Method for the preparation of lactic acid and calcium sulphate dihydrate
A technology of calcium sulfate dihydrate and calcium sulfate hemihydrate, which is applied in the direction of carboxylate preparation, carboxylate preparation, separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, etc., and can solve problems such as unsuitable dihydrate crystal growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
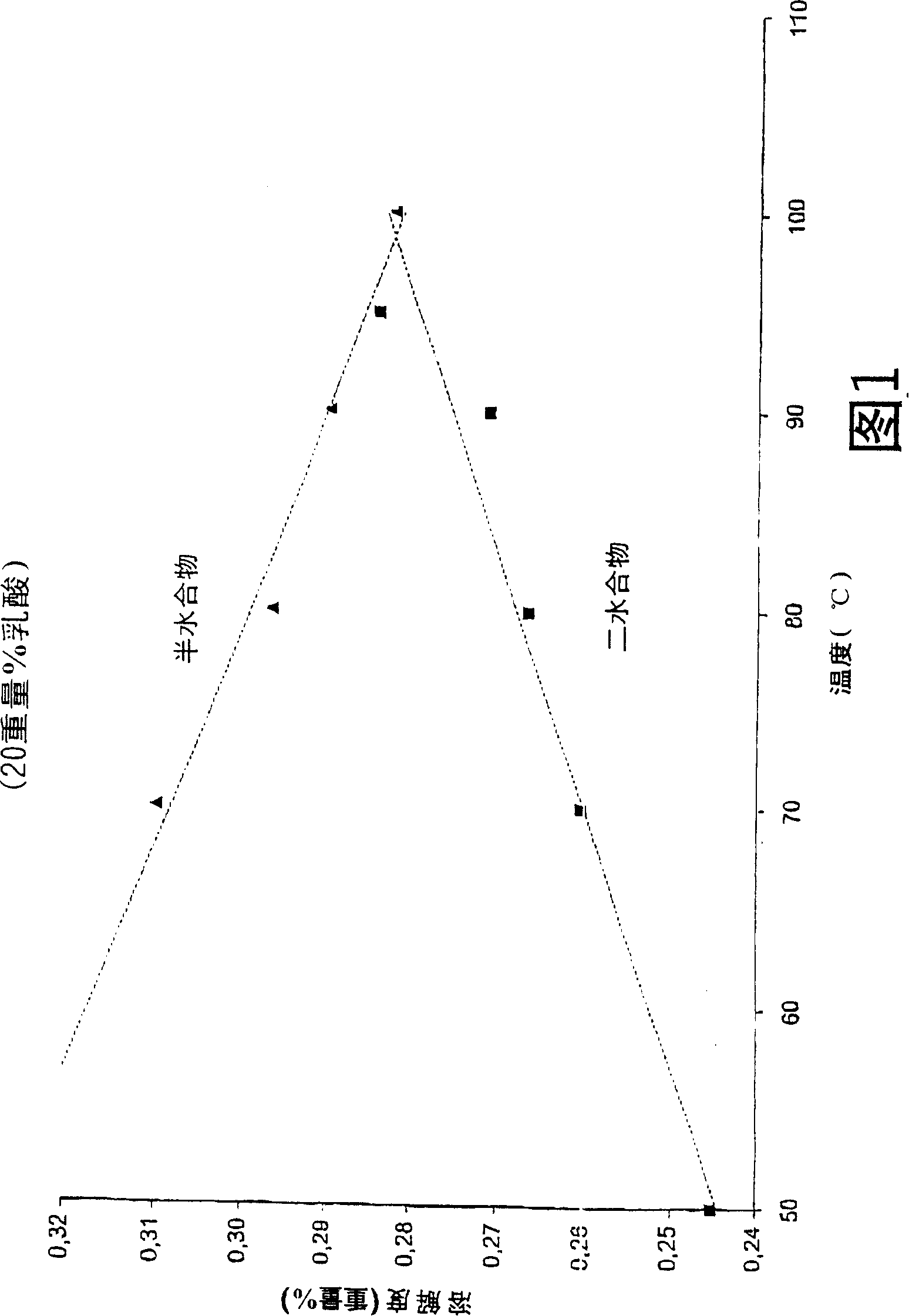
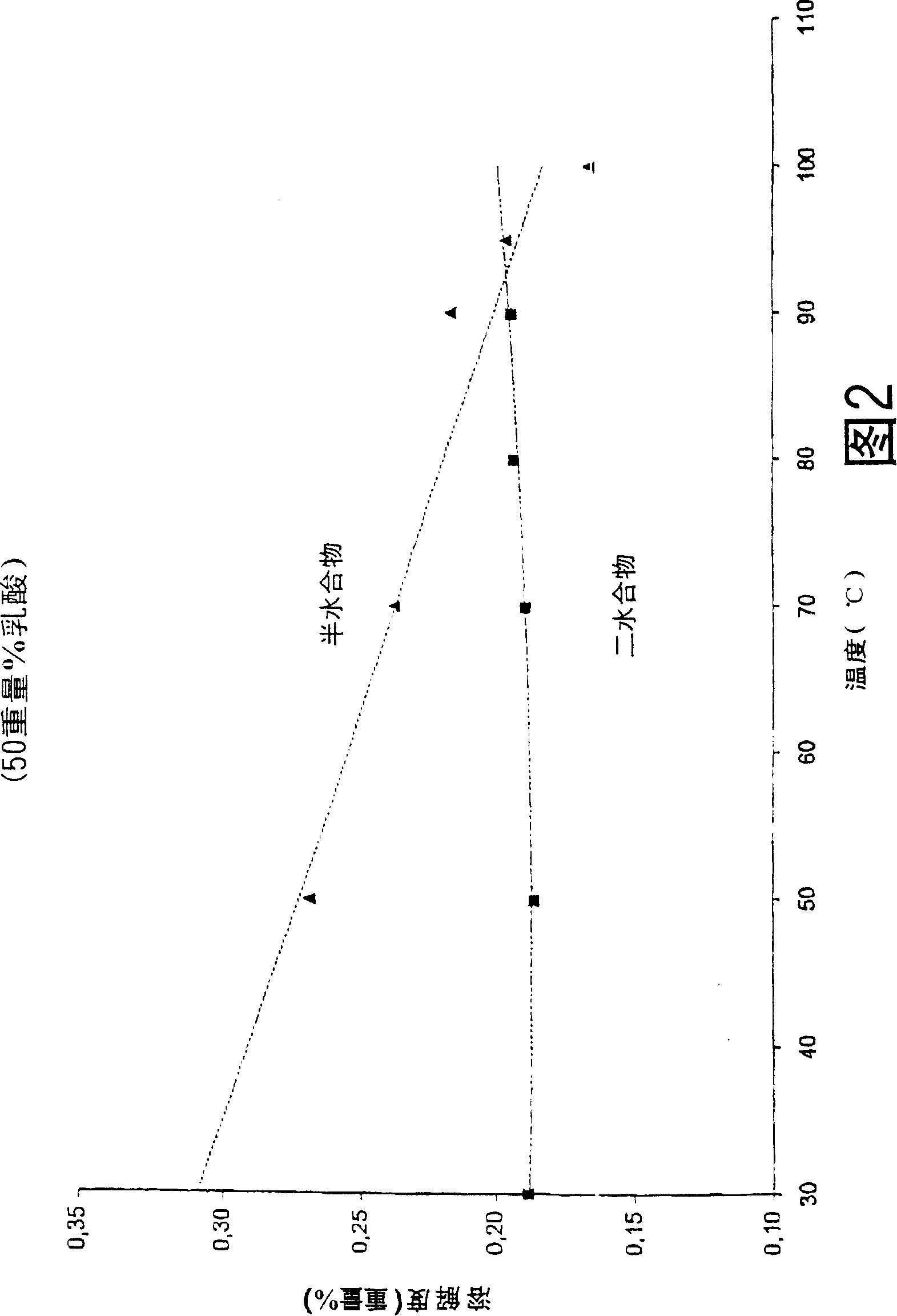
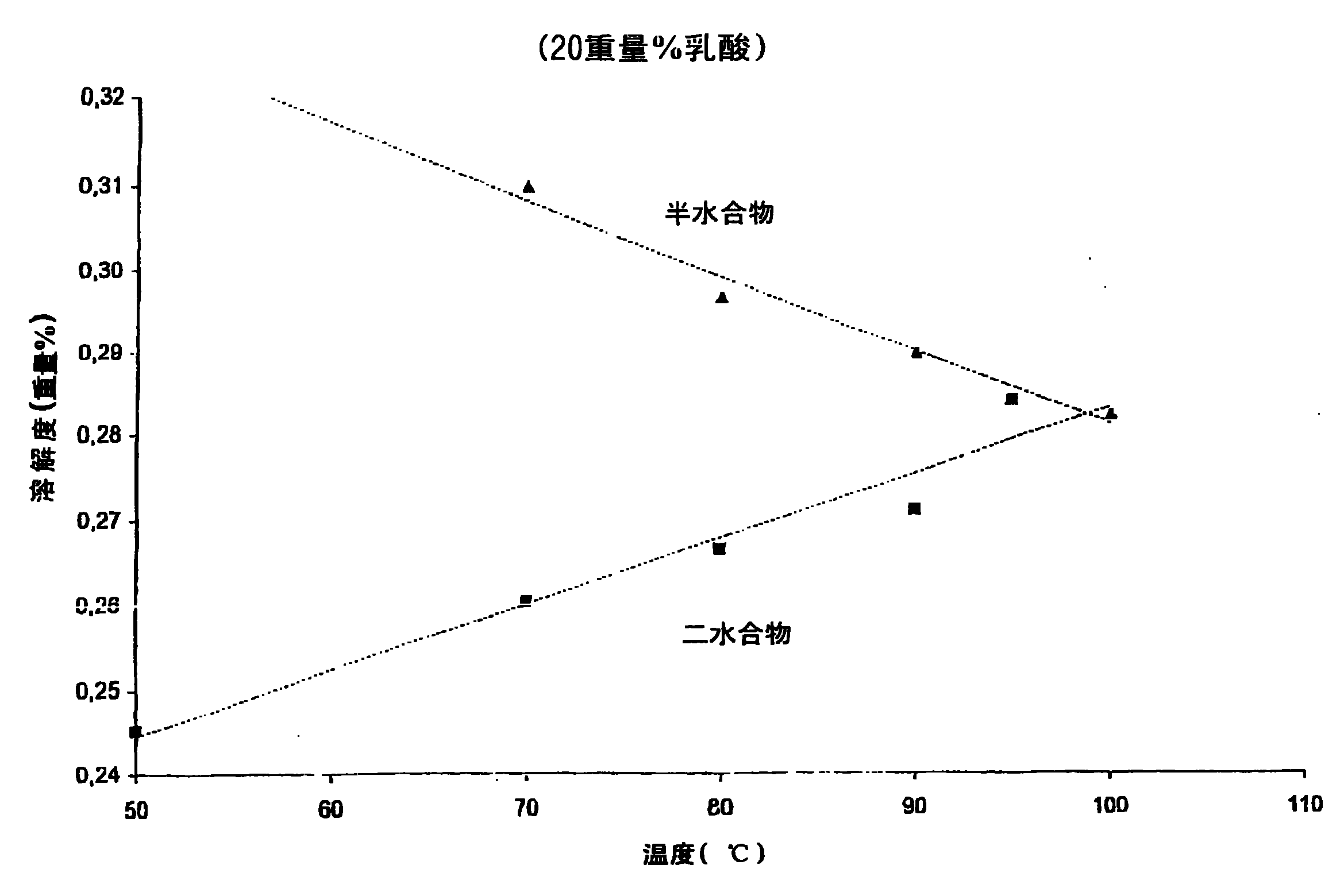
[0021] The solubility of calcium sulfate dihydrate and calcium sulfate hemihydrate was determined at each concentration as a function of temperature. A lactic acid stock solution was prepared by diluting pharmaceutical quality 90% lactic acid aqueous solution (PH90 batch number 200200003) to 20 wt% and 50 wt% respectively with water, and heating at 80° C. for 4 days. 50 ml samples of these solutions were heated at various temperatures for 30 minutes, after which 10 g of calcium sulfate dihydrate or calcium sulfate hemihydrate were added to form a suspension. Samples of 20 ml of this suspension were taken after 15 and 20 minutes and filtered through a G4 glass filter. Analyze mother liquor to determine Ca 2+ content. The filtered calcium sulfate crystals were washed twice with 20 ml of acetone and twice with 10 ml of acetone, and finally dried at 30° C. to remove residual acetone. The water of crystallization content was determined by drying the crystals at 160°C for at leas...
Embodiment 2
[0026]In a 3-liter volume double-wall reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer (stirring speed 600rpm), continuously acidify an aqueous solution containing 34.01% by weight of calcium lactate ( The solution temperature is 95°C; the flow rate is 30.57ml / min), forming more than 95.7% by weight of CaSO 4 0.5H 2 O. The reaction was controlled by measuring the conductivity (min 10.0, max 14.5 mS / cm). The residence time in the reaction vessel was about 75 minutes. The reaction mixture was then fed successively into two 5-liter double-walled crystallization vessels equipped with stirrers (crystallization vessel 1: T=80° C., stirring speed 400 rpm; crystallization vessel 2: T=80° C., stirring speed 400 rpm). The results obtained during the experiments are given in Table 2 below. Table 3 presents the analysis results of the dihydrate crystals obtained after the second step and the aqueous lactic acid solution.
[0027] Table 2 (crystallization vessel 2)
[0028] time (hou...
Embodiment 3
[0032] In a 3-liter volume double-wall reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer (stirring speed 800rpm), continuously acidify an aqueous solution containing 50% by weight of calcium lactate ( Solution temperature is 83-85°C; flow rate 28ml / min), forming more than 97.5% by weight of CaSO 4 0.5H 2 O. The reaction was controlled by measuring the conductivity (min 5.4, max 5.80 mS / cm). The residence time in the reaction vessel was about 62 minutes. The reaction mixture was then fed successively into two 5-liter double-walled crystallization vessels equipped with stirrers (crystallization vessel 1: T=62° C., stirring speed 300 rpm; crystallization vessel 2: T=60° C., stirring speed 300 rpm). The results obtained during the experiment are given in Table 4 below. Table 5 shows the analysis results of the dihydrate crystals obtained after the second crystallization and the aqueous lactic acid solution.
[0033] Table 4 (crystallization vessel 2)
[0034] time (hours)
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com