Disproportionation/transalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
A hydrogen form of mordenite with a mole ratio of silica / alumina of 90 was molded, together with gamma alumina as a binder, into a cylindrical shape 2 mm in diameter and 10 mm in length, so as to give a carrier in which the mordenite amounted to 50 wt %. After being dried at 150° C. for 10 hours, the carrier was calcined at 500° C. for 3 hours. Using an aqueous SnCl2 solution, 0.5 weight parts of tin were impregnated in 100 weight parts of the carrier, which was then dried at 150° C. for 10 hours and calcined at 500° C. for 3 hours. This tin-impregnated carrier was treated with an aqueous H2PtCl6 solution such that 0.05 weight parts of platinum were impregnated in 100 weight parts of the mordenite and binder. The resulting carrier was subjected to drying at 150° C. for 10 hours and then to calcination at 500° C. for 3 hours to allow a catalyst.
For disproportionation / transalkylation testing, 2.0 g of the catalyst were charged in a fixed-bed reactor and subjected to reduction at 400° ...
example ii
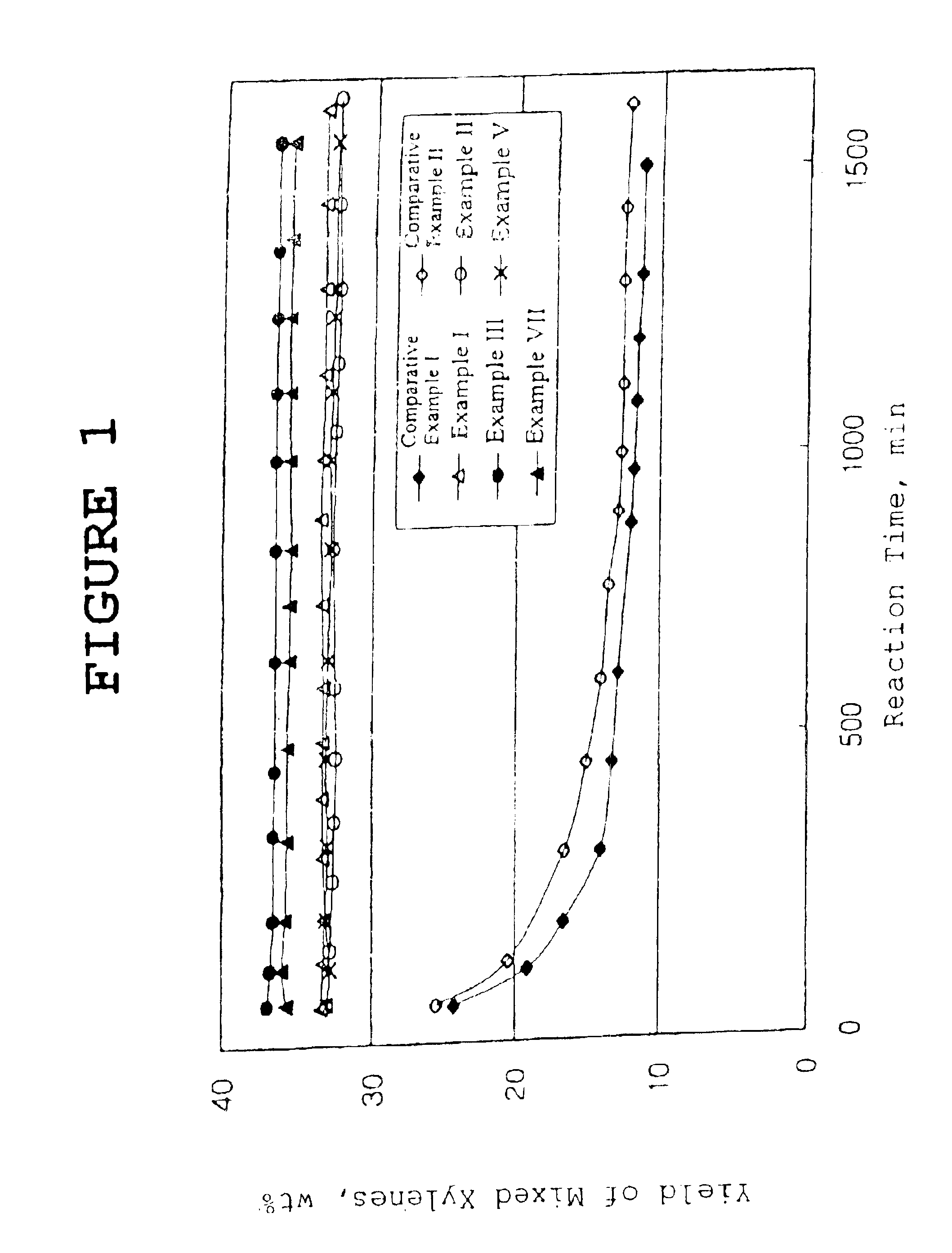
A catalyst was prepared in the same manner as that of Example I, except for using a hydrogen form of beta zeolite with a mole ratio of silica / alumina of 25. The catalyst was tested for disproportionation / transalkylation as in Example I, but using the reactant mixture indicated in Table 2. The results are given as shown in Table 2 and FIG. 1. As apparent from the data, this catalyst showed similar catalytic performance to that of the catalyst of Example I.
example iii
A hydrogen form of mordenite and a hydrogen form of ZSM-5 which had mole ratios of silica / alumina of 90 and 80, respectively, were molded, together with gamma alumina as a binder, into a cylindrical shape 2 mm in diameter and 10 mm in length, so as to give a carrier in which the mordenite and the ZSM-5 amounted to 40 wt % and 15 wt %, respectively. After being dried at 150° C. for 10 hours, the carrier was calcined at 500° C. for 3 hours. Using an aqueous SnCl2 solution, 0.5 weight parts of tin were impregnated in 100 weight parts of the carrier, which was then dried at 150° C. for 10 hours and calcined at 500° C. for 3 hours. This tin-impregnated carrier was treated with an aqueous H2PtCl solution such that 0.05 weight parts of platinum were impregnated in 100 weight parts of the mordenite, ZSM-5 and binder. The resulting carrier was subjected to drying at 150° C. for 10 hours and then to calcination at 500° C. for 3 hours to allow a catalyst.
The catalyst was tested for disproporti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com