Method for manufacturing iron nuggets
a manufacturing method and technology for iron nuggets, applied in metal processing, furnace types, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of significant expansion, decarburization and reduction of the amount of carbon in the iron nuggets, and degradation of the quality of the iron nuggets, so as to increase the feo amount in a slag, reduce the amount of sulfur contained in the iron nuggets, and improve the quality of the reduced iron
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental example 1
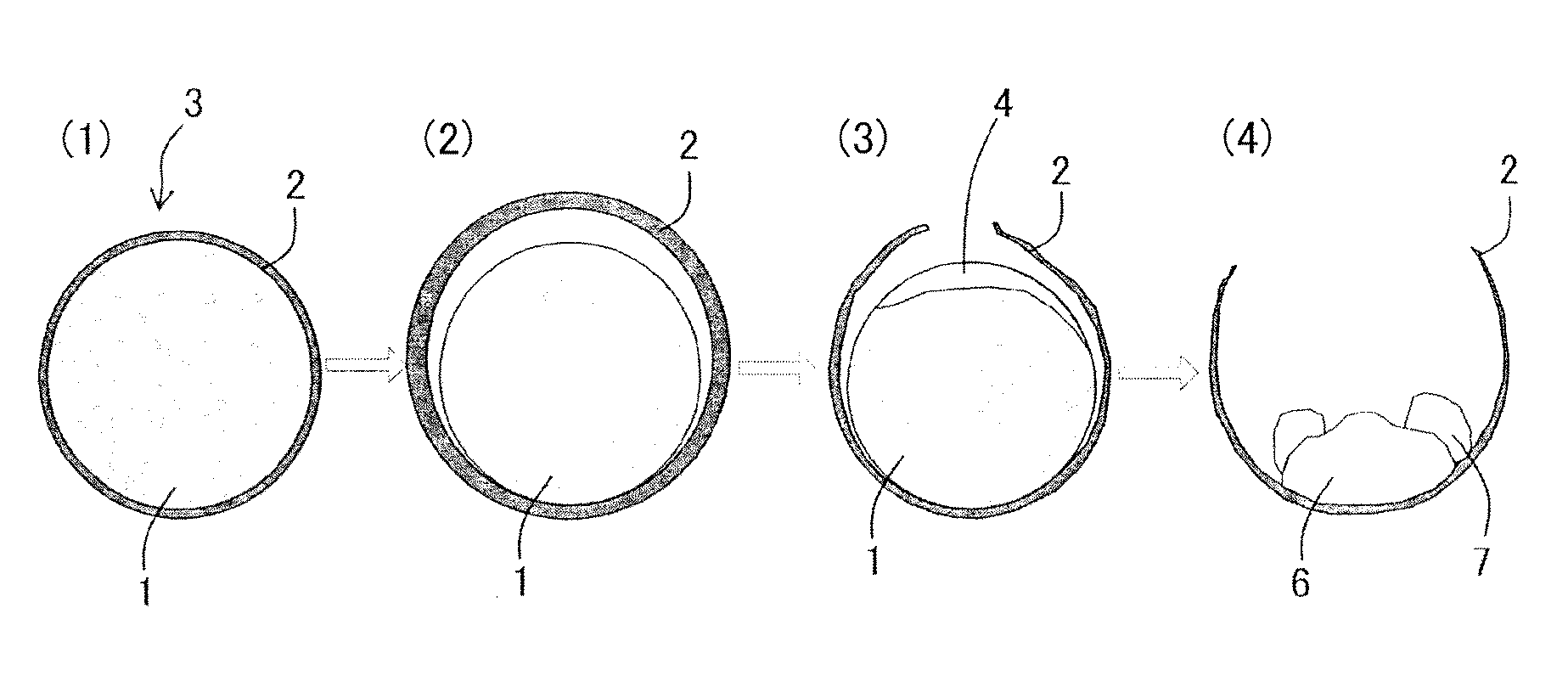
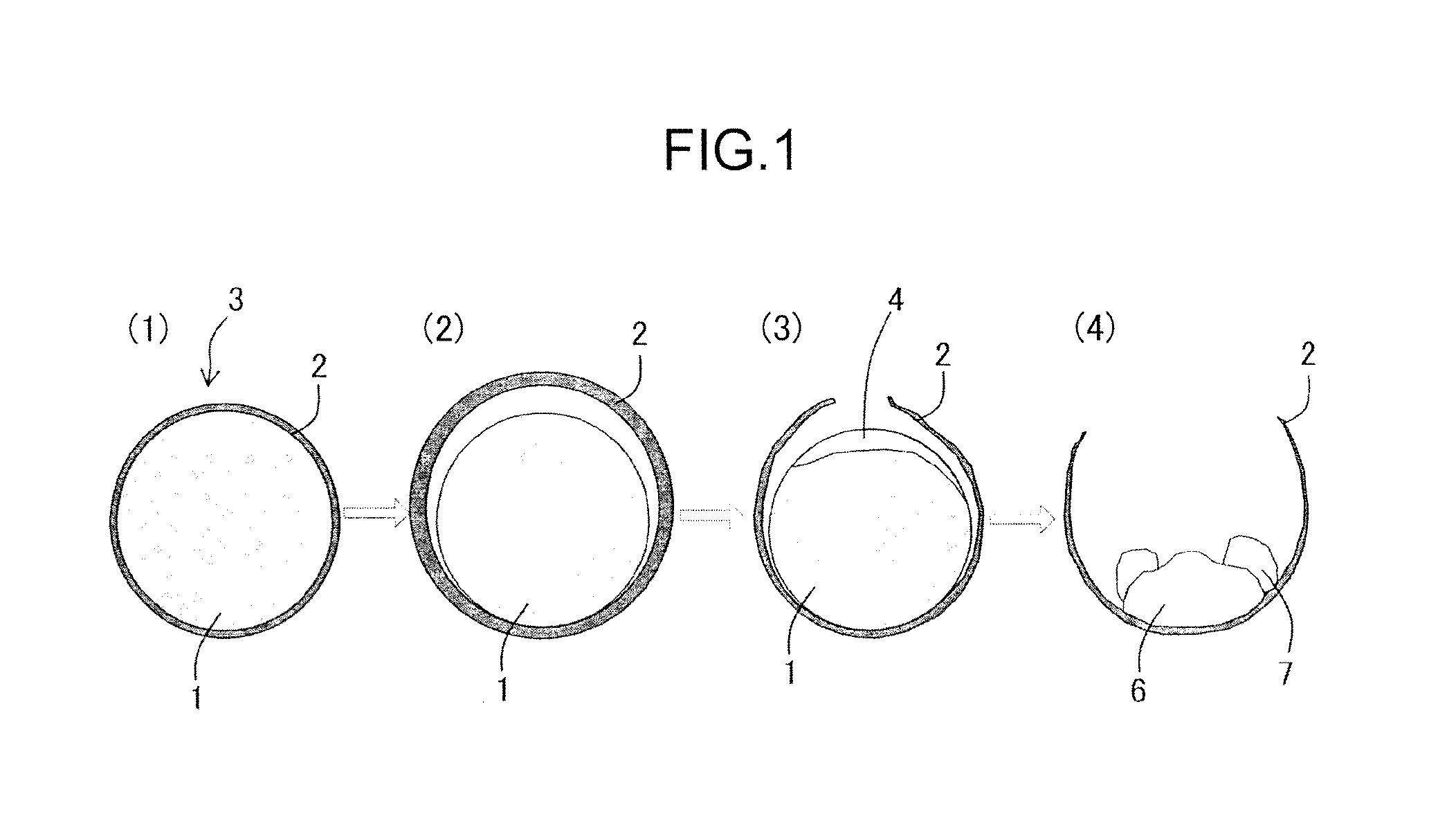
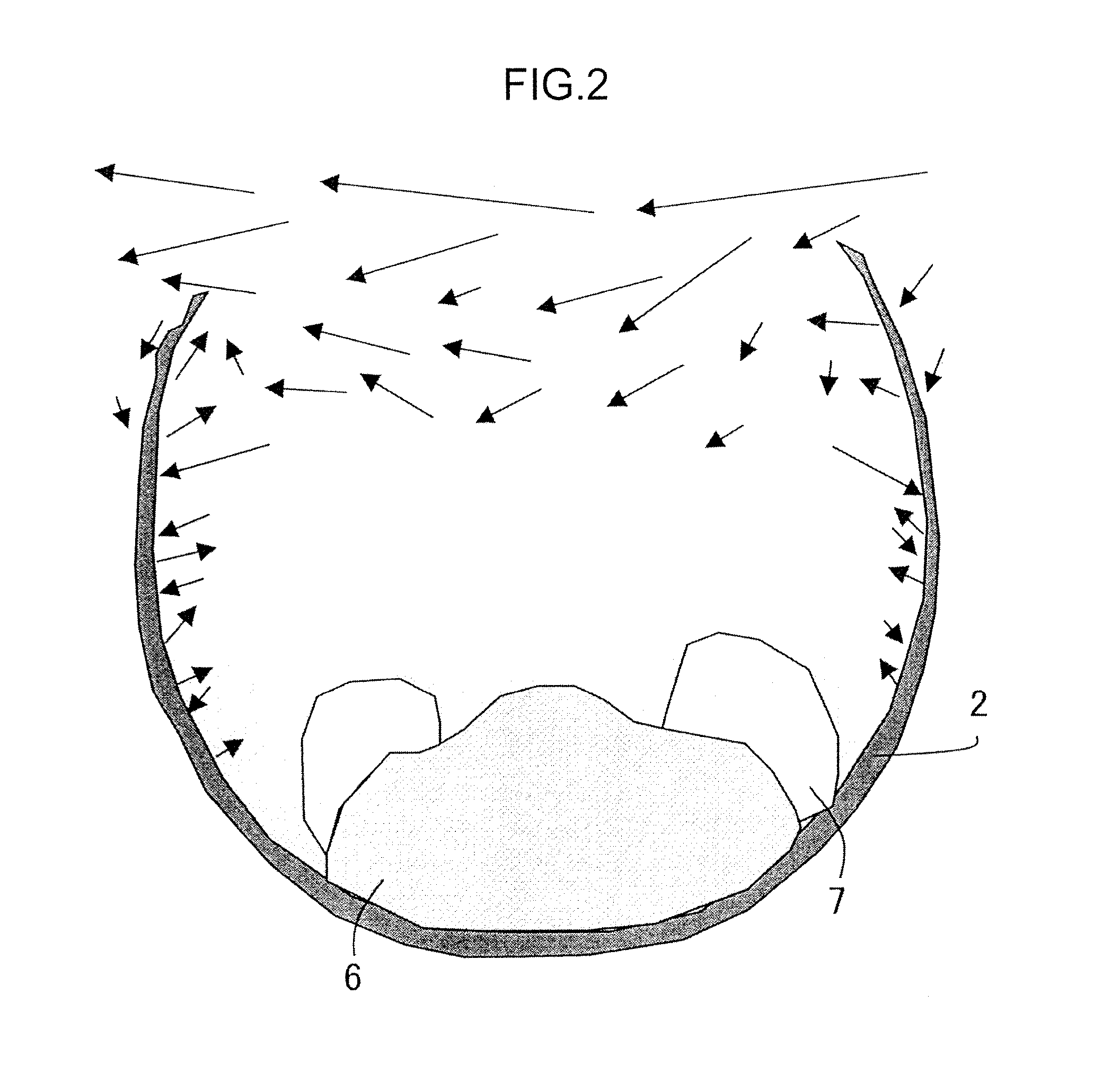
[0086]In the present experimental example, agglomerates having on the surface a coating layer including a fluid carbonaceous material and agglomerates having no coating layer were prepared, the agglomerates were heated in a heating furnace, and it was investigated whether or not the reoxidation of the obtained iron nuggets was suppressed.
[0087]Initially the agglomerates including iron oxide and a carbonaceous reducing agent were manufactured.
[0088]An iron ore of the composition presented in Table 1 below was used as the iron oxide. In Table 1, T. Fe means “total iron”. The iron ore to be used was ground such that the ore with a particle size of 44 μm or less constituted 67 mass %.
[0089]A carbonaceous material with the composition presented in Table 2 was used as the carbonaceous reducing material. In Table 2, T. C means “total carbon” and F. C means “fixed carbon”. The carbonaceous material to be used was ground such that the coal with a particle size of 75 μm or less constituted ab...
experimental example 2
[0108]In the present experimental example, the agglomerates were manufactured by changing the thickness of the coating layer formed on the surface of core portions, the produced agglomerates were heated in a heating furnace, and it was investigated whether or not the reoxidation of the obtained iron nuggets was suppressed.
[0109]Initially, green pellets in which the coating layer was formed on the surface of core portions were manufactured according to the procedure of Experimental Example 1 by changing the thickness of the coating portion. The core portions on which the coating layer was formed were cut and the thickness of the coating layer was checked by observing the cross section under an optical microscope. As a result, the average thickness of the coating layer was 0.30 mm to 2.00 mm.
[0110]The green pellets obtained by forming the coating layer on the surface of the core portions were charged into a drier and heated for about 1.0 h at 160° C. to 180° C. to remove the adhered w...
experimental example 3
[0124]In the present experimental example, the agglomerates were manufactured by using a non-fluid carbonaceous material for including in the coating layer to be formed on the surface of the core portions, the agglomerates were heated in the heating furnace, and it was examined whether or not the reoxidation of the obtained iron nuggets was suppressed.
[0125]Initially, green pellets in which the coating layer with an average thickness of 0.50 mm was formed on the surface of the core portions were manufactured according to the procedure of Experimental Example 1. In this case, anthracite was used as a non-fluid carbonaceous material instead of the fluid bituminous coal. The composition of the anthracite is presented in Table 6 below.
[0126]The green pellets obtained by forming the coating layer on the surface were charged into a drier and heated for about 1.0 h at 160° C. to 180° C. to remove the adhered water, thereby producing spherical dry pellets (i.e., agglomerates).
[0127]Then, th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com