Zanamivir nasal in situ jellies with phase variation property and preparing method thereof
A zanamivir and phase transition technology, which is applied in non-active ingredients medical preparations, antiviral agents, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problem of excessive drug clearance, poor oral absorption, and oral bioavailability of only 2%, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Prepare ion-sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel, the prescription is as follows (see Table 1):
[0023] Table 1 ion-sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel prescription (wt%)
[0024]
[0025] Preparation Process:
[0026] The above ion-sensitive polymer was placed in an appropriate amount of deionized water, magnetically stirred in a water bath at 80-100°C to disperse and dissolve, and left to stand in a refrigerator at 4°C (12h) to obtain a clear solution. Dissolve the drug zanamivir and other water-soluble excipients in deionized water, mix the two solutions, adjust the pH to 6.2, and add water to the full amount.
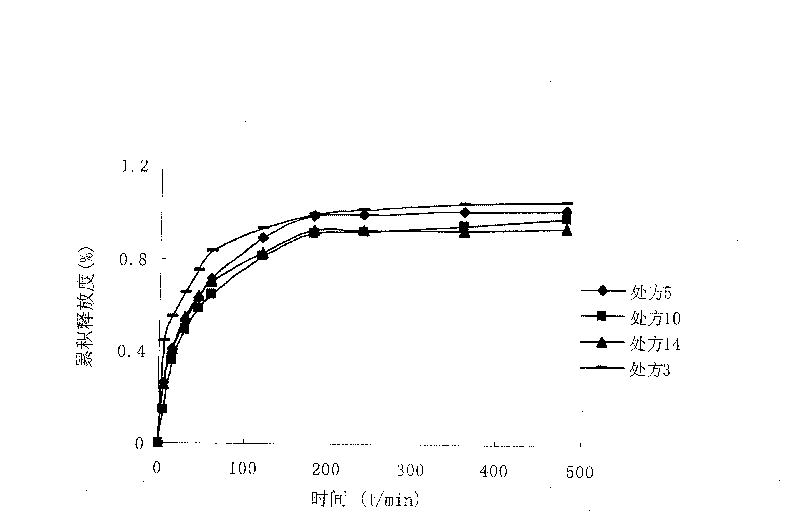
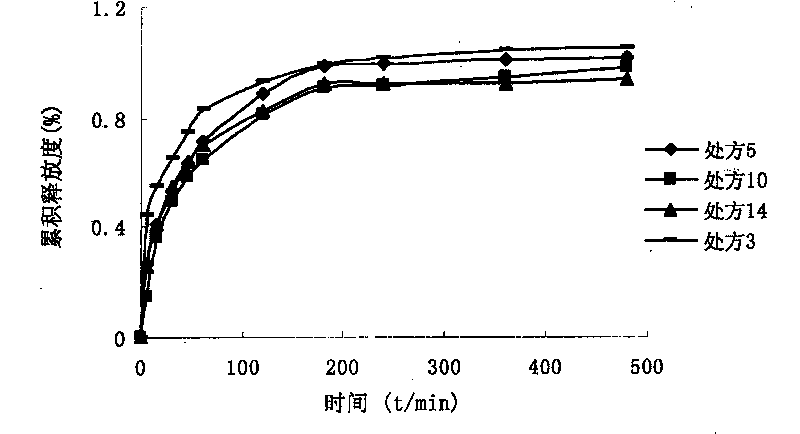
[0027] The rheological properties of the above four formulations were measured at room temperature (20° C.) using a Brookfield DV-III rotational viscometer. The viscosity of the above prescriptions shows a downward trend in varying degrees with the increase of the shear rate, and they belong to pseudoplastic fluids. Prescriptions 1 and 4 have a viscosi...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Prepare temperature-sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel, the prescription is as follows (see Table 2):
[0033] Table 2 temperature-sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel prescription (wt%)
[0034]
[0035] Preparation Process:
[0036] The above temperature-sensitive polymer was added to a low-temperature phosphate buffer (pH6.5), dispersed and dissolved under magnetic stirring, and left to stand in a refrigerator at 4°C (12h) to obtain a clear solution. Stir the gel property regulator (PEG, PEO, HPMC) at room temperature to dissolve it, and stand still for 12 hours to obtain a clear solution. Dissolve the drug zanamivir and other water-soluble excipients in deionized water, mix the three solutions, adjust the pH to 6.5, and add water to the full amount.
[0037] The rheological properties of the above four formulations at different shear rates were measured at room temperature (20°C) using a Brookfield DV-III rotational viscometer. The viscosity of the above f...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Prepare pH sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel, the prescription is as follows (see Table 3):
[0041] Table 3 pH-sensitive zanamivir nasal in situ gel prescription (wt%)
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] Preparation:
[0045] Dissolve the pH-sensitive gel material in distilled water, in which CAP was stirred and dissolved in HCL solution with pH 3.0, and left in a refrigerator at 4°C for 12 hours to obtain a clear solution; Carbopol 934 was dispersed in a certain amount of water, fully Swell to make it a blank matrix; chitosan was dissolved in 0.33M citric acid solution, and stood in a refrigerator at 4°C (12h) to obtain a clear solution. Dissolve the drug zanamivir and other water-soluble excipients in a certain amount of distilled water, mix with the solution prepared by the gel regulator (HPMC, GMO), drop into the pH-sensitive gel solution, adjust the pH to 4.0, and supplement the remaining Measure water to full volume.
[0046] The rheological properties of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com