Method of preparing nickel-aluminum base alloy porous material
A porous material, nickel-aluminum-based technology, applied in the field of preparation of nickel-aluminum-based alloy porous materials, can solve the problems of uncontrollable pore size, uneven pore distribution, and non-free adjustment of porosity, so as to reduce the preparation cost and facilitate detachment. In addition, the effect of small degree of pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
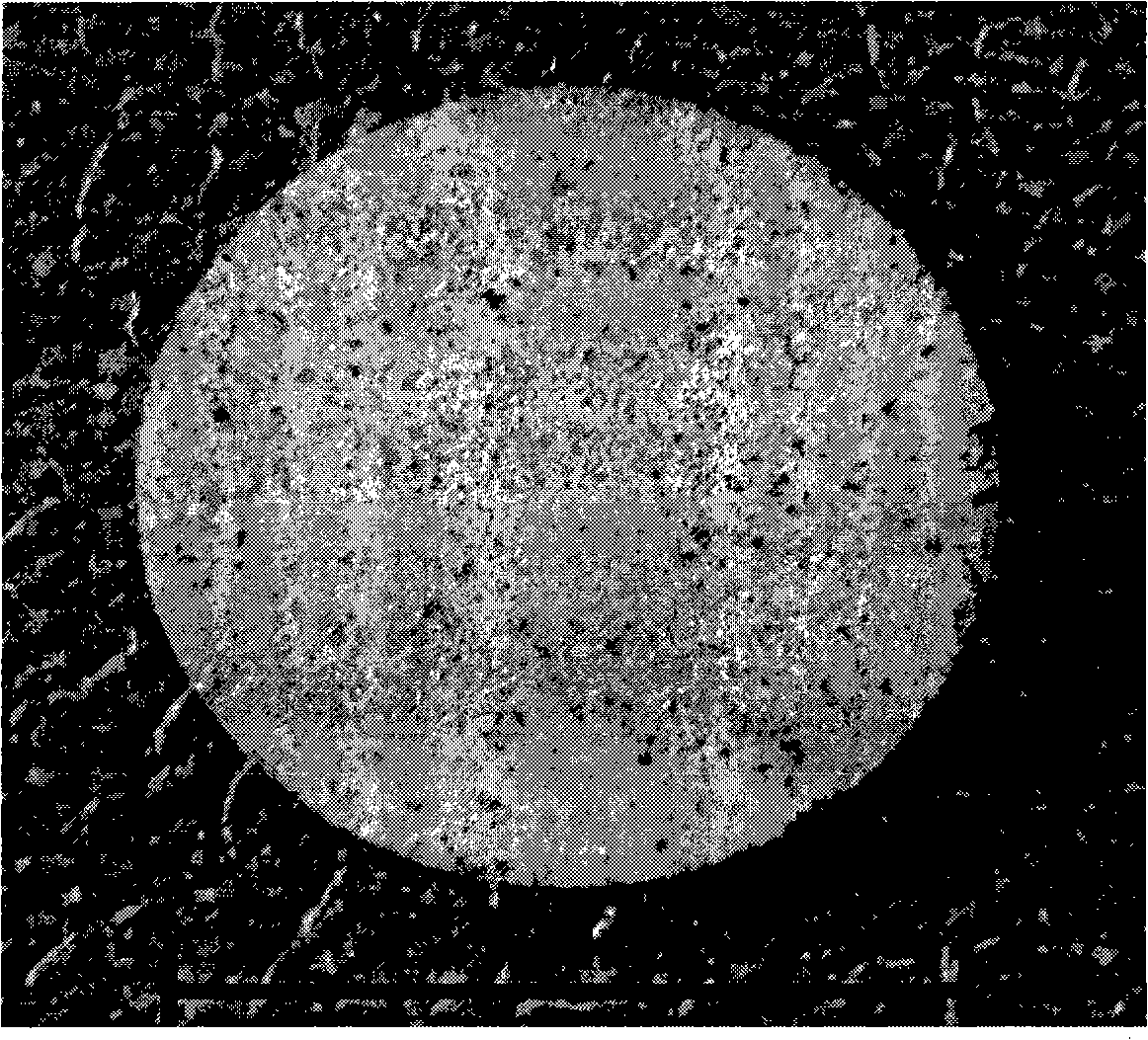
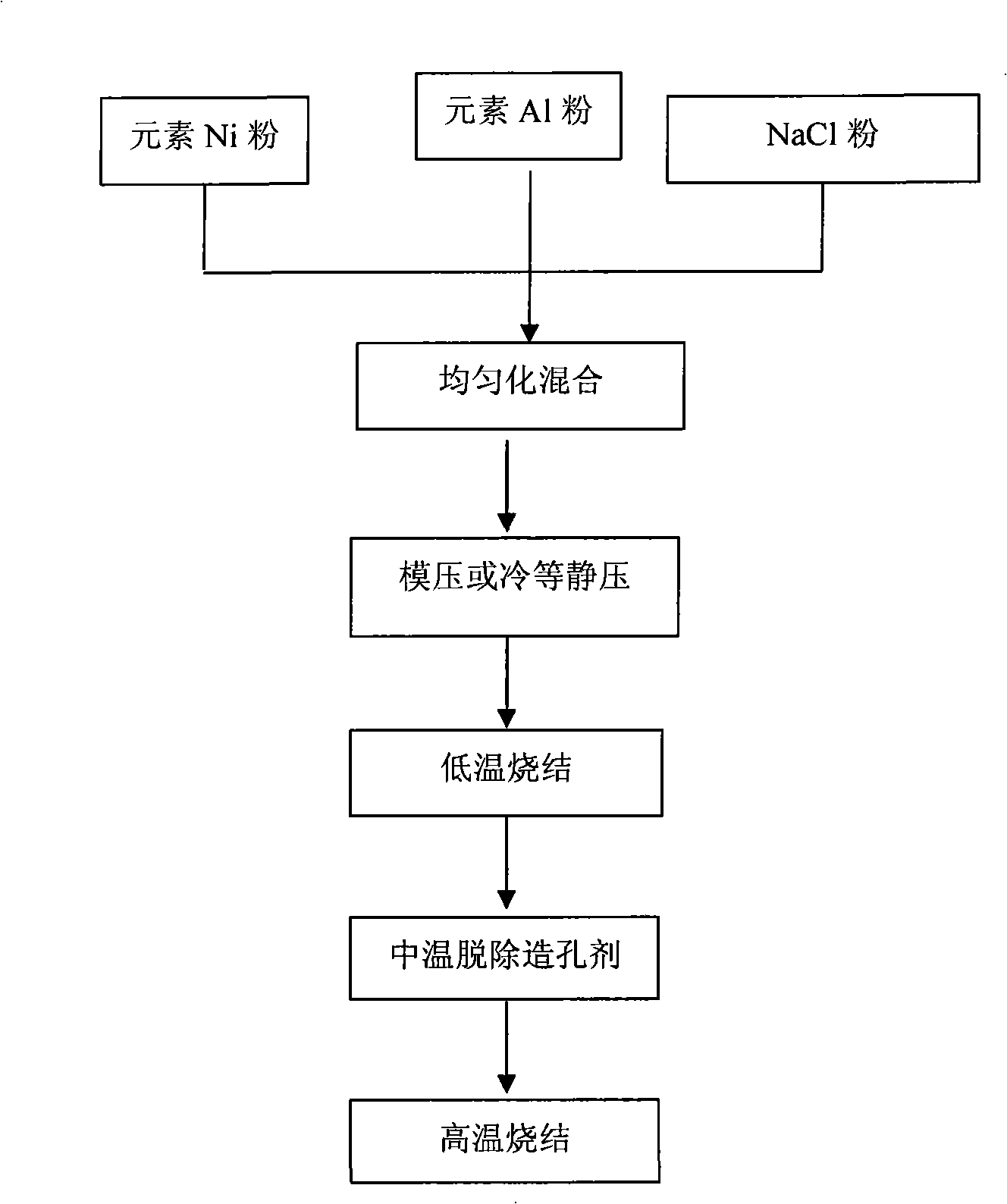
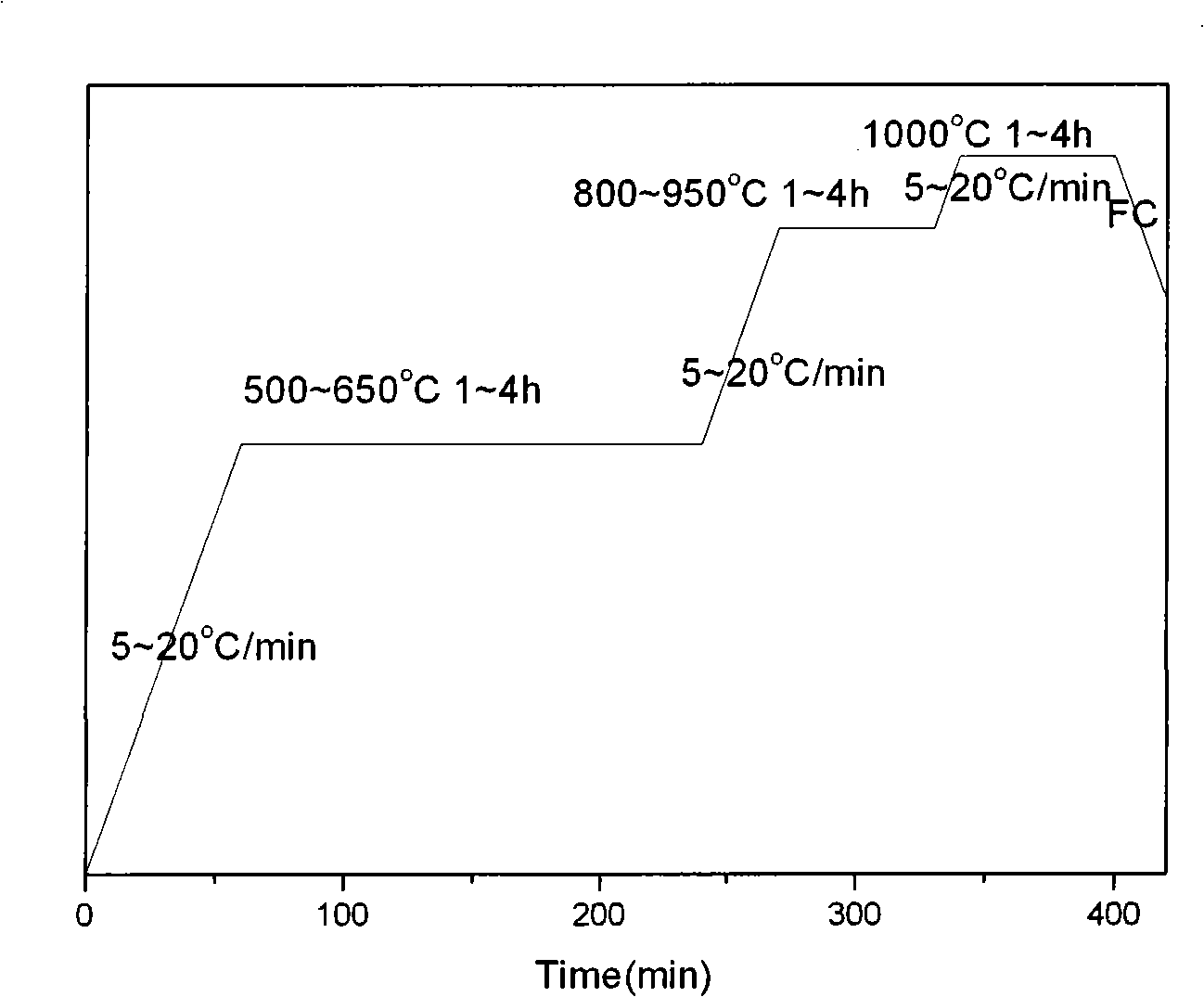
[0033] Embodiment 1: Ni powder with a particle size of 1-10 μm, Al powder with a particle size of 10-100 μm and NaCl powder with a particle size of 100-200 μm are used, and Ni:Al:NaCl is proportioned according to the mass ratio of 6.5:1:3. Molding or cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 500Mpa to make a cold compact with a diameter of d 50mm×5mm, then place it in a vacuum sintering furnace, control the vacuum degree to 0.1~10Pa, and raise the temperature at a rate of 5~20°C Sintering at 500~650°C, holding time: 1~4h, then continue to heat up to 800~950°C at a rate of 5~20°C, keep warm for 1~4h, and finally, still heat up to 1000 at a rate of 5~20°C ℃, heat preservation for 1~4h, and then cool in the furnace to prepare a porous nickel-aluminum-based alloy material with a size of d 50mm×5mm, and its porosity is 60.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Ni powder with a particle size of 1-10 μm, Al powder with a particle size of 10-100 μm and NaCl powder with a particle size of 100-200 μm are used, and Ni:Al:NaCl is proportioned according to the mass ratio of 6.5:1:7.5, Molding or cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 500Mpa to make a cold compact with a diameter of d50mm×5mm, then place it in a vacuum sintering furnace, control the vacuum degree to 0.1~10Pa, and raise the temperature at a rate of 5~20°C to Sintering at 500~650°C, holding time: 1~4h, then continue to heat up to 800~950°C at a rate of 5~20°C, hold for 1~4h, and finally, still heat up at a rate of 5~20°C to change to 1000°C, heat preservation for 1~4h, and then cooling in the furnace to prepare a porous nickel-aluminum-based alloy material with a size of d 50mm×5mm, and its porosity is 71%.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: Ni powder with a particle size of 1-10 μm, Al powder with a particle size of 10-100 μm and NaCl powder with a particle size of 100-200 μm are used, and the ratio of Ni:Al:NaCl is 6.5:1:23 by mass, Molding or cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 500Mpa to make a cold compact with a diameter of d50mm×5mm, then place it in a vacuum sintering furnace, control the vacuum degree to 0.1~10Pa, and raise the temperature at a rate of 5~20°C to Sintering at 500~650°C, holding time: 1~4h, then continue to heat up to 800~950°C at a rate of 5~20°C, hold for 1~4h, and finally, still heat up to 1000°C at a rate of 5~20°C , heat preservation for 1~4h, and then cooled with the furnace to prepare a porous nickel-aluminum-based alloy material with a size of d50mm×5mm and a porosity of 90%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com