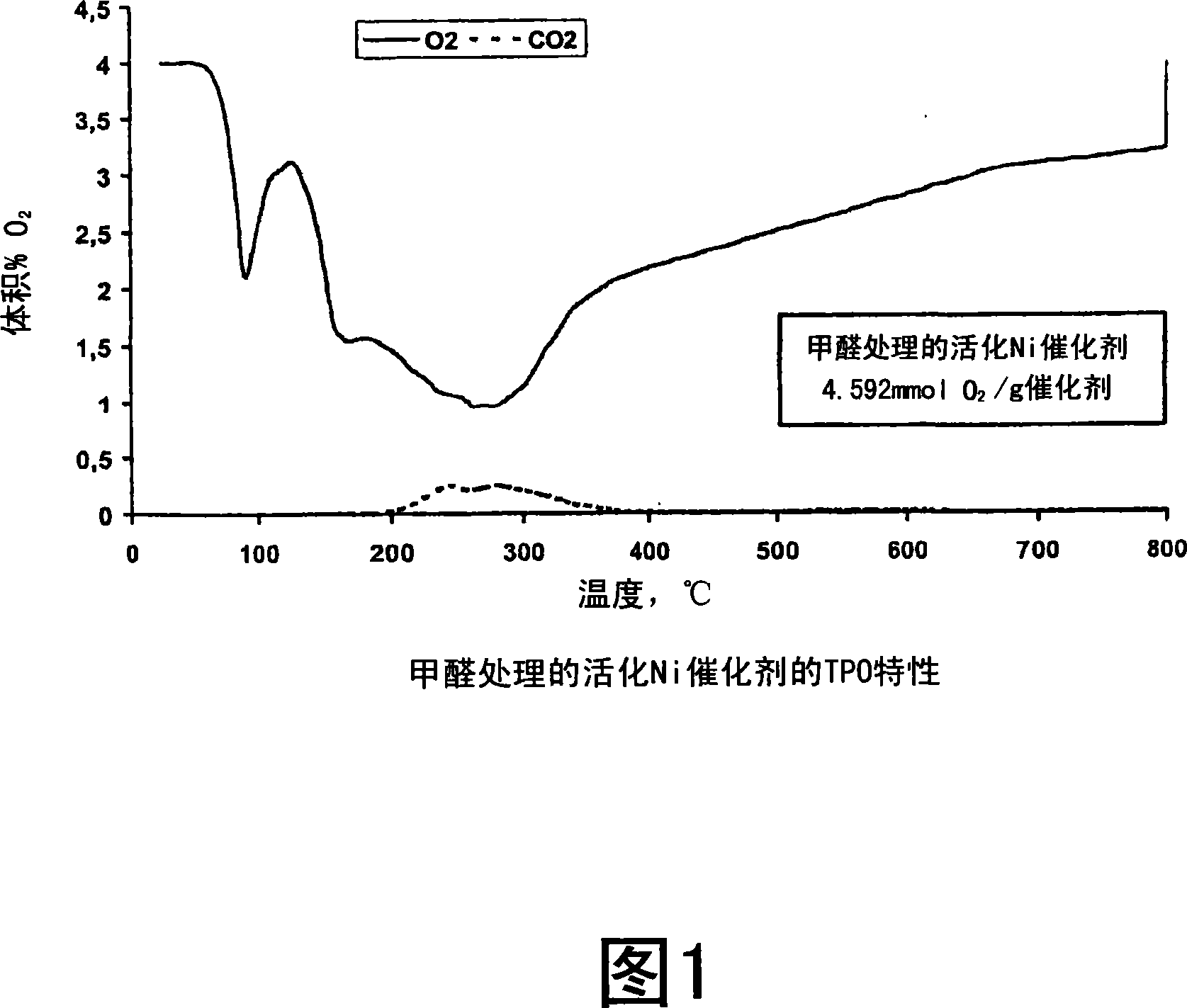
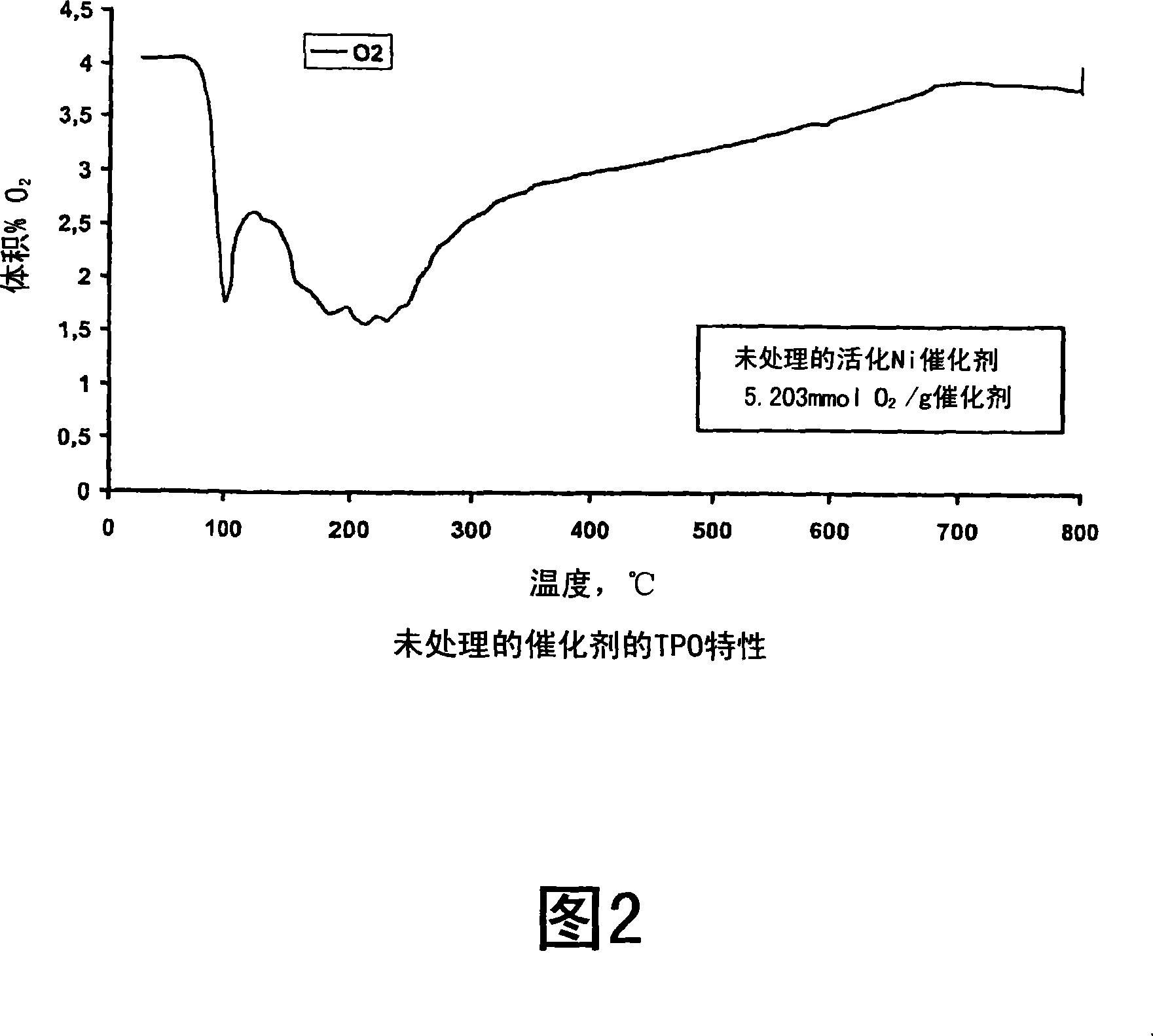
Process for modifying catalysts and the use of the catalysts
A catalyst and modification technology, which is applied in the direction of Reine catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effects and additional costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0172] Example 1: Treatment of Raney-type Ni catalyst with formaldehyde
[0173] A commercially available Raney-type nickel catalyst having an average particle size of about 53 μm was treated with different levels of formaldehyde according to the method described herein.
[0174] The desired amount of catalyst is suspended in an aqueous solution containing formaldehyde. The suspension was stirred at room temperature under air or nitrogen for 1 hour.
[0175] After the treatment, the catalyst settled, the overstanding aqueous solution was decanted, and the catalyst was washed three times with distilled water. Table 1 details the specific conditions used to prepare each catalyst.
[0176] Table 1: Formaldehyde treatment conditions of Raney-type Ni catalyst
[0177] Catalyst N °
[0178] RT = room temperature
Embodiment 2
[0179]Example 2: Treatment of Raney-type Ni catalyst containing Mo in its precursor alloy with formaldehyde
[0180] 27.7 g (dry basis) of the catalyst containing Mo in its precursor alloy was suspended in 121 ml of an aqueous solution containing formaldehyde. The suspension was stirred in air at room temperature for 1 hour. After the treatment, the catalyst settled, the upper aqueous solution was decanted, and the catalyst was washed three times with 400 ml of distilled water. Table 2 details the specific conditions used to prepare each catalyst.
[0181] Table 2: Formaldehyde treatment conditions for Raney-type Ni catalyst containing Mo in its precursor alloy
[0182] Catalyst N °
[0183] RT = room temperature
Embodiment 3
[0184] Example 3: Treatment of Raney-type Ni catalyst with sodium formate
[0185] 32.35 g (dry basis) of Raney-type Ni catalyst with an average particle size of about 53 μm was suspended in 141 ml of an aqueous solution containing sodium formate. The suspension was stirred in air at 25°C or 90°C for 1 hour. After the modification, as the catalyst settles to the bottom of the container, the treated suspension is cooled (as required), the upper aqueous solution is decanted, and the catalyst is washed three times with distilled water. Table 3 details the specific conditions used to prepare these catalysts.
[0186] Table 3: Conditions for the treatment of Raney-type Ni catalyst with sodium formate
[0187] Catalyst N °
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com