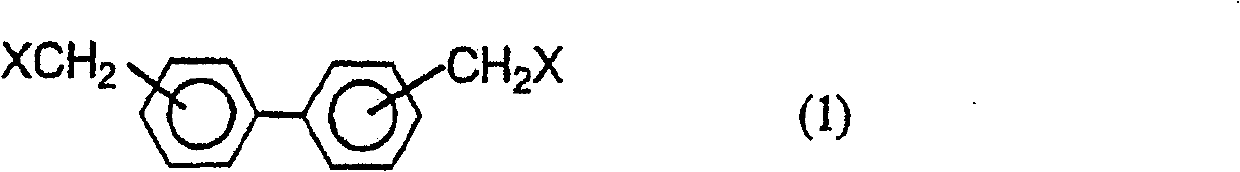Biphenylene-bridged phenol novolak resins and use thereof
A novolac resin and biphenyl technology, which is applied in the field of biphenylene cross-linked novolac resins, can solve the problems of slow curing speed, long curing time, adverse effects on productivity or production cost, etc., and achieves low water absorption. sex, improve productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
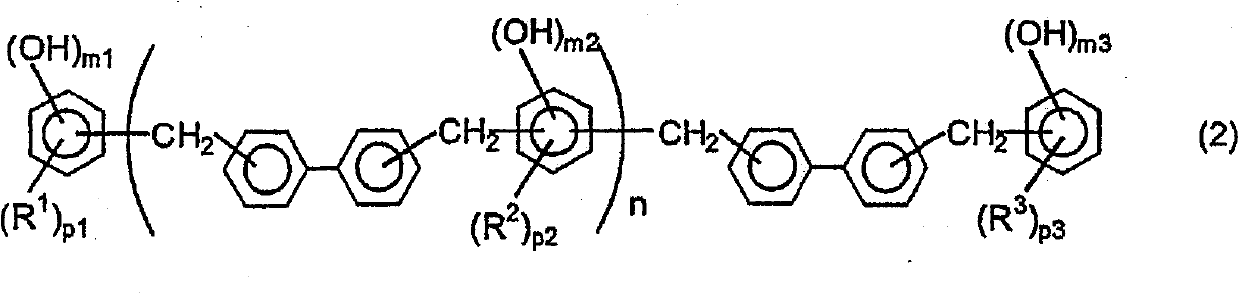
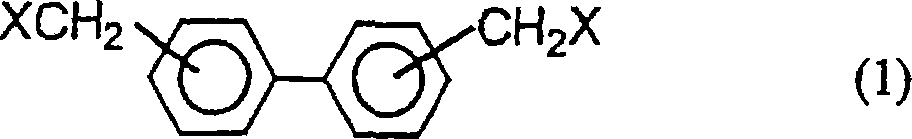
[0053] 169.2 parts (1.8 moles) of phenol, 22 parts (0.2 moles) of catechol, 112.6 parts (0.465 moles) of 4,4'-bismethoxymethylbiphenyl and 0.10 parts of 50% by weight sulfuric acid. Under nitrogen flow, the reaction was carried out at an internal temperature of 110°C to 140°C for 3 hours, then at 165°C for 3 hours, and cooled to 95°C. After cooling, 250 parts of pure water of 90° C. or higher were added and washed with water. Then, the internal temperature was raised to 160° C., and unreacted components were removed by decompression-steam treatment. A resin having a softening point of 65.3°C was obtained. As analyzed by gel permeation chromatography (hereinafter referred to as GPC), the polystyrene-equivalent number average molecular weight (Mn) was 773, and the weight average molecular weight (Mw) was 920.
Embodiment 2
[0055] 169.2 parts (1.8 moles) of phenol, 22 parts (0.2 moles) of resorcinol, 112.6 parts (0.465 moles) of 4,4'-bismethoxymethylbiphenyl and 0.10 parts of 50% by weight sulfuric acid. Under nitrogen flow, the reaction was carried out at an internal temperature of 110°C to 140°C for 3 hours, then at 165°C for 3 hours, and cooled to 95°C. After cooling, 250 parts of pure water of 90° C. or higher were thrown in and washed with water. Then, the internal temperature was raised to 160° C., and unreacted components were removed by decompression-steam treatment. A resin having a softening point of 78.8°C was obtained. By GPC analysis, the number average molecular weight (Mn) in terms of polystyrene was 858, and the weight average molecular weight (Mw) was 1116.
Embodiment 3
[0057] 169.2 parts (1.8 moles) of phenol, 22 parts (0.2 moles) of hydroquinone, 112.6 parts (0.465 moles) of 4,4'-bismethoxymethylbiphenyl and 0.10 parts of 50% by weight sulfuric acid. Under nitrogen flow, the reaction was carried out at an internal temperature of 110°C to 140°C for 3 hours, then at 165°C for 3 hours, and cooled to 95°C. After cooling, 250 parts of pure water of 90° C. or higher were thrown in and washed with water. Then, the internal temperature was raised to 160° C., and unreacted components were removed by decompression-steam treatment. A resin having a softening point of 70.6°C was obtained. By GPC analysis, the number average molecular weight (Mn) was 778 and the weight average molecular weight (Mw) was 930 in terms of polystyrene.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com