Methods for increasing the refractive index of high-index nanoimprint lithography films
a nanoimprint and refractive index technology, applied in nanoinformatics, photomechanical equipment, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high shrinkage of imprint features and cost effectiveness, and achieve high refractive index, high hardness, yield strength and/or etch resistance, and reduce the effect of etch ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
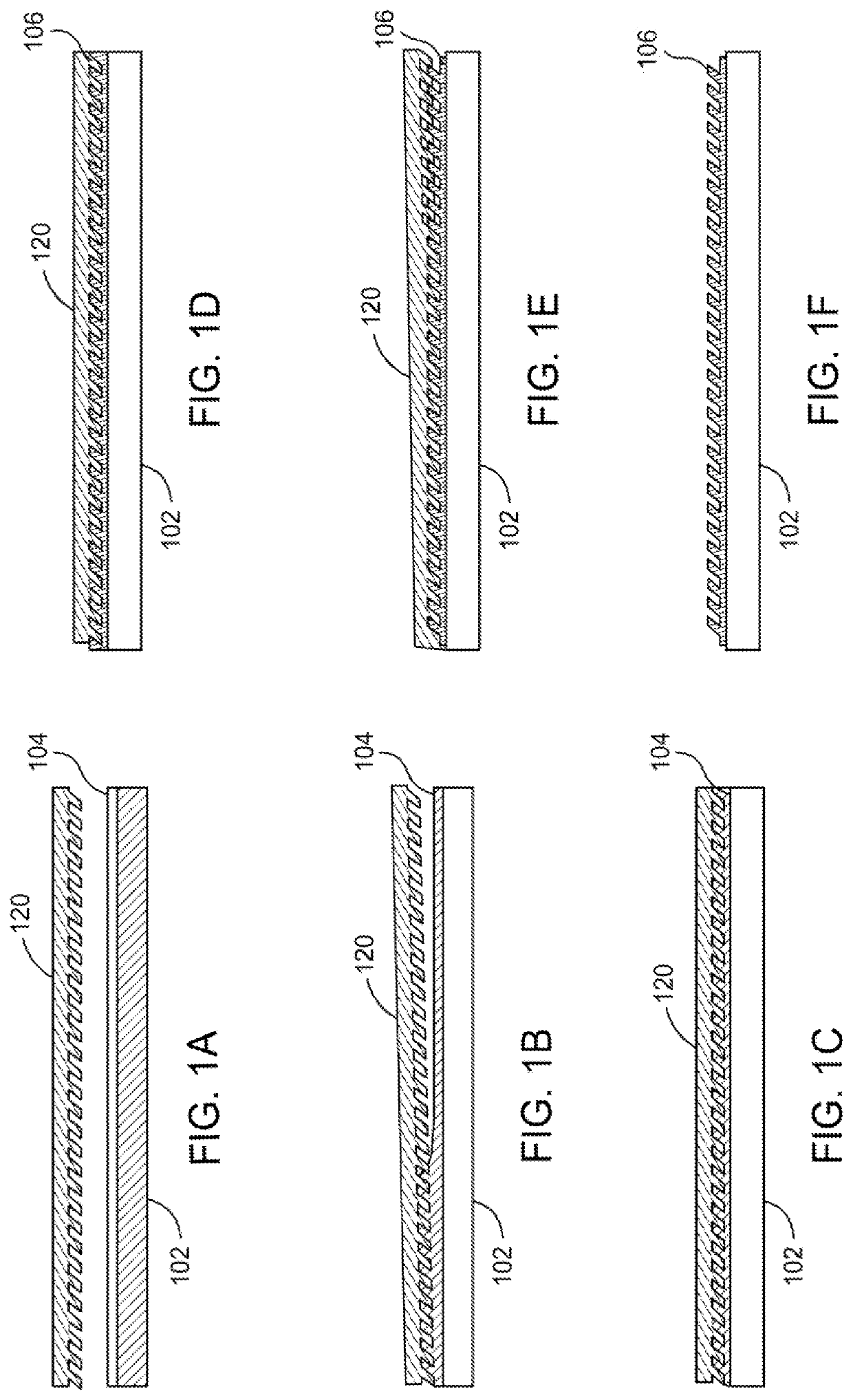
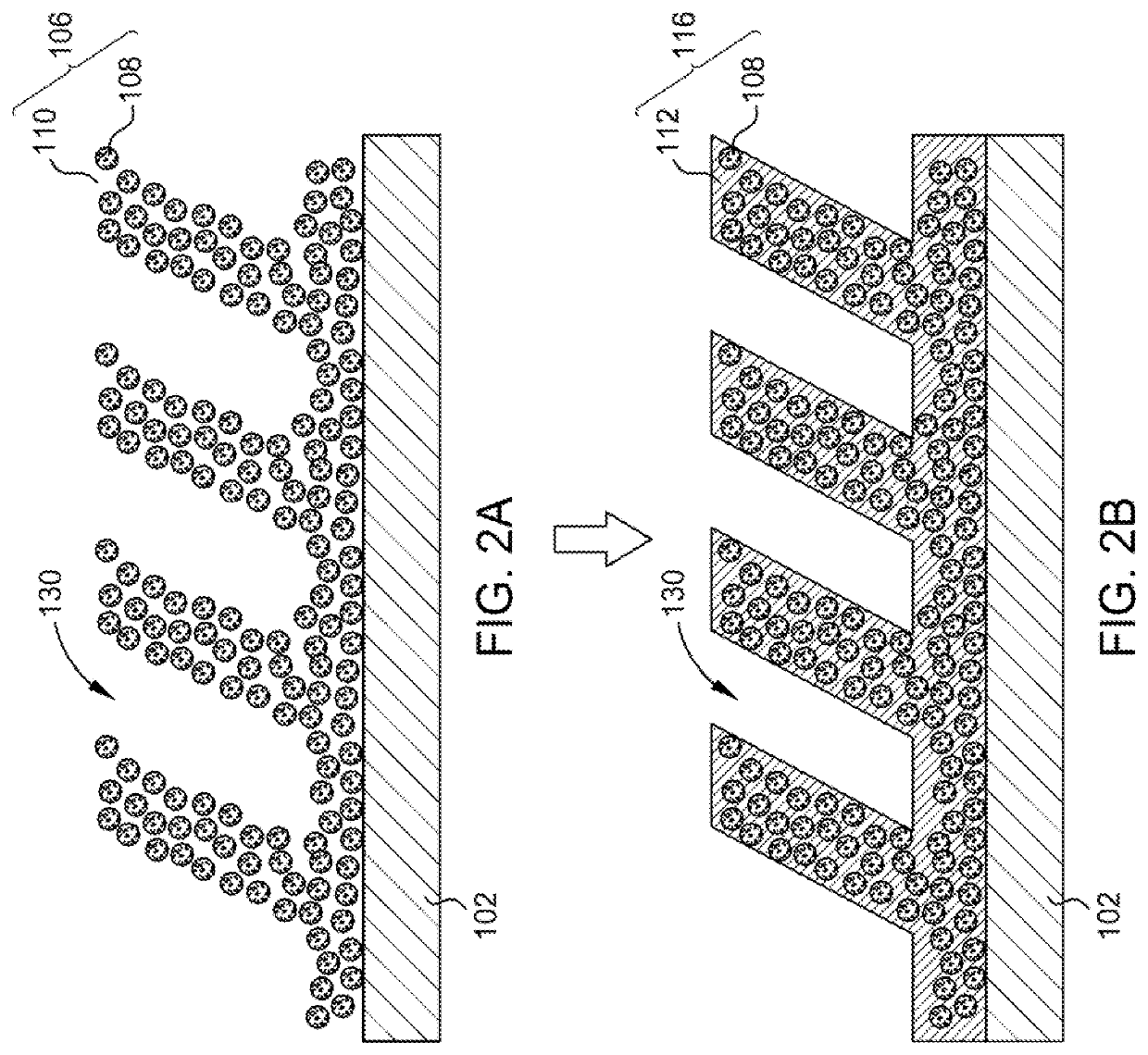
lass="d_n">[0015]In one or more embodiments, a method of forming a nanoimprint film includes positioning a substrate containing a base or porous nanoimprint film within a processing chamber, where the porous nanoimprint film contains nanoparticles and voids between the nanoparticles, and the porous nanoimprint film has a refractive index of less than 2. The voids, such as the spaces disposed between the nanoparticles, can contain ambient air, residual organic materials (e.g., one or more hydrocarbons and / or other organic compounds), particulates, and / or one or more other contaminants which can have a relatively low refractive index, such as from about 1, about 1.2, or about 1.3 to about 1.4 or about 1.5.
[0016]The method also includes depositing one or more metal oxides on the porous nanoimprint film and within at least a portion of the voids to produce an optically densified nanoimprint film during an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The voids can be at least partially filled,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com