Method for producing quantum dot silicate thin film for light emitting device
A silicic acid and quantum dot technology, applied in laser parts, chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology for information processing, etc., can solve the problems of thin film application limitation, inability to increase quantum dot concentration, quantum dot thermal stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0096] Preparation of Quantum Dot Films
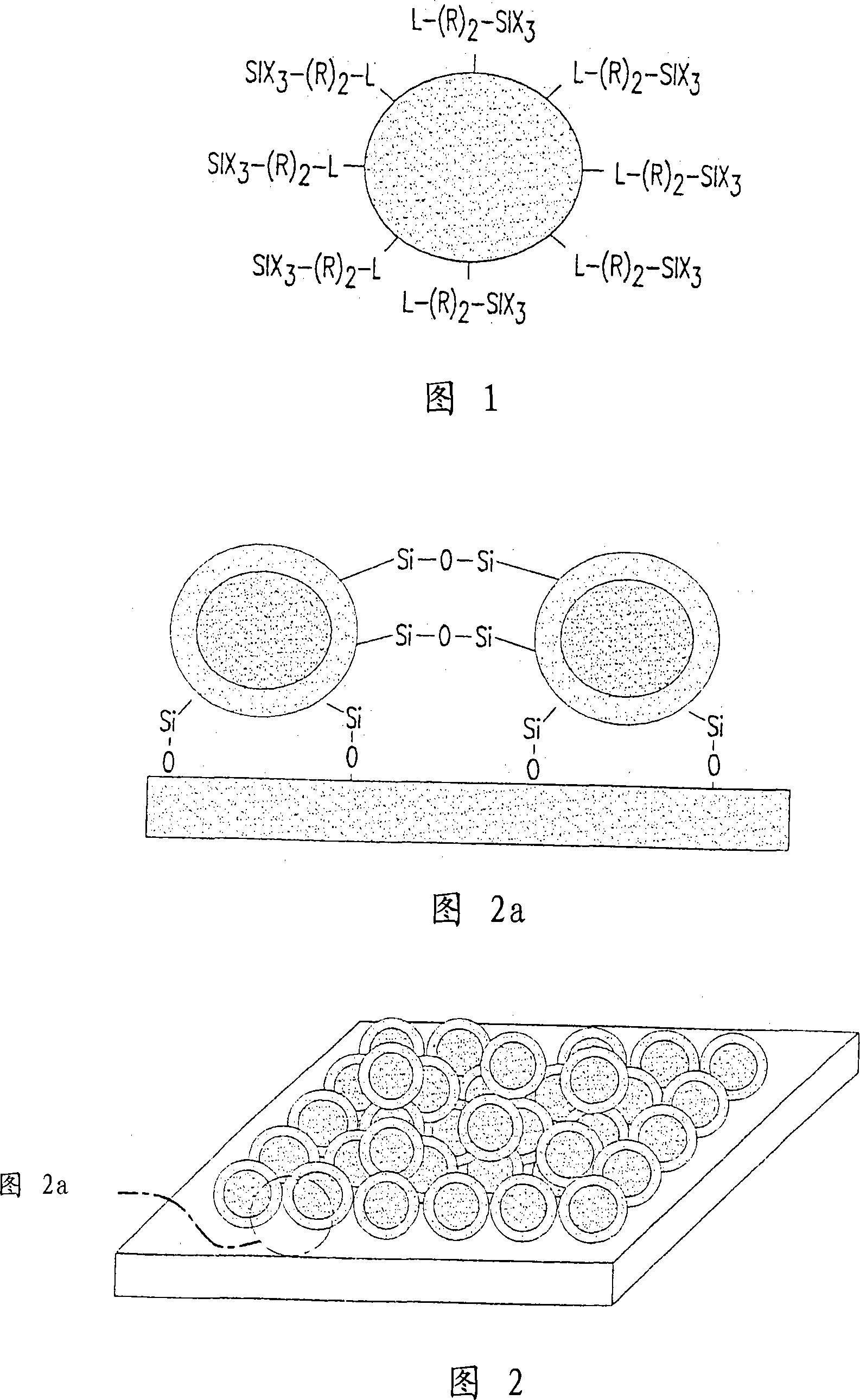
[0097] Since the reactive groups for the sol-gel operation are distributed at the ends of the quantum dots, siloxane bonds can be formed between the quantum dots through the sol-gel operation under acidic or alkaline conditions.
[0098] In order to prepare quantum dot films, quantum dots are dispersed in a solvent capable of sol-gel operation. Acid or base catalysts are added to the dispersion for sol-gel operation. When the reaction mixture has increased viscosity, it is coated onto a substrate. Finally, the coated substrate is heat-treated to prepare a quantum dot film. Alternatively, after the reactive groups for the sol-gel operation have been coordinated to the quantum dots and the quantum dots are coated onto the substrate, they can be sol-gel operated on the substrate by treatment with acid or base, And heat treatment to prepare quantum dot film.
[0099] The structure of the quantum dot film thus prepared is shown in Fig. ...
Embodiment 1
[0134] Embodiment 1: Synthesis of cadmium sulfide quantum dots emitting yellow light
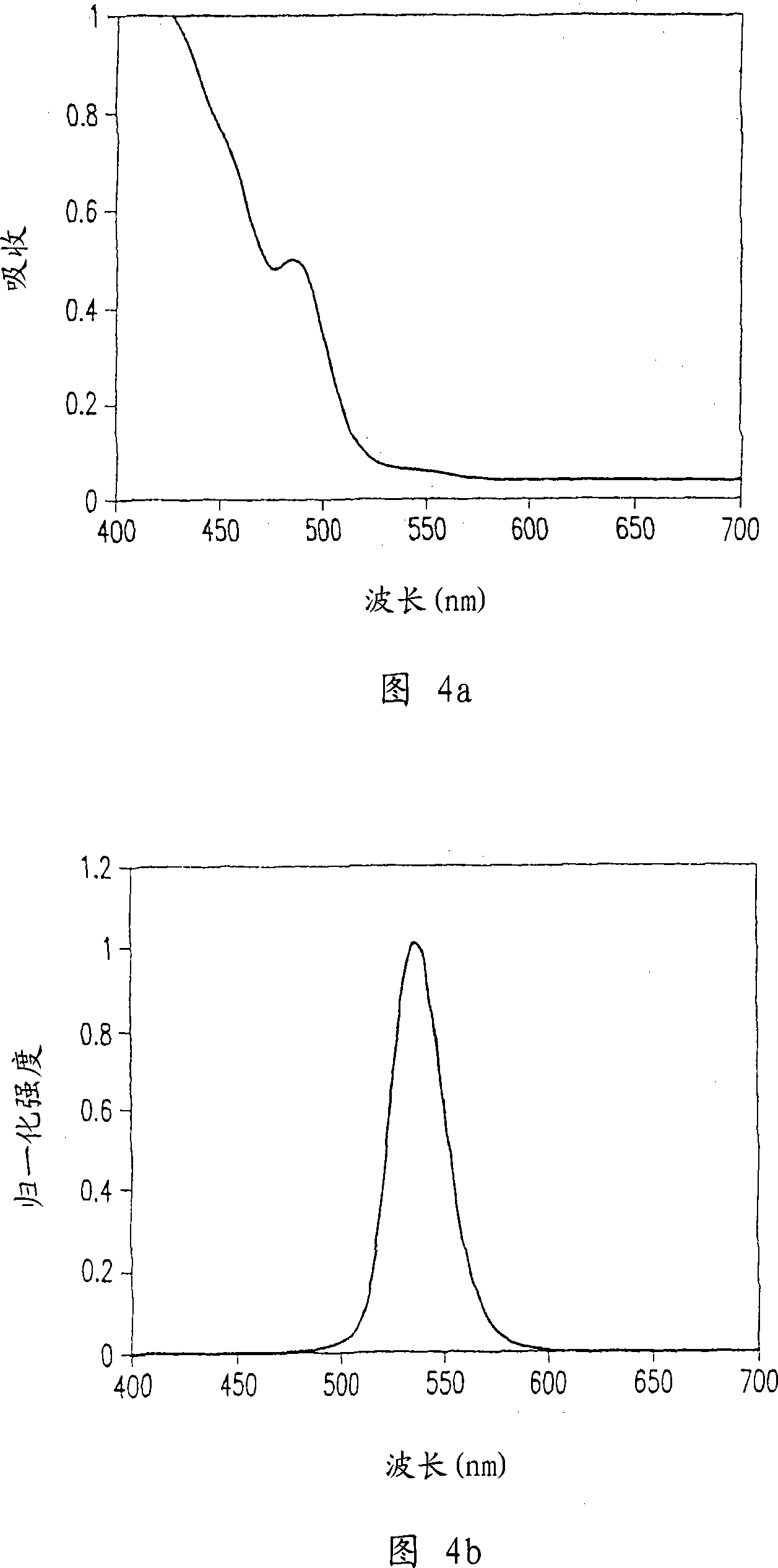
[0135] 2.5 ml of trioctylamine as a solvent was added to a 25 ml flask equipped with a reflux condenser, and the temperature of the flask was adjusted to 180°C while stirring. A solution of 50 mg of cadmium dithio diethyl carbamate in 0.9 ml of trioctylphosphine was rapidly injected into the flask. After 10 minutes, a solution of 20 mg of zinc dithiodiethylcarbamate in 0.3 ml of trioctylphosphine was slowly added dropwise. Five minutes after the addition of the zinc dithiodiethylcarbamate was complete, the temperature of the reactor was cooled and ethanol was added to quench the reaction. Quantum dots were obtained from the obtained mixture by centrifugation and dispersed in toluene. Photoluminescence spectroscopy confirmed that the compound semiconductor quantum dots emitted light at 536nm.
Embodiment 2
[0136] Embodiment 2: Synthesis of cadmium sulfide quantum dots emitting blue light
[0137] This operation was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that after the rapid injection of the solution of cadmium carbamate in trioctylphosphine, the reaction was maintained for about 7 minutes. Quantum dots were obtained from the obtained mixture by centrifugation and dispersed in toluene. Photoluminescence spectroscopy confirmed that the compound semiconductor quantum dots emitted blue light at 470nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com