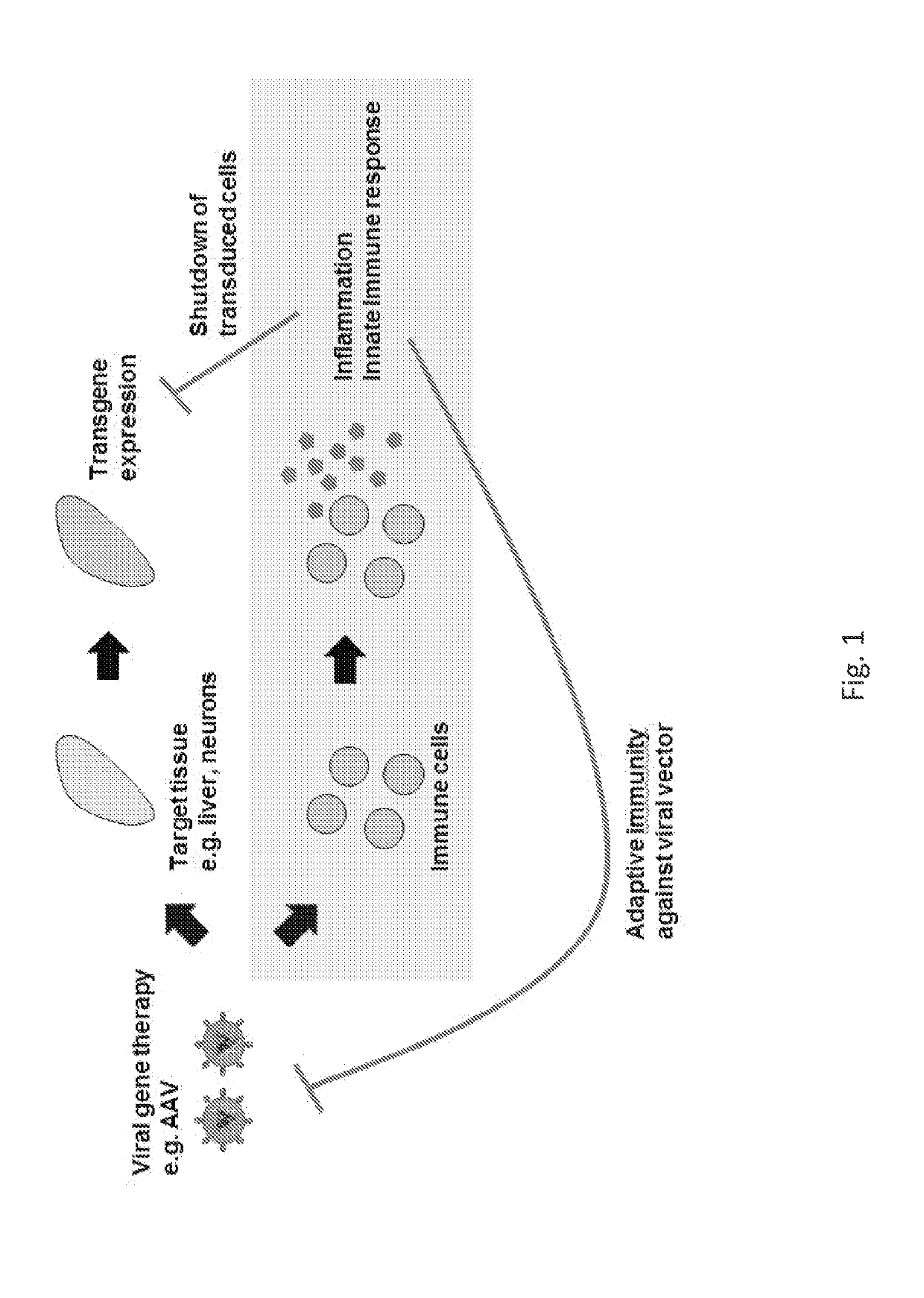
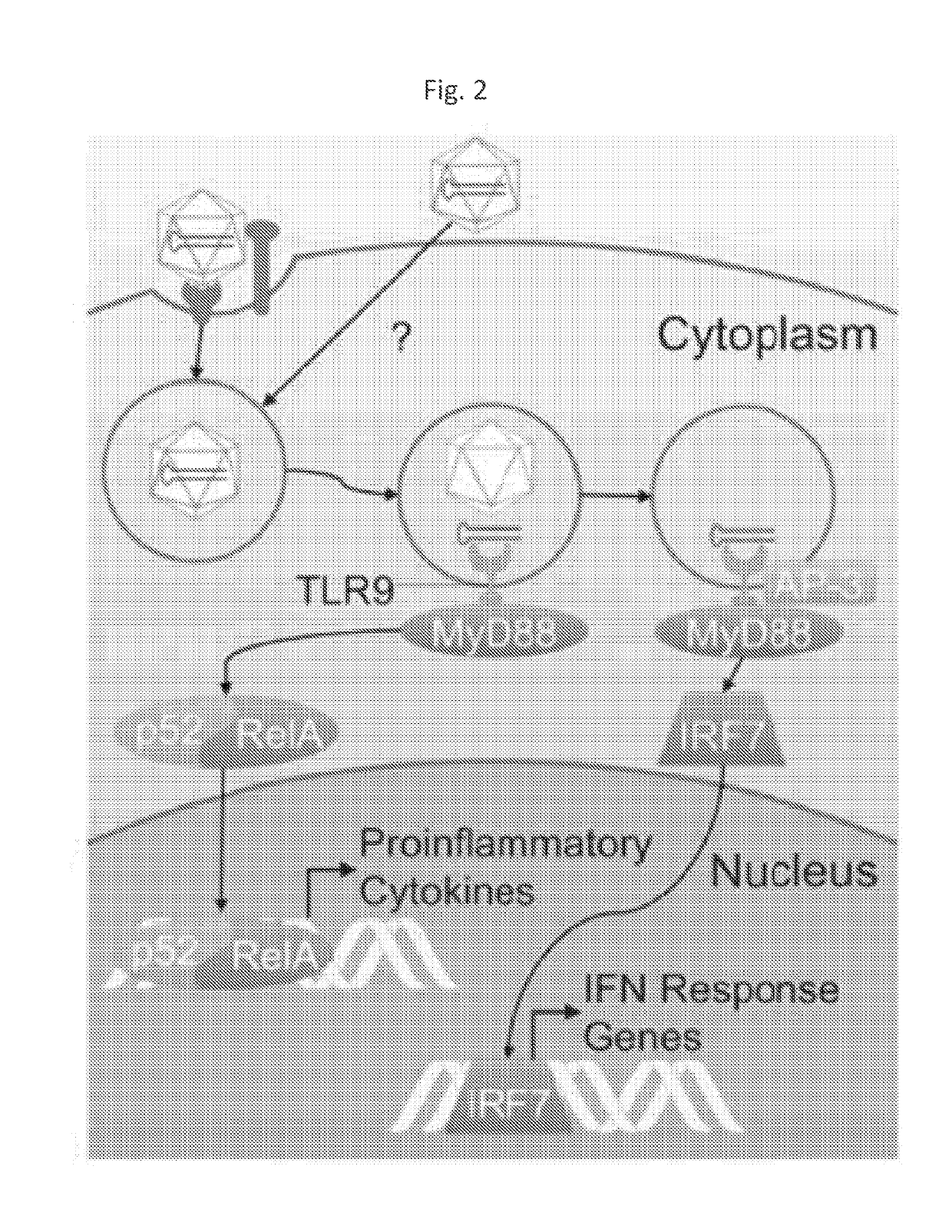
Engineered viral vector reduces induction of inflammatory and immune responses
a technology of inflammatory and immune responses, applied in the field of recombinant viruses, can solve the problems of compromising the immune system of patients during treatment, hammering the therapeutic effect of humans, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the immunogenicity of a modified virus, reducing the inflammatory response, and inhibiting the tlr9-mediated inflammation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Modified Viral Genome
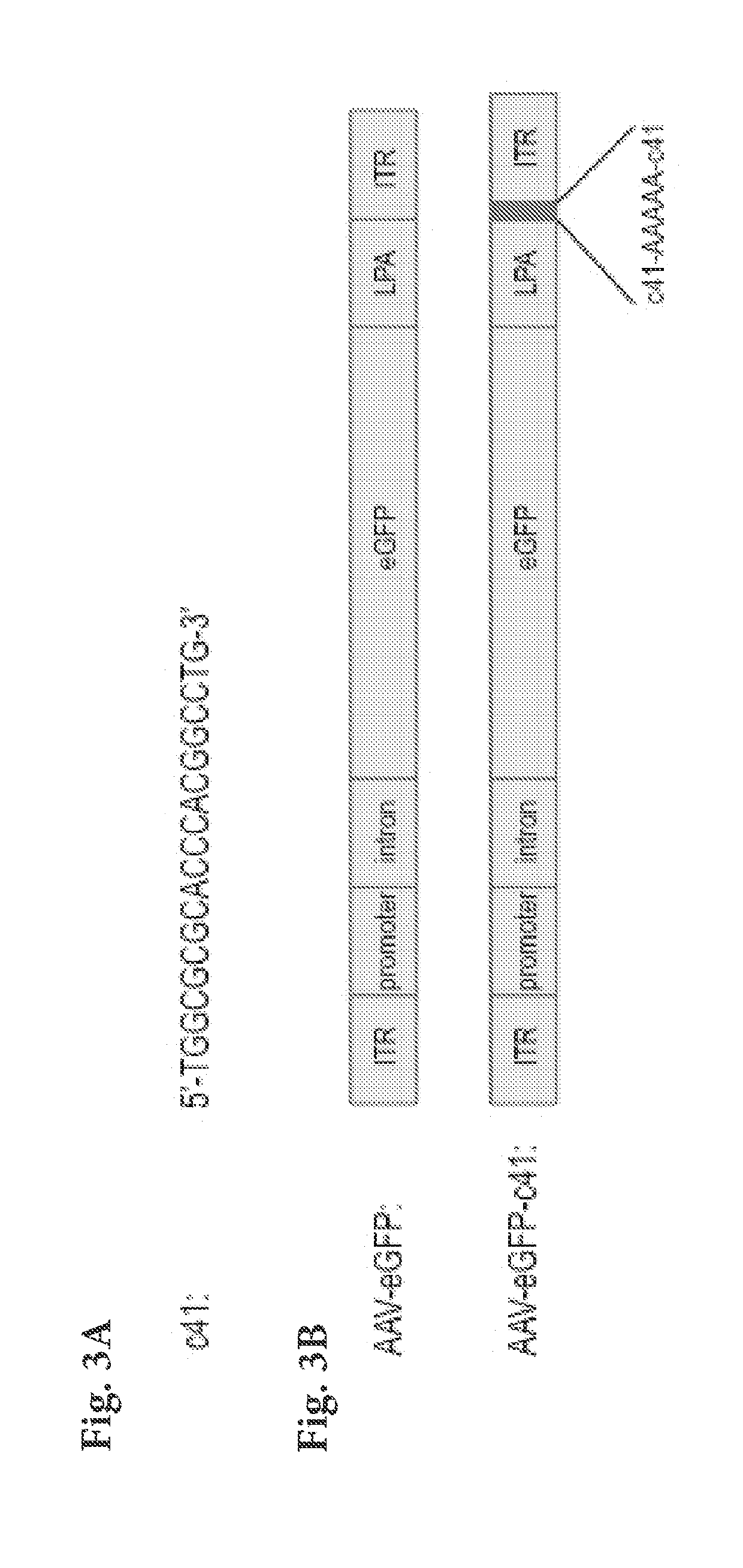
[0111]To engineer an AAV vector that has the ability to specifically evade TLR9 activation in immune cells, we inserted two copies of c41 separated by a 5-nucleotide-long spacer (AAAAA; SEQ ID NO: 8) into the 3′ untranslated region of AAV vector encoding enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) (FIG. 3B). Subsequently, we produced wild-type AAV-eGFP virus and AAV-eGFP-c41 virus (harboring two c41 insertions). Infectious titers of both viruses were comparable (˜109 infectious units / ml, as determined by titering on HeLa cells), suggesting that addition of c41 into the viral genome did not hamper viral packaging and infectivity, an important consideration for viral vectors that have to be mass-produced for gene therapy.
example 2
Modified Viral Genome Reduces NF-kB Activation
[0112]To measure the inflammatory response, we used HEK293 cells stably expressing TLR9 (HEK293 TLR9 cells), which senses AAV DNA genomes, and also expressing alkaline phosphatase under the transcriptional control of NF-kB. When NF-kB is activated, which indicates inflammation, alkaline phosphatase is secreted into the media and acts on a provided substrate, leading to a change in color of the media that can be measured on a plate reader. We mock-infected HEK293 TLR9 cells or infected them with either AAV-eGFP or AAV-eGFP-c41. In agreement with the literature, AAV-eGFP infection induced a small but statistically significant increase in NF-kB activity (FIG. 4). In contrast, AAV-eGFP-c41 infection was not significantly different compared to mock-infected cells, indicating that the virus was able to evade eliciting an inflammatory response.
example 3
Modified Viral Genome Transduced More Cells and Expresses More Transgene
[0113]We analyzed the above three conditions (described in FIG. 4) for eGFP expression using flow cytometry. We found that AAV-eGFP-c41 transduced more cells than AAV-eGFP (52.7% GFP+ compared to 34.6% GFP+) (FIG. 5). In addition, GFP+ cells from AAV-eGFP-c41 infection expressed ˜twice as much eGFP as GFP+ cells from AAV-eGFP infection (mean fluorescence intensity [MFI] of 5335 compared to 2749).
[0114]In summary, we engineered an AAV vector to evade TLR9-mediated inflammation by incorporating an inhibitory oligonucleotide in the viral genome.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com