Auxiliary screening method for indica rice and japonica rice
A technology for indica rice and japonica rice, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., to achieve the effects of speeding up breeding, reducing breeding costs, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1. Discovery and verification of different expression patterns of gene LOC_0s12g07950 in indica and japonica rice
[0021] First, by mining and analyzing the chip data of indica and japonica rice at different developmental stages and different tissue positions, it was found that the gene LOC_Os12g07950 has two sets of probes in the GengChip data, and the expression patterns of these two sets of probes in indica and japonica rice are opposite , The expression level of probe P1 in indica rice is very low or even not expressed, but the expression level in japonica rice is extremely high, while the expression level of the other probe P2 in indica rice is extremely high, but the expression level in japonica rice is extremely low . According to previous research results, the main reason for the difference in gene expression may be the difference in base sequence (InDel), or the regulation of other genes. Therefore, using the method of comparative genomics, firstly, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2. Design of primers for auxiliary screening of indica and japonica rice
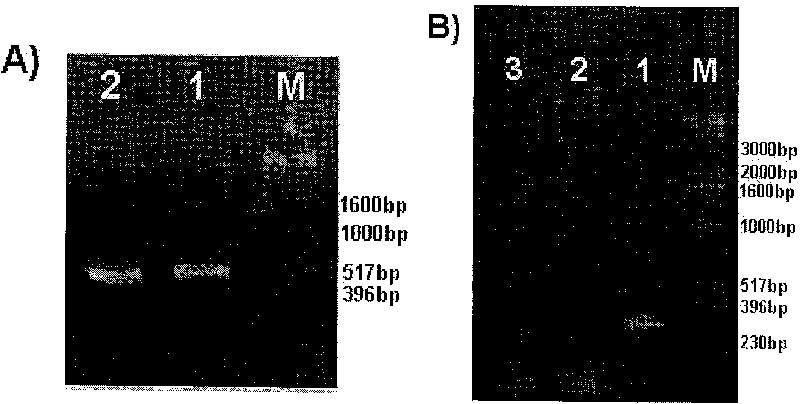
[0023] In order to further verify whether there is a genomic difference between 93-11 and Nipponbare, based on the Nipponbare sequence, primers SIR2-2 were designed in areas where there may be genomic differences between the two. One primer sequence is shown in sequence 1 in the sequence table, and the other The sequence of a primer is shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table, and the genomic DNA of Nipponbare and 93-11 were used as templates for PCR amplification verification. The PCR amplification reaction system is: 20ng rice genomic DNA template, 0.5U Taq Plus DNA polymerase, 2.0μl 10×PCR buffer (100mM Tris·HClpH9.0, 500mM KCl, 15mM Mg 2+ , 1% Triton X-100), 100μM dNTPs, forward primer 4μM, reverse primer 4μM, supplement the reaction system with DEPC water to 20μl. The PCR reaction conditions are: first 94°C for 5 minutes; then 94°C for 30sec, 58°C for 45sec, 72°C for 1min30sec, a total...
Embodiment 3
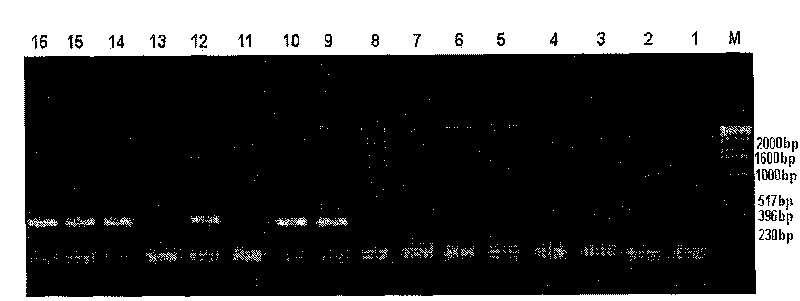
[0025] Example 3 Verification of the feasibility of using primer SIR2-3 to assist in screening of subspecies of rice indica and japonica
[0026] Rice varieties and local species (all from the National Germplasm Bank): 93-11, Xianmazuo, Zinuo, Nepa (deep rice), Guichao No. 2, Aus6538 (Bamalaia), IR24, Teqing, Nipponbare, Dwarf Dazhong, Muli (light shell japonica rice), glutinous japonica rice, Yuefu, Qiuguang, Hongguang and Yunfeng 7.
[0027] First, 8 varieties and landraces of Indica and Japonica subspecies were randomly selected using morphological indicators and related literature search, as shown in Table 1:
[0028] Table 1. Identification results of indica and japonica subspecies of 16 rice varieties and landraces
[0029] Variety name
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com