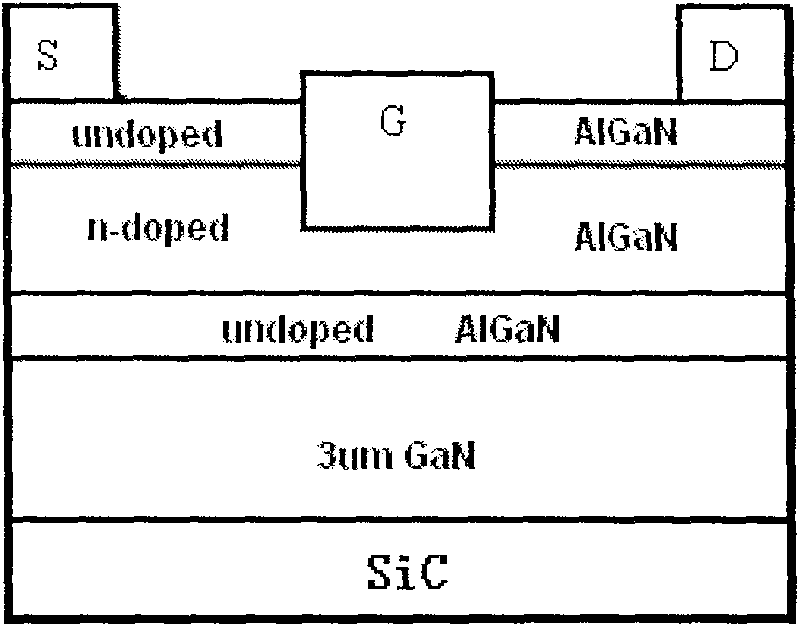
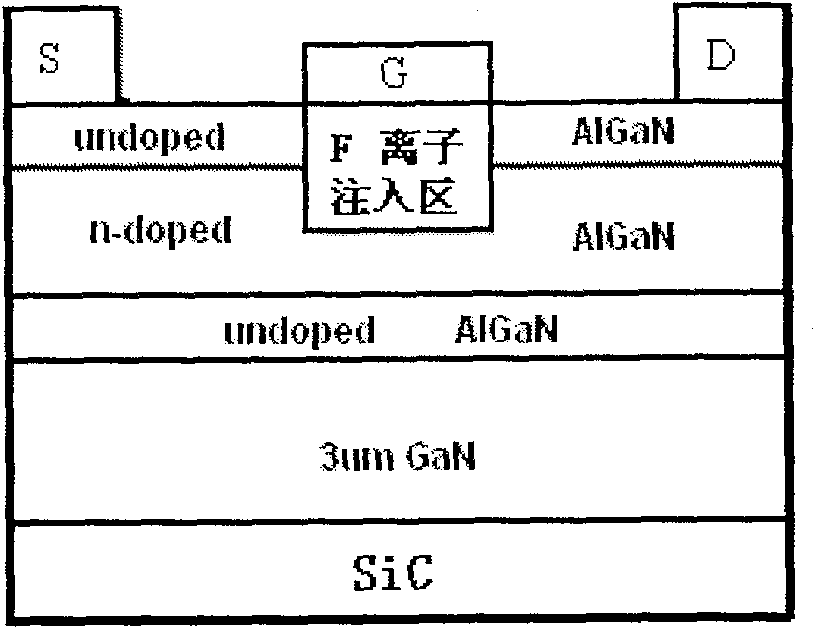
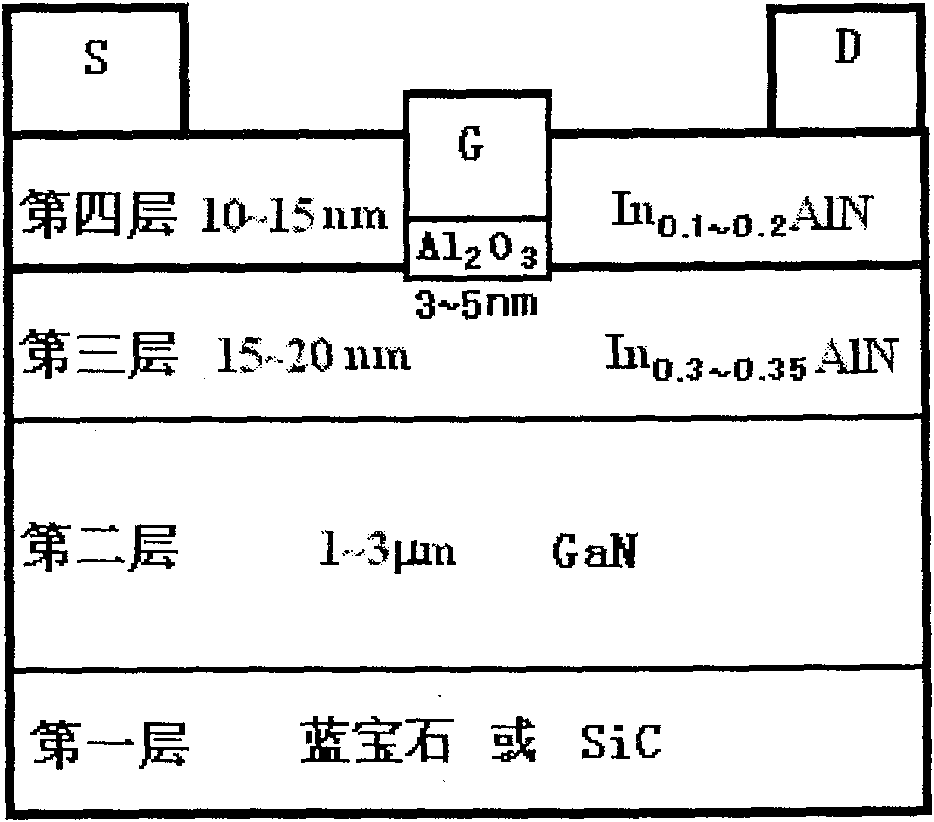
InA1N/GaN heterojunction enhancement type high electron mobility transistor structure and production method thereof
A high electron mobility, enhanced technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems of enhanced device injection damage, depletion effect stability to be verified, etc., to achieve increased operating voltage range, high forward threshold voltage, reduced Effect of Small Gate Leakage Current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] 1. Epitaxial growth of heterojunction materials
[0040] In the first step, a GaN buffer layer is grown.
[0041] Use single crystal sapphire as the substrate material to grow the GaN buffer layer in the (0001) direction, that is, NH at 950°C 3 and H 2 The sapphire substrate was pretreated at high temperature for 10 minutes in the mixed gas, and then a 30nm low-temperature nucleation layer was grown at 520°C, and then the temperature was raised to 920°C to grow a 1 μm thick GaN buffer layer.
[0042] In the second step, the first InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the GaN layer.
[0043] After the growth of the 1 μm thick GaN buffer layer is completed, the temperature is set to 800° C., and the first InAlN layer with an In composition of 30% is continuously grown, and the thickness of the first InAlN layer is 20 nm.
[0044] In the third step, a second InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the first InAlN layer.
[0045] After the epitaxial growth on the first InAlN ...
example 2
[0061] 1. Epitaxial growth of heterojunction materials
[0062] In the first step, a GaN buffer layer is grown.
[0063] The GaN buffer layer was grown on the Si surface of the 4H SiC substrate, that is, the NH 3 and H 2 The sapphire substrate was pretreated at high temperature for 10 minutes in the mixed gas, and then a 30nm low-temperature nucleation layer was grown at 520°C, and then the temperature was raised to 920°C to grow a 2μm thick GaN buffer layer.
[0064] In the second step, the first InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the GaN layer.
[0065] After the growth of the 2 μm thick GaN buffer layer is completed, the temperature is set to 800° C., and the first InAlN layer with an In composition of 33% is grown continuously, and the thickness of the first InAlN layer is 18 nm.
[0066] In the third step, a second InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the first InAlN layer.
[0067] After the epitaxial growth on the first InAlN layer is completed, the temperature is s...
example 3
[0083] 1. Epitaxial growth of heterojunction materials
[0084] In the first step, a GaN buffer layer is grown.
[0085] The GaN buffer layer was grown on the Si surface of the 4H SiC substrate, that is, the NH 3 and H 2 The sapphire substrate was pretreated at high temperature for 10 minutes in the mixed gas, and then a 30nm low-temperature nucleation layer was grown at 520°C, and then a 3μm thick GaN buffer layer was grown at 920°C.
[0086] In the second step, the first InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the GaN layer.
[0087] After the growth of the 3 μm thick GaN buffer layer is completed, the temperature is set to 800° C., and the first InAlN layer with an In composition of 35% is grown continuously, and the thickness of the first InAlN layer is 15 nm.
[0088] In the third step, a second InAlN layer is epitaxially grown on the first InAlN layer.
[0089] After the epitaxial growth on the first InAlN layer is completed, the temperature is set to 800° C., and a seco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com