Application of embedded lactobacillus in animal feed and bacteriostatic promoting production
A technology of animal feed and lactic acid bacteria, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve the problems of difficult preparation and long-term storage, high difficulty in cultivation and proliferation, poor external resistance, etc., and achieve strong anti-microbial decomposition performance and chemical stability Good performance and extended service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Embodiment 1, the preparation of embedding lactobacillus:
[0012] Sodium alginate and polyvinyl alcohol were selected as embedding agents respectively, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0013] (1) Culture of lactic acid bacteria
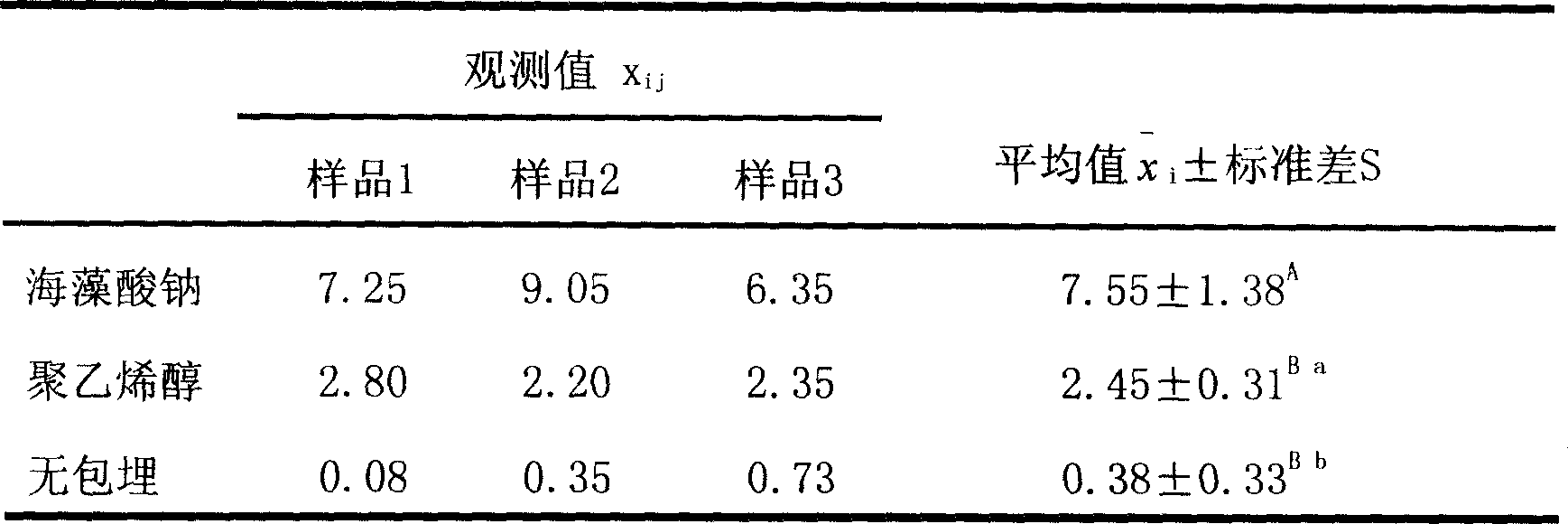
[0014] Inoculate 0.1ml of lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus casei) into 5ml of deoxygenated MRS medium, and culture it in a 37°C incubator for 18h. After the cultivation, the obtained bacterial concentration was 1.072×10 8 pieces / ml.
[0015] MRS anaerobic medium: tryptone 10g / l, beef extract 10g / l, yeast extract 5g / l, glucose 20g / l, Tween (80) 1ml / l, K 2 HPO2g / l, sodium acetate 5g / l, triammonium citrate 2g / l, MgSO 4 0.2g / l, MnSO 4 0.05g / l, autoclave at 120°C for 20min.
[0016] (2) Preparation of sodium alginate immobilized pellets
[0017] 1. Embedding material
[0018] Sodium Alginate, 1% CaCl 2 , sterile water, 50% sucrose solution
[0019] 2. Experimental method
[0020] First, use an electronic balance to accurately...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2, the feeding test selects 24 dwarf Gushi laying hens at the later stage of the egg production peak, and randomly divides them into 3 groups, with 8 chickens in each group. The control group was fed with common laying hen feed (balanced with sterile culture solution and diluent), the test I group added fresh samples of lactic acid bacteria (balanced with diluent) in the diet of the control group, and the experimental group II was fed with the diet of the control group. Add 0.1% embedding lactic acid bacteria (balanced with aseptic culture solution) in the medium, and the test period is 34 days. The results showed that the diarrhea rate of chickens in the two test groups decreased by 8.5-23.4% compared with the control group, and the egg production rate and egg weight increased by 2.0-6.7% and 4.7-7.8% respectively compared with the control group. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0050] At the end of the feeding experiment, all the participating chickens w...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, the feeding test selects 24 dwarf Gushi laying hens in the later stage of the egg production peak, and adds 0.01% embedded lactic acid bacteria in the diet of the control group except that the test II group, its grouping situation and experimental conditions are the same as in Example 2 .
[0060] The results showed that the diarrhea rate of chickens in the two test groups decreased by 8-21% compared with the control group, and the egg production rate and egg weight increased by 3-6% and 4-7% respectively compared with the control group. At the end of the feeding experiment, all the participating chickens were subjected to the Shigella Escherichia coli challenge protection experiment. The mortality rate of the chickens in the control group was 31%, while none of the chickens in the two test groups died. During the challenge experiment, the egg production rate and egg weight of chickens added with embedded lactic acid bacteria group increased by 35% and 11%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com