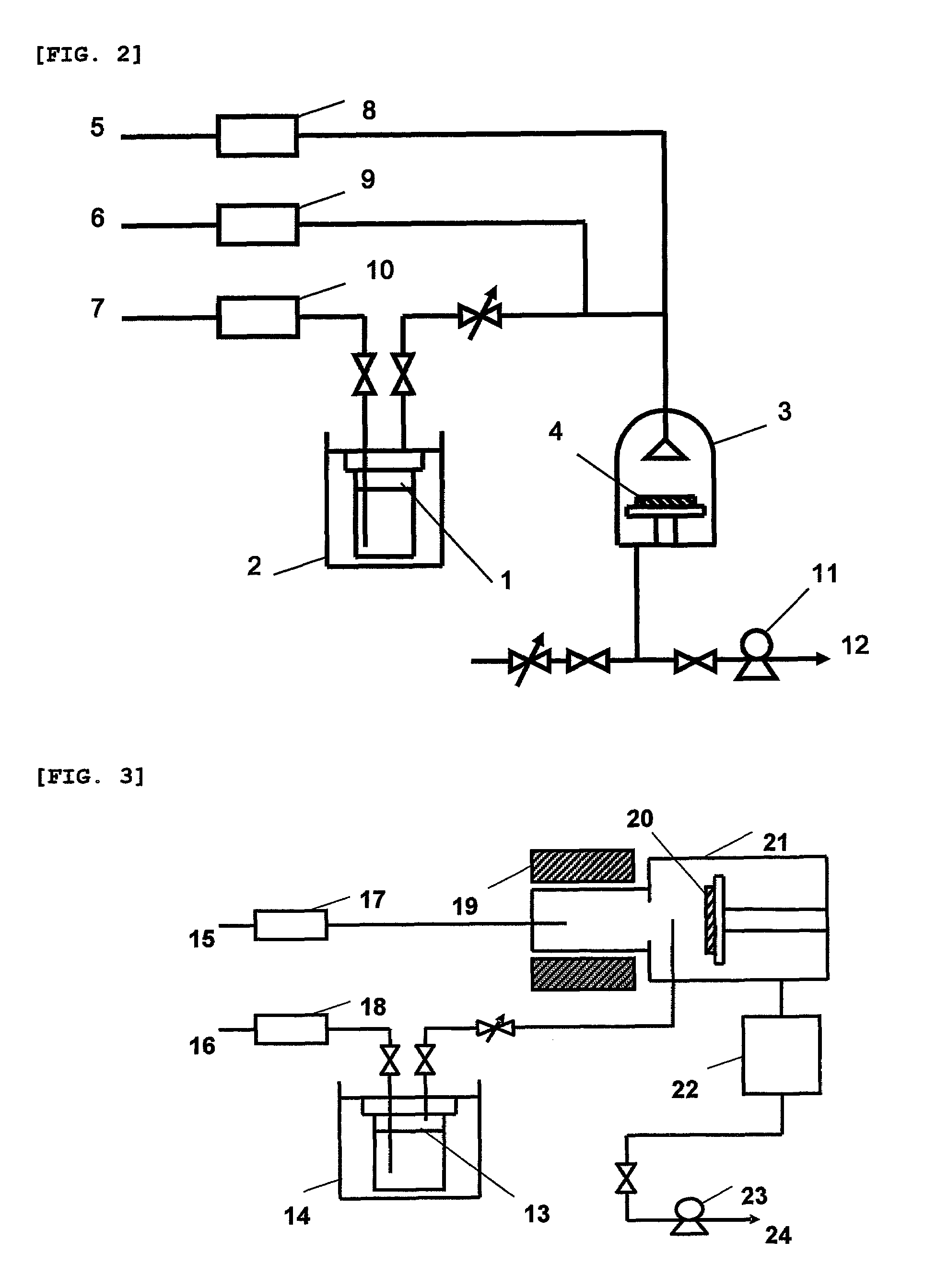
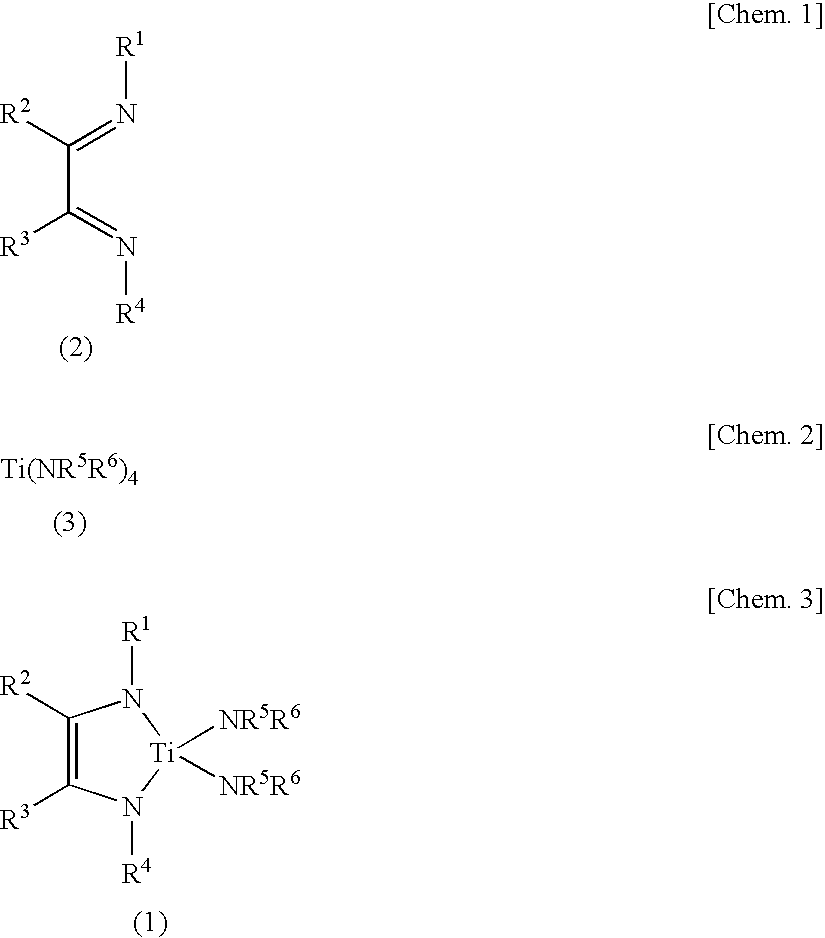
Titanium complexes, their production methods, titanium-containing thin films, and their formation methods
InactiveUS7632958B2Improve volatility characteristicsImprove thermal stabilityGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesTitanium organic compoundsMetallic lithiumHydrogen atom
Owner:TOSOH CORP +1
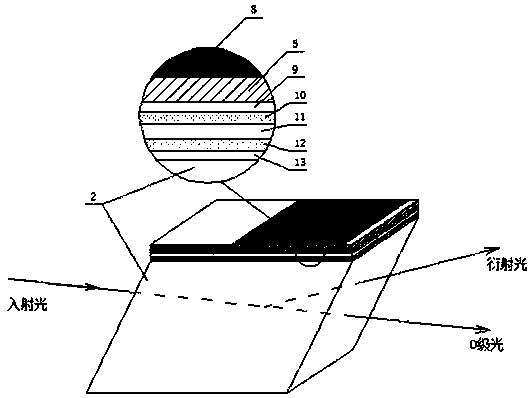
Large-aperture acousto-optical tunable filter
ActiveCN108107610ASolving Thickness Uniformity IssuesSolve the problem of uniformity of diffraction efficiencyNon-linear opticsIndiumEvaporation
The invention discloses a large-aperture acousto-optical tunable filter which comprises an acousto-optical medium, an energy converter and five welding layers. The energy converter is connected with the acousto-optical medium through the welding layers, a bottoming layer I, a transition layer I, a bonding layer, a transition layer II and a bottoming layer II are sequentially arranged from the acousto-optical medium to the energy converter, a surface electrode is plated on the energy converter, both the bottoming layer I and the bottoming layer II are titanium film layers, both the transition layer I and the transition layer II are copper film layers, and the bonding layer is a tin silver indium alloy layer. During manufacture, evaporation sources are arranged on two sides of the energy converter and the acousto-optical medium and evaporate bonding layer materials for the energy converter and the acousto-optical medium to obtain large-area uniform thickness bonding layer films, and thebonding layer films simultaneously cover the copper film layers of the energy converter and the acousto-optical medium. The acousto-optical tunable filter solves the problems that the optical apertureof an existing acousto-optical tunable filter is difficultly made large, welding quality is not good enough and cannot bear high driving electric power and the like.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
Method for detecting artificial synthetic pigment by combination of thin layer chromatography technique and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy technique
InactiveCN108693297AEasy to operateLow costComponent separationRaman scatteringSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for detecting artificial synthetic pigment by combination of a thin-layer chromatography technique and a surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy technique, comprising thefollowing steps: A, preparation of a silver nanorod array substrate: a titanium film and a silver film are deposited on the surface of a glass substrate by a glancing angle deposition technique, and the glancing angle is regulated and then the silver nanorod continues to be deposited; B, development of thin-layer chromatography: development of thin-layer chromatography is carried out on artificialsynthetic pigments on the silver nanorod array substrate by using methanol; C, surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection: Raman spectroscopy detection is carried out on a sample after the development. The method provided by the invention can help quickly distinguish different artificial synthetic pigments, and has the advantages of simple operation process, low cost, high sensitivity and thelike.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ferroelectric memory
ActiveCN103762311ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric thin filmsTitanium thin film
The invention discloses a ferroelectric thin-film capacitor of a ferroelectric memory. The ferroelectric thin-film capacitor comprises a substrate layer 1, an upper electrode layer 2, an upper electrode buffer layer 3, a ferroelectric thin-film layer 4, a lower electrode buffer layer 5, a lower electrode layer 6, a bonding layer 7 and a barrier layer 8, wherein multi-substituent silicon heterocyclic diallyl is doped into a lead-zirconium-titanium thin-film layer to form the ferroelectric thin-film layer 4.
Owner:江苏巨邦环境工程集团股份有限公司
A method for preparing nitrogen-containing titanium dioxide film by magnetron sputtering
ActiveCN105648414BCrystal phase controllableUniform grainVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTitaniumOxygen
Owner:太湖县市场监督检验所(太湖县功能膜检测研究院)
Method of preparing titanium oxide film by adopting sedimentation
InactiveCN107245702ADeposition process parameters are easy to controlExcellent wide bandgap performanceChemical vapor deposition coatingPolyesterAtomic layer deposition
The invention discloses a method of preparing a titanium oxide film by adopting sedimentation. The method effectively solves the key problems that the matching performance of a transparent oxide conductive film to a flexible polyester base is not good, the adhesiveness is poor, and the probability of falling is high. By adopting atom layer sedimentation, based on excellent wide bandgap performance of TiO2, tris(ethyl methylamino) butanamide chromium capable of being gasified at a low temperature is taken as a chromium precursor source, so that experiment conditions and energy consumption are reduced effectively, and atomic layer deposition process parameters are easy to control.
Owner:SUZHOU NANER MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com