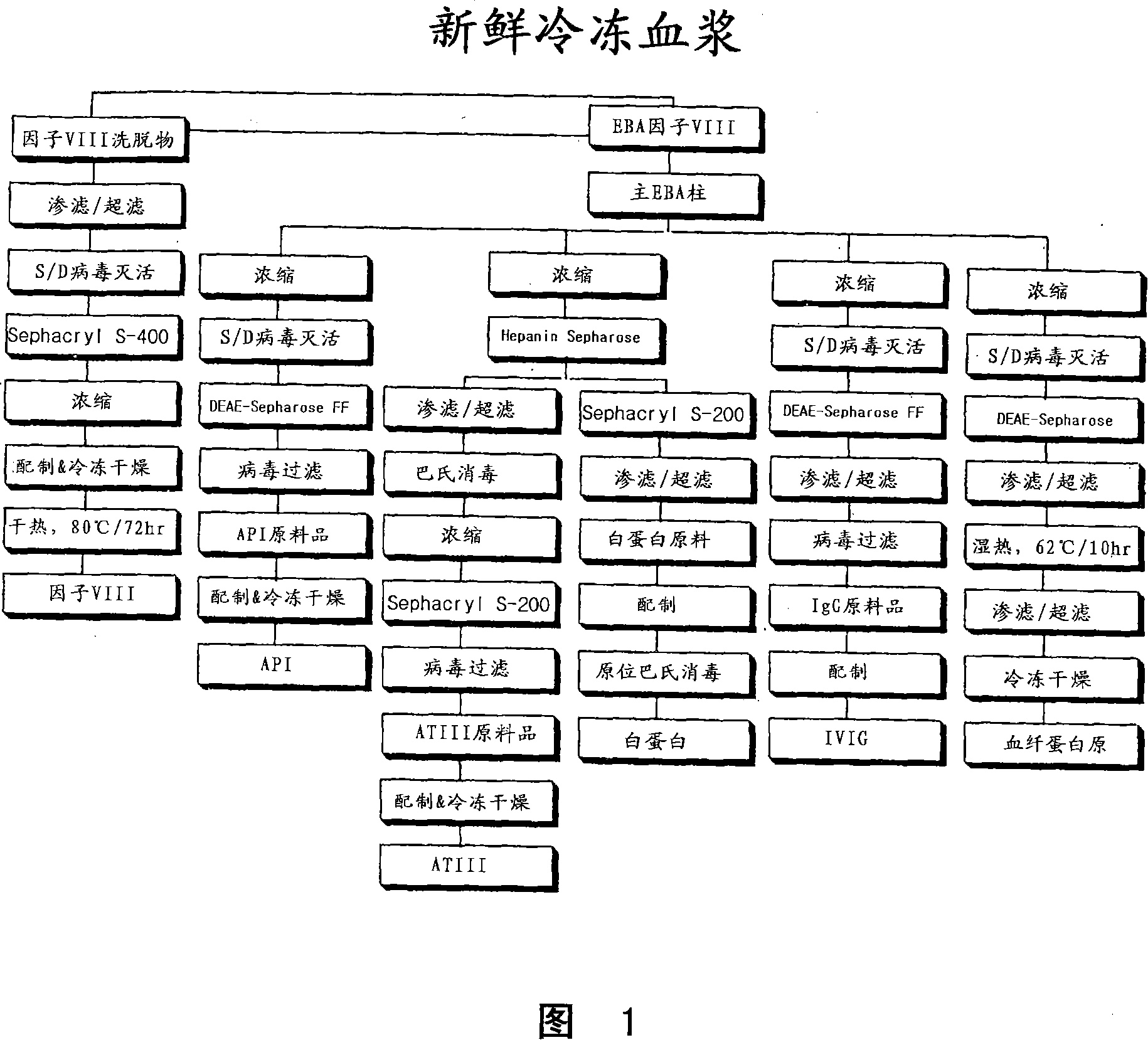
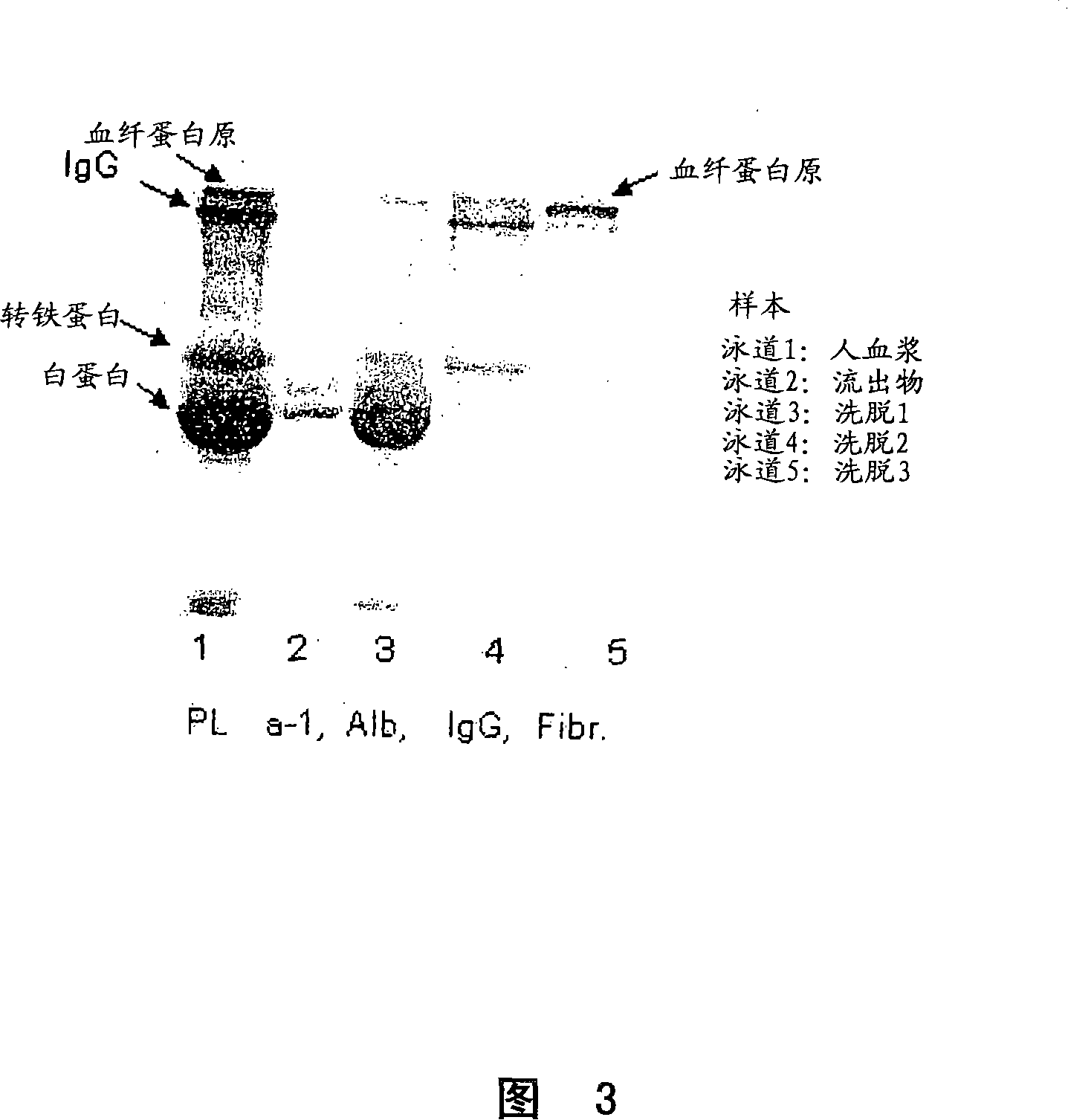
Process for protein isolation
A protein and solid separation technology, applied in the direction of animal/human protein, albumin peptide, serum albumin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] Example 1 α-1-Protease Inhibitor, Antithrombin III, Fibrinogen, Immunoglobulin Protein and Albumin Separation
[0151] step 1. Solid separation medium: Sepharose-tungsten carbide microspheres reacted with 2-mercaptonicotinic acid. The size distribution of the agarose-tungsten carbide microspheres ranges from 40-120 microns, with an average diameter of 70 microns. The density of the microspheres was 2.9 g / ml (FastLine UFC NNSDW cat. No.: CS48, UpFront Chromatography A / S, Copenhagen, Denmark.). The microspheres were loaded into an EBA column (FastLine 100, UpFront Chromatography A / S, Copenhagen, Denmark) (diameter 10 cm; bed height set at 50 cm; set bed volume = 3.926 L). Linear at 7.5 cm / min with 2.5 column volumes (9.8 L) of 40 mM sodium citrate (pH 4.5) then another 2.5 column volumes (9.8 L) of 40 mM sodium citrate (pH 5.0) at 25 °C The flow rate is balanced.
[0152] Step 2. 2 L of thawed human plasma was diluted 1:2 with 4 L of water, and 6 liters of the d...
Embodiment 2
[0158] Example 2 Alpha-1-Protease Inhibitors, Albumin, Immunoglobulin and Fibrinogen separation, which also includes washing steps
[0159] The solid separation medium used in this example is the same as that used in Example 1.
[0160] step 1. At a temperature of 21°C, an EBA column (FastLine 20, UpFront Chromatography A / S, Copenhagen Denmark) (diameter 2 cm; bed height is 25 cm; set bed volume = 78.5 mL).
[0161] Step 2. 39.3 mL of thawed human plasma was diluted 1:2 with 78.5 mL of water, and 117.8 mL of the diluted plasma solution of thawed human plasma was applied to the column. The pH of the diluted plasma solution was adjusted to pH 5.0 with 1 M HCl before use on the column, and the loading ratio was 1.5 liters of plasma solution per liter of resin.
[0162] Step 3. After loading the diluted plasma solution, the column was eluted with 3.3 column volumes (259.2 mL) of elution buffer 1 containing 10 mM sodium citrate, pH 5.0. Unbound proteins, lipids and oth...
Embodiment 3
[0168] Example 3 α-1-Protease Inhibitors, Albumin, Transferrin, Immunoglobulin and Isolation of Fibrinogen
[0169] The solid separation medium used in this example is the same as that used in Example 1.
[0170] step 1. Equilibrate an EBA column (FastLine 20, UpFront Chromatography A / S, Copenhagen Denmark) (diameter 2 cm; bed height is 25 cm; set bed volume = 78.5 mL).
[0171] Step 2. 39.3 mL of thawed human plasma was diluted 1:2 with 78.5 mL of water, and 117.8 mL of the diluted plasma solution containing thawed human plasma was applied to the column. The pH of the diluted plasma solution was adjusted to pH 5.0 with 1 M HCl before use on the column, and the loading ratio was 1.5 liters of plasma solution per liter of resin.
[0172] Step 3. After loading the diluted plasma solution, the column was eluted with elution buffer 1 containing 9.4 column volumes (738.3 mL) of demineralized water. Unbound proteins, lipids and coagulation factors including 100% alpha-1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com