Method of preparing lithium iron phosphate having high conductivity and superior low temperature discharge property
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and high conductivity, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of poor low-temperature discharge performance and low conductivity of lithium iron phosphate, and achieve strong high-current discharge capability and enhanced Effect of low temperature discharge performance and good low temperature performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
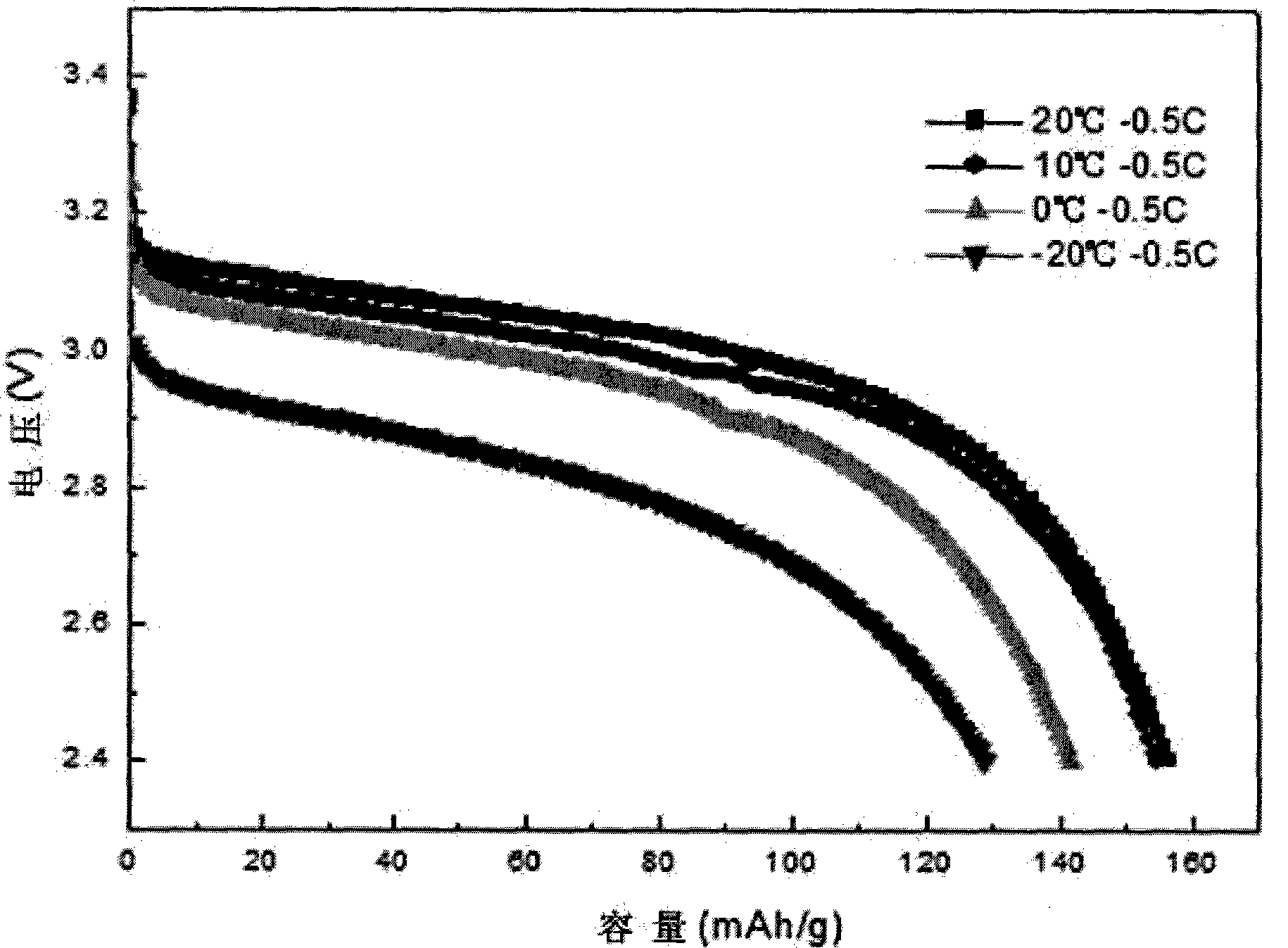
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Ferrous sulfate solution with a molar concentration of iron salt of 0.1mol / L is mixed with phosphoric acid solution, the mixing condition is iron: phosphorus molar ratio 3:2.5, and then rapidly neutralized with ammonia water with a molar concentration of 0.1mol / L at a temperature of -20°C And, stir the solution during neutralization to speed up the neutralization speed, and obtain ultra-fine Fe in an instant 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitation, ultrafine Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitate particle size D 50 At 4 μm, the Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 The O precipitate was washed and dried under vacuum, then mixed with Fe at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O, lithium phosphate, conductive agent, the conductive agent is sucrose, mixed evenly, and sintered at 550°C for 20 hours to obtain lithium iron phosphate material, the particle size of lithium phosphate used in sintering is D 50 at 1 μm.
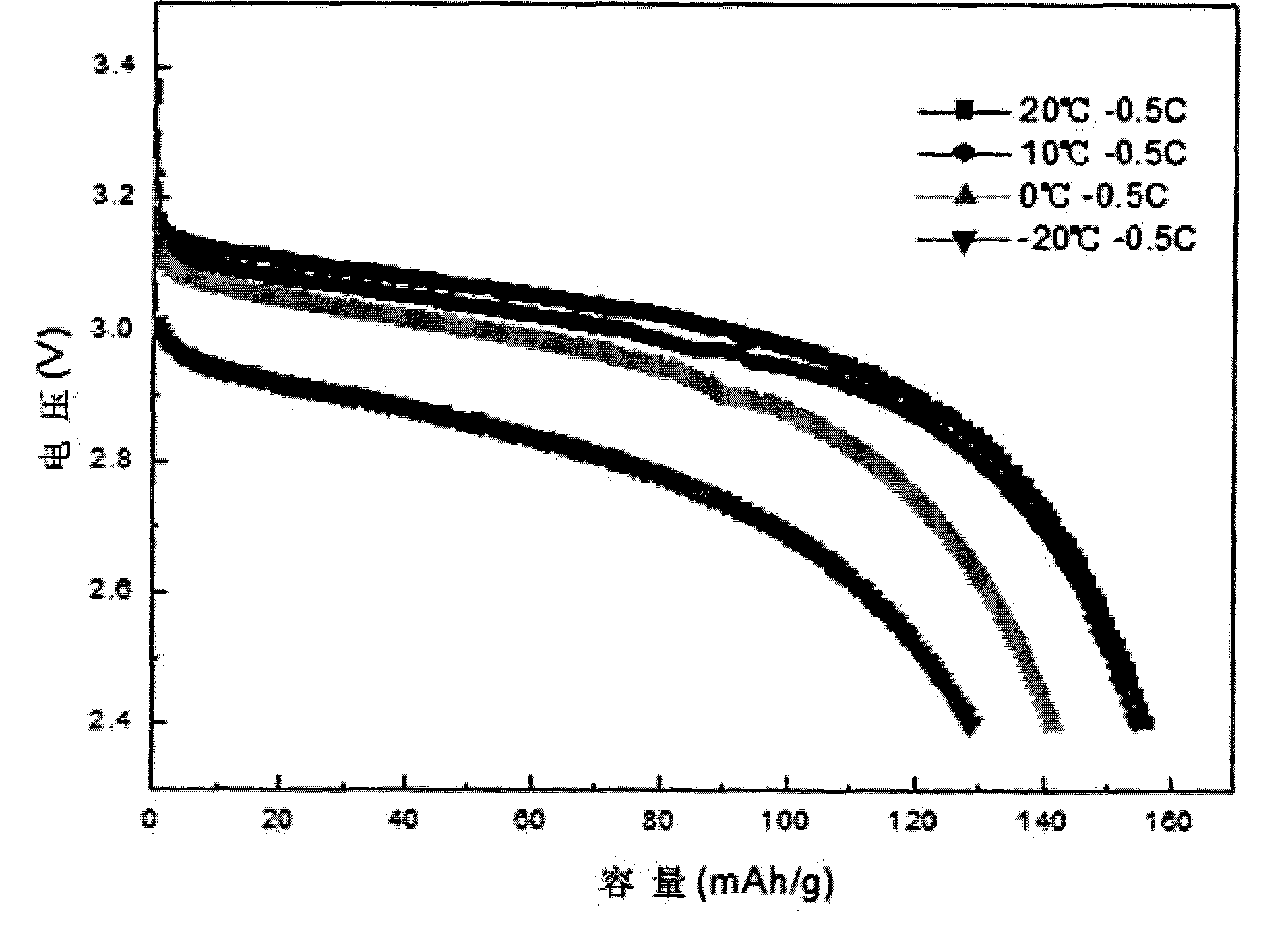
Embodiment 2
[0030] Ferrous sulfate solution with a molar concentration of iron salt of 0.25mol / L is mixed with phosphoric acid solution, the mixing condition is iron:phosphorus molar ratio 3:2.4, and then rapidly neutralized with ammonia water with a molar concentration of 0.5mol / L at a temperature of -10°C And, stir the solution during neutralization to speed up the neutralization speed, and obtain ultra-fine Fe in an instant 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitation, ultrafine Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitate particle size D 50 At 3 μm, the Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 The O precipitate was vacuum-dried and then mixed with Fe at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O, lithium phosphate, conductive agent, the conductive agent is glucose, mixed evenly, and sintered at 600°C for 10 hours to obtain lithium iron phosphate material, the particle size of lithium phosphate used in sintering is D 50 at 5 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Ferrous sulfate solution with a molar concentration of iron salt of 0.5mol / L is mixed with phosphoric acid solution, the mixing condition is iron: phosphorus molar ratio 3:2.3, and then at a temperature of 0°C, the sodium hydroxide solution with a molar concentration of 1mol / L is rapidly Neutralize, stir the solution during neutralization to speed up the neutralization speed, and obtain ultra-fine Fe in an instant 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitation, ultrafine Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O precipitate particle size D 50 At 5 μm, the Fe 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 The O precipitate was vacuum-dried and then mixed with Fe at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ·xH 2 O, lithium phosphate, conductive agent, the conductive agent is sucrose, mixed evenly, and sintered at 650°C for 5 hours to obtain lithium iron phosphate material, the particle size of lithium phosphate used in sintering is D 50at 3 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com