Hydrothermal process for the treatment of lead glass with recovery of lead metal, soluble and insoluble silicates and silica
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
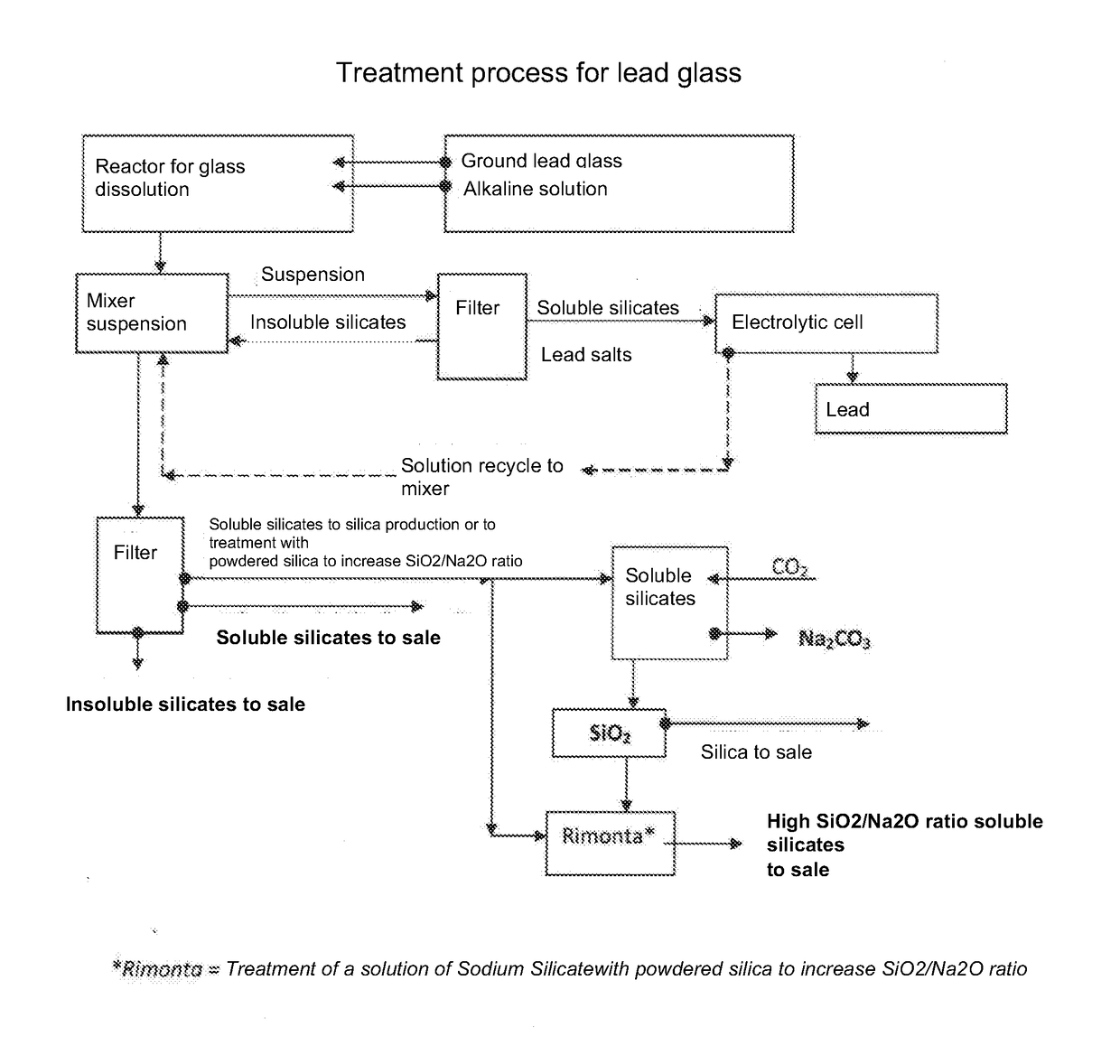
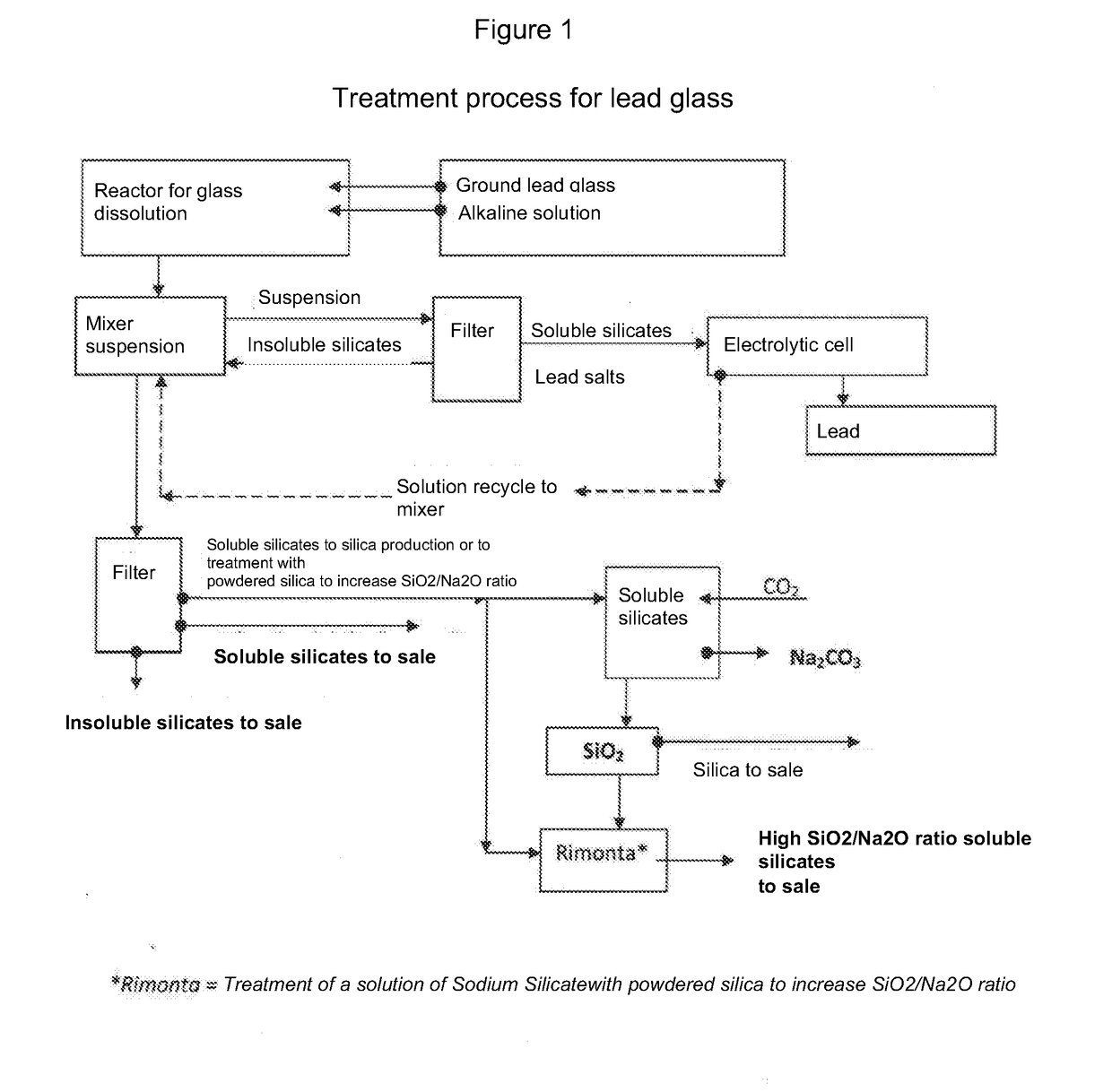
[0026]The following masses are loaded in an autoclave: 600 kg of lead glass ground with a particle size less than 1 mm, 180 kg of 99.9% pure solid sodium hydroxide and 420 kg of water. The lead glass being used had a PbO content of 18.31% by weight, determined by X-ray diffraction, equal to 17% of Pb expressed as metal. The mass was heated to 205° C. and stirred for two hours. The registered autogenous pressure was 16 bar. At the end of the reaction, the mass was cooled and diluted with 900 liters of water. 102 kg of lead, expressed as metal, was found in the resulting suspension.
[0027]The suspension was transferred into a mixer and maintained under constant stirring at a temperature of 55-60° C. The suspension was continuously sent to a filter so as to separate the solid phase, constituted by insoluble silicates, fromt part of the liquid phase, consisting of sodium and potassium soluble silicates. The separated solid phase was recycled into the mixer while the separated liquid phas...
example 2
[0031]The procedure of Example 1 has been repeated, with the differences that the mass is cooled down and diluted with 600 liters of water at the end of the alkaline etching reaction on the ground glass. By operating as described in Example 1, 1200 kg of soluble silicate with a concentration of 37% by weight, a density of 1.38 g / ml and a value of R=1.7 were eventually obtained. The recovery of metallic lead and insoluble silicates were the same as those indicated in Example 1.
example 3
[0032]The procedure of Example 1 has been repeated, with the differences that the time of the alkaline etching reaction on the glass was reduced to 1 hour and 30 minutes, but the temperature was elevated to 215-218° C. The reaction mass was diluted with 400 kg of water, obtaining eventually 1000 kg of soluble silicate with a concentration of 41.9% by weight, density of 1.43 g / ml, and R=1.8 (by moles). The recovery of metallic lead was higher than 99.84%. Furthermore, the electrolysis reaction was carried out with a current density of 700 A / m2, with a 15% reduction of the time for the electrolytic recovery of lead without significant changes on current efficiency.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com