Intravenous medicine carrier material and its prepn process
A carrier material, intravenous drug technology, applied in the direction of non-active components of polymer compounds, etc., can solve problems such as limited application scope, and achieve the effects of easy to master, standardized equipment, and widely available sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] The intravenous drug carrier material of this embodiment is made of commercially available gelatin (Wenzhou Huabao Gelatin Co., Ltd.) as the base material.
[0056] Its preparation method is:
[0057] 1) gelatin is formulated into an aqueous solution according to 3% by weight;
[0058] 2) According to the weight ratio of gelatin and proteolytic enzyme is 100:1, add neutral protease into gelatin solution, and degrade at 50° C. for 60 min;
[0059] 3) According to the weight ratio of gelatin and cross-linking agent of 100:2, the glutaraldehyde aqueous solution was added to the gelatin degradation solution, and the cross-linking reaction was carried out at 25° C. for 20 h;
[0060] 4) The cross-linking reaction product is filtered and dried at 45°C for 20 hours to form a material.
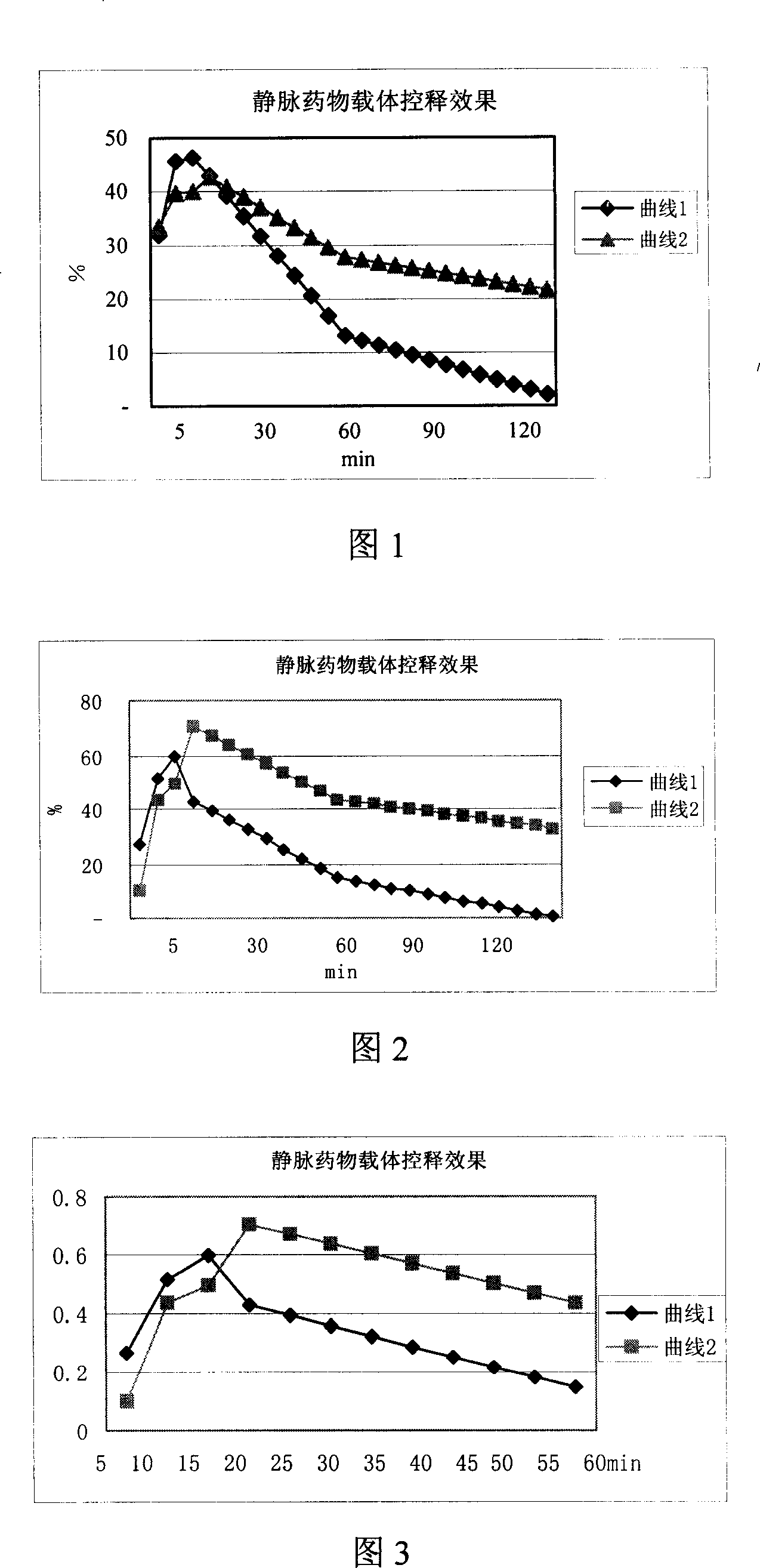
[0061] The material prepared by the above method was mixed with urokinase to prepare a solution as the injection of the test group, and the solution prepared with simple urokinase was used as...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The method and equipment are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the gelatin in this example is formulated into an aqueous solution at 5% by weight; the crosslinking agent is a carbodiimide solution, and the crosslinking reaction is carried out at 5° C. for 12 hours. The measurement results of dynamic fibrinolysis rate are shown in curve 1 and curve 2 of Fig. 2 .
[0065] Figure 2 dynamic fibrinolysis rate
[0066] Curve 1 is the dynamic fibrinolysis rate of simple urokinase.
[0067] Curve 2 is the dynamic fibrinolysis rate of carrier-urokinase complex.
[0068] It can be seen from the figure that the intravenous drug carrier material of this embodiment has a good controlled release effect.
Embodiment 3
[0070] The method and equipment are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the gelatin in this example is formulated into an aqueous solution at 5% by weight; the crosslinking agent is a carbodiimide solution, and the crosslinking reaction is carried out at 15° C. for 18 hours. The measurement results of dynamic fibrinolysis rate are shown in curve 1 and curve 2 of Fig. 3 .
[0071] Figure 3 dynamic fibrinolysis rate
[0072] Curve 1 is the dynamic fibrinolysis rate of simple urokinase.
[0073] Curve 2 is the dynamic fibrinolysis rate of carrier-urokinase complex.
[0074] It can be seen from the figure that the intravenous drug carrier material of this embodiment has a good controlled release effect.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com