Highly Potent Glucocorticoids
a glucocorticoid, high-potency technology, applied in the direction of steroid, organic chemistry, skeletal disorders, etc., can solve the problems of insensitivity, resistance to glucocorticoid therapy, and many adverse effects, so as to reduce unwanted side effects, reduce side effects, and reduce side effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
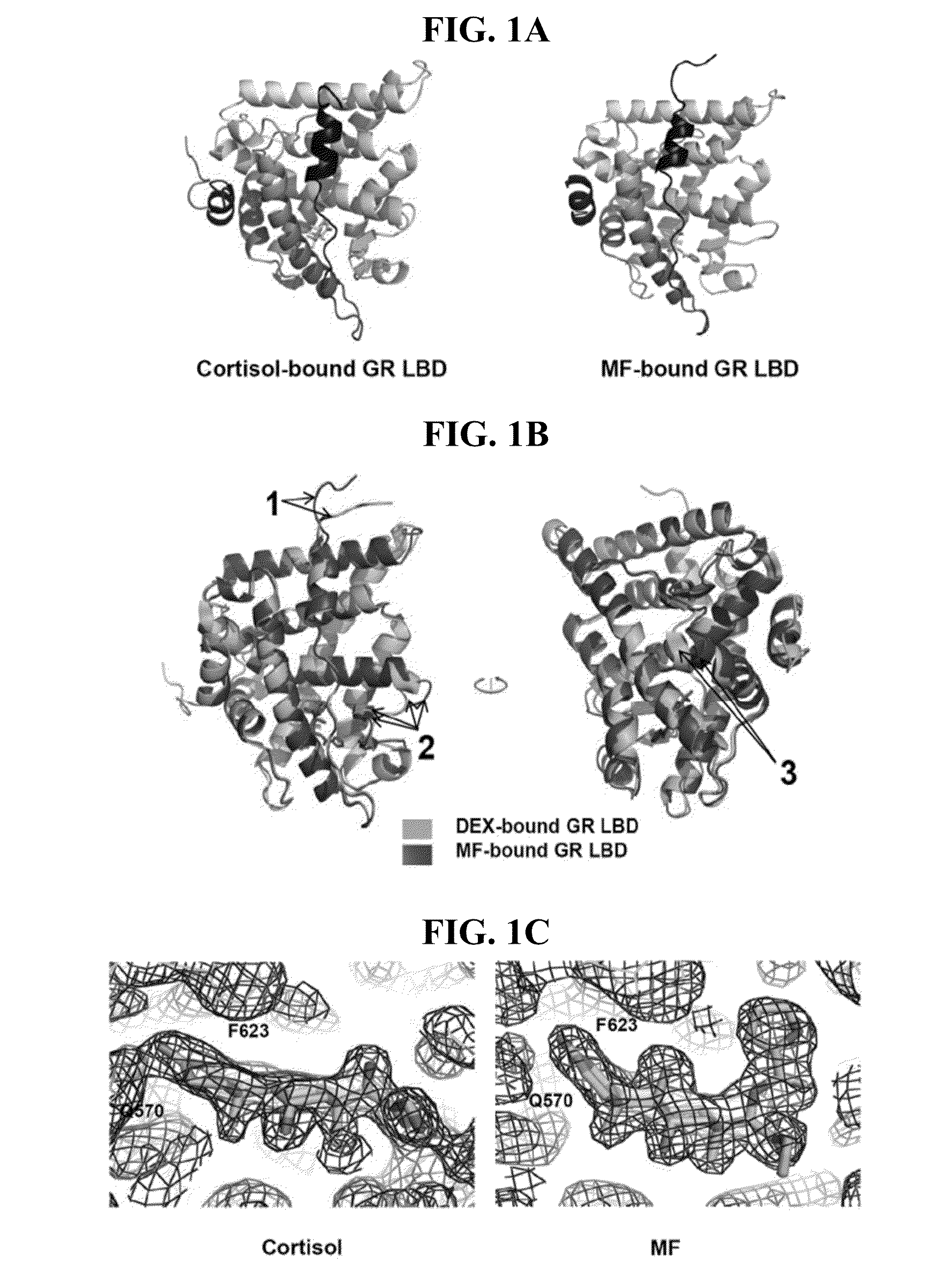
Overall Structure of the Cortisol- and MF-Bound GR LBDs
[0196]Crystallization of the GR LBD has always been a challenge due to its solubility problem. The original GR LBD structure was determined with a high affinity ligand DEX (27), bound to the GR LBD with F602S mutation, which improve protein solubility. However, cortisol is a much weaker ligand than DEX and the F602S mutation is not sufficient for stabilizing the GR LBD bound to cortisol, an endogenous hormone (FIG. 8, lane 1). To identify amino acids that might increase GR LBD solubility without affecting overall structure, we aligned GR with the closest members of steroid hormone family, MR, androgen receptor (AR) and progesterone receptor (PR), which are much more soluble than GR. Besides F602, residue C622, T668, S674 and V675 distinguish from the conserved sequences of the family, so the inventors mutated those amino acids back to the conserved residues (F602A, C622Y, T668V, S674T and V675I, termed AYVTI). Most of these resi...
example 2
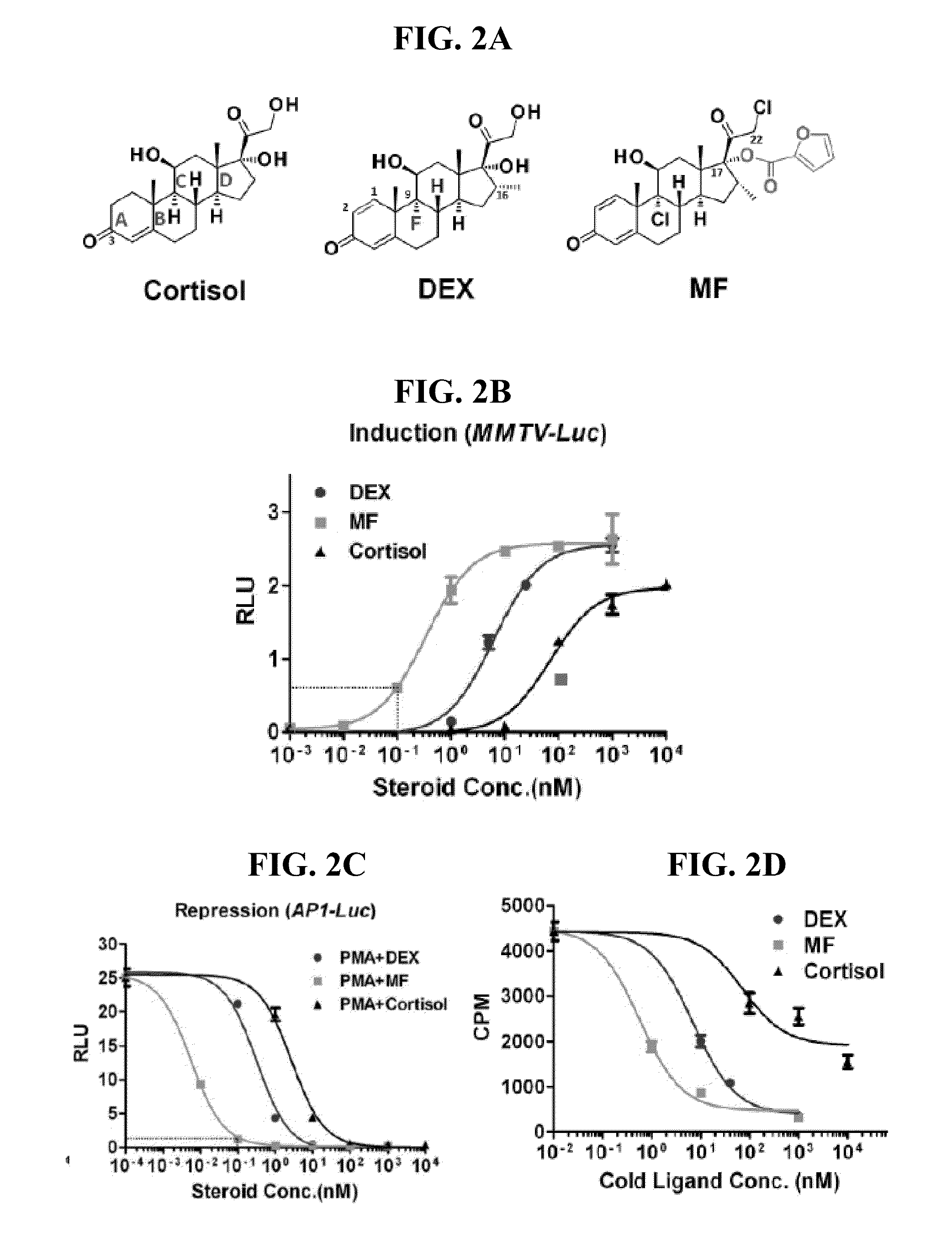
Potency, Affinity of Cortisol, DEX and MF
[0198]The change of chemical structures (FIG. 2A) of cortisol, DEX and MF silhouettes the evolution of glucocorticoid: from simple to complex and from one level to multiple levels. The cortisol structure provides a basic 4 ring steroid backbone; then DEX adds 1,2 double bone, 16 methylation and 9α halogenation (FIG. 2A); and MF further chloridizes at 22, and more importantly, adds a lipophilic furoate ester group at 17α (FIG. 2A), replacing the hydroxyl group of DEX and cortisol. To test the effects of those chemical changes on GR potency, the inventors side by side compared MF, DEX, and cortisol activities on both GR transactivation and transrepression in the format of full dose-response curve. For transactivation, the inventors used an MMTV-driven luciferase reporter system (FIG. 2B). MF and DEX showed almost the same efficacy (maximal activity) at the saturation concentration (1 μM), whereas cortisol at its saturation concentration (10 μM)...
example 3
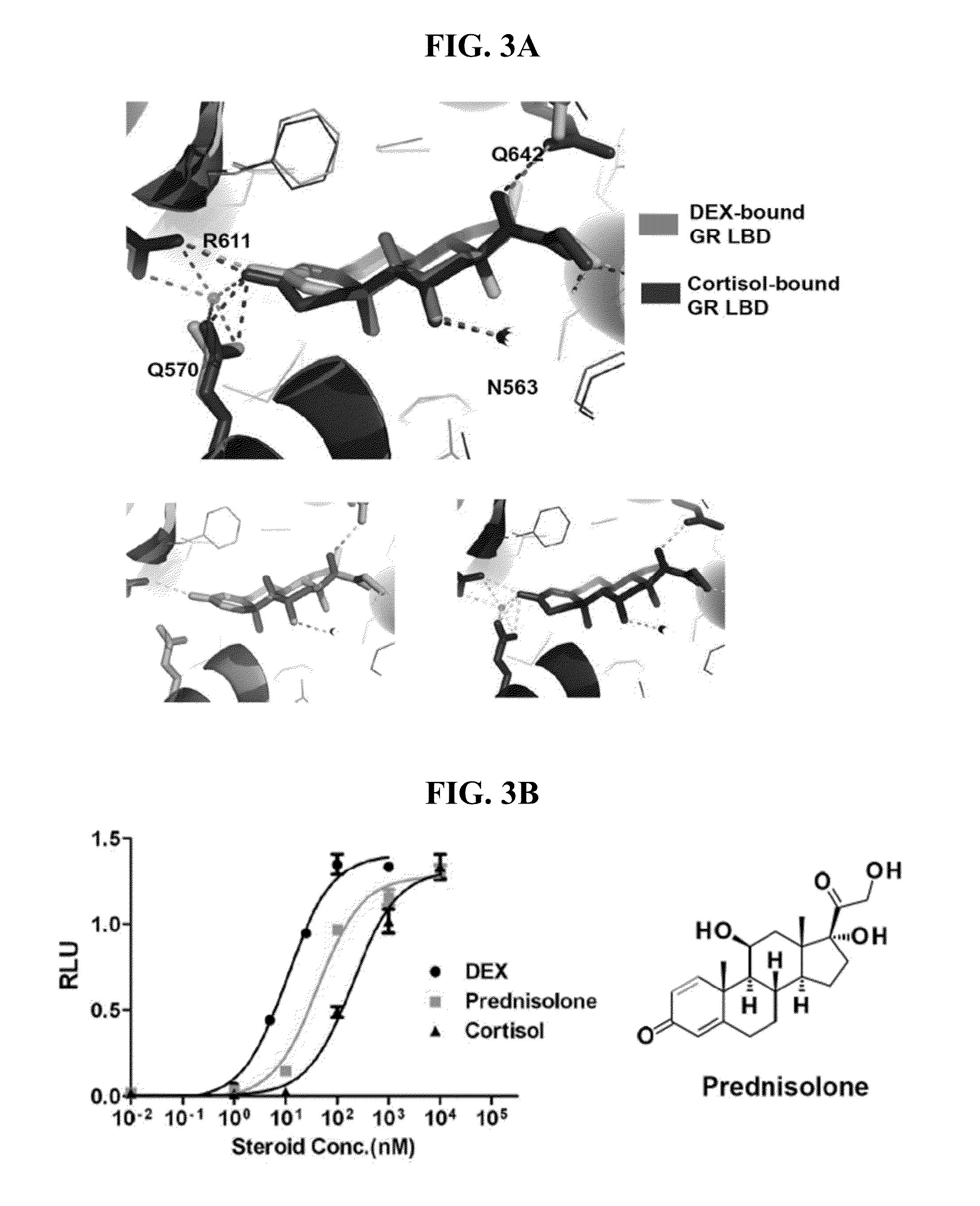
The Flexibility of 1,2 Single Bond Attributed to the Low Affinity of Cortisol to GR
[0201]To understand the underlying mechanism of the low affinity of cortisol, the inventors did a structural comparison of cortisol-bound GR LBD and DEX-bound GR LBD. The overall structure of cortisol-bound GR LBD is almost exactly same as DEX-bound GR LBD, there is no notable conformation change. Then the inventors looked into the detail of ligand binding. As mentioned above, DEX differentiate from cortisol only via: 1,2 double bond, 9α halogenation and 16 methylation (FIG. 2A). The C1-C2 double bond of DEX causes the steroid A ring and the C3-ketone group to become planar, thus allowing the C3-ketone to readily interact with R611 and Q570 (FIG. 3A). In contrast, because of the flexibility of the cortisol C1-C2 single bond, the steroid A ring needs to bend to form a hydrogen bond with R611 and Q570. Also, since the C1-C2 single bond of unbound cortisol oscillates between two conformations (above and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com