Digital Analysis of Molecular Analytes Using Electrical Methods
a technology of molecular analytes and electrical signals, applied in the field of digital analysis of molecular analytes using electrical methods, can solve the problems of insensitivity limitations of current methods, biases and inaccuracy of quantification of amplification techniques, and various limitations of current analyte analysis technologies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
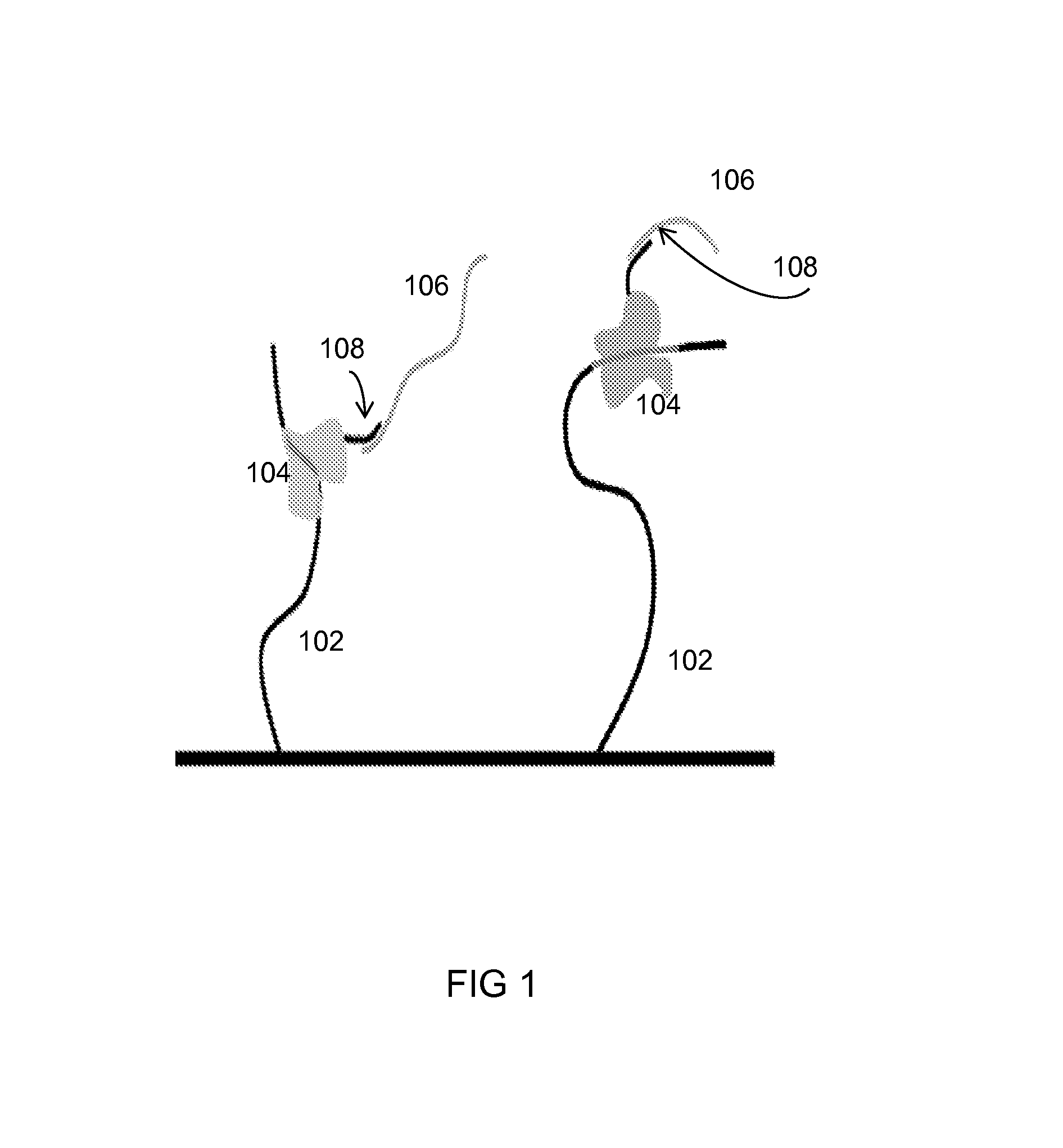
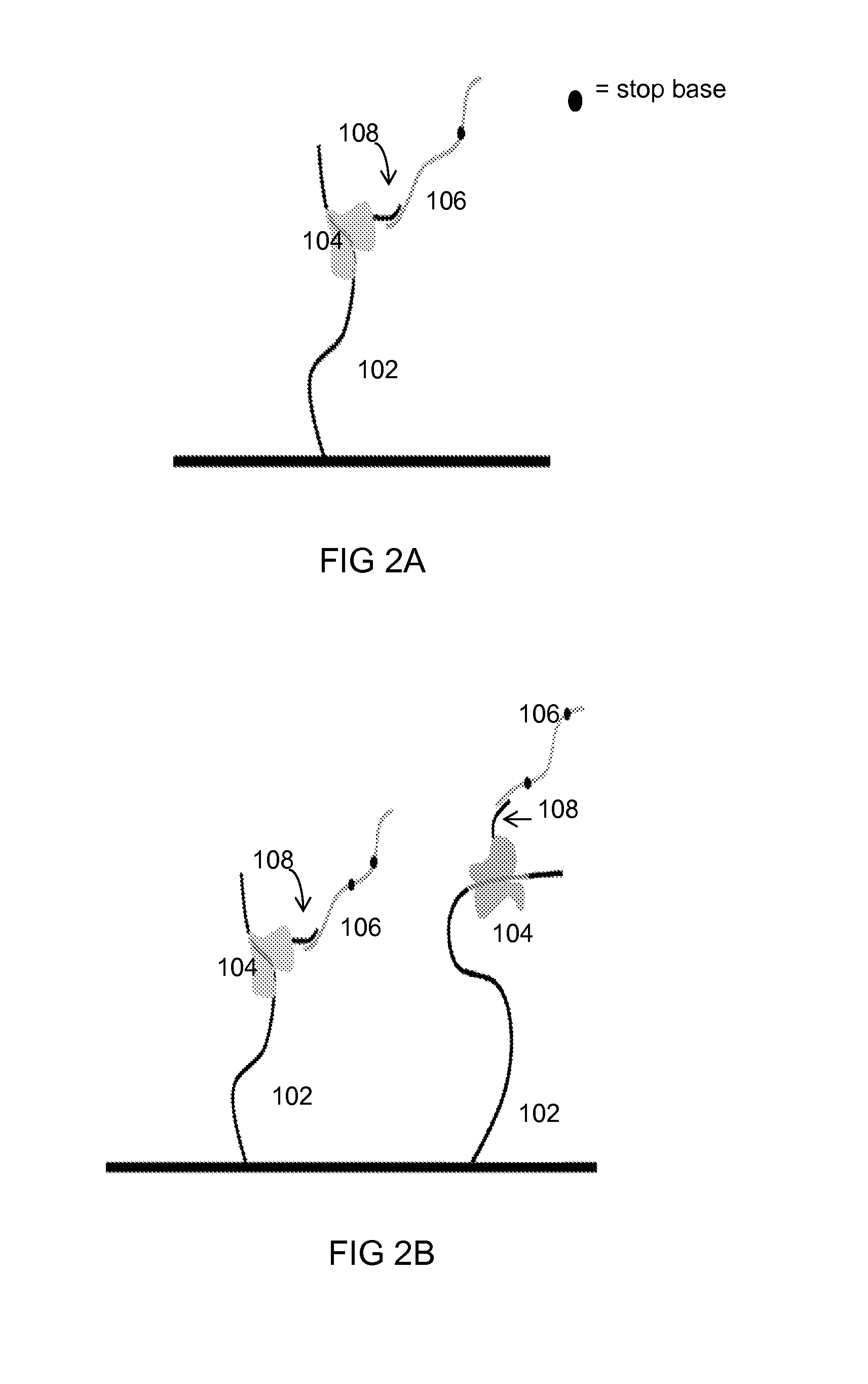
[0072]There are 8 distinct target analytes 102 immobilized on an integrated-circuit chip containing a plurality of transistors (i. e., ISFETs). Each target analyte 102 is specific for a distinct probe region 104 that includes one or more linker regions 108, each of which is specific for a particular tail region 106. 8 poly-A tail regions 106 are used in this Example, all having a length of 901 nucleotides. The identification length is 100 nucleotides, and one stop base of one stop base type (cytosine) is inserted within the tail. Table 1A shows the different tail regions 106 used, where “Leader length” represents the number of nucleotides upstream of the stop base, and “Trailer length” represents the number of nucleotides downstream of the stop base.
TABLE 1ATail regionLeaderStopTrailerNumberlengthBaselengthTail region #1100C800Tail region #2200C700Tail region #3300C600Tail region #4400C500Tail region #5500C400Tail region #6600C300Tail region #7700C200Tail region #8800C100
[0073]The n...
example 2
[0075]There are 16 distinct target analytes 102 immobilized on an integrated-circuit chip containing a plurality of transistors. Each target analyte 102 is specific for a distinct probe region 104 that includes one or more linker regions 108, each of which is specific for a particular tail region 106. 16 poly-A tail regions 106 are used in this Example, all having a length of 701 nucleotides. The identification length is 100, and one stop base of three stop base types (cytosine, guanine, or thymine) is inserted within the tail. Table 2A shows the different tail regions 106 used, where “Leader length” represents the number of nucleotides upstream of the stop base, and “Trailer length” represents the number of nucleotides downstream of the stop base.
TABLE 2ATail regionLeaderStopTrailerNumberlengthBaselengthTail region #1100C600Tail region #2200C500Tail region #3300C400Tail region #4400C300Tail region #5500C200Tail region #6600C100Tail region #7100G600Tail region #8200G500Tail region #...
example 3
[0078]There are 256 distinct target analytes 102 immobilized on an integrated-circuit chip containing a plurality of transistors. Each target analyte 102 is specific for a distinct probe region 104 that includes one or more linker regions 108, each of which is specific for a particular tail region 106. 16 poly-A tail regions 106 are used in this Example, all having a length of 402 nucleotides. The identification length is 100, and two stop bases of a combination of three stop base types (cytosine, guanine, or thymine) are inserted within the tail. Table 3A shows the different tail regions 106 used, where “Leader length” represents the number of nucleotides upstream of Stop base #1, “Mid length” represents the number of nucleotides upstream of Stop base #2, and “Trailer length” represents the number of nucleotides downstream of Stop base #2.
TABLE 3ATail region 106LeaderStopMidStopTrailernumberlengthbase #1Lengthbase #2lengthTail region #1100C100C200Tail region #2100C200C100Tail regio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| lengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass spectrometry | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com