Bi-component polyester coarse fibre, filter material and preparation thereof
A filter material and crude fiber technology, applied in the field of polyester crude fiber, can solve the problems of low porosity, air permeability, poor water permeability, large rolling point, etc., to improve water permeability, slow increase in pressure loss, and long life long effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The two-component polyester crude fiber has a skin-core structure, the skin is a low-melt polymer, the core is a high-melt polyester, and the fiber thickness is 4-8dpf; the high-melt polyester and the low-melt polymer The difference between the melting points is ≥15°C.
[0039] The low-melting-point polymer is a modified polyester with a melting point of 215-235° C., which is purchased through commercial channels.
[0040] The high-melting-point polyester is a polyester (polyethylene terephthalate) with a melting point of 250-255° C., which is commercially available.
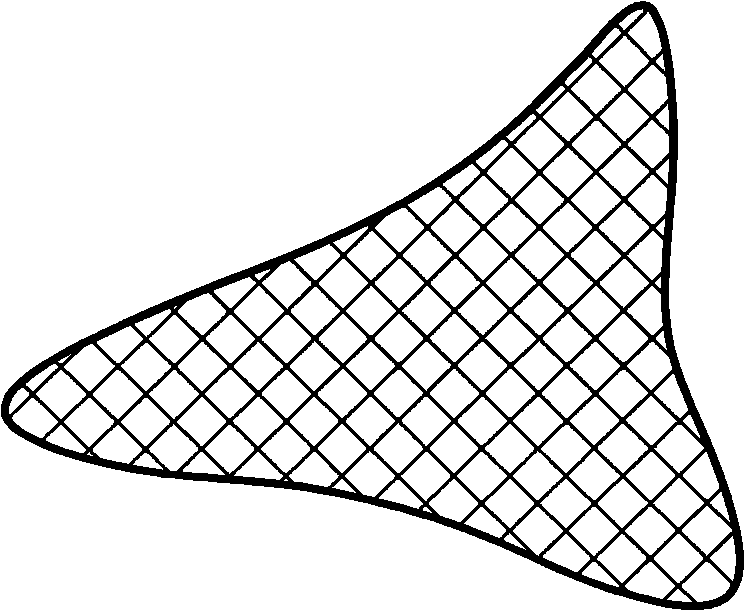
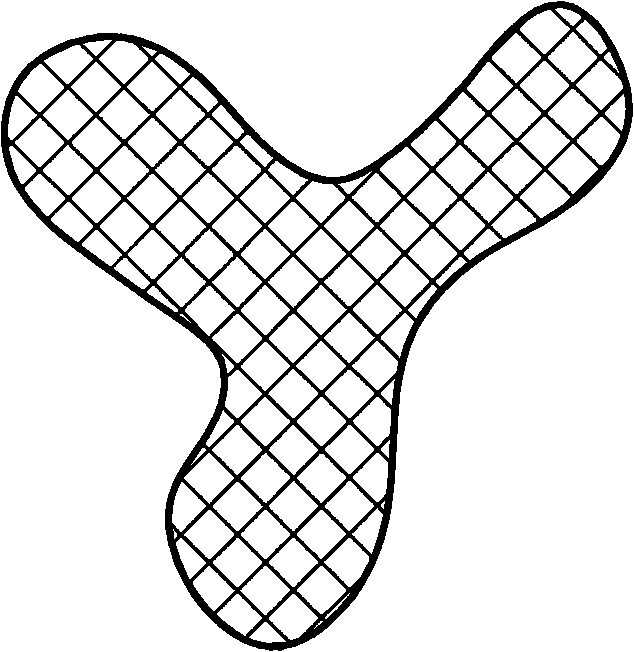
[0041] Described crude fiber section is trefoil (referring to figure 1 ).
[0042] The preparation method of the two-component polyester crude fiber filter material of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Extrude the low-melting point polymer and the high-melting point polyester from two groups of different extruders in a molten state, and spin through a composite spinneret...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The low-melting-point polymer is changed to polypropylene with a melting point of 165° C. to 175° C., purchased through commercial channels. Others are the same as in Example 1.
[0053] The filter material prepared in this embodiment is tested and compared with the traditional filter material as shown in Table 2.
[0054] Table 2
[0055] Test items
Embodiment 3
[0057]The low-melting-point polymer is changed to polyethylene with a melting point of 132° C. to 135° C., purchased through commercial channels. The high-melting-point polyester is changed to PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) with a melting point of 225-235° C., which is commercially available. Described crude fiber cross-section is changed into triangular (referring to figure 2 ). Others are the same as in Example 1.
[0058] The prepared different filter materials are tested and compared with the traditional filter materials as shown in Table 3.
[0059] table 3
[0060] Test items
[0061] It can be seen from the data in Tables 1 to 3 that the filter material of the present invention has better air permeability and water permeability, higher mechanical properties and lower pressure loss than the traditional polyester spunbonded nonwoven fabric.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com