Lubricating oil compositions
a technology of lubricating oil and composition, which is applied in the direction of additives, petroleum industry, liquid carbonaceous fuels, etc., can solve the problems of lead and copper corrosion, anti-wear additives, and the use of organic friction modifier additives, so as to reduce and/or inhibit corrosion, suppress corrosion, and reduce the effect of corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Polymeric Friction Modifier (B)
[0160]A 500 cm3 5-necked round-bottomed flask equipped with a nitrogen purge, stirrer with a gas-tight stirrer bearing, temperature probe and distillation arm attached to an exit bubbler was charged with PIBSA (158.4 g, 0.128 mol), PEG600 (101.0 g, 0.168 mol), sebacic acid (10.4 g, 0.0514 mol) and glycerol (7.7 g, 0.0835 mol) and the mixture heated at 180° C. with stirring for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was then heated to a temperature of 230° C. for 1 hour and then tetrabutyl titanate (0.5 ml) added thereto and heating and stirring continued for 2 hours at a temperature of 230° C. and a reduced pressure of between 50 to 150 mbar. The reaction mixture was cooled to below 100° C. and the polymeric friction modifier (B) poured from the round bottom flask. The polymeric friction modifier (B) had an acid value of 1.7 mg KOH / g.
example 2
Anti-Corrosion Performance
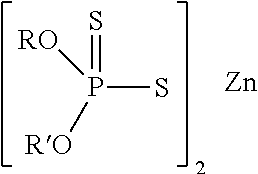
[0161]Six lubricating oil compositions (referred to as the base lubricant and Oils 1 to 5) were prepared. Each of the base lubricant and Oils 1 to 5 contained an identical Group II base stock and equal amounts of the following identical additives: an overbased calcium sulphonate detergent (TBN 300 mg KOH / g); a dispersant; anti-oxidants; a molybdenum friction modifier; and a viscosity modifier. Oils 1 to 5 also included the additional additive(s), on an active ingredient basis, as detailed in Table 1. Those oils which included ZDDP (i.e. Oils 3 to 5) had a phosphorus content of 880 ppm as measured by ASTM D5185. Oil 5 represents a lubricating oil composition of the present invention.
TABLE 1BaseOil 1Oil 2Oil 3Oil 4Oil 5ComponentlubricantMass %Mass %Mass %Mass %Mass %ZDDP———1.101.101.10Polymeric—0.50———0.50frictionmodifier(B)1Glycerol——0.50—0.50—monooleate1The polymeric friction modifier was the compound of Example 1.
Testing and Results
[0162]Corrosion control ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com