Photoelectric conversion device
A conversion device and optoelectronic technology, applied in the field of condensing structure and electrode structure, can solve the problems of not neglecting boundary reflection, narrow bonding area, difficult to maintain the shape of the substrate, etc., so as to reduce the dependence of the incident angle and reduce the shielding. Loss, the effect of reducing power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
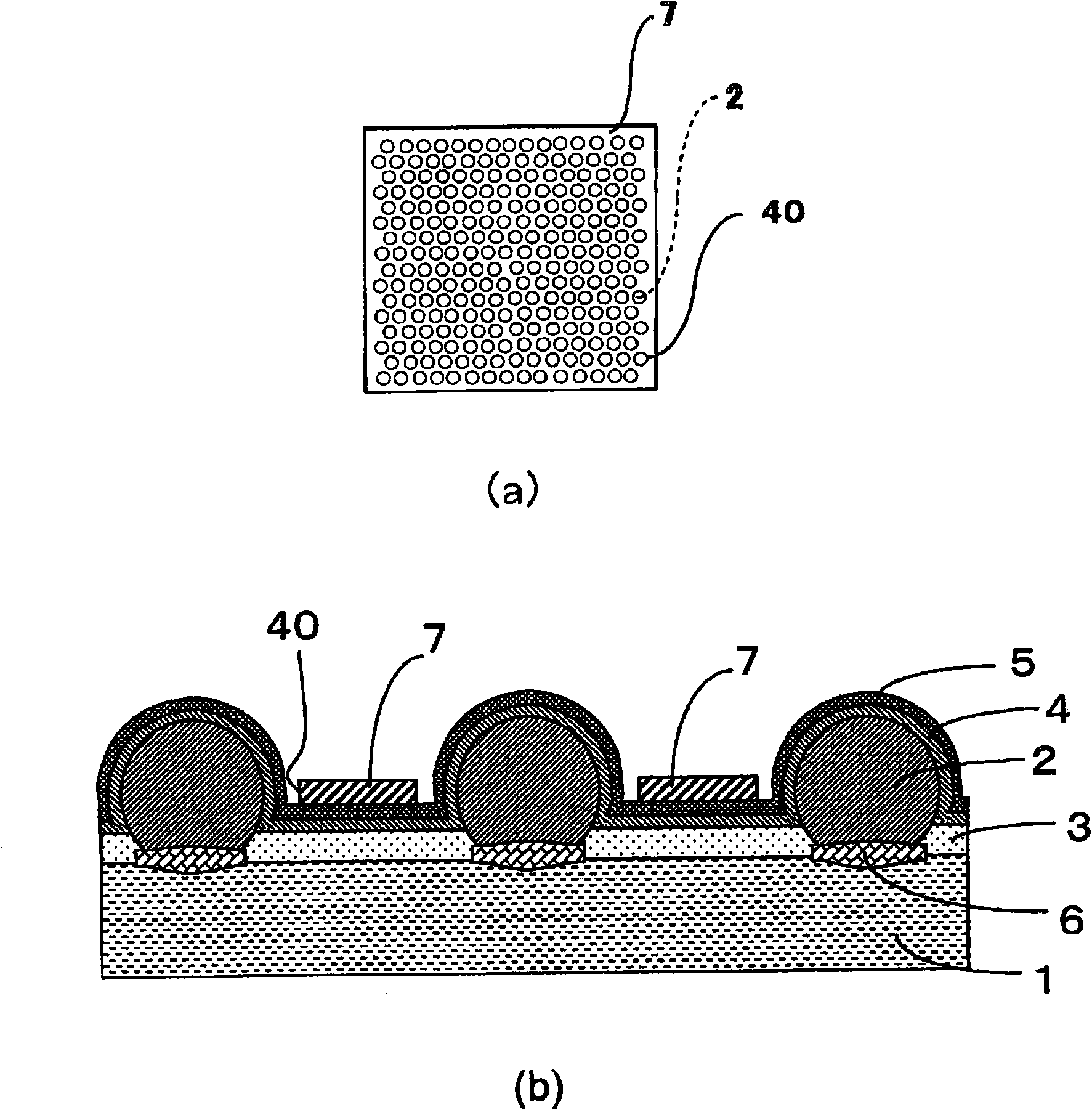
[0053] figure 1 (a) and (b) are a plan view showing an example of the first embodiment of the photoelectric conversion device of the present invention and an enlarged cross-sectional view of main parts thereof, respectively. The photoelectric conversion device of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown in (b), on the conductive substrate 1, a plurality of spherical crystalline semiconductor particles 2 of the first conductivity type are arranged at intervals from each other, and both are formed by the material of the conductive substrate 1 (for example, aluminum) and crystallization. The material (for example, silicon) of the semiconductor particle 2 is bonded by the cladding layer 6. An insulating layer 3 is formed on the conductive substrate 1 between the crystalline semiconductor particles 2, and a semiconductor layer 4, which is a semiconductor part of the second conductivity type, is formed on the insulating layer 3 and on the crystalline semiconductor particl...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
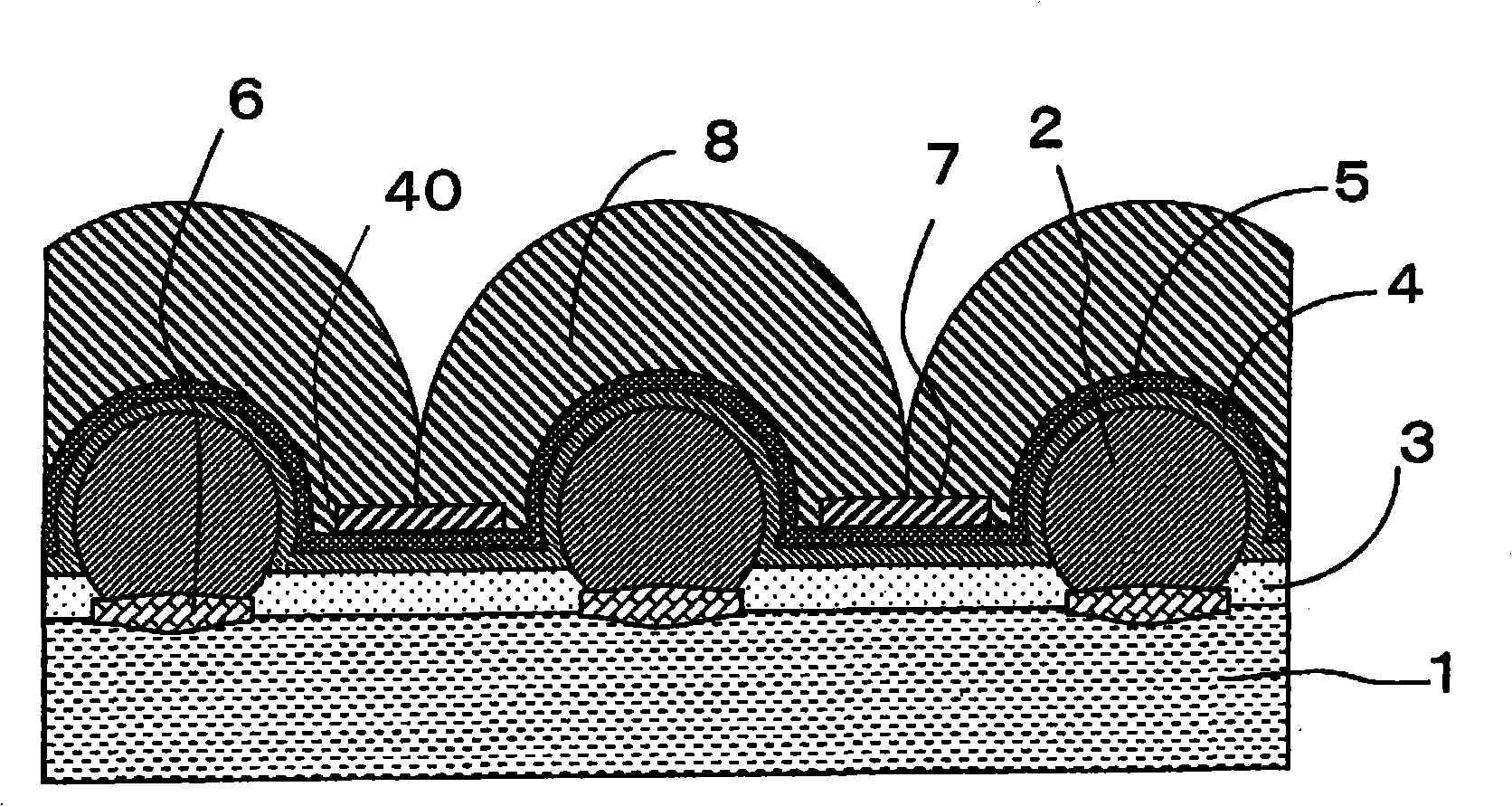
[0083] In the photoelectric conversion device of the first embodiment described above, for example, figure 2 As shown, on the crystalline semiconductor particle 2, a light-transmitting light-collecting layer 8 composed of a lens-shaped member is provided to efficiently introduce light into the crystalline semiconductor particle 2 while avoiding the conductive plate 7 arranged in the non-photoactive part. Light.
[0084] The above-mentioned light-transmitting light-collecting layer 8 is composed of an aspherical shape with a convex curved surface shape on the upper side for the purpose of efficiently taking in light rays at all incident angles into the crystalline semiconductor particles 2, and is formed in each crystalline semiconductor particle. On the translucent conductor layer 5 formed on the particle 2, the outline shape in the longitudinal section is a substantially semicircular convex shape having a diameter larger than that of the crystalline semiconductor particle 2 ...
no. 4 Embodiment approach
[0140] In the present invention, the photoelectric conversion device such as Figure 10 As shown, in the photoelectric conversion device produced in the above-mentioned third embodiment, the translucent light-collecting layer 8 composed of a lens-shaped member capable of efficiently introducing light may be provided on the crystalline semiconductor particles 2 . The translucent light-collecting layer 8 has already been described in the second embodiment.
[0141] According to the above-mentioned structure, by providing the above-mentioned light reflection member 27, even if the area occupied by the crystalline semiconductor particles 2 on the conductive substrate 1 is reduced, the light can be efficiently condensed on the crystalline semiconductor particles 2, and by providing the above-mentioned translucent The light concentrating layer 8 can efficiently introduce light and efficiently condense the light onto the crystalline semiconductor particles 2 . Thereby, while maintai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com